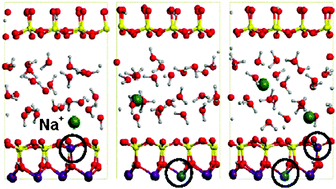
The present work reports ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, based on density functional theory using the PBE functional, of Li+- Na+- and K+-montmorillonites, considering three types of isomorphic substitutions in the montmorillonite layer: tetrahedral (Tsub), octahedral (Osub) and both (OTsub). These simulations allow us to evaluate the effect of each type of substitution on the inner- outer-sphere complex formation of the alkali cations. It is observed that, for the three kinds of substituted montmorillonites, K+ remains bound to the surface confirming its role as swelling inhibitor. In contrast, Li+ tends to hydrate and coordinate to 4 water molecules in all cases, except for OTsub, for which one of the two Li+ cations remains bound to the oxygens close to the substituted tetrahedral site. Finally, Na+ presents an intermediate behaviour, binding to the surface in Tsub montmorillonite but being hydrated in Osub. These simulations show that the hydration/adsorption behaviour of alkali cations in the swelling process of montmorillonite depends on the affinity of the cation for water and the surface, as well as on the type of substitution that controls the negative charge on surface oxygen atoms.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...