Mitochondrial targeting of radioprotectants using peptidyl conjugates
Abstract
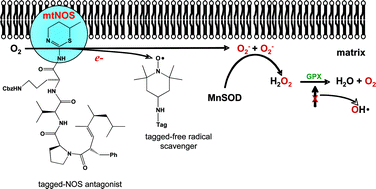
Ionizing radiation activates a mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase, leading to inhibition of the respiratory chain, generation of excess superoxide, peroxynitrite production and nitrosative damage. We have measured the radioprotective effects of a nitric oxide synthase

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...