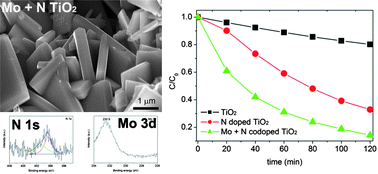
The photocatalytic activity of TiO2 can be mainly improved from three approaches: (1) enhancing surface energy, (2) increasing availability of visible light and (3) improving the separation efficiency of photo-induced electrons and holes. Here, we report a one-step route to obtain Mo + N codoped TiO2 sheets with dominant {001} facets by a hydrothermal process using TiN, MoO3, HF and HNO3 as precursor. The XRD patterns confirmed Mo and N doping into the lattice of anatase TiO2 and the XPS survey spectrum shows nitrogen (N) acting as interstitial N or an O–Ti–N structure and molybdenum (Mo) existed as Mo6+ in TiO2 sheets. All Mo + N codoped TiO2 sheets can absorb visible light, but compared with N-doped TiO2 sheets, further Mo-doping elevates the conduction band edge and expands the band gap of anatase TiO2 slightly. The separation efficiencies of photo-induced electrons and holes of Mo + N codoped TiO2 sheets were enhanced compared with that of N-doped TiO2 sheets, as confirmed by detecting the production of hydroxyl radicals (˙OH), and their photocatalytic activities on decomposition of methylene blue and methyl violet was improved. The Mo + N codoped TiO2 sheets showed the highest photocatalyst activity when the Mo-doping ratio reached 1%, indicating an appropriate codoping ratio is necessary for synergistic effect between doped metal and nonmetal elements.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...