Conformation and binding properties of polymethylene-linked bisviologens–2-naphthol complexes
Abstract
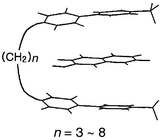
The effect of chain length on charge transfer (CT) complexation behavior between N′,N″-poly(methylene)bis(1-methyl-4,4′-bipyridinium) (VCnV; bisviologen, n = 3–8) and 2-naphthol was studied by using NMR, UV and molecular modeling techniques. Complexation constants, determined by fitting both NMR and UV titration data, show that bisviologens were more effective in complex formation with 2-naphthol than N,N′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium (MV; methylviologen). For example, the complexation constant of VC7V–2-naphthol obtained was more than 12 times as large as that of MV–2-naphthol. This implies formation of a sandwich-type complex for bisviologens, which is further supported by the increase of the CT band with added salts due to decreasing electrostatic repulsion. The complexation constants show significant dependence on the linkage chain length of bisviologen with an alternation phenomenon. The extent of complexation of VCnV–2-naphthol was more pronounced for n = 5 and 7 than for n = 4, 6, and 8. The stabilization energies for sandwich-type complexes of VCnV–2-naphthol obtained by molecular modeling showed the same trend. The even–odd alternate trend was explained by the backbone strain of folding that occurs in the formation of sandwich-type complexs, where VCnV behaves like molecular tweezers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...