Synthesis and strong heavy-metal ion sorption of copolymer microparticles from phenylenediamine and its sulfonate
Abstract
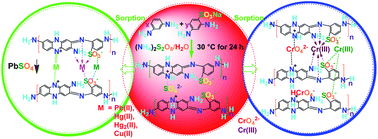
Strong heavy-metal-ion sorbents based on copolymer microparticles with many functional groups including amino, imino and sulfonic groups were synthesized by a chemical oxidative polymerization of m-phenylenediamine (mPD) and p-sulfonic-m-phenylenediamine (SPD) in pure water. The sorbent performance has been investigated with regard to mPD/SPD ratio, functional group densities, metal ion species, and sorption conditions. It is found that mPD/SPD (95/5) copolymer microparticles demonstrate the maximal yield, maximal electrical conductivity, maximal Pb(II) and Cr(VI) (mainly as HCrO4−) adsorbability, but the minimal Cu(II) adsorbability, while mPD/SPD (50/50) copolymer microparticles demonstrate the maximal Hg(II) adsorbability, suggesting that the polymers are real copolymers rather than a mixture of both homopolymers. The sorption rate of the metal ions steadily rises in the order of Cr(VI) ≪ Hg(II) ≪ Pb(II), the adsorbance rises in the order of Cu(II) ≪ Pb(II) < Cr(VI) ≪ Hg(II), whereas the adsorptivity rises in the order of Cu(II) ≪ Cr(VI) < Pb(II) < Hg(II). In particular, the mPD/SPD (95/5) copolymer microparticles reach adsorption equilibrium within 3 min, achieving an initial Pb(II) adsorption rate of up to 509.5 g g−1 h−1. The microparticles are simultaneously strong, rapid, sustainable sorbent towards Pb(II), Hg(II), and Cr(VI). The HCrO4− sorption is endothermic and enhanced by properly elevating the temperature. The pH of the ion solutions declines after the sorption, implying that the sorption includes the replacement of H+ by the ions. The microparticles also exhibit good selectivity for Hg(II) and Pb(II) over Cu(II) ions, possessing the highest selective adsorptivity of up to 99.9%. The sorption mechanism of the ions onto the microparticles was analyzed.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...