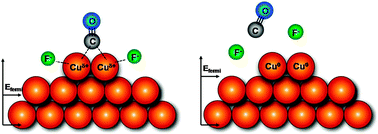
The adsorption of CO on low index copper single crystals in electrochemical environments has been investigated. The results, analysed through a combination of in situinfrared spectroscopy, DFT and cyclic voltammetry, reveal a unique adsorption behaviour when compared to previous studies on copper and the more widely studied noble metal surfaces. By employing small, weakly specifically adsorbed electrolytes, it is shown that carbon monoxide is adsorbed over a much wider electrode potential range than previously reported. The electrochemical Stark shift (δν/δE) observed is similar for the three Cu(hkl) surfaces examined despite different surface coverages. Most notably, however, is an electrochemical feature observed at ca. −1.0 V (vs.Ag/AgCl) on the (110) surface. It is proposed that this voltammetric feature arises from the reduction/oxidation of Cuδ+ surface sites involved in the binding of carbon monoxide with the participation of the electrolyte anion. This provides additional specific sites for CO adsorption. DFT calculations support the proposed presence of low-coordination copper sites stabilised by electrolyte anions. An experimental electron transfer rate constant of 4.2 s−1 to the Cuδ+ surface sites formed was found. These new observations concerning the surface electrochemistry of CO on Cu indicate that the electrocatalytic behaviour of Cu electrodes in processes such as CO2 reduction need to be re-evaluated to take account of the rich adsorption behaviour of CO, including the co-adsorption of the electrolyte anion to these sites.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...