Intramolecularly OH⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C hydrogen bonded phenols, 2-HO–C6H2-3,5-(t-Bu)2–CONH–t–Bu (1–OH), 2-HO–C6H2-5-t-Bu-1,3-(CONH-t-Bu)2 (2–OH) and 2-HO–C6H2-3,5-(t-Bu)2–NHCO–t–Bu (4–OH), were synthesized and their phenolate anions were prepared as tetraethylammonium salts (1–O−(NEt4+), 2–O−(NEt4+) and 4–O−(NEt4+)) with intramolecular NH⋯O(oxyanion) hydrogen bonds. 4-HO–C6H2-3,5-t-Bu2–CONH–t–Bu (3–OH) and its phenolate anion, 3–O−(NEt4+), were synthesized as non-hydrogen bonded references. The presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonds was established through the crystallographic analysis and/or 1H NMR spectroscopic results. Intramolecular NH⋯O(phenol) hydrogen bonds shift the pKa of the phenol to a more acidic value. The results of cyclic voltammetry show that the intramolecular OH⋯O
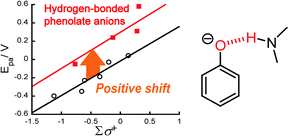
C hydrogen bonded phenols, 2-HO–C6H2-3,5-(t-Bu)2–CONH–t–Bu (1–OH), 2-HO–C6H2-5-t-Bu-1,3-(CONH-t-Bu)2 (2–OH) and 2-HO–C6H2-3,5-(t-Bu)2–NHCO–t–Bu (4–OH), were synthesized and their phenolate anions were prepared as tetraethylammonium salts (1–O−(NEt4+), 2–O−(NEt4+) and 4–O−(NEt4+)) with intramolecular NH⋯O(oxyanion) hydrogen bonds. 4-HO–C6H2-3,5-t-Bu2–CONH–t–Bu (3–OH) and its phenolate anion, 3–O−(NEt4+), were synthesized as non-hydrogen bonded references. The presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonds was established through the crystallographic analysis and/or 1H NMR spectroscopic results. Intramolecular NH⋯O(phenol) hydrogen bonds shift the pKa of the phenol to a more acidic value. The results of cyclic voltammetry show that the intramolecular OH⋯O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C hydrogen bond negatively shifts the oxidation potential of the phenol. In contrast, the intramolecular NH⋯O(oxyanion) hydrogen bond positively shifts the oxidation potential of the phenolate anion, preventing oxidation. These contributions of the hydrogen bond to the pKa value and the oxidation potentials probably play an important role in the formation of a tyrosyl radical in photosystem II.
C hydrogen bond negatively shifts the oxidation potential of the phenol. In contrast, the intramolecular NH⋯O(oxyanion) hydrogen bond positively shifts the oxidation potential of the phenolate anion, preventing oxidation. These contributions of the hydrogen bond to the pKa value and the oxidation potentials probably play an important role in the formation of a tyrosyl radical in photosystem II.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C hydrogen bonded
C hydrogen bonded ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C hydrogen bond negatively shifts the oxidation potential of the
C hydrogen bond negatively shifts the oxidation potential of the 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...