Photodynamic inactivation of Escherichia coli by porphyrin cytochrome c†
Abstract
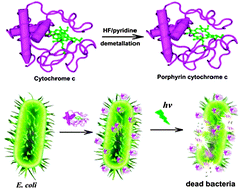
The positively charged porphyrin cytochrome c (porphyrin Cyt c) was found to be able to bind to Escherichia coli, and showed efficient antimicrobial activity upon visible light irradiation, opening avenues for the development of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...