Perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides for efficient sunlight-driven artificial synthesis
Jeongsuk
Seo
 *a and
Kazunari
Domen
*a and
Kazunari
Domen
 bc
bc
aDepartment of Chemistry, College of Natural Sciences, Chonnam National University, 77 Yongbong-ro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 61186, Republic of Korea. E-mail: j_seo@chonnam.ac.kr
bResearch Initiative for Supra-Materials, Shinshu University, 4-17-1 Wakasato, Nagano 380-8553, Japan
cOffice of University Professors, The University of Tokyo, 2-11-16 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8656, Japan
First published on 5th December 2023
Abstract
Perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides are regarded as promising visible-light-responsive semiconductors for efficient artificial photosynthesis to produce renewable value-added energy resources, including H2, formic acid (HCOOH), and ammonia (NH3). This is because of their chemical stability in aqueous electrolytes at various pH values, along with a narrow bandgap and a suitable band position bestowing ideal optical properties. In this review, we discuss recent advances in photocatalysis using perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides responsive to a wide wavelength range of the visible-light spectrum. Next, we address in detail how the photoactivity of oxynitrides can be enhanced with respect to their synthesis, including bulk and surface engineering such as doping (or substitution), controlling their morphology, and crystal facet engineering. Finally, we discuss the existing challenges to realizing efficient artificial photosynthesis using these materials.
1. Perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides
Perovskite-type oxynitrides are mixed metallic compounds with the general formula AB(O,N)3, where A and B represent a large alkali-earth metal or La (i.e., A = Ca, Sr, Ba, or La) and a relatively small transition metal (i.e., B = Ti, Ta, or Nb), respectively.1–3 The stoichiometry of anions O and N in the perovskite is determined by the combination of cations at the A and B sites. Fig. 1 displays the crystal structure of an ideal cubic perovskite AB(O,N)3 whereby the B(O,N)6 octahedron is at the center of the cube while the large A atoms occupy the corners. The relationship between the ionic radii (r) expressed as rA + r(O,N) = √2(rB + r(O,N)) is valid for the ideal cubic perovskite structure. The ratio of left- to right-hand sides of the expression is called the tolerance factor t, and the ideal cubic perovskites have a t value of unity. Tilting of the octahedron in the cubic structure originates from the subtle differences between the ionic radii of the cations leading to a t value less than unity. However, structural distortion producing orthorhombic or tetragonal shapes is commonly found, except for very few combinations including BaBO2N (B = Ta or Nb). In addition, the perovskite oxynitrides can adopt the A1x−1A2x and/or B1y−1B2y configurations at the A and/or B sites. In these cases, the stoichiometry of the anions deviates from the ideal coordination configuration if the cations at the A and B sites undergo a change in their oxidation state.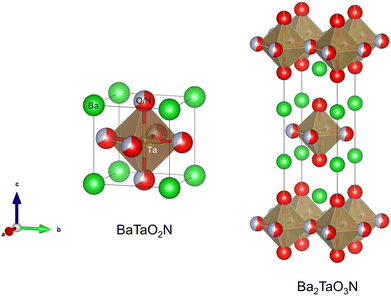 | ||
| Fig. 1 Crystal structures of perovskite oxynitride BaTaO2N and Ruddlesden–Popper (RP) phase layered perovskite oxynitride Ba2TaO3N. | ||
Besides the ideal cubic structure, perovskites can also adopt layered structures in which AB(O,N)3 layers are separated by thin layers of intrusive materials (commonly metal oxides), as shown in Fig. 1. Depending on the intruding layers, the perovskite derivatives designated layered perovskites are generally classified as (i) Aurivillius ((Bi2O2)(An−1BnO3n+1)), (ii) Ruddlesden–Popper (RP) (An+1BnO3n+1 or A′An−1BnO3n+1), or (iii) Dion–Jacobson (A′An−1BnO3n+1) phases (n = 1, 2, or 3 represents the number of stacked octahedra separated by a rock salt AO layer). The oxygen in the layered perovskites can be partially exchanged with another anion such as halogen and nitrogen. Sillen–Aurivillius layered perovskite oxyhalides A4A′n−1BnO3n+5X (A and A′ = Sr, Ba, Pb, or Bi; B = Ti, Nb, or Ta; X = Cl or Br) were prepared by the substitution of oxygen by halogen.4,5 Moreover, RP phase oxynitrides An+1Bn(O,N)3n+1 and Dion–Jacobson phase oxynitrides A′An−1Bn(O,N)3n+1 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba, or La; A′ = Li, Na, K, or Cs; B = Ti, Nb, or Ta), composed of mixed anions of O2− and N3−, have been studied as a novel layered perovskite oxynitride family active for various artificial photosynthesis approaches.6–10
Perovskite oxides (e.g., SrTiO3) and layered perovskite oxides (e.g., Ba5Nb4O15) (well-known active catalysts for water splitting to produce H2 gas) possess large bandgap energy values (Eg) of up to or even above 3.2 eV (λ < 380 nm), which are too high to harvest a wide range of the solar spectrum, including visible light.11–13 Introducing N into the oxide (i.e., nitridation) shifts the valence band maximum (VBM) to a more negative potential because the potential of the N 2p atomic orbitals is lower than that of the O 2p orbitals.14 Although nitridation leaves the conduction band (CB) potential of the oxide almost unchanged, hybridization of the N 2p and O 2p orbitals during nitridation narrows the Eg value of the oxide, resulting in a visible-light-responsive perovskite or layered perovskite oxynitride.
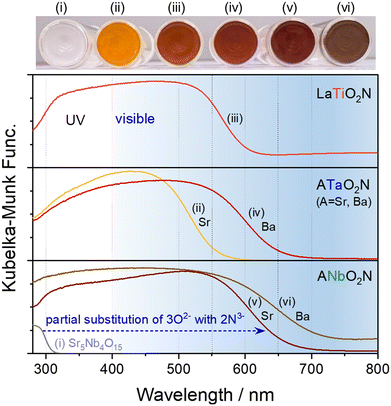
The wavelength edges of the visible-light absorption by perovskite oxynitrides vary depending on the combination of cations at the A and B sites, as presented in Fig. 2. For instance, SrNbO2N can be prepared by the partial exchange of 3O2− for 2N3− during the nitridation of layered perovskite Sr5Nb4O15, with the resulting reddish-brown oxynitride SrNbO2N able to absorb visible light up to a wavelength of approximately 680 nm.15 In the same manner, in the syntheses of SrTaO2N, LaTiO2N, BaTaO2N, and BaNbO2N, complete nitridation of the corresponding starting oxide resulted in oxynitrides capable of absorbing photons up to ca. 560, 620, 660, and 740 nm, respectively.16–19 The apparent colors of the oxynitrides became orange, red, dark red, or brown based on their light absorption edge. As discussed previously, the VBM positions of perovskite oxynitrides are composed of hybridized N 2p and O 2p atomic orbitals. The CB minimum (CBM) of the oxynitrides mainly consists of empty Ti 3d, Nb 4d, or Ta 5d orbitals for the respective B-site cation with d0 electronic configuration.20,21 The Eg value of oxynitrides typically decreases as the effective electronegativity of the B-site cations increases.21 The effective electronegativity of Nb5+ is larger than that of Ta5+, so Nb-based oxynitrides can absorb longer wavelengths of visible light (Fig. 2). Furthermore, the CBM positions of the oxynitrides are determined by the B–O/N–B bond angles.21,22 The tilt of the B(O,N)6 octahedra in a perovskite structure is larger for a smaller A-site cation, resulting in a narrower CB. The reduced dispersion of the CBs shifts the CBM positions to a more negative potential, thereby causing an increase in Eg. Thus, the Eg values of BaBO2N, SrBO2N, and CaBO2N are sequentially larger according to the size of the A-site cation (rBa > rSr > rCa).
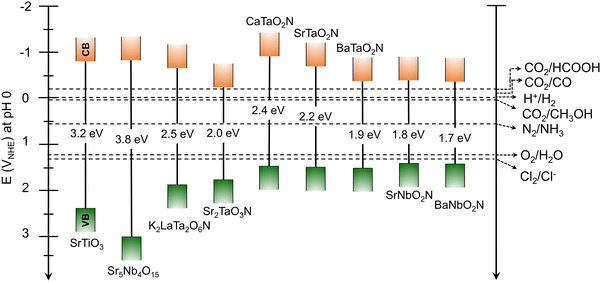
In addition to the narrow bandgap, the band positions of the perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides straddle the water redox potential (Fig. 3). This indicates that perovskite oxynitrides acting as a single absorber thermodynamically drive overall water splitting to produce H2 and O2 without the need to supply additional energy for the reaction. The favorable optical properties of the oxynitrides are distinguishable from those of other n-type oxide semiconductors exclusively driving water oxidation, such as visible-light-responsive BiVO4 (λ < 530 nm) and α-Fe2O3 (λ < 600 nm).23–25 Moreover, since the CBM potentials of the oxynitrides are more negative than the reduction potential of CO2, HCOOH, carbon monoxide (CO), and methanol (CH3OH) can be produced via photocatalysis. N2 fixation to synthesize NH3 gas is theoretically possible via photocatalysis with oxynitrides. Finally, since the VBM potentials of the oxynitrides are located below the potential of water oxidation reactions, they can catalyze the oxidation of various anions in seawater (including mineral salts).
Over several decades, perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides have been regarded as promising visible-light-responsive semiconductors for efficient artificial photosynthesis to produce value-added eco-friendly and renewable energy resources such as H2, HCOOH, CH3OH, and NH3.2,3,26–28 This is because the oxynitrides are chemically stable in aqueous electrolytes at various pH values and have ideal optical properties due to a narrow bandgap and a suitable band position, which makes them favorable for sunlight-driven photocatalysis. Therefore, we discuss recent advances in photocatalysis using various perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides responsive to a wide wavelength range of the solar spectrum. How the photoactivity of these compounds can be enhanced by their synthesis method for use in photoelectrodes, bulk and surface engineering by doping (or substitution), controlling their morphology, and crystal facet engineering is discussed in detail. We also discuss the challenges associated with using perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides for efficient artificial photosynthesis.
2. Visible-light-driven photocatalysis
A representative photocatalytic process using perovskite or layered perovskite oxynitrides is water splitting to produce renewable H2 energy. The half water oxidation of water splitting typically exhibits very slow kinetics compared with half water reduction so that alternative oxidations using the oxynitrides have been addressed to boost water splitting and then produce H2 gas with a higher evolution rate.29 Recently, CO2 reduction using these compounds has also been reported since carbon neutrality is becoming critical globally.30,31 First, we discuss the various reactions that can be photocatalyzed by perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides under sunlight (or only visible-light irradiation), the standard reduction potentials for which are reported in Table 1.| Half redox reactions | Balanced chemical reactions | Potential (VNHE) |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 reduction | CO2 + e− ⇌ CO2− | −1.90 |
| CO2 + 2H+ + 2e− ⇌ HCOOH | −0.20 | |
| CO2 + 2H+ + 2e− ⇌ CO + H2O | −0.11 | |
| CO2 + 4H+ + 4e− ⇌ HCHO + H2O | −0.07 | |
| CO2 + 6H+ + 6e− ⇌ CH3OH + H2O | 0.03 | |
| 2CO2 + 12H+ + 12e− ⇌ C2H5OH + 3H2O | 0.08 | |
| CO2 + 8H+ + 8e− ⇌ CH4 + 2H2O | 0.17 | |
| Water reduction (HER) | 2H+ + 2e− ⇌ H2 | 0 |
| N2 reduction | N2 + H+ + e− ⇌ N2H | −3.2 |
| N2 + 2H+ + 2e− ⇌ N2H2 | −1.1 | |
| N2 + 4H+ + 4e− ⇌ N2H4 | −0.36 | |
| N2 + 8H+ + 6e− ⇌ 2NH4+ | 0.27 | |
| N2 + 6H+ + 6e− ⇌ 2NH3 | 0.55 | |
| Water oxidation (OER) | O2 + 4H+ + 4e− ⇌ 2H2O | 1.23 |
| Chloride oxidation (CER) | Cl2 + 2e− ⇌ 2Cl− | 1.36 |
| ClO4− + 8H+ + 8e− ⇌ Cl− + 4H2O | 1.39 | |
| ClO3− + 6H+ + 6e− ⇌ Cl− + 3H2O | 1.45 | |
| HClO + H+ + 2e− ⇌ Cl− + H2O | 1.48 | |
| HClO2 + 3H+ + 4e− ⇌ Cl− + 2H2O | 1.57 | |
| Hydrogen peroxide production | H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e− ⇌ 2H2O | 1.78 |
| Sulfate oxidation | S2O82− + 2e− ⇌ 2SO42− | 2.01 |
2.1. Overall water splitting via one-step photoexcitation
The most ideal means of producing H2 is overall water splitting using a single semiconductor capable of absorbing visible light. Water redox reactions, i.e., hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER), are simultaneously activated at the separate surfaces of a semiconductor particle via one-step photoexcitation to produce H2 and O2, respectively, as follows:| 2H2O → 2H2 + O2 ΔG0 = 237 kJ mol−1 (E0 = −1.23 V) | (1) |
The solar-to-hydrogen (STH) conversion efficiency (η), a benchmark figure used to estimate the performance of a semiconductor for solar water splitting, is defined by
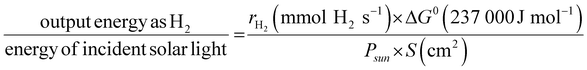 | (2) |
Overall water splitting with a quantum efficiency of almost unity using one-step photoexcitation of cuboidal Al-doped SrTiO3 (SrTiO3:Al) particles with a perovskite crystal structure has been reported.12 The remarkable water-splitting activity was attributed to the selective depositions of Rh/Cr2O3 (for HER) and a CoOOH cocatalyst (for OER) at the (100) and (110) crystal facets of SrTiO3:Al, respectively. HER and OER could be separated and strongly promoted by the anisotropic transport of photogenerated electrons and holes in the single crystal. Overall water splitting on a 100 m2 panel comprising modified SrTiO3:Al particles is an example of a safe mass hydrogen production system with a maximum STH of 0.76%.34 Although the system design of the panel for scale-up is simple and cost-effective, the low STH efficiency for mass water splitting is still a significant limitation.
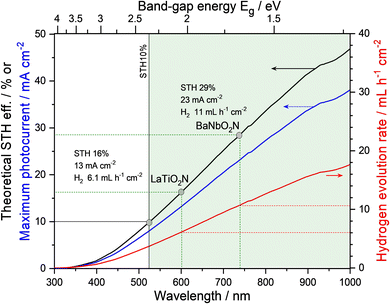
Nevertheless, several semiconductors capable of absorbing visible light, such as graphitic-C3N4 (Eg = 2.8 eV),37 (Ga1−xZnx)(N1−xOx) (Eg = 2.4 eV),38 Ta3N5 (Eg = 2.1 eV),39 and Y2Ti2O5S2 (Eg = 1.9 eV),40 have been successfully applied to overall water splitting via one-step photoexcitation. Moreover, several perovskite oxynitrides have also been utilized. Complex LaB(O,N)3 (B = Ta or Nb) solid solutions were successfully employed in the overall water splitting, resulting from the precise tuning of both Eg and bandgap positions of the oxynitrides via the substitution of B5+ with Mg2+.41,42 These results are discussed in detail in the following section concerning doping (or substitution). Recently, overall water splitting under visible-light irradiation has also been achieved using ATaO2N (A = Sr, Ba) particles with few defects.35,36Fig. 5 represents the first demonstration of overall water splitting by particulate ATaO2N crystals and the corresponding strategies based on the deposition of active cocatalysts. Under Xe lamp irradiation (λ > 420 nm), CrOx/Ru/IrO2/SrTaO2N particles, which are more photoactive than BaTaO2N, split water to produce H2 and O2 gases with initial evolution rates of 9.1 and 3.0 μmol h−1, respectively.36 The apparent quantum yield of surface-modified SrTaO2N at the wavelength of 420 ± 30 nm was 0.34% in the initial stage of water splitting, which became decreasingly saturated to 0.005% during the reaction over 48 h.
