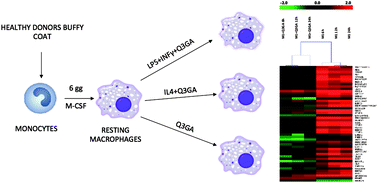
Due to their recently discovered plasticity, macrophages could be an important target in the treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis, and it is of interest that quercetin has been shown to modulate inflammation in humans through mechanisms involving macrophages. The aim of this work was to investigate the effect of quercetin-3-O-glucuronide (Q3GA), a major circulating human metabolite of quercetin, on gene expression in differently polarized human macrophages. Classical (M1) and alternative (M2a) macrophages were exposed to Q3GA (500 nM). Gene expression was monitored after incubation periods of 6, 12 and 24 h. M1 and M2a macrophages maintained their respective traits. Q3GA did not affect M1 macrophages in the promotion of a defense response, which remains the principal characteristic of this type of activation, but it was able to reduce the transcription of genes involved in inflammation, such as pro-inflammatory interleukins and enzymes involved in oxidative stress responses. Exposure of M2a to Q3GA elicited an improvement in anti-inflammatory features resulting from further down-regulation of pro-inflammatory genes. Thus, Q3GA is a potential anti-atherogenic metabolite, enhancing the anti-inflammatory properties of M2a macrophages and modulating immune response effects in the presence of pro-inflammatory stimuli.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...