Electrospray ionisation mass spectrometric detection of weak non-covalent interactions in nogalamycin–DNA complexes
Abstract
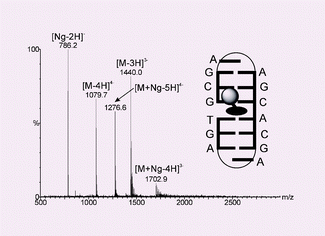
We demonstrate the use of electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) in high salt solutions for the analysis of weak non-covalent complexes of the anthracycline antibiotic nogalamycin with novel DNA hairpin structures; high signal-to-noise ratios for the complexes in the absence of bound Na+ ions permits relative binding affinities to be estimated.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...