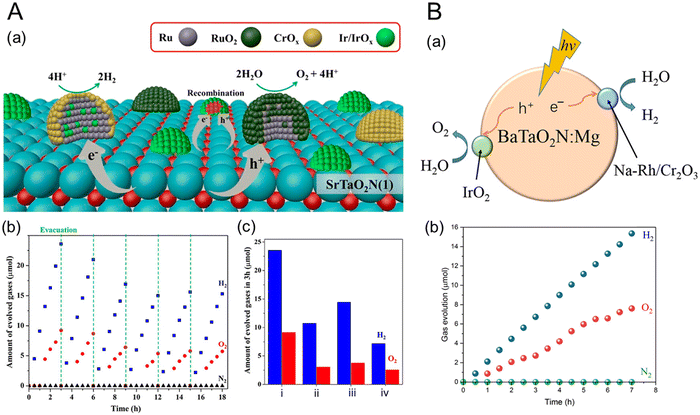 | ||
| Fig. 5 Overall water splitting by (A) perovskite CrOx/Ru/IrO2/SrTaO2N and (B) IrO2/Cr2O3/Na–Rh/BaTaO2N:Mg. (a) Deposition strategies for the HER and OER cocatalysts and (b) the corresponding gas evolution activities over time under visible-light irradiation (λ > 420 nm) using a 300 W Xe lamp in ultrapure water under an Ar atmosphere with an initial background pressure of 5 or 10 kPa. (c) The amounts of H2 and O2 gases generated during water splitting for 3 h using SrTaO2N with various cocatalysts: (i) CrOx/Ru/IrO2, (ii) CrOx/Ru, (iii) CrOx/Ru/IrO2(AD) (AD: by adsorption of colloidal IrO2), and (iv) IrO2/CrOx/Ru. Reproduced with permission.35 Copyright 2022, ACS. Reproduced with permission.36 Copyright 2023, ACS. | ||
Although the H2 evolution rate using ATaO2N particles is very limited compared with that using SrTiO3:Al particles,12 it is remarkable that overall water splitting using the perovskite oxynitrides is achieved under visible-light illumination. Interestingly, a general strategy for designing oxynitride particles was employed for overall water splitting via one-step photoexcitation. Both perovskite oxynitrides were initially prepared with few defects via different synthetic routes. During nitridation, SrCl2 and NaOH as fluxes, as well as Sr and O as sources, were introduced to obtain SrTaO2N with few defects, while doping with Mg2+ with an Mg/Ta ratio of 0.1 into BaTaO2N suppressed the Ta3N5 phase as an impurity. Subsequently, HER and OER cocatalysts were sequentially deposited on the perovskite oxynitride particles to promote the overall water-splitting ability. Ru or Rh covered with CrOx or Cr2O3 was employed as the HER catalyst. It is well-known that chromium oxides prevent the reverse reaction (i.e., the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR)) at HER sites.43,44 RuO2 or IrO2 catalysts deposited on the oxynitride surface promoted OER under light irradiation. For overall water splitting, although the bare surfaces of perovskite or layered perovskite oxides with a large bandgap (e.g., SrTiO3) can be employed as OER sites for overall water splitting,11,45 ATaO2N particles with a narrow bandgap are still necessary to load the OER cocatalyst. In the solid solution case, a thin coating of amorphous oxyhydroxide on the surface of RhCrOy/LaMg1/3Ta2/3O2N suppressed N2 evolution by self-photooxidation of the oxynitride, thereby improving overall water splitting.46 Moreover, the deposition of HER and OER cocatalysts on ATaO2N particles effectively suppresses the decomposition of the oxynitride and separates the reaction sites. Subsequently, the separation strategy of both types of reaction sites via the deposition of cocatalysts is mainly ascribed to the overall water-splitting activity of a single ATaO2N particle.
2.2. Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting
PEC water splitting using semiconductor electrodes is a potential means of producing H2 and O2. The HER and OER sites are divided into a p-type photocathode and an n-type photoanode, respectively. Based on this, the STH efficiency of a PEC water-splitting cell is typically higher than that of the overall water splitting using a photocatalyst.47 Various combinations of p- and n-type electrodes have been studied for PEC water splitting without supplying electricity.48–50 Unbiased PEC water splitting using an inverted and planar lead halide perovskite (LHP) based on the material of a perovskite solar cell (i.e., an NiFe/LHP photoanode and an NiPCoP/LHP photocathode) has recently been reported to generate a high STH conversion efficiency of 10.64% with a photocurrent density of 8.65 mA cm−2.50 A PEC cell using a perovskite BaTaO2N photoanode combined with an La5Ti2Cu0.9Ag0.1S5O7 photocathode has also shown potential for the unbiased overall water splitting, albeit its activity is very low.51Eqn (2) can be rearranged for the PEC water-splitting system to provide the STH efficiency (η) as follows:
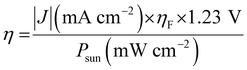 | (3) |
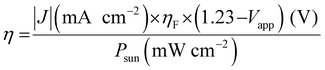 | (4) |
The B-site cations in perovskite AB(O,N)3 can easily be reduced to a lower oxidation state (e.g., Nb5+ to Nb4+ or Nb3+) during high-temperature nitridation under a reducing NH3 atmosphere owing to their high electronegativity. The reduced B-site cations cause the generation of anion defects and impurity traces that compensate for the charge imbalance, which increases the recombination of photogenerated holes and electrons during water splitting and leads to a decrease in photoactivity. In fact, the photoreaction takes place on the surface of the oxynitride, and surface defects therein negatively influence the PEC water-splitting activity.18,53 The sunlight-driven PEC activities of LaTiO2N, BaNbO2N, and BaTaO2N photoanodes have been significantly advanced compared to the other perovskite AB(O,N)3 by controlling the surface defect density.17–19 Prior to deposition of the OER electrocatalyst, Akiyama et al. cleaned the surfaces of synthesized LaTiO2N particles by using mild poly(4-styrene sulfonic acid) (PSS) (Fig. 6(A)).17 This resulted in etching of the defective surface layer of the oxynitride; although longer acid treatment increased the number of fine pores in the surface, it decreased the weight of the oxynitride layer. Afterward, the CoOx/LaTiO2N photoanode produced a high photocurrent density of 8.9 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE in a 1 M NaOH electrolyte at pH 13.5 under AM 1.5G irradiation, which is the highest reported so far. Moreover, its PEC water-splitting activity was more than two times higher than that of the as-prepared CoOx/LaTiO2N photoanode. Similarly, eliminating the surface defects in an LaTiO2N layer via acid treatment with aqua regia doubled the photocatalytic HER and OER activities of the oxynitride particles.54 Therefore, the effect of the acid treatment on photoactivity suggests that an oxynitride surface with a low number of defects is necessary to suppress the recombination of charge carriers and thereby boost water-splitting activity.
 | ||
| Fig. 6 PEC water splitting. (A) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images (a)–(d) and high-resolution (HR) transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images (e)–(h) of the surface of perovskite LaTiO2N treated with poly(4-styrene sulfonic acid) (PSS) for (a), (e) 0, (b), (f) 1, (c),(g) 17, and (d), (h) 72 h. Corresponding linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) curves of CoOx/LaTiO2N photoanodes not treated (lower line) or treated with PSS for 17 h (upper line) used for PEC water splitting in a 1 M NaOH electrolyte at pH 13.5 under chopped AM 1.5G irradiation. Reproduced with permission.17 Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH. (B) HRTEM images of the surface of perovskite BaNbO2N as-prepared (a) or annealed under an Ar atmosphere at 873 K for 1 h (b). Corresponding LSV curves of Co(OH)x–FeOy/BaNbO2N photoanodes used for PEC water splitting in a 0.5 M KBi electrolyte at pH 13 under AM 1.5G irradiation. Reproduced with permission.18 Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH. (C) (a) LSV curves in various scan directions of a Co(OH)x–FeOy/BaTaO2N photoanode annealed under an Ar atmosphere at 1073 K for 1 h after nitridation used for PEC water splitting in a 0.5 M KBi electrolyte at pH 13 under AM 1.5G irradiation. (b) The chronoamperometry curve obtained during long-term water splitting at the applied potential of 1.23 VRHE for 24 h. (c) The half-cell STH (HC-STH) conversion efficiency (%) estimated from the LSV curve presented in (a). Reproduced with permission.19 Copyright 2019, ACS. | ||
In another approach, annealing the surface of perovskite oxynitrides was effective in improving the water-splitting activity of Co(OH)x–FeOy/BaBO2N (B = Nb, Ta) photoanodes under sunlight (Fig. 6(B) and (C)).18,19 The surfaces of the as-prepared oxynitrides were amorphous as a result of mild nitridation of Lewis base Ba-rich Ba5B4O15 as the starting oxide. Subsequently, their highly defective surface with a high concentration of oxygen atoms became a single crystal by annealing under an Ar atmosphere at a suitable temperature. For instance, Ar-annealing of BaNbO2N at 873 K for 1 h resulted in a photocurrent density of 5.2 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE for sunlight-driven PEC water splitting in a 0.5 M KBi aqueous electrolyte at pH 13, which is five times higher than that of the as-prepared oxynitride.18 Although using inert Ar gas has provided the most favorable results, the amorphous surface of oxynitrides can also be crystallized by annealing under other gas atmospheres, such as NH3. The degree of improvement in photoactivity is inversely proportional to the surface defect concentration of the as-prepared oxynitride. Moreover, a highly defective oxynitride surface can become polycrystalline rather than a single crystal via Ar-annealing, leading to a small increase in photocurrent. The effect of the annealing temperature on the oxynitride is also dependent on the thermal stability of the oxynitride under an Ar atmosphere.53 Prolonged annealing at the decomposition temperature of BaNbO2N (>873 K) decreases the photoactivity. For instance, Ar-annealing highly enhanced the surface crystallinity of BaTaO2N, probably because of its high thermal stability nearly up to 1200 K. Thus, the increased crystallinity of as-prepared bulk BaTaO2N and its surface via Ar-annealing at 1073 K for 1 h induced a high photocurrent density of 6.5 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE for water splitting in a 0.5 M KBi aqueous electrolyte at pH 13.19 The photoactivity of the oxynitride corresponded to a maximum half-cell STH energy conversion efficiency of 1.4% at 0.88 VRHE, which is still the highest value yet reported using perovskites AB(O,N)3. Moreover, the improved crystallinity both on the surface and in the bulk of BaTaO2N led to long-term stability during water splitting over 24 h (79% retention of the initial photocurrent). These remarkable results clearly demonstrate that modifying the surface crystallinity of AB(O,N)3via annealing or using acid etching to improve the surface texture, both of which lower the defect density, is an excellent way of providing strong separation and fast transfer of photogenerated charges therein, thus leading to highly active and stable PEC water splitting.
2.3. Alternative oxidation reactions to the OER
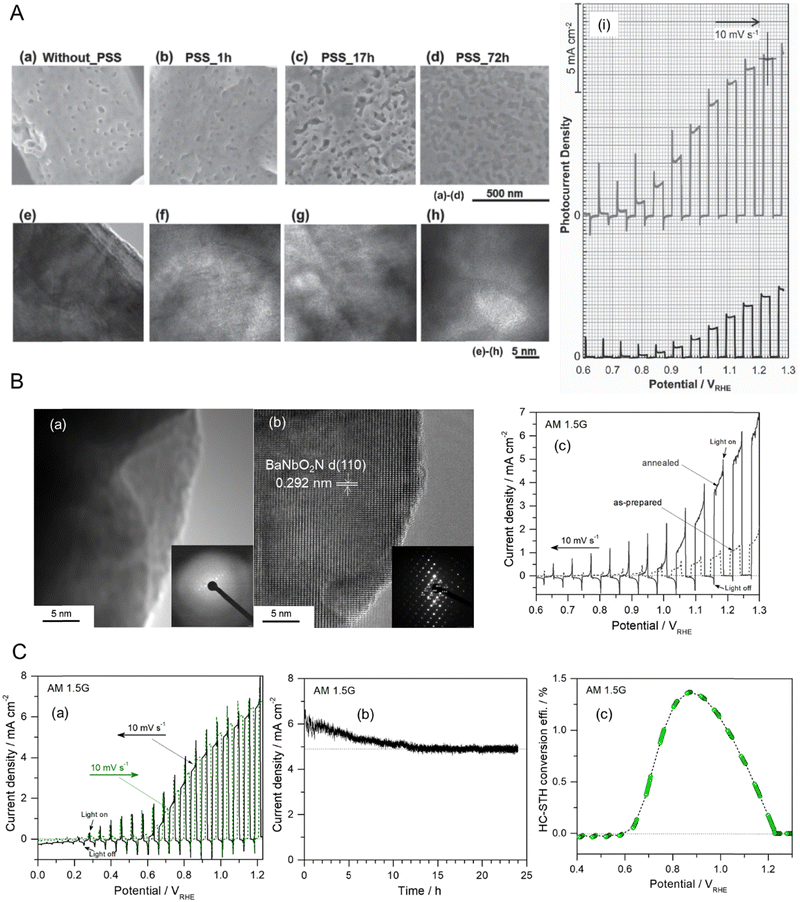
OER driven by four-electron transfer is relatively sluggish compared with HER activated via a two-electron pathway, the former creating a bottleneck for water splitting leading to a significant overpotential. The sluggish kinetics of OER typically become much slower in neutral electrolytes regardless of the electrocatalysts and/or semiconductors used, which indirectly causes a low production rate of hydrogen. Alternatively, a high evolution rate of hydrogen from water at neutral pH can be achieved via other oxidation reactions with relatively fast kinetics,28,55,56 such as the chlorine evolution reaction (CER). In particular, the splitting of seawater with a high concentration (ca. 0.55 M) of Cl− involving the CER can be driven under sunlight. In seawater, the thermodynamic potential for the oxidation of Cl− driven via two-electron transfer to produce Cl2 is 1.36 VNHE at pH 0 (Table 1). Fig. 7(A) represents a calculated Pourbaix diagram for an artificial chlorine system in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous electrolyte.57 The disproportionation of Cl− in water to produce hypochlorous acid (HClO), which is also activated by the two-electron pathway, is possible in the pH range of approximately 3–7.5 while the dissociation of HClO producing hypochlorite (ClO−) occurs at neutral and alkaline pH values because of its pKa of 7.5. Although CER is thermodynamically less favorable than OER (E0 = 1.23 VNHE at pH 0), the oxidation driven via the two-electron pathway in the former is kinetically catalyzed faster than in the latter. The CER is selectively more catalyzed than the competing OER even in strong acidic electrolytes due to its independence from the concentration of H+.58 Moreover, using seawater instead of pure water is cost-effective for artificial H2 production systems because the former is very abundant. Based on the advantages of the CER over the OER, PEC seawater splitting using WO3 and BiVO4 semiconductors at neutral pH has recently been reported.58–60 | ||
| Fig. 7 Chlorine evolution reaction (CER) in seawater as an alternative oxidation pathway. (A) A computed Pourbaix diagram for an artificial chlorine system in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous electrolyte without any other mineral salts. Reproduced with permission.57 Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH. (B) The feasible mechanism for PEC seawater splitting using a perovskite oxynitride in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous electrolyte. (C) (a) A schematic of the bottom-up fabrication of an SrNbO2N/Nb photoanode involving oxidation and two-step nitridation. (b) LSV curves for the corresponding Co(OH)x/SrNbO2N/Nb photoanode during seawater splitting in a 0.2 M NaPi buffer with and without 0.5 M NaCl electrolyte (at pH 6.4 and 6.7, respectively) under AM 1.5G irradiation. (c) Time courses of O2, ClO−, and H2 generation during seawater splitting using the same photoanode and a Pt wire at an applied potential of 1.23 VRHE in a 0.5 M NaCl electrolyte buffered with 0.2 M NaPi under AM 1.5G simulated sunlight for 150 min. The dashed lines indicate the amounts of H2, ClO− (e−/2), and O2 (e−/4) estimated for a faradaic efficiency of unity. Reproduced with permission.29 Copyright 2023, ACS. | ||
The photoactivity of perovskite oxynitrides for OER is relatively low in neutral electrolytes compared to strong alkaline electrolytes (e.g., at pH 13).61–63 This is because the band edge and flat band potential energies of AB(O,N)3 are dependent on the pH value, and their OER kinetics are very slow under neutral conditions.14,53 However, the limited activity of AB(O,N)3 at a neutral pH makes them unfavorable for commercial water-splitting applications. Recently, the PEC activity of SrNbO2N for water splitting at a neutral pH was largely enhanced via the bottom-up fabrication of the photoanode and the addition of NaCl to an aqueous electrolyte.29 The feasible mechanism to simultaneously drive the HER and CER using the perovskite oxynitride in artificial seawater is illustrated in Fig. 7(B). The band edge potentials of SrNbO2N thermodynamically span the standard electrode potential for CER, as well as those for OER and HER, indicating that the holes photogenerated at the surface of the oxynitride are consumed to drive the CER and OER. Fig. 7(C) demonstrates sunlight-driven seawater splitting in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous electrolyte at pH 6.4 using an SrNbO2N photoanode prepared via bottom-up fabrication including oxidation and flux-assisted nitridation: the oxidation process was necessary for growing the crystalline Nb2O5 layer on an Nb substrate while the subsequent two-step nitridation process at different temperatures caused the complete conversion of crystalline Nb2O5 to porous cuboidal SrNbO2N with high crystallinity and a large surface area. Consequently, the Co(OH)x/SrNbO2N/Nb photoanode exhibited an mA-level photocurrent in a neutral 0.2 M NaPi aqueous electrolyte, which is a remarkable result for water splitting using a perovskite oxynitride. Moreover, the photoactivity of the oxynitride became three times higher in artificial seawater including 0.5 M NaCl providing the activation of the CER as well as the OER. Quantitative analysis proved that seawater splitting by SrNbO2N resulted in the generation of HClO, ClO−, and O2 in the oxidation compartment and H2 evolution in the reduction compartment, corresponding to a faradaic efficiency of almost 90%. These results clearly indicate that the CER is more preferentially driven over the OER during seawater splitting at neutral pH. It also indicates that the CER can be an alternative oxidation reaction to the OER that improves the H2 production activity of perovskite oxynitrides in strong alkaline to neutral environments.
