Synthesis and physicochemical characterization of new squalenoyl amphiphilic gadolinium complexes as nanoparticle contrast agents†
Abstract
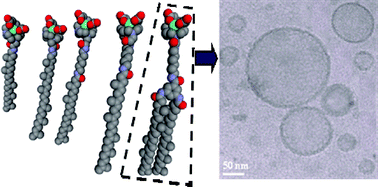
A family of novel amphiphilic gadolinium chelates was successfully obtained by coupling the hydrophilic DOTA
* Corresponding authors
a
Univ. Paris-Sud XI, Faculté de Pharmacie, UMR CNRS 8612, 5 rue J.-B. Clément, 92296 Châtenay-Malabry Cedex, France
E-mail:
ruxandra.gref@u-psud.fr
Fax: +33 1 46 83 59 46
Tel: +33 1 46 83 59 09
b Univ. Paris-Sud XI, Faculté de Pharmacie, UMR CNRS 8076 BIOCIS, 92296 Châtenay-Malabry Cedex, France
c Univ. Mons, Laboratoire de RMN et d'Imagerie Moléculaire, 19, avenue Maistriau, Mons, Belgique
d LVMH Recherche Parfums et Cosmétiques, Département Innovation Matériaux et Technologies, 185 Avenue de Verdun, Saint Jean de Braye, France
e CNRS, UPR 2301, (ICSN), 91198 Gif-sur-Yvette, France
A family of novel amphiphilic gadolinium chelates was successfully obtained by coupling the hydrophilic DOTA

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
M. Othman, D. Desmaële, P. Couvreur, L. Vander Elst, S. Laurent, R. N. Muller, C. Bourgaux, E. Morvan, T. Pouget, S. Lepêtre-Mouelhi, P. Durand and R. Gref, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 4367 DOI: 10.1039/C1OB00015B
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
