Many M©Bn boron wheels are local, but not global minima
Abstract
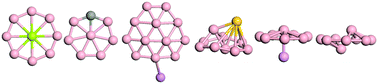
Twenty-six planar boron wheels with a central hypercoordinate atom (M©Bn, M is a 2nd or 3rd period element) were designed following the Schleyer–Boldyrev concept of geometric and electronic fit whereby in-plane σ- as well as π-aromaticity contribute to the chemical bonding. Global minimum searches using an efficient newly implemented method reveal that most of these boron wheels are only local, rather than global minima. However, the Be©B8 triplet planar wheel global minimum is a new member of the planar hypercoordinate M©Bn family. Six categories classify the structures of the other global minima: planar wheels, planar non-wheel forms, quasi-two-center-wheels, as well as leaf-like, pyramid-like, and umbrella-like geometries.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Predicting new molecules by quantum chemical methods

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...