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production from water oxidation is regarded as an alternative oxidation reaction to the OER,28,64 and H2O2 is also generated via the ORR using semiconductor photocathodes.65,66 In this review, we only discuss H2O2 production from water oxidation in terms of improving H2 production. As reported in Table 1, although H2O2 production is driven via a two-electron pathway similar to the CER leading to kinetically fast activation, its thermodynamic potential of 1.78 VNHE is significantly unfavorable compared with the competing OER. The overall reaction for H2O2 production and water reduction via one-step photoexcitation is as follows:
| 2H2O → H2 + H2O2, E0 = −1.78 V | (5) |
Despite the thermodynamic disadvantage, the production of H2O2 based on the photocatalytic oxidation of water has recently been attempted because H2O2 is a much higher value-added product than O2.67–69 Moreover, attempts at suppressing the competitive OER and selectively improving the valuable H2O2 production have been successful. In particular, it has been reported that the HCO3− electrolyte in the pH range of 7–8 promotes the PEC activity of a BiVO4/WO3 photoanode for H2O2 production.70 However, the very low faradaic efficiency for the PEC H2O2 production (approximately 54%) was improved up to 79% by introducing an Al2O3 overlayer on the photoanode.67 In the reaction mechanism, the weakly basic HCO3− as a hole acceptor is adsorbed at the weakly acidic Al2O3 surface and oxidized to unstable HCO4−, which then reacts with H2O to produce H2O2. Furthermore, a faradaic efficiency of more than 90% for H2O2 production using the Gd-doped BiVO4 photoanode in the potential range of 1.8–2.5 VRHE has been reported.69 The authors theorized that the Gd doping of BiVO4 shifted the binding energy of OH− on the active sites of Bi–Bi to a more optimal energy level, thereby boosting H2O2 production. Although the catalytic mechanism for H2O2 production is still uncertain,64 it is remarkable that the selectivity and faradaic efficiency of the H2O2 production can be highly improved despite its unfavorable thermodynamic characteristics compared with the OER.
Although semiconductors with a wide bandgap (e.g., TiO2, WO3, and BiVO4) have been employed as photocatalysts or photoelectrodes for H2O2 production,28,64,65 photocatalytic oxidation to produce valuable H2O2 using perovskite or layered perovskite oxynitrides has not yet been reported. Based on the electromotive force of H2O2 production (1.78 V) being higher than that of water splitting, the band structures of perovskite oxynitrides with a negative VBM potential could make them unsuitable. However, the band structures of layered perovskite oxynitrides with relatively large Eg values possibly make them suitable for H2O2 production (Fig. 3). Moreover, the bandgap engineering of perovskite oxynitrides via substitution with alien elements could make them capable of thermodynamically driving H2O2 production.41,46 Therefore, in addition to CER, H2O2 production using perovskite or layered perovskite oxynitrides may be an alternative oxidation reaction to OER that efficiently produces not only valuable H2O2 but also H2.
2.4. CO2 reduction
The photocatalytic reduction of CO2 using a semiconductor is driven via a multiple-electron transfer process that generates many different products, such as formic acid (HCOOH), carbon monoxide (CO), methanol (CH3OH), methane (CH4), and so on, depending on the number of transferred electrons and the subsequent reaction pathway (Table 1). The catalytic mechanism is complex and has been unclear until very recently. Indeed, much research effort toward understanding it and increasing the selectivity for its high-value reaction products has been made because of the current global drive toward carbon neutrality.71–73 Photocatalytic and PEC systems employing perovskite or layered perovskite oxynitrides for CO2 reduction under visible-light irradiation have also been reported.30,74The band edge potentials of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides straddling the various CO2 reduction potentials in Fig. 3 suggest their suitability as a semiconductor for sunlight-driven CO2 reduction. In fact, the overall reaction including the CO2 reduction and OER in (sea)water containing dissolved CO2 catalyzed by oxynitrides is thermodynamically feasible via one-step photoexcitation. However, this has still not been realized because of the small driving force of oxynitrides with a narrow bandgap for CO2 reduction and sluggish OER kinetics driven via the simultaneous transfer of four electrons. Alternatively, a hybrid PEC cell constructed using a CuGaO2/PRu-Re photocathode and a CoOx/TaON photoanode exhibited visible-light-driven CO2 reduction to produce CO and oxidation via the OER to release O2 in an aqueous electrolyte with no external bias,75 albeit the efficiency of the system was very poor.
In the study by Yoshitomi et al., although triethanolamine (TEOA) in an organic solvent instead of water was used as the hole acceptor, a hybrid perovskite CaTaO2N coupled with a binuclear Ru(II) complex (RuRu′) catalyst activated CO2 reduction under visible-light illumination to produce HCOOH with high selectivity.76Fig. 8(A) illustrates the expected Z-scheme CO2 reduction mechanism of the hybrid catalyst under visible light. The binuclear RuRu′ complex is composed of a redox photosensitizer unit (Ru(PS)) and a catalytic unit (Ru(Cat)). Both CaTaO2N and RuRu′ are capable of absorbing visible light up to a wavelength of 500 nm. The authors proposed that the transfer of photoexcited electrons from the CBM potential of CaTaO2N to Ru(PS) and then to Ru(Cat) provides the Z-scheme for CO2 reduction. The effect of each component in the hybrid catalyst on the CO2 reduction activity is summarized in Table 2. The combination of CaTaO2N with RuRu′ exclusively enabled the detection of formate resulting from the dissociation of HCOOH with a high selectivity of greater than 99%. The oxynitride with only Ru(Cat) adsorbed thereon produced less formate and accompanying byproduct H2, while its combination with Ru(PS) did not produce either product. These results indicate that both CaTaO2N and the binuclear RuRu′ complex were necessary to realize HCOOH production. Moreover, the deposition of Ag particles on the CaTaO2N surface resulted in three times higher CO2 reduction activity. The metallic Ag particles did not act as a cocatalyst but instead as an intermediate promoter by accumulating photogenerated electrons and then mediating charge transfer from CaTaO2N to RuRu′. This high activation and selectivity for visible-light-driven CO2 reduction can be attributed to fast electron transfer caused by the suitable arrangement of the energy levels of CaTaO2N and RuRu′ and by the deposition of Ag particles.
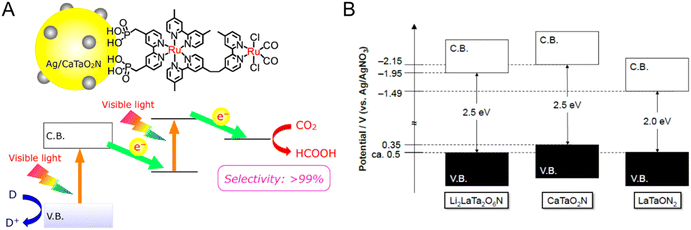 | ||
| Fig. 8 CO2 reduction. (A) The catalytic mechanism for visible-light-driven Z-scheme CO2 reduction using a hybrid catalyst consisting of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides and a binuclear Ru complex (RuRu′). Reproduced with permission.76 Copyright 2015, ACS. (B) Band structure diagrams of layered perovskite Li2LaTa2O6N and perovskites CaTaO2N and LaTaON2 estimated in an anhydrous acetonitrile (MeCN) electrolyte containing 0.1 M tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate (Et4NBF4) at pH 7. Reproduced with permission.26 Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH. | ||
| Parameter | Photocatalysta | Product amount (nmol) | Selectivity for formate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formate | H2 | |||
a Reaction conditions: CO2 reduction for 15 h using 4.0 mg of photocatalyst in a CO2-purged N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMA)/triethanolamine (TEOA) (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v) electrolyte of 4 mL under a 400 W high-pressure Hg lamp with a filter comprising sodium nitrite (NaNO2) solution. In each case, the adsorbed amount of RuRu′ and the loading amount of Ag on the semiconductor were 2.5 μmol g−1 and 1.0 wt%, respectively.
b The semiconductor upon which 3 μmol g−1 of RuRu′ was adsorbed was immersed in mixed anhydrous acetonitrile (MeCN)/TEOA (4 1 v/v) electrolyte of 4 mL under a 400 W high-pressure Hg lamp with a filter comprising sodium nitrite (NaNO2) solution. In each case, the adsorbed amount of RuRu′ and the loading amount of Ag on the semiconductor were 2.5 μmol g−1 and 1.0 wt%, respectively.
b The semiconductor upon which 3 μmol g−1 of RuRu′ was adsorbed was immersed in mixed anhydrous acetonitrile (MeCN)/TEOA (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 v/v). RuRu′ is composed of a redox photosensitized unit (Ru(PS)) and a catalytic unit (Ru(Cat)). ND, not detected. 1 v/v). RuRu′ is composed of a redox photosensitized unit (Ru(PS)) and a catalytic unit (Ru(Cat)). ND, not detected.
|
||||
| Reaction medium | CaTaO2N | ND | ND | — |
| Ag/CaTaO2N | ND | ND | — | |
| RuRu′ | ND | ND | — | |
| RuRu′/CaTaO2N | 93 | ND | — | |
| Ag | RuRu′/Ag/CaTaO2N | 320 | ND | >99 |
| RuRu′ | Ru(Cat)/Ag/CaTaO2N | 114 | 2.6 | — |
| Ru(PS)/Ag/CaTaO2N | ND | 3.8 | — | |
| Semiconductorb | Li2LaTa2O6N | ND | ND | — |
| RuRu′/LaTaON2 | ND | ND | — | |
| RuRu′/Li2LaTa2O6N | 660 | 16 | 97 | |
| RuRu′/Ag/Li2LaTa2O6N | 1440 | 16 | 99 | |
It has been reported that visible-light-driven CO2 reduction can be highly activated by introducing a 2D-layered perovskite Li2LaTa2O6N instead of CaTaO2N.26 Although the Eg value of layered perovskite Li2LaTa2O6N is the same as that of CaTaO2N, its band structure is slightly shifted to a more positive potential from that of the perovskite oxynitride due to its different A-site cations and lower concentration of nitrogen (Fig. 8(B)). According to the CO2 reduction activity reported in Table 2, the CBM potential of Li2LaTa2O6N, even though reduced, is sufficient to transfer photogenerated electrons to RuRu′. The tendency for the photoactivity of Li2LaTa2O6N is identical to that of CaTaO2N, i.e., the combination with RuRu′ and the deposition of Ag nanoparticles thereon are essential for driving the photoreaction with high selectivity. Interestingly, the CO2 reduction activity using Li2LaTa2O6N was almost five times higher than that using CaTaO2N. The largely enhanced photoactivity was mainly ascribed to the high crystallinity of Li2LaTa2O6N with a lower density of defect traps and higher density of reactive electrons, as analyzed by using transient absorption spectroscopy. However, the effect of the 2D structure of Li2LaTa2O6N on the photoactivity has not yet been elucidated.9,77
Perovskite oxynitrides employed as a single photocatalyst rather than in a hybrid catalyst with organic compounds for visible-light-driven CO2 reduction have recently been reported.78–80 The deposition of a core–shell Ni–Ag bicomponent cocatalyst on CaTaO2N increased interfacial electron transfer and thus enhanced the CO2 reduction activity, showing a synergistic effect of the bicomponent catalyst.78 Moreover, heterojunction structures composed of a metal oxide (e.g., CeO2) and LaTiO2N have been shown to improve CO2 reduction, which is a well-known strategy for effectively suppressing the recombination of photogenerated charges and thereby boosting the photoreaction.79,80 This approach for CO2 reduction mainly results in CO production accompanied by CH4 as a secondary product, thereby indicating relatively low selectivity for them. Therefore, there is still room for improvement in sunlight-driven CO2 reduction activity and product selectivity using perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides. Nevertheless, successful CO2 reduction using the oxynitrides also demonstrates the suitability of their band structures for various artificial photosynthetic processes and H2 production via water splitting.
