Synthesis and photophysical properties of a highly fluorescent azo derivative
Abstract
A highly fluorescent and photochromic azo derivative has been obtained by linking in a covalent manner a red-emitting squaraine unit to an
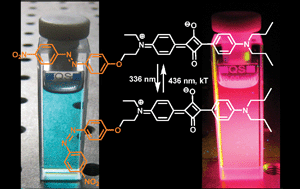
- This article is part of the themed collection: New Horizons of Photochromism

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...