Understanding the hcp anisotropy in Cd and Zn: the role of electron correlation in determining the potential energy surface
Abstract
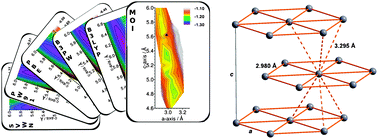
* Corresponding authors
a
MacDiarmid Institute for Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology, Industrial Research Limited, Lower Hutt, New Zealand
E-mail:
n.gaston@irl.cri.nz
b Institut für Chemie and Biochemie,, Physikalische und Theoretische Chemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustraße 3, D-14195 Berlin, Germany
c Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research, Heisenbergstraße 1, D-70569 Stuttgart, Germany

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
N. Gaston, D. Andrae, B. Paulus, U. Wedig and M. Jansen, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 681 DOI: 10.1039/B915967C
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