3. Synthesis of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides
3.1. Powder
Perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides are typically prepared via high-temperature nitridation of the starting oxides with a stoichiometric A/B ratio identical to that of the resulting oxynitride under an NH3 atmosphere (e.g., Ca2Ta2O7 for CaTaO2N, Sr2Nb2O7 for SrNbO2N, or amorphous Sr2TaOx for Sr2TaO3N).81–83 During nitridation, NH3 thermally decomposes into H2 and N2, and N3− from N2 exchanges with O2− in the starting oxide under the reducing atmosphere exemplified in the following equation for CaTaO2N synthesis:| Ca2Ta2O7 + 2NH3 → 2CaTaO2N + 3H2O | (6) |
Otherwise, the oxynitrides are synthesized via calcination of the starting nitride precursor under an inert N2/Ar atmosphere. For instance, BaTaO2N has been prepared using TaN as the Ta precursor based on the following reaction:84
| BaCO3 + TaN → BaTaO2N + CO | (7) |
The ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) powder instead of toxic NH3 gas has also been used as the nitrogen source for nitridation because it thermally decomposes into NH3 and HCl at a temperature higher than 610 K.85
| A5Nb4O15 + xNb → 5ANb(4+x)/5O3 (stoichiometric ANbO3 when x = 1.0) | (8) |
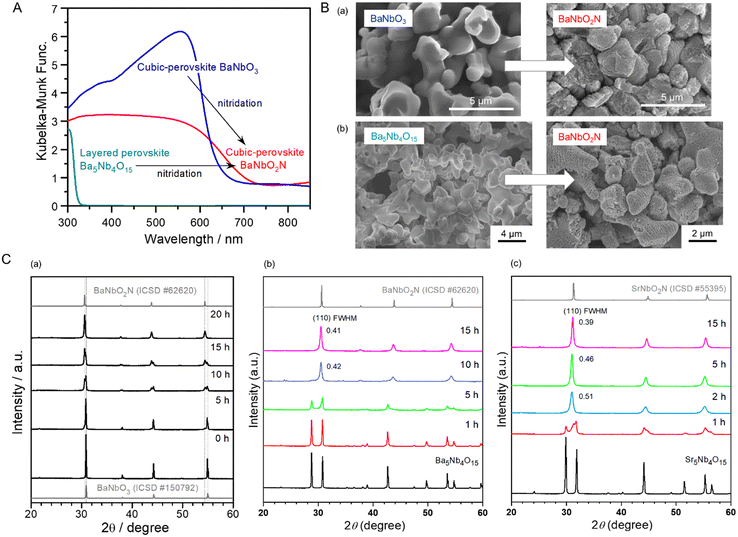 | ||
| Fig. 9 Conversion of perovskite BaNbO3 and layered perovskite Ba5Nb4O15 to BaNbO2N via nitridation. (A) UV-vis (DRS) spectra of starting BaNbO3 and Ba5Nb4O15 oxides for the synthesis of visible-light-responsive BaNbO2N. (B) SEM images of the different starting oxides and the corresponding oxynitrides after nitridation. (C) X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns for perovskite ANbO2N (A = (a), (b) Ba, (c) Sr) and intermediate derivatives obtained via the nitridation of (a) BaNbO3 and (b), (c) A5Nb4O15 at 1123 and 1173 K, respectively. FWHM, full-width at half-maximum. Reproduced with permission.15 Copyright 2022, Elsevier. Reproduced with permission.90 Copyright 2016, ACS. | ||
The SEM images in Fig. 9(B) and the XRD patterns in Fig. 9(C)-(a) show the transformation of smooth perovskite BaNbO3 to randomly porous BaNbO2N via nitridation at 1173 K for 20 h. The perovskite BaNbO3 was monotonically converted to perovskite oxynitride BaNbO2N without involving any structural transition, leading to the exchange of oxygen with nitrogen. Thus, the use of ANbO3 as the starting precursor was effective in the preparation of surface- and bulk-crystalline ANbO2N. Nevertheless, the high water-splitting activity of ANbO2N was not achieved from stoichiometric ANbO3 (as x = 1.0). The high bulk crystallinity of ANbO2N was accompanied by an impurity phase of NbOxNy and a surface concentration ratio of A/Nb lower than unity, resulting in an oxynitride with rather low photoactivity. An A-site-rich oxide (as x < 1.0) was necessary to obtain stoichiometric oxynitrides without the impurity phase because of the volatility of the A-site cation in the presence of alkali and alkali-earth metal groups during high-temperature nitridation. In response, the use of A-site-rich precursors has been applied in various syntheses of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides.62,94–96 Layered perovskite A5B4O15 (A = Sr, Ba; B = Ta, Nb) has been employed in the synthesis of photoactive ABO2N, as presented in Fig. 9(A).15,18,19 The starting oxides have a crystal structure similar to that of ABO2N, with the A-rich concentration being replenished during high-temperature nitridation to compensate for the volatility of the A-site cations. The layered perovskite was converted to perovskite oxynitride ABO2N via the following reaction:
| A5B4O15 + 4NH3 → 4ABO2N + AO + 6H2O | (9) |
The smooth-layered perovskites were completely changed to their porous ABO2N counterpart via a process analogous to the conversion of perovskite ANbO3. However, they are distinguishable in that the pores are orderly located in a layered structure, probably resulting from the decomposition of an AO slate layer in A5B4O15 and the exchange of three O2− ions in the equatorial plains of octahedral BO6 with two N3− (Fig. 9(B)).98 As shown in Fig. 9(C)-(b), (c), the transformation of A5Nb4O15 to ANbO2N was completed with no AO impurity traces after 15 h of nitridation.15 The excess of A species, undoubtedly in the form of the amorphous phase and/or nanoparticles, was easily removed with distilled water in the washing step of ANbO2N due to the A species being a Lewis base. The Lewis base A-rich species positively suppressed the reduction of the B-site cation, leading to ABO2N with fewer defects and an adjusted stoichiometric A/B ratio in the oxynitride. However, it caused an amorphous surface to form on ABO2N, which became crystalline via subsequent Ar-annealing treatment at a suitable temperature depending on the thermal property of ABO2N that enhanced water-splitting photoactivity. In another conversion, employing a (Na1/4Ba3/4)(Zn1/4Ta3/4)O3 solid solution with a perovskite structure to synthesize active BaTaO2N maximized the evaporation of volatile Na and Zn elements during nitridation.99
Fig. 10(A) illustrates the anticipated growth mechanism of cubic-type BaTaO2N particles showing how the flux-assisted nitridation conditions change the surface morphology of the resulting oxynitride. The following reaction steps are based on the XRD results:92
| BaCO3 → BaO + CO2 | (10) |
| BaO + Ta2O5 → BaTa2O6 | (11) |
| 2BaTa2O6 + 3BaO → Ba5Ta4O15 | (12) |
| 2Ba5Ta4O15 + 2BaTa2O6 + 12NH3 → 12BaTaO2N + 18H2O | (13) |
First, BaCO3 as the Ba precursor is decomposed to BaO, after which BaO and Ta2O5 as the Ta source are dissolved in the KCl flux at a high temperature. The diffusion of the reactants through the molten flux leads to nucleation and growth of plate-like BaTa2O6 and Ba5Ta4O15 (eqn (11) and (12), respectively). Finally, nitridation of the crystalline oxides under NH3 flow causes the crystallization and growth of BaTaO2N particles (eqn (13)). The crystalline growth during nitridation at 1123 K for 0 h (i.e., as the temperature was rising) provided vertically aligned plate-like shapes (Fig. 10(B)) comprising a mixture of BaTaO2N, Ba5Ta4O15, BaTa2O6, and Ta2O5. The plate-like shapes became thicker and irregular with increasing nitridation time up to 4 h. After 6 h of nitridation, the irregular particles had completely turned into the intrinsic crystal shape of cubic BaTaO2N with clear edges. Subsequently, after 10 h, the cubic-like BaTaO2N particles displaying specific (100) and (110) facets were more homogeneously dispersed. Interestingly, the surface morphology of BaTaO2N during nitridation with a different flux was dissimilar to that during the KCl-assisted nitridation (Fig. 10(C)).103 As RbCl and CsCl were utilized in the latter process, BaTaO2N particles maintained their cubic crystal structure, although their edges were slightly truncated and the exposed facets were predominantly along the (100) plane. In particular, the BaTaO2N crystals prepared using CeCl possessed many small steps at the edges of the cubic structure. Meanwhile, the oxynitride crystals prepared via BaCl2-assisted nitridation had a tetradecahedral shape with exposed (111) and (100) facets. The various fluxes of cations changed the electrostatic forces between the precursor ions during the growth of BaTaO2N, which thus determined the surface morphology and predominant crystal facets of the resulting oxynitride.
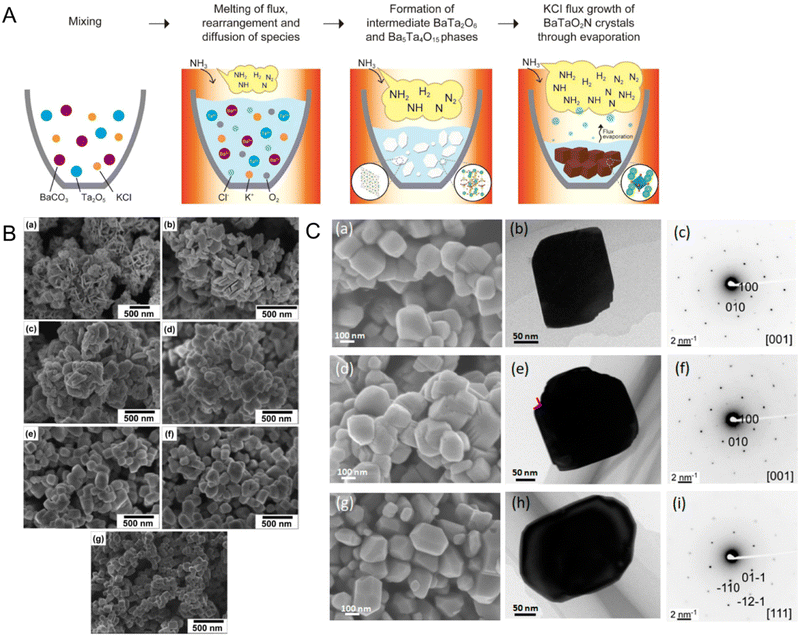 | ||
| Fig. 10 Flux-assisted nitridation. (A) A schematic of the growth mechanism of cube-like BaTaO2N crystals during nitridation using molten KCl. Reproduced with permission.92 Copyright 2015, ACS. (B) SEM images of BaTaO2N particles grown via nitridation using molten KCl at 1223 K for (a) 0, (b) 1, (c) 2, (d) 4, (e) 6, (f) 8, or (g) 10 h. Reproduced with permission.92 Copyright 2015, ACS. (C) SEM images, TEM images, and SAED patterns of BaTaO2N prepared via flux-assisted nitridation using different fluxes of (a)–(c) RbCl, (d)–(f) CsCl, and (g)–(i) BaCl2. Reproduced with permission.103 Copyright 2020, ACS. | ||
3.2. Photoelectrodes
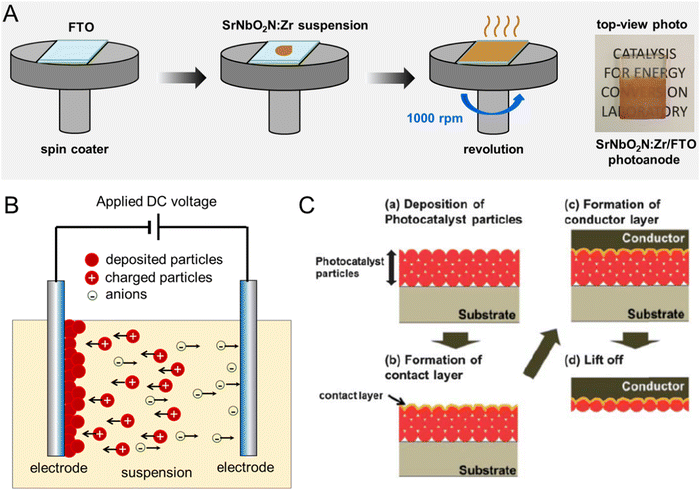 | ||
| Fig. 11 Particulate photoelectrodes. Schematic diagrams of the preparation of perovskite oxynitride photoanodes via (A) spin coating, (B) electrophoretic deposition (EPD), and (C) particle transfer methods. Reproduced with permission.104 Copyright 2013, RSC. Reproduced with permission.105 Copyright 2023, Elsevier. | ||
Several studies showing the improved PEC water-splitting activity using perovskite oxynitrides prepared via bottom-up fabrication have recently been reported.52,113,114Fig. 12 presents top-view and cross-sectional SEM images of various bottom-up-fabricated oxynitride films. Vertical SrNbO2N nanorod arrays have been grown on an Nb substrate via a hydrothermal method and subsequent nitridation.52 SrNbOx nanorod arrays were grown on the Nb substrate at a low temperature of 473 K, after which the oxide was transformed to SrNbO2N nanorod arrays through nitridation at 1273 K for 2 h. As shown in Fig. 12(A), the diameter and length of the oxynitride nanorods were approximately 60 and 500 nm, respectively, thereby allowing favorable visible-light absorption and vertical separation of photogenerated charges. Interestingly, perovskite oxynitrides with 1D surface morphology have been reported for the first time. After the loading of CoOx nanoparticles, SrNbO2N nanorod arrays produced a notable photocurrent density of 1.3 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE in an aqueous electrolyte at pH 13 under AM 1.5G simulated sunlight. Although the synthesis of the starting oxide at low temperature and a short nitridation period caused no additional interlayers detrimental to photoreactions, the light absorption edge of the SrNbO2N nanorod arrays was approximately 630 nm, which is significantly shorter than 700 nm reported previously.15,93
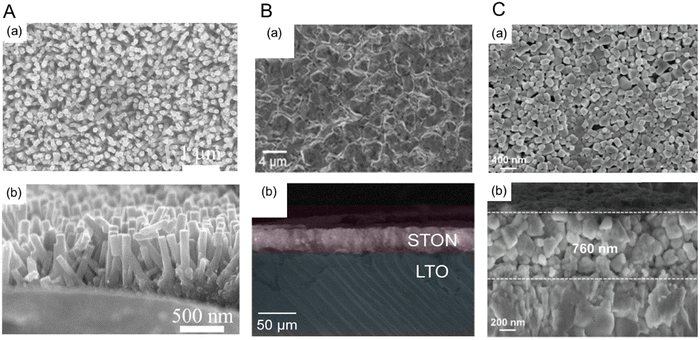 | ||
| Fig. 12 Bottom-up fabrication of perovskite oxynitride photoanodes. (a) Top-view and (b) cross-sectional SEM images of (A) SrNbO2N nanorod arrays prepared via a hydrothermal method followed by nitridation, (B) SrTaO2N crystals grown on a LiTaO3 substrate synthesized by using a reactive inorganic vapor method including nitridation, and (C) BaTaO2N nanoparticle films deposited on a Nb substrate prepared via co-evaporation followed by nitridation. Reproduced with permission.52 Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH. Reproduced with permission.113,114 Copyright 2022, Elsevier. | ||
Centimeter-scale perovskite SrTaO2N crystals have been prepared by using a reactive inorganic vapor method including nitridation.114 The oxynitride crystals were epitaxially grown on a (110)-oriented LiTaO3 substrate via the evaporation of Sr sources under an NH3 atmosphere. During the evaporation step, Sr2+ was exchanged with Li+ in the (110)-oriented LiTaO3 and nitrogen diffused into the oxide substrate simultaneously, leading to the growth of the SrTaO2N crystals. Interestingly, different crystal orientations of LiTaO3 (i.e., the (110) and (001) facets) resulted in nitridation rather than the intercalation of Sr2+ because the sizes of the lattice voids in the (110) and (001) facets are not large enough for the insertion of Sr2+ in the oxide substrate whereas they are in the (100) orientation. As shown in Fig. 12(B), the epitaxial growth of the perovskite SrTaO2N crystals produced a dense film several tens of micrometers thick because of lattice expansion resulting from the insertion of Sr2+. The dense film layer minimized inter-particle interfaces and grain boundaries, thereby resulting in a high photocurrent density of 1.20 mA cm−2 at 0.6 VRHE (with a low onset potential of 0.35 VRHE) for water splitting in a 1 M NaOH electrolyte at pH 13.6. However, lattice expansion during the conversion to oxynitride caused the limited diffusion of Sr2+, so the oxide substrate was not completely transformed to SrNbO2N. Thus, these results indicate that the suitable selection of both the starting substrate and its crystal orientation is critical for the epitaxial growth of perovskite oxynitrides.
A co-evaporation method followed by nitridation to prepare a BaTaO2N nanoparticle film directly grown on an Nb substrate has been reported.113 BaF2 and Ta2O5 precursors were uniformly evaporated onto the substrate via electron beam deposition and then completely transformed to BaTaO2N via nitridation under an NH3 atmosphere. The resulting ∼760 nm-thick BaTaO2N film comprised nanosized cubic crystalline particles, as shown in Fig. 12(C). The high crystallinity of the oxynitride was due to the uniform dispersion of Ba and Ta atoms in the resulting film. As a result, the BaTaO2N photoanode produced a high photocurrent density of 4.7 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE for water splitting in a 1 M KOH electrolyte at pH 13.6 under sunlight irradiation. The advantage of the co-evaporation method is the ability to regulate the reduction of Ta5+ during high-temperature nitridation by tuning the Ba/Ta ratio, which is similar to powder syntheses. In conclusion, the various bottom-up fabrication methods for perovskite oxynitrides reviewed in this article could enhance water-splitting activity by suppressing the generation of defects and additional interlayers in the resulting oxynitride film.
