Characterization of a membrane-based gradient generator for use in cell-signaling studies†
Abstract
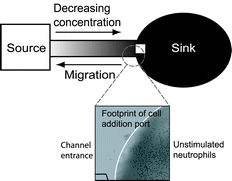
This paper describes a method to create stable chemical gradients without requiring fluid flow. The absence of fluid flow makes this device amenable to cell signaling applications where soluble factors can impact cell behavior. This device consists of a membrane-covered source region and a large volume sink region connected by a microfluidic channel. The high fluidic resistance of the membrane limits fluid flow caused by pressure differences in the system, but allows diffusive transport of a chemical species through the membrane and into the channel. The large volume sink region at the end of the microfluidic channel helps to maintain spatial and temporal stability of the gradient. The chemical gradient in a 0.5 mm region near the sink region experiences a maximum of 10 percent change between the 6 and 24 h data points. We present the theory, design, and characterization of this device and provide an example of neutrophil chemotaxis as proof of concept for future quantitative cell-signaling applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...