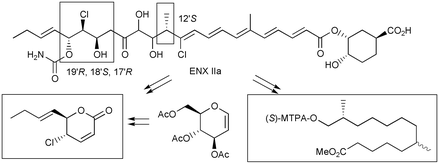
The absolute configuration of the 12′,17′,18′,19′-positions of enacyloxins (ENXs), a series of polyhydroxy-polyenic antibiotics from Frateuria sp. W-315, was determined. As degradation of decarbamoyl (dec) ENX IIa gave (5R,6S,1′E)-6-(but-1′-enyl)-5-chloro-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one, which corresponded to the 15′–23′ skeleton of dec ENX IIa, its enantiomers were synthesized from tri-O-acetyl-D-glucal. Comparison of the HPLC retention time of these naturally derived and synthetic compounds revealed the 17′R,18′S,19′R-configuration of ENXs. Hydrogenation and oxidation of ENX IIa gave methyl 13-hydroxy-6,12-dimethyltridecanoate, which was converted to the 13-MTPA ester. Comparison of the 1H NMR chemical shifts and the coupling constants with the model compounds revealed the 12′S-configuration. This absolute stereochemistry is necessarily applicable to other enacyloxins.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...