4. Bulk and surface engineering
4.1. Cation doping and substitution
The doping (or substitution) of foreign elements into a semiconductor is a typical means of modifying its bulk and/or surface properties, which can lead to enhanced photocatalytic or PEC water-splitting activities. In this review, doping and substitution are distinguished from each other according to the amount of the alternative species introduced into the perovskite oxynitride: doping is below 10 at% and substitution is above 10 at%. Moreover, we cover the doping (or substitution) of the A- and/or B-site cations in the perovskite or layer perovskite oxynitrides. Perovskite BaBO2N (B = Ta, Nb) has an ideal cubic crystal structure and the volume of its unit cells is markedly small.90,115 By contrast, the cubic lattices of AB(O,N)3 (A = La, Ca, or Sr; B = Ta, Nb) are distorted because of the A-site cations being smaller than Ba2+ and the tilting of B(O,N)6 octahedra. These findings imply that the isostructural replacement of cations in perovskite oxynitrides with alternative ones could be significantly limited in terms of the size and amount of the dopant (or substituent).The doping of perovskite SrNbO2N with 2 at% Zr4+ reduced the bulk and surface defect densities of the oxynitride by suppressing the reduction of Nb5+ during nitridation, thereby improving its PEC water-splitting activity.105 Although the limited replacement of Nb5+ with Zr4+ maintained the optical properties of the oxynitride (i.e., the absorption of visible light up to a wavelength of 680 nm), using a larger amount of Zr4+ caused Zr-related impurity phases, thereby notably decreasing the photoactivity. Moreover, doping the Nb5+ sites in BaNbO2N with Ti4+, Zr4+, W6+, or Mo6+ has been attempted to control the donor density in the oxynitride bulk originating from the generation of reduced species during nitridation.116 Doping with lower-valent cations Ti4+ and Zr4+ suppressed the generation of Nb4+ during nitridation whereas doping with higher-valent cations W6+ and Mo6+ rather increased the donor density. Moreover, doping with up to 4 at% Ti4+ resulted in the synthesis of BaNbO2N without impurity traces, which thus exhibited the highest water-splitting activity. However, doping of the lower-valent cations at the Ta-sites in BaTaO2N did not effectively lower the defect density and thus improve photoactivity despite the similarity of the ionic radii of 6-coordinate Ta5+ (78 pm) and 6-coordinate Nb5+ (78 pm). Selective replacement at the Ta-site in perovskite BaTaO2N using 5 at% Al3+, Ga3+, Sc3+, or Zr4+ for improving photocatalytic HER and OER activity has also been considered.117 In particular, the doping of BaTaO2N with Mg2+ or Zr4+ enhanced OER photoactivity in a sacrificial reagent by modifying the optoelectronic and surface properties of the oxynitride. Therefore, limited doping of AB(O,N)3 using alternative cations alters the surface properties of oxynitrides (such as defect and donor densities) while maintaining their bulk properties (such as the crystalline structure and optical properties).
Co-substitution of the Ta5+ site of Ta3N5 with 33 at% 6-coordinate Mg2+ (86 pm) and Zr4+ (86 pm) led to significant improvement in the anodic photocurrent density and onset potential for PEC water splitting.118 This large amount of substitution modified not only the band structure but also the surface morphology of the original Ta3N5. The difference in valence between parent Ta5+ and alternative cations Mg2+ and Zr4+ caused additional N3−/O2− replacement to replenish the charge imbalance. Increasing and decreasing the concentration of Mg2+/Zr4+ cations and N3− anions respectively shifted the CBM and VBM potentials negatively from those of parent Ta3N5. This strategy was also applied in the synthesis of perovskite LaMgxB1−xO1+3xN2−3x (B = Ta, Nb; x = 0 to 2/3) solid solutions, leading to overall water-splitting activity via one-step photoexcitation.41,42Fig. 13(A)-(a) portrays the crystal structures of LaMgxTa1−xO1+3xN2−3x solid solutions after substituting Ta5+ with Mg2+.41 The general formula of these perovskite oxynitrides is given by
| (1 − 3/2x) LaTaON2 + 3/2x LaMg2/3Ta1/3O3 → LaMgxTa1−xO1+3xN2−3x (x = 0 to 2/3) | (14) |
 | ||
| Fig. 13 Substitution of B5+ with Mg2+ in perovskite LaBON2 (B = Ta, Nb). (A) (a) Crystalline structure and (b) UV-vis DRS spectra of the LaMgxTa1−xO1+3xN2−3x (x = 0 to 2/3) powder after replacing some of the Ta5+ with Mg2+. Reproduced with permission.41 Copyright 2015, Wiley-VCH. (B) (a) UV-vis DRS spectra and (b) band structure diagrams of LaMgxNb1−xO1+3xN2−3x (x = 0 to 2/3) after replacing some of the Nb5+ with Mg2+. Reproduced with permission.42 Copyright 2021, RSC. | ||
The composition of the LaMgxTa1−xO1+3xN2−3x solid solutions was easily modified by mixing perovskite oxynitride LaTaON2 and perovskite oxide LaMg2/3Ta1/3O3 at the atomic level. The significant substitution of Mg2+ in LaTaON2 was realized after the nitridation of the starting oxides blended at the atomic level via a polymerized-complex method. The greater the level of substitution of Ta5+ with Mg2+, the greater the increase in the composition ratio of LaMg2/3Ta1/3O3, resulting in a marked change in the optical properties of the resulting oxynitrides (Fig. 13(A)-(b)). The wavelength of the light absorption edge of LaMgxTa1−xO1+3xN2−3x blue-shifted gradually from 640 nm (pure LaTaON2) to 270 nm (fully substituted LaMg2/3Ta1/3O3).
This phenomenon was also observed in the substitution of Nb5+ with Mg2+ in counterpart LaNbON2.42Fig. 13(B)-(a) presents UV-vis DRS spectra of LaMgxNb1−xO1+3xN2−3x (x = 0 to 2/3) showing a gradual blue-shift of the absorption onset wavelengths from 700 to 320 nm. In addition to the increase in the Eg, the CBM and VBM potentials of the solid solutions also shifted to the negative and positive sides, respectively, as portrayed in Fig. 13(B)-(b). The band structure diagrams of the solid solution series demonstrate that the substitution of Nb5+ with Mg2+ in LaNbON2 not only increases the concentration of the O 2p atomic orbital (leading to the positive shift of the VBM) but also decreases the concentration of the Nb 4d orbital (causing the negative shift of the CBM). The substitution of Mg2+ largely reduced the bulk and surface defect densities of LaMgxNb1−xO1+3xN2−3x solid solutions, which is similar to the effect of the small-cation doping of oxynitrides. Moreover, the subsequent changes in the optical properties (i.e., the Eg value and band structure) of the oxynitrides were significant. In addition, surface modification using cocatalysts finally activated the overall water-splitting capability of LaMgxB1−xO1+3xN2−3x, thereby producing stoichiometric H2 and O2 evolution. Interestingly, the highest gas evolution rates for water-splitting were achieved using LaMg1/3B2/3O2N (i.e., x = 1/3) irrespective of the cationic occupancy of the B sites in the oxynitride. As a result, the visible-light-driven overall water-splitting activity is mainly attributed to the expanded bandgap enabling a photoresponse of up to 600 and 650 nm for LaMg1/3Ta2/3O2N and LaMg1/3Nb2/3O2N, respectively. Likewise, the bulk modification of oxynitrides via substitution with alternative cations has been subsequently applied: Zn2+ for Ta5+ in perovskite BaTaO2N,119 Zr4+ for Ta5+ in LaTaON2,120 Mg2+ for Ti4+ in LaTiO2N,121 La3+ for Ti4+ in layered perovskite Sr2TiO4,122 and so on. All these outcomes obviously demonstrate that the substitution of the B sites in oxynitrides with alternative cations is a very useful way of modifying the bulk properties of the parent oxynitride and thus improving the latter's photocatalytic water-splitting capability.
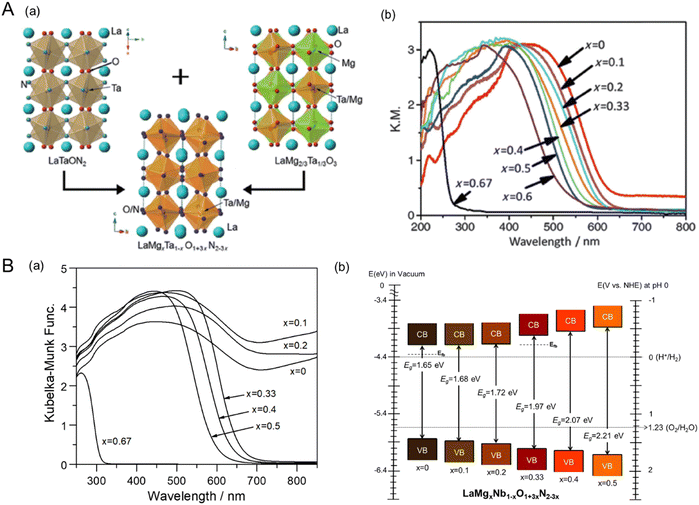
4.2. Varying the surface morphology
The electrochemical activity of an electrocatalyst (e.g., Pt nanoparticles) for oxidation and reduction reactions is typically proportional to its electrochemically active surface area containing its reaction sites for accessing the electrolyte.124–127 The surface morphology (including the particle size and shape) of the electrocatalyst to increase reaction sites is thus critical for progressing electrochemical reactions efficiently. In contrast, the surface morphology of a semiconductor influences visible-light harvesting, the reaction efficiency of photocarriers, and the deposition coverage of cocatalysts (e.g., CoOx) on which the actual photoreaction takes place. Because the small size of semiconductor particles can lead to a short diffusion distance for the photogenerated charges, it increases the charge separation, transfer, and collection efficiencies, thereby enhancing photoactivity.128 BaNbO2N particles of various sizes prepared via the nitridation of Ba5Nb4O15 size-controlled in the range from 0.2 to 50 μm exhibit photocatalytic water oxidation activity depending on the particle size in an aqueous electrolyte including a sacrificial reagent.129 Similarly, small scheelite-type LaNbO4 particles as the starting oxide produced small LaNbON2 particles with fewer defects after nitridation with significantly high photocatalytic water oxidation activity under visible-light Xe lamp irradiation (λ > 420 nm).94,95Fig. 14(A) presents the size dependence of perovskite BaNbO2N particles on PEC water-splitting activity88 The size of the oxynitride particles was systematically tuned via the nitridation of Ba5Nb4O15 with various average sizes (1.05, 1.93, 4.11, or 6.92 μm). The oxide particles synthesized via a polymerized-complex method were gradually grown by increasing the calcination temperature from 1073 to 1373 K. Their conversions to the corresponding oxynitride exclusively increased the surface porosity without an increase in particle size, except for the nitridation of the oxide calcined at 1073 K. The small, porous oxynitride prepared from the oxide via calcination at 1173 K provided both the largest BET and electrochemical surface areas, resulting in the highest photocurrent density of 2.2 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE for sunlight-driven water splitting. The photocurrent decreased upon increasing the oxynitride particle size. Although the smallest non-porous BaNbO2N particles prepared via nitridation of the oxide calcined at 1073 K were highly crystalline, this did not contribute to increasing the surface reaction sites. This result demonstrates that the size reduction of oxynitride particles accompanied by an increase in the surface reaction area clearly enhances the water-splitting photoactivity. In fact, the photon flux in the solar spectrum (used to determine the number of charges generated during photoreactions) is constant depending on the light wavelength. Therefore, the activity result of perovskite BaNbO2N depending on its particle size implies that the photoresponse of the oxynitride is still relatively poor, and there is a large room for improvement in the activity up to the theoretical maximum STH efficiency of each oxynitride.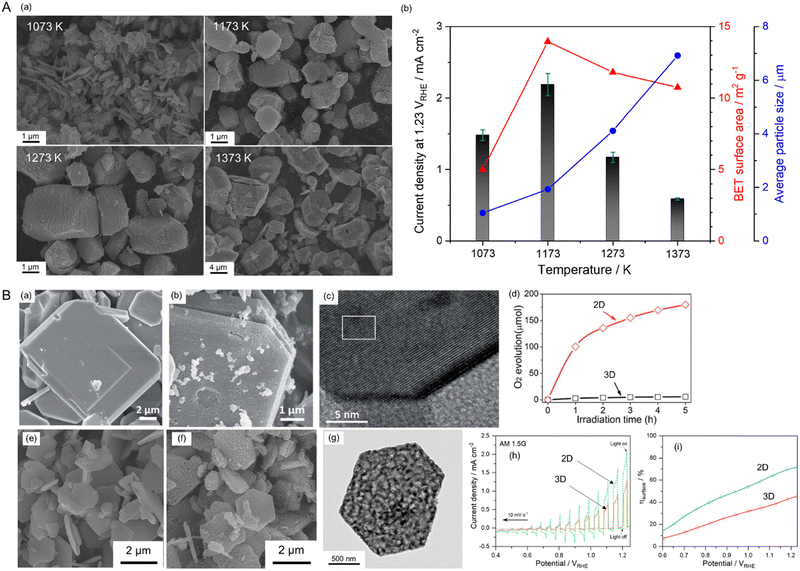 | ||
| Fig. 14 Varying the surface morphology of Nb-based perovskite oxynitrides. (A) SEM images (a) and the corresponding PEC water-splitting activity (b) of BaNbO2N particles of various sizes. Reproduced with permission.88 Copyright 2022, Elsevier. (B) SEM images of starting LaKNaNbO5 (a) and the corresponding 2D LaNbON2 (b) after nitridation along with an HRTEM image (c) and the photocatalytic O2 evolution activity (d) of the 2D oxynitride particles. Reproduced with permission.123 Copyright 2020, RSC. SEM images of starting Sr5Nb4O15 (e) and the resulting 2D SrNbO2N (f) after nitridation along with an HRTEM image (g) and the PEC water-splitting activity (h) and charge separation efficiency (i) of the 2D oxynitride photoanode. The photoactivities of both 2D oxynitrides were compared with those of typical 3D oxynitrides. Reproduced with permission.105 Copyright 2023, Elsevier. | ||
Besides the particle size, the surface shape of a perovskite or layered perovskite oxynitride also influences its photoactivity. As discussed previously, fluxes during nitridation can be used to readily change the shape of the oxynitride particles. The employment of different fluxes during nitridation and/or calcination of the starting oxide has been applied to vary the shape and size of 3D SrNbO2N particles.93 Moreover, the nitridation of La2Ti2O7 using an NaCl–KCl flux produced highly porous brick-like LaTiO2N particles.16 The surface shape of the oxynitride with a large surface area improved its photocatalytic water oxidation activity because of the high dispersion of CoOx or IrO2 cocatalysts over the large surface of the oxynitride. Meanwhile, rarely reported vertical SrNbO2N nanorod arrays (as discussed earlier) with a 1D structure of the semiconductor promoted the strong separation of photogenerated charges exclusively in the vertical direction, thereby enhancing PEC activity.
