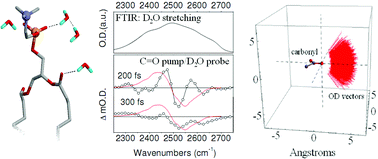
Being largely driven by electrostatic interactions, hydration compensates hydrophobic repulsion and, thus, contributes decisively in structural expressions of molecules in a phospholipid membrane environment. Here, we explore the nature of the aqueous state associated with carbonyl moieties of a phospholipid bilayer. The task is of an obvious difficulty, since water clustering at a membrane interface implies the presence of various aqueous states giving rise to spectral inhomogeneity. The resultant frequency overlap of the optical response from states of differing nature obscures the structural analysis. We extract the information on water next to phospholipid carbonyls by monitoring the O–D stretch perturbation upon direct infrared excitation of lipid carbonyl groups. Modelling the signal with the help of quantum computations and molecular dynamics simulation, we extract the geometry for the optimal placement of water next to carbonyl moieties, and anticipate the time scale of the water molecule displacement, leading to the disruption of the hydrogen bond, upon direct excitation of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group. The picture we provide here is of general and applied value. The practical importance stems from the necessity of experimentally characterizing the hydration of polar moieties in polypeptides (of pharmacological significance) when in a phospholipid environment, a task not yet achieved.
O group. The picture we provide here is of general and applied value. The practical importance stems from the necessity of experimentally characterizing the hydration of polar moieties in polypeptides (of pharmacological significance) when in a phospholipid environment, a task not yet achieved.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group. The picture we provide here is of general and applied value. The practical importance stems from the necessity of experimentally characterizing the hydration of polar moieties in
O group. The picture we provide here is of general and applied value. The practical importance stems from the necessity of experimentally characterizing the hydration of polar moieties in 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...