Anti-diabetic effect of a traditional Chinese medicine formula
Abstract
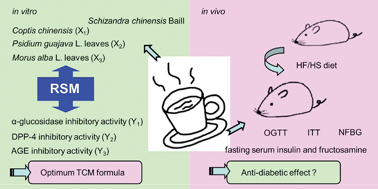
An anti-diabetic TCM formula consisting of Schizandra chinensis Baill. (SC), Coptis chinensis (CC), Psidium guajava L. leaves (PG) and Morus alba L. leaves (MA) was developed based on its α-glucosidase, DPP-4 and AGE inhibitory activities in vitro using response surface methodology (RSM). Then, the in vivo study was carried out to confirm the anti-diabetic function of the formula. RSM results showed that the optimum anti-diabetic TCM formula is the combination SC (3000 μg mL−1), CC (80 μg mL−1), PG (374.56 μg mL−1) and MA (480 μg mL−1). For the in vivo study, insulin resistant mice were induced by high-fat/high-sucrose (HF/HS) feeding for 6 weeks. Administration of the developed formula significantly decreased non-fasting blood glucose in the HF/HS diet mice. Moreover, the formula decreased blood glucose levels in the insulin tolerance test. These results indicated that the anti-diabetic mechanism of the formula might be due to decreased insulin resistance. The serum fructosamine level in the high dose group was significantly lower than the HF/HS and normal control groups, indicating that the formula could improve middle term glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications. The contents of berberine and 1-deoxynojirimycin in the formula were 4.7 ± 0.4 and 77.1 ± 1.1 μg mL−1, respectively. These two compounds can be used as indicators for quality control during production.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...