Over the past few years, newly emerged 2D configurations of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides have been found to provide a short diffusion transfer route for the photoexcited charges and thus lower their recombination.31,130–133 The electrons and holes photogenerated in HCa2Nb3O10 nanosheets and selectively transferred to the surface of 2D Ca2Nb3O10− plates without their self-recombination significantly improved photocatalytic water reduction activity under UV irradiation (λ > 300 nm).134 A 2D layered perovskite K2LaTa2O6N was also stably active during the same photoreaction under visible-light illumination (λ > 400 nm).89 The optical and electrical properties and charge transport of 2D RP-type A2BO3N (A = Ca, Sr, or Ba; B = Ta or Nb) layered perovskites have been studied based on density functional theory.135 Thereby, the mobility of the electrons (or holes) photogenerated in the 2D layered perovskites was found to be much quicker than in the 3D perovskites. These results indicate that the advantages of 2D morphology (i.e., the fast vertical charge transfer to the surface of the oxynitride plates) enhance water-splitting photoactivity.
Because the crystal structure of perovskite AB(O,N)3 is cubic, the 3D shape of the oxynitride is typically synthesized. However, 2D-type starting oxides with a layered perovskite structure could be transformed into 2D oxynitrides capable of absorbing visible light. Fig. 14(B) shows the surface morphologies of the starting oxides and their corresponding oxynitrides, along with the visible-light-driven photoactivity of the 2D oxynitrides compared with the corresponding 3D type. In the upper row, it can be seen that the smooth layered LaKNaNbO5 plates were converted to porous 2D LaNbON2via nitridation accompanied by volatilization of the K and Na species.123 This conversion also worked well in the synthesis of counterpart LaTaON2 using LaKNaTaO5.131 Interestingly, volatilization of the layered oxide along the [001] direction resulted in the shape of the oxynitride with exposed (010) surface facets remaining unchanged. The photocatalytic water oxidation activity of 2D LaNbON2 with (010) facets was much higher than that of conventional 3D LaNbON2 with mostly (100) facets. The efficient transfer of charges along the (010) facets of the 2D oxynitride and its low defect density resulting from the fast nitridation and the volatilization of the K and Na species led to its enhanced photoactivity. Meanwhile, layered perovskite Zr-doped Sr5Nb4O15 with a 2D-type truncated octahedral structure was completely transformed to porous 2D-type SrNbO2N particles with an identical morphology, as shown in the bottom row of Fig. 14(B).105 The conversion process yielded oxynitrides with fewer defects, as discussed in detail in the earlier synthesis section using A-site cation-rich starting oxides. The 2D shape of the SrNbO2N particles, as well as their high crystallinity, significantly heightened the PEC water-splitting activity of the oxynitride. The efficiency of charge separation by the 2D SrNbO2N was much higher than that by the conventional 3D oxynitride. Moreover, the charge transfer resistance in the 2D oxynitride was relatively low. These results enable us to draw the same conclusion that oxynitrides with a 2D surface structure facilitate strong charge separation and fast transfer of charges photogenerated during water splitting.
4.3. Controlling the crystallographic facets
Crystal facet engineering for more efficient photoreaction activity by effectively promoting the preferential separation of charges between two adjacent anisotropic facets in a semiconductor during the reaction has been recently reported.27,136 Representatively, it has been demonstrated that monoclinic BiVO4 particles with two different facets prepared via a hydrothermal method and the selective photo-deposition of cocatalysts could separate photogenerated holes in the (110) facets while collecting the counterpart electrons in the (010) facets.137 Au, Pt, or Ag nanoparticles were deposited on the (010) facets of BiVO4 under light irradiation while MnOx or PbO2 particles were coated on the (110) facets of the oxide in the same manner. Both selective depositions of the cocatalysts, particularly the Pt and MnOx particles, dramatically enhanced the photocatalytic water oxidation activity of the BiVO4 particles. Similarly, spatial separation of the photogenerated holes and electrons with CoOx and RhOx cocatalysts, respectively, also improved the PEC water oxidation activity.138 Moreover, optoelectrical simulation proved that facet engineering increased the efficiencies of not only charge injection but also charge separation during the water oxidation reaction.The facet engineering of cubic perovskite SrTiO3:Al was very effective at spatially separating the photogenerated charges to two different facets, thus driving overall water splitting via one-step photoexcitation.12 Rh/Cr2O3 as an HER cocatalyst and CoOOH as an OER catalyst were sequentially photo-deposited onto the electron-attracting (100) facets and the hole-collecting (110) facets, respectively. The resulting anisotropic charge transport achieved high overall water-splitting activity that was almost consistent with the theoretical quantum efficiency of SrTiO3. Unlike the oxide, it is difficult to prepare perovskite oxynitrides with exposed crystal facets to spatially separate charges because their crystal growth is not easily controlled during typical high-temperature nitridation. Fortunately, flux-assisted nitridation may offer a feasible means of tuning the surface morphology of oxynitrides, as discussed in the synthesis section. Symmetric BaTaO2N particles with only the (100) and (110) facets exposed have been successfully prepared via flux-assisted nitridation, as displayed in Fig. 15(A).139 The starting precursors of Ba and Ta were rearranged and then recrystallized in the molten salt during nitridation, which resulted in well-defined cubic BaTaO2N particles of approximately 200 nm in size. Interestingly, the BaTaO2N crystals prepared using an NaCl flux exhibited a cubic structure with six isotropic (100) facets whereas the oxynitride synthesized using a KCl flux presented a cubic-like structure with additional smooth (110) facets at the twelve corners of the (100) facets. The ionic species of fluxes become adsorbed on the crystal facets, thereby enabling faster growth and changes in the electrostatic interactions between the crystals. Because the ionic radius of six-coordinate K+ (152 pm) is very similar to that of six-coordinate Ba2+ (149 pm), K+ can more easily occupy the Ba2+ positions at the interface between BaTaO2N and KCl. This not only suppresses the crystal growth of BaTaO2N with the most stable (100) facets but also leads to the formation of secondary stable (110) facets. According to density functional theory calculations (Fig. 15(B)), the estimated surface energy of the (110) facets is higher than that of the (100) facets, meaning that the CBM and VBM potentials of the (110) facets are located above those of the (100) facets. Thus, a facet junction is generated between the anisotropic (100) and (110) facets of a BaTaO2N particle, thereby boosting the selective transfer of photogenerated electrons and holes to the (100) and (110) facets, respectively. Like the previously described BiVO4 system, Pt and MnOx particles were separately photo-deposited onto the (100) and (110) facets of BaTaO2N. As a result, the BaTaO2N crystals prepared using a KCl flux presented significantly improved water reduction activity compared with those using NaCl. Therefore, crystal facet engineering promoting selective separation and transfer of charges during photoreactions offers an effective strategy for enhancing the photoactivity of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides by adjusting the crystal facets during their synthesis.
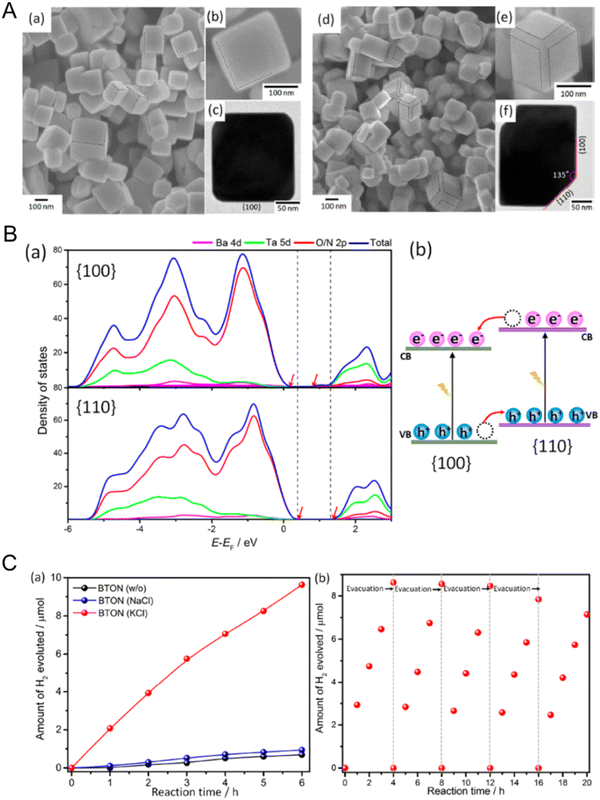 | ||
| Fig. 15 Crystal facet engineering of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides. (A) SEM and TEM images of BaTaO2N particles prepared via flux-assisted nitridation using (a)–(c) NaCl and (d)–(f) KCl molten salts. (B) The density of states of the different energy levels of the (100) and (110) facets of BaTaO2N prepared via KCl-assisted nitridation. (C) (a) Photocatalytic H2 evolution activity using the two different BaTaO2N particles and (b) cyclic testing using the oxynitride particles prepared via KCl-assisted nitridation. Reproduced with permission.139 Copyright 2019, ACS. | ||
5. Conclusions and challenges
We discussed the preparation and use of perovskite AB(O,N)3 and layered perovskite oxynitrides An+1Bn(O,N)3n+1 as potential semiconductors for visible-light-driven artificial photosynthesis, as shown in Fig. 16. The materials are capable of absorbing visible light wavelengths up to 750 nm at most, and their band structures straddle the various redox potentials of the HER, OER, CER, H2O2 production, and CO2 reduction, among others. Moreover, they are chemically stable in aqueous media over a wide pH range where photoreactions can take place. They fulfill the thermodynamic requirements for various photocatalytic processes to generate renewable, eco-friendly, and/or high value-added products such as H2 and NH3 with high theoretical solar-to-fuel energy conversion efficiency. Based on their favorable optical and chemical properties, perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides have been employed as both light absorbers and photocatalysts for visible-light-driven water splitting to produce H2 over several decades. In addition, using them for CO2 reduction and the CER as an alternative oxidation reaction to the OER to obtain high value-added products such as HCOOH have recently been reported. The adaption of the CER, feasible by using seawater instead of fresh water, not only boosted the oxidation kinetics but also enhanced the H2 production activity in neutral electrolytes. However, the perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides have shown low photoactivity and long-term stability during various photoreactions, which are still far from the requirements for commercialization (corresponding to STH values of above 10%). | ||
| Fig. 16 Sunlight-driven catalysis and the challenges of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides to artificially synthesize renewable, high value-added products such as H2. | ||
Because Ti4+, Ta5+, and Nb5+ in the perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides are readily reduced during high-temperature nitridation, the surface and bulk properties of the latter can change due to the presence of defects and/or traces of impurities. Defects in perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides boost the recombination of photogenerated holes and electrons during photoreactions, thereby limiting their photoactivity. This phenomenon can be reduced by various synthesis strategies and surface and bulk engineering including doping and substitution. Moreover, photooxidation of the oxynitride surface, which results in the release of N2 and a positive shift in the surface Fermi level, can be completely suppressed via surface modification to provide separated compartments for HER and OER cocatalysts or passivation layers.
Controlling the surface morphology of the oxynitride particles and/or electrodes can spatially separate the transfer orientation of photogenerated holes and electrons, thus leading to dramatic improvement in the sunlight-driven catalytic activity. Although 1D and 2D perovskite AB(O,N)3 were rarely studied in terms of the synthesis method, the morphologically modified surfaces of the oxynitrides were found to largely increase the separation efficiency of charges generated during PEC water splitting. It is known that the surface shape of metal oxynitrides such as Ta3N5 is relatively easy to be transformed even through high-temperature nitridation. However, it is difficult to prepare AB(O,N)3 with 1D or 2D surface morphology because two different cations at A- and B-sites are typically sintered at the high temperature probably causing the change in the surface structure. Alternatively, the charges generated during photoreactions can be spatially separated by crystal facet engineering and the employment of layered perovskite oxynitrides. The crystal facet engineering of BaTaO2N, materialized by flux-assisted nitridation including a recrystallization stage, proved that (100) and (110) facets play roles as electron-attracting and hole-collecting sites, respectively. The layered perovskite oxynitrides with a 2D crystal structure, which allow selective transfer of holes and electrons in crystal lattices intrinsically, can be also utilized for sunlight-driven catalysis. The spatial charge separation in photoelectrodes, as well as on oxynitride particles, is likely to be necessary for efficient, stable photoreactions. In particulate photoelectrodes, the electron transfer from oxynitride particles to a conductive substrate is significantly resistive due to the loose adhesion between them. The bottom-up fabrication to directly grow oxynitride crystals on the conductive substrate can be a solution to obtain a fast electron pathway comparable to the hole transfer rate to surfaces of oxynitrides. Therefore, both the novel synthesis of less-defective oxynitrides to reduce the recombination of photogenerated charges and the surface design of the oxynitrides to make spatially selective separation and transfer of the charges must be challenges to achieving efficient, stable sunlight-driven artificial synthesis using perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides.
The overall water splitting of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides by one-step photoexcitation can be the most ideal way to facilitate the low-cost production of H2 gas on a large scale. The overall water splitting of a ATaO2N (A = Sr, Ba) particle has been demonstrated; however its activity is still limited. The separation of both HER and OER sites at the oxynitride surface is likely to be necessary to drive water splitting, while HER sites with a cocatalyst were distinguished from the surface of oxides such as SrTiO3. The selective deposition of the cocatalyst and crystal facet engineering of the oxynitrides are challenging for efficient overall water splitting. In a PEC system, the anodic photoresponse of perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides should be below 0 VRHE based on their flat band potentials (which are negative). However, the actual photocurrent onset is limited to the range of 0.5 to 0.6 VRHE. Unassisted solar water splitting via PEC cells comprising perovskite and layered perovskite oxynitrides combined with other cathode materials has rarely been reported. Thus, efficient photoanodes must be able to generate significant photocurrent density at a moderate potential (0.4 to 0.6 VRHE) based on the overlap with the photocathode during overall water splitting. It is necessary to apply various approaches to improve their water-splitting activity by, for instance, optimizing their optical and physical properties. Moreover, a better understanding of the effect of pH (photoanodes are more active at higher pH values while photocathodes work well at lower pH values) must also be achieved to obtain a high rate of H2 production. Therefore, these challenges are directly related to the photoactivity and long-term stability of these materials for efficient artificial photosynthesis.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study to disclose.Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Basic Science Research Program (no. RS-2023-00243439) and Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS) (no. 2021RIS-002) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE). This study was also supported by the NRF grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (no. 2021M3I3A1084818).References
- G. Zhang, G. Liu, L. Wang and J. T. Irvine, Inorganic perovskite photocatalysts for solar energy utilization, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 5951–5984 RSC.
- T. Hisatomi, J. Kubota and K. Domen, Recent advances in semiconductors for photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 7520–7535 RSC.
- J. Seo, H. Nishiyama, T. Yamada and K. Domen, Visible-Light-Responsive Photoanodes for Highly Active, Stable Water Oxidation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 8396–8415 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Fujito, H. Kunioku, D. Kato, H. Suzuki, M. Higashi, H. Kageyama and R. Abe, Layered Perovskite Oxychloride Bi4NbO8Cl: A Stable Visible Light Responsive Photocatalyst for Water Splitting, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 2082–2085 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Nakada, M. Higashi, T. Kimura, H. Suzuki, D. Kato, H. Okajima, T. Yamamoto, A. Saeki, H. Kageyama and R. Abe, Band Engineering of Double-Layered Sillén–Aurivillius Perovskite Oxychlorides for Visible-Light-Driven Water Splitting, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 3419–3429 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Hojamberdiev, M. F. Bekheet, E. Zahedi, H. Wagata, Y. Kamei, K. Yubuta, A. Gurlo, N. Matsushita, K. Domen and K. Teshima, New Dion–Jacobson Phase Three-Layer Perovskite CsBa2Ta3O10 and Its Conversion to Nitrided Ba2Ta3O10 Nanosheets via a Nitridation–Protonation–Intercalation–Exfoliation Route for Water Splitting, Cryst. Growth Des., 2016, 16, 2302–2308 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Suemoto, Y. Masubuchi, Y. Nagamine, A. Matsutani, T. Shibahara, K. Yamazaki and S. Kikkawa, Intergrowth between the Oxynitride Perovskite SrTaO2N and the Ruddlesden–Popper Phase Sr2TaO3N, Inorg. Chem., 2018, 57, 9086–9095 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Gou, M. Zhao, J. Shi, J. K. Harada and J. M. Rondinelli, Anion Ordered and Ferroelectric Ruddlesden–Popper Oxynitride Ca3Nb2N2O5 for Visible-Light-Active Photocatalysis, Chem. Mater., 2020, 32, 2815–2823 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Tang, K. Kato, T. Oshima, H. Mogi, A. Miyoshi, K. Fujii, K. I. Yanagisawa, K. Kimoto, A. Yamakata, M. Yashima and K. Maeda, Synthesis of Three-Layer Perovskite Oxynitride K2Ca2Ta3O9N·2H2O and Photocatalytic Activity for H2 Evolution under Visible Light, Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 11122–11128 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Shiroma, H. Mogi, T. Mashiko, S. Yasuda, S. Nishioka, T. Yokoi, S. Ida, K. Kimoto and K. Maeda, Interlayer modification and single-layer exfoliation of the Ruddlesden–Popper perovskite oxynitride K2LaTa2O6N to improve photocatalytic H2 evolution activity, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 9485–9492 RSC.
- Y. Ham, T. Hisatomi, Y. Goto, Y. Moriya, Y. Sakata, A. Yamakata, J. Kubota and K. Domen, Flux-mediated doping of SrTiO3 photocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 3027–3033 RSC.
- T. Takata, J. Jiang, Y. Sakata, M. Nakabayashi, N. Shibata, V. Nandal, K. Seki, T. Hisatomi and K. Domen, Photocatalytic water splitting with a quantum efficiency of almost unity, Nature, 2020, 581, 411–414 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Miseki, H. Kato and A. Kudo, Water Splitting into H2 and O2 over Ba5Nb4O15 Photocatalysts with Layered Perovskite Structure Prepared by Polymerizable Complex Method, Chem. Lett., 2006, 35, 1052–1053 CrossRef CAS.
- W.-J. Chun, A. Ishikawa, H. Fujisawa, T. Takata, J. N. Kondo, M. Hara, M. Kawai, Y. Matsumoto and K. Domen, Conduction and Valence Band Positions of Ta2O5, TaON, and Ta3N5 by UPS and Electrochemical Methods, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107, 1798–1803 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Ramaraj and J. Seo, Intensive-visible-light-responsive ANbO2N (A = Sr, Ba) synthesized from layered perovskite A5Nb4O15 for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting, J. Energy Chem., 2022, 68, 529–537 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Zhang, A. Yamakata, K. Maeda, Y. Moriya, T. Takata, J. Kubota, K. Teshima, S. Oishi and K. Domen, Cobalt-modified porous single-crystalline LaTiO2N for highly efficient water oxidation under visible light, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 8348–8351 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Akiyama, M. Nakabayashi, N. Shibata, T. Minegishi, Y. Asakura, M. Abdulla-Al-Mamun, T. Hisatomi, H. Nishiyama, M. Katayama, T. Yamada and K. Domen, Highly Efficient Water Oxidation Photoanode Made of Surface Modified LaTiO2 N Particles, Small, 2016, 12, 5468–5476 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Seo, T. Hisatomi, M. Nakabayashi, N. Shibata, T. Minegishi, M. Katayama and K. Domen, Efficient Solar-Driven Water Oxidation over Perovskite-Type BaNbO2N Photoanodes Absorbing Visible Light up to 740 nm, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1800094 CrossRef.
- J. Seo, M. Nakabayashi, T. Hisatomi, N. Shibata, T. Minegishi and K. Domen, Solar-Driven Water Splitting over a BaTaO2N Photoanode Enhanced by Annealing in Argon, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2, 5777–5784 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Maeda and K. Domen, New Non-Oxide Photocatalysts Designed for Overall Water Splitting under Visible Light, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 7851–7861 CrossRef CAS.
- H. W. Eng, P. W. Barnes, B. M. Auer and P. M. Woodward, Investigations of the electronic structure of d0 transition metal oxides belonging to the perovskite family, J. Solid State Chem., 2003, 175, 94–109 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Balaz, S. H. Porter, P. M. Woodward and L. J. Brillson, Electronic Structure of Tantalum Oxynitride Perovskite Photocatalysts, Chem. Mater., 2013, 25, 3337–3343 CrossRef CAS.
- T. W. Kim and K.-S. Choi, Nanoporous BiVO4 Photoanodes with Dual-Layer Oxygen Evolution Catalysts for Solar Water Splitting, Science, 2014, 343, 990–994 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Kuang, Q. Jia, G. Ma, T. Hisatomi, T. Minegishi, H. Nishiyama, M. Nakabayashi, N. Shibata, T. Yamada, A. Kudo and K. Domen, Ultrastable low-bias water splitting photoanodes via photocorrosion inhibition and in situ catalyst regeneration, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2, 16191 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Sharma, J. W. Jang and J. S. Lee, Key Strategies to Advance the Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Performance of α-Fe2O3 Photoanode, ChemCatChem, 2018, 11, 157–179 CrossRef.
- T. Oshima, T. Ichibha, K. S. Qin, K. Muraoka, J. J. M. Vequizo, K. Hibino, R. Kuriki, S. Yamashita, K. Hongo, T. Uchiyama, K. Fujii, D. Lu, R. Maezono, A. Yamakata, H. Kato, K. Kimoto, M. Yashima, Y. Uchimoto, M. Kakihana, O. Ishitani, H. Kageyama and K. Maeda, Undoped Layered Perovskite Oxynitride Li2LaTa2O6N for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction with Visible Light, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 8154–8158 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wang and K. Domen, Particulate Photocatalysts for Light-Driven Water Splitting: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Design Strategies, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 919–985 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. M. C. Ta, R. Daiyan, T. K. A. Nguyen, R. Amal, T. Tran-Phu and A. Tricoli, Alternatives to Water Photooxidation for Photoelectrochemical Solar Energy Conversion and Green H2 Production, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12, 2201358 CrossRef CAS.
- V.-H. Trinh and J. Seo, Porous Cuboidal SrNbO2N Crystals Grown on a Nb Substrate as an Active Photoanode for Neutral Seawater Splitting under Sunlight, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2023, 11, 1655–1665 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Shi, G. I. N. Waterhouse and T. Zhang, Recent Progress in Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Over Perovskite Oxides, Sol. RRL, 2017, 1, 1700126 CrossRef.
- K. Maeda and T. E. Mallouk, Two-Dimensional Metal Oxide Nanosheets as Building Blocks for Artificial Photosynthetic Assemblies, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn., 2019, 92, 38–54 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Murphy, P. Barnes, L. Randeniya, I. Plumb, I. Grey, M. Horne and J. Glasscock, Efficiency of solar water splitting using semiconductor electrodes, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2006, 31, 1999–2017 CrossRef CAS.
- A. G. Tamirat, J. Rick, A. A. Dubale, W.-N. Su and B.-J. Hwang, Using hematite for photoelectrochemical water splitting: a review of current progress and challenges, Nanoscale Horiz., 2016, 1, 243–267 RSC.
- H. Nishiyama, T. Yamada, M. Nakabayashi, Y. Maehara, M. Yamaguchi, Y. Kuromiya, Y. Nagatsuma, H. Tokudome, S. Akiyama, T. Watanabe, R. Narushima, S. Okunaka, N. Shibata, T. Takata, T. Hisatomi and K. Domen, Photocatalytic solar hydrogen production from water on a 100-m(2) scale, Nature, 2021, 598, 304–307 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Li, J. Xiao, J. J. M. Vequizo, T. Hisatomi, M. Nakabayashi, Z. Pan, N. Shibata, A. Yamakata, T. Takata and K. Domen, One-Step Excitation Overall Water Splitting over a Modified Mg-Doped BaTaO2N Photocatalyst, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 10179–10185 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Chen, J. Xiao, J. J. M. Vequizo, T. Hisatomi, Y. Ma, M. Nakabayashi, T. Takata, A. Yamakata, N. Shibata and K. Domen, Overall Water Splitting by a SrTaO2N-Based Photocatalyst Decorated with an Ir-Promoted Ru-Based Cocatalyst, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 3839–3843 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, K. Maeda, A. Thomas, K. Takanabe, G. Xin, J. M. Carlsson, K. Domen and M. Antonietti, A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 76–80 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Maeda, K. Teramura, D. Lu, T. Takata, N. Saito, Y. Inoue and K. Domen, Photocatalyst releasing hydrogen from water, Nature, 2006, 440, 295 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wang, Y. Inoue, T. Hisatomi, R. Ishikawa, Q. Wang, T. Takata, S. Chen, N. Shibata, Y. Ikuhara and K. Domen, Overall water splitting by Ta3N5 nanorod single crystals grown on the edges of KTaO3 particles, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 756–763 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Wang, M. Nakabayashi, T. Hisatomi, S. Sun, S. Akiyama, Z. Wang, Z. Pan, X. Xiao, T. Watanabe, T. Yamada, N. Shibata, T. Takata and K. Domen, Oxysulfide photocatalyst for visible-light-driven overall water splitting, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18, 827–832 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Pan, T. Takata, M. Nakabayashi, T. Matsumoto, N. Shibata, Y. Ikuhara and K. Domen, A complex perovskite-type oxynitride: the first photocatalyst for water splitting operable at up to 600 nm, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 2955–2959 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Seo, D. Ishizuka, T. Hisatomi, T. Takata and K. Domen, Effect of Mg2+ substitution on the photocatalytic water splitting activity of LaMgxNb1−xO1+3xN2−3x, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 8655–8662 RSC.
- K. Maeda, K. Teramura, D. Lu, N. Saito, Y. Inoue and K. Domen, Roles of Rh/Cr2O3 (core/shell) nanoparticles photodeposited on visible light responsive (Ga1−xZnx)(N1−xOx) solid solutions in photocatalytic overall water splitting, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 7554–7560 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yoshida, K. Takanabe, K. Maeda, A. Ishikawa, J. Kubota, Y. Sakata, Y. Ikezawa and K. Domen, Role and Function of Noble-Metal/Cr-Layer Core/Shell Structure Cocatalysts for Photocatalytic Overall Water Splitting Studied by Model Electrodes, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 10151–10157 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Kato, K. Asakura and A. Kudo, Highly Efficient Water Splitting into H2 and O2 over Lanthanum-Doped NaTaO3 Photocatalysts with High Crystallinity and Surface Nanostructure, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 3082–3089 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Pan, T. Takata, K. Kumamoto, S. S. Khine Ma, K. Ueda, T. Minegishi, M. Nakabayashi, T. Matsumoto, N. Shibata, Y. Ikuhara and K. Domen, Band engineering of perovskite-type transition metal oxynitrides for photocatalytic overall water splitting, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 4544–4552 RSC.
- J. H. Kim, D. Hansora, P. Sharma, J. W. Jang and J. S. Lee, Toward practical solar hydrogen production – an artificial photosynthetic leaf-to-farm challenge, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 1908–1971 RSC.
- Y. Zhang, H. Lv, Z. Zhang, L. Wang, X. Wu and H. Xu, Stable Unbiased Photo-Electrochemical Overall Water Splitting Exceeding 3% Efficiency via Covalent Triazine Framework/Metal Oxide Hybrid Photoelectrodes, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, e2008264 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Ye, W. Shi, Y. Liu, D. Li, H. Yin, H. Chi, Y. Luo, N. Ta, F. Fan, X. Wang and C. Li, Unassisted Photoelectrochemical Cell with Multimediator Modulation for Solar Water Splitting Exceeding 4% Solar-to-Hydrogen Efficiency, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 12499–12508 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rhee, T. G. Kim, G. Y. Jang, G. Bae, J. H. Lee, S. Lee, S. Kim, S. Jeon and J. H. Park, Unassisted overall water splitting with a solar-to-hydrogen efficiency of over 10% by coupled lead halide perovskite photoelectrodes, Carbon Energy, 2022, 5, 1–10 Search PubMed.
- T. Higashi, Y. Shinohara, A. Ohnishi, J. Liu, K. Ueda, S. Okamura, T. Hisatomi, M. Katayama, H. Nishiyama, T. Yamada, T. Minegishi and K. Domen, Sunlight-Driven Overall Water Splitting by the Combination of Surface-Modified La5Ti2Cu0.9Ag0.1S5O7 and BaTaO2N Photoelectrodes, ChemPhotoChem, 2016, 1, 1–7 Search PubMed.
- M. Cao, H. Li, K. Liu, J. Hu, H. Pan, J. Fu and M. Liu, Vertical SrNbO2N Nanorod Arrays for Solar-Driven Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting, Sol. RRL, 2020, 5, 2000448 CrossRef.
- J. Seo, M. Nakabayashi, T. Hisatomi, N. Shibata, T. Minegishi, M. Katayama and K. Domen, The effects of annealing barium niobium oxynitride in argon on photoelectrochemical water oxidation activity, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 493–502 RSC.
- M. Matsukawa, R. Ishikawa, T. Hisatomi, Y. Moriya, N. Shibata, J. Kubota, Y. Ikuhara and K. Domen, Enhancing photocatalytic activity of LaTiO2N by removal of surface reconstruction layer, Nano Lett., 2014, 14, 1038–1041 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. R. Lhermitte and K. Sivula, Alternative Oxidation Reactions for Solar-Driven Fuel Production, ACS Catal., 2019, 9, 2007–2017 CrossRef CAS.
- J. C. Hill and K.-S. Choi, Effect of Electrolytes on the Selectivity and Stability of n-type WO3 Photoelectrodes for Use in Solar Water Oxidation, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116, 7612–7620 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Dionigi, T. Reier, Z. Pawolek, M. Gliech and P. Strasser, Design Criteria, Operating Conditions, and Nickel-Iron Hydroxide Catalyst Materials for Selective Seawater Electrolysis, ChemSusChem, 2016, 9, 962–972 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Jadwiszczak, K. Jakubow-Piotrowska, P. Kedzierzawski, K. Bienkowski and J. Augustynski, Highly Efficient Sunlight-Driven Seawater Splitting in a Photoelectrochemical Cell with Chlorine Evolved at Nanostructured WO3 Photoanode and Hydrogen Stored as Hydride within Metallic Cathode, Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 10, 1903213 CrossRef.
- S. Iguchi, Y. Miseki and K. Sayama, Efficient hypochlorous acid (HClO) production via photo electrochemical solar energy conversion using a BiVO4-based photoanode, Sustain, Energy Fuels, 2018, 2, 155–162 CAS.
- R.-T. Gao, X. Guo, S. Liu, X. Zhang, X. Liu, Y. Su and L. Wang, Ultrastable and high-performance seawater-based photoelectrolysis system for solar hydrogen generation, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 304, 120883 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Higashi, K. Domen and R. Abe, Fabrication of an efficient BaTaO2N photoanode harvesting a wide range of visible light for water splitting, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 10238–10241 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Ueda, T. Minegishi, J. Clune, M. Nakabayashi, T. Hisatomi, H. Nishiyama, M. Katayama, N. Shibata, J. Kubota, T. Yamada and K. Domen, Photoelectrochemical oxidation of water using BaTaO2N photoanodes prepared by particle transfer method, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2227–2230 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Takanabe, Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Quantitative Approaches toward Photocatalyst by Design, ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 8006–8022 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Liu, Y. Zou, B. Jin, K. Zhang and J. H. Park, Hydrogen Peroxide Production from Solar Water Oxidation, ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4, 3018–3027 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Hou, X. Zeng and X. Zhang, Production of Hydrogen Peroxide by Photocatalytic Processes, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 17356–17376 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Mase, M. Yoneda, Y. Yamada and S. Fukuzumi, Seawater usable for production and consumption of hydrogen peroxide as a solar fuel, Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 11470 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Miyase, S. Takasugi, S. Iguchi, Y. Miseki, T. Gunji, K. Sasaki, E. Fujita and K. Sayama, Modification of BiVO4/WO3 composite photoelectrodes with Al2O3via chemical vapor deposition for highly efficient oxidative H2O2 production from H2O, Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2018, 2, 1621–1629 RSC.
- Y. Miseki and K. Sayama, Photocatalytic Water Splitting for Solar Hydrogen Production Using the Carbonate Effect and the Z-Scheme Reaction, Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 9, 1801294 CrossRef.
- J. H. Baek, T. M. Gill, H. Abroshan, S. Park, X. Shi, J. Nørskov, H. S. Jung, S. Siahrostami and X. Zheng, Selective and Efficient Gd-Doped BiVO4 Photoanode for Two-Electron Water Oxidation to H2O2, ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4, 720–728 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Saito, Y. Miseki and K. Sayama, Highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting using a thin film photoanode of BiVO4/SnO2/WO3 multi-composite in a carbonate electrolyte, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 3833 RSC.
- S. N. Habisreutinger, L. Schmidt-Mende and J. K. Stolarczyk, Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 on TiO2 and other semiconductors, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 7372–7408 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Ran, M. Jaroniec and S. Z. Qiao, Cocatalysts in Semiconductor-based Photocatalytic CO(2) Reduction: Achievements, Challenges, and Opportunities, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1704649 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Kalamaras, M. M. Maroto-Valer, M. Shao, J. Xuan and H. Wang, Solar carbon fuel via photoelectrochemistry, Catal. Today, 2018, 317, 56–75 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Kumagai, Y. Tamaki and O. Ishitani, Photocatalytic Systems for CO2 Reduction: Metal-Complex Photocatalysts and Their Hybrids with Photofunctional Solid Materials, Acc. Chem. Res., 2022, 55, 978–990 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Kumagai, G. Sahara, K. Maeda, M. Higashi, R. Abe and O. Ishitani, Hybrid photocathode consisting of a CuGaO2 p-type semiconductor and a Ru(II)–Re(I) supramolecular photocatalyst: non-biased visible-light-driven CO2 reduction with water oxidation, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 4242–4249 RSC.
- F. Yoshitomi, K. Sekizawa, K. Maeda and O. Ishitani, Selective Formic Acid Production via CO2 Reduction with Visible Light Using a Hybrid of a Perovskite Tantalum Oxynitride and a Binuclear Ruthenium(II) Complex, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7, 13092–13097 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Oshima, T. Ichibha, K. Oqmhula, K. Hibino, H. Mogi, S. Yamashita, K. Fujii, Y. Miseki, K. Hongo, D. Lu, R. Maezono, K. Sayama, M. Yashima, K. Kimoto, H. Kato, M. Kakihana, H. Kageyama and K. Maeda, Two-Dimensional Perovskite Oxynitride K2LaTa2O6N with an H(+)/K(+) Exchangeability in Aqueous Solution Forming a Stable Photocatalyst for Visible-Light H2 Evolution, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 9736–9743 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhou, Y. Luo, J. Xu, L. Deng, Z. Wang and H. He, Bicomponent Cocatalyst Decoration on Flux-assisted CaTaO2N Single Crystals for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction under Visible Light, Chem. – Eur. J., 2022, 28, e202202044 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Lin, L. Xiao, Y. Lu, Z. Zhang, X. Wang and W. Su, Anchoring 0D CeO2 Nanoparticles on 2D LaTiO2N Nanosheets for Efficient Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction, ChemCatChem, 2022, 14, e202201041 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Lin, P. Lin, J. Song, Z. Zhang, X. Wang and W. Su, Boosting the photocatalytic activity and stability of Cu2O for CO2 conversion by LaTiO2N, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2023, 630, 352–362 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Urabe, T. Hisatomi, T. Minegishi, J. Kubota and K. Domen, Photoelectrochemical properties of SrNbO2N photoanodes for water oxidation fabricated by the particle transfer method, Faraday Discuss., 2014, 176, 213–223 RSC.
- J. Xu, C. Pan, T. Takata and K. Domen, Photocatalytic overall water splitting on the perovskite-type transition metal oxynitride CaTaO2N under visible light irradiation, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 7191–7194 RSC.
- S. Wei and X. Xu, Boosting photocatalytic water oxidation reactions over strontium tantalum oxynitride by structural laminations, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 228, 10–18 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Nishimae, Y. Mishima, H. Nishiyama, Y. Sasaki, M. Nakabayashi, Y. Inoue, M. Katayama and K. Domen, Fabrication of BaTaO2N Thin Films by Interfacial Reactions of BaCO3/Ta3N5 Layers on a Ta Substrate and Resulting High Photoanode Efficiencies During Water Splitting, Sol. RRL, 2020, 4, 1900542 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xiang, B. Zhang, J. Liu, S. Chen, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen and G. Ma, A one-step synthesis of a Ta3N5 nanorod photoanode from Ta plates and NH4Cl powder for photoelectrochemical water oxidation, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 11843–11846 RSC.
- B. Siritanaratkul, K. Maeda, T. Hisatomi and K. Domen, Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of perovskite niobium oxynitrides with wide visible-light absorption bands, ChemSusChem, 2011, 4, 74–78 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Maeda and K. Domen, Water oxidation using a particulate BaZrO3–BaTaO2N solid-solution photocatalyst that operates under a wide range of visible light, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 9865–9869 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. T. T. Tran, S. Kim and J. Seo, Size dependence of perovskite-type BaNbO2N particles on sunlight-driven photoelectrochemical water splitting, J. Catal., 2022, 406, 157–164 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Oshima, T. Ichibha, K. Oqmhula, K. Hibino, H. Mogi, S. Yamashita, K. Fujii, Y. Miseki, K. Hongo, D. Lu, R. Maezono, K. Sayama, M. Yashima, K. Kimoto, H. Kato, M. Kakihana, H. Kageyama and K. Maeda, Two-Dimensional Perovskite Oxynitride K2LaTa2O6N with an H+/K+ Exchangeability in Aqueous Solution Forming a Stable Photocatalyst for Visible-Light H2 Evolution, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 9736–9743 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Seo, Y. Moriya, M. Kodera, T. Hisatomi, T. Minegishi, M. Katayama and K. Domen, Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting on Particulate ANbO2N (A = Ba, Sr) Photoanodes Prepared from Perovskite-Type ANbO3, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 6869–6876 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Hisatomi, C. Katayama, Y. Moriya, T. Minegishi, M. Katayama, H. Nishiyama, T. Yamada and K. Domen, Photocatalytic oxygen evolution using BaNbO2N modified with cobalt oxide under photoexcitation up to 740 nm, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6, 3595 RSC.
- M. Hojamberdiev, K. Yubuta, J. J. M. Vequizo, A. Yamakata, S. Oishi, K. Domen and K. Teshima, NH3-Assisted Flux Growth of Cube-like BaTaO2N Submicron Crystals in a Completely Ionized Nonaqueous High-Temperature Solution and Their Water Splitting Activity, Cryst. Growth Des., 2015, 15, 4663–4671 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Kodera, H. Urabe, M. Katayama, T. Hisatomi, T. Minegishi and K. Domen, Effects of flux synthesis on SrNbO2N particles for photoelectrochemical water splitting, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 7658–7664 RSC.
- J. Seo, Size Control of LaNbON2 Particles for Enhanced Photocatalytic Water Oxidation Under Visible Light Irradiation, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2021, 42, 571–576 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Seo, S. Jeong and S. Kim, Visible-Light-Driven Water Splitting over Particulate LaNbON2 Prepared from La-Rich Lanthanum Niobium Oxides, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2021, 4, 3141–3150 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Hisatomi, C. Katayama, K. Teramura, T. Takata, Y. Moriya, T. Minegishi, M. Katayama, H. Nishiyama, T. Yamada and K. Domen, The effects of preparation conditions for a BaNbO2N photocatalyst on its physical properties, ChemSusChem, 2014, 7, 2016–2021 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Xu, C. Randorn, P. Efstathiou and J. T. Irvine, A red metallic oxide photocatalyst, Nat. Mater., 2012, 11, 595–598 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Lu, G. Hitoki, E. Katou, J. N. Kondo, M. Hara and K. Domen, Porous Single-Crystalline TaON and Ta3N5 Particles, Chem. Mater., 2004, 16, 1603–1605 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Jadhav, S. Hasegawa, T. Hisatomi, Z. Wang, J. Seo, T. Higashi, M. Katayama, T. Minegishi, T. Takata, J. M. Peralta-Hernández, O. Serrano Torres and K. Domen, Efficient photocatalytic oxygen evolution using BaTaO2N obtained from nitridation of perovskite-type oxide, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 1127–1130 RSC.
- D. E. Bugaris and H. C. zur Loye, Materials discovery by flux crystal growth: quaternary and higher order oxides, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 3780–3811 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Yamada, Y. Murata, H. Wagata, K. Yubuta and K. Teshima, Facile Morphological Modification of Ba5Nb4O15 Crystals Using Chloride Flux and in Situ Growth Investigation, Cryst. Growth Des., 2016, 16, 3954–3960 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang, Y. Song, J. Feng, T. Fang, Y. Zhong, Z. Li and Z. Zou, Photoelectrochemical water oxidation of LaTaON2 under visible-light irradiation, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39, 7697–7704 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Luo, Z. Wang, S. Suzuki, K. Yubuta, N. Kariya, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen and K. Teshima, Fabrication of Single-Crystalline BaTaO2N from Chloride Fluxes for Photocatalytic H2 Evolution under Visible Light, Cryst. Growth Des., 2019, 20, 255–261 CrossRef.
- T. Minegishi, N. Nishimura, J. Kubota and K. Domen, Photoelectrochemical properties of LaTiO2N electrodes prepared by particle transfer for sunlight-driven water splitting, Chem. Sci., 2013, 4, 1120–1124 RSC.
- T. T. T. Tran, V.-H. Trinh and J. Seo, Two-dimensional perovskite SrNbO2N with Zr doping for accelerating photoelectrochemical water splitting, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2023, 142, 176–184 CrossRef CAS.
- M. V. Kelso, N. K. Mahenderkar, Q. Chen, J. Z. Tubbesing and J. A. Switzer, Spin coating epitaxial films, Science, 2019, 364, 166–169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. G. Ebbinghaus, H.-P. Abicht, R. Dronskowski, T. Müller, A. Reller and A. Weidenkaff, Perovskite-related oxynitrides – Recent developments in synthesis, characterisation and investigations of physical properties, Prog. Solid State Chem., 2009, 37, 173–205 CrossRef CAS.
- M. D. Tyona, A theoritical study on spin coating technique, Adv. Mater. Res., 2013, 2, 195–208 CrossRef.
- H. Takeuchi, D. Miyamoto, Y. Masubuchi, M. Higuchi, K. Ishii and T. Uchikoshi, Preparation of thick dense ceramic films of dielectric BaTaO2N through electrophoretic deposition, Ceram. Int., 2023, 49, 21825–21829 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Abe, T. Takata, H. Sugihara and K. Domen, The Use of TiCl4 Treatment to Enhance the Photocurrent in a TaON Photoelectrode under Visible Light Irradiation, Chem. Lett., 2005, 34, 1162–1163 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Pichler, W. Si, F. Haydous, H. Téllez, J. Druce, E. Fabbri, M. E. Kazzi, M. Döbeli, S. Ninova, U. Aschauer, A. Wokaun, D. Pergolesi and T. Lippert, LaTiOxNy Thin Film Model Systems for Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Physicochemical Evolution of the Solid-Liquid Interface and the Role of the Crystallographic Orientation, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1605690 CrossRef.
- K. Kawashima, M. Hojamberdiev, O. Mabayoje, B. R. Wygant, K. Yubuta, C. B. Mullins, K. Domen and K. Teshima, NH3-assisted chloride flux-coating method for direct fabrication of visible-light-responsive SrNbO2N crystal layers, CrystEngComm, 2017, 19, 5532–5541 RSC.
- X. Luo, Y. Xiao, B. Zhang, C. Feng, Z. Fan and Y. Li, Direct synthesis of BaTaO2N nanoparticle film on a conductive substrate for photoelectrochemical water splitting, J. Catal., 2022, 411, 109–115 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Xu, W. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Chen, H. Huang, T. Fang, Y. Li, Z. Li and Z. Zou, Centimeter-scale perovskite SrTaO2N single crystals with enhanced photoelectrochemical performance, Sci. Bull., 2022, 67, 1458–1466 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-I. Kim, P. M. Woodward, K. Z. Baba-Kishi and C. W. Tai, Characterization of the Structural, Optical, and Dielectric Properties of Oxynitride Perovskites AMO2N(A = Ba, Sr, Ca; M = Ta, Nb), Chem. Mater., 2004, 16, 1267–1276 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Iwai, A. Nakada, M. Higashi, H. Suzuki, O. Tomita and R. Abe, Controlling the carrier density in niobium oxynitride BaNbO2N via cation doping for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting under visible light, Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2021, 5, 6181–6188 RSC.
- M. Hojamberdiev, R. Vargas, Z. C. Kadirova, K. Kato, H. Sena, A. G. Krasnov, A. Yamakata, K. Teshima and M. Lerch, Unfolding the Role of B Site-Selective Doping of Aliovalent Cations on Enhancing Sacrificial Visible Light-Induced Photocatalytic H2 and O2 Evolution over BaTaO2N, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 1403–1414 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Seo, T. Takata, M. Nakabayashi, T. Hisatomi, N. Shibata, T. Minegishi and K. Domen, Mg–Zr Cosubstituted Ta3N5 Photoanode for Lower-Onset-Potential Solar-Driven Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 12780–12783 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Bao, H. Zou, N. Yang, G. Li and F. Zhang, Synthesis of perovskite BaTaO2N with low defect by Zn doping for boosted photocatalytic water reduction, J. Energy Chem., 2021, 63, 358–363 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, S. Jin, G. Pan, Z. Li, L. Chen, G. Liu and X. Xu, Zr doped mesoporous LaTaON2 for efficient photocatalytic water splitting, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 5702–5711 RSC.
- G. Lin, X. Sun and X. Xu, Mg modified LaTiO2N with ameliorated photocarrier separation for solar water splitting, Appl. Catal., B, 2023, 324, 122258 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Sun, Y. Mi, F. Jiao and X. Xu, Activating Layered Perovskite Compound Sr2TiO4via La/N Codoping for Visible Light Photocatalytic Water Splitting, ACS Catal., 2018, 8, 3209–3221 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, T. Hisatomi, J. Liang, Z. Wang, Y. Xiang, Y. Zhao, X. Dai, T. Takata and K. Domen, Facet engineering of LaNbON2 transformed from LaKNaNbO5 for enhanced photocatalytic O2 evolution, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 11743–11751 RSC.
- M. Shao, A. Peles and K. Shoemaker, Electrocatalysis on platinum nanoparticles: particle size effect on oxygen reduction reaction activity, Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 3714–3719 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. J. Coleman, M. H. Chowdhury and A. C. Co, Insights Into the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity of Pt/C and PtCu/C Catalysts, ACS Catal., 2015, 5, 1245–1253 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-W. Park and J. Seo, Ultrafine TaOx/CB Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalyst Operating in Both Acidic and Alkaline Media, Catalysts, 2021, 12, 35 CrossRef.
- J. Seo, W.-J. Moon, W.-G. Jung and J.-W. Park, A N-doped NbOx nanoparticle electrocatalyst deposited on carbon black for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions in alkaline media, Mater. Adv., 2022, 3, 5315–5324 RSC.
- J. Liu, T. Hisatomi, M. Katayama, T. Minegishi, J. Kubota and K. Domen, Effect of particle size of La5Ti2CuS5O7 on photoelectrochemical properties in solar hydrogen evolution, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 4848–4854 RSC.
- T. Yamada, Y. Murata, S. Suzuki, H. Wagata, S. Oishi and K. Teshima, Template-Assisted Size Control of Polycrystalline BaNbO2N Particles and Effects of Their Characteristics on Photocatalytic Water Oxidation Performances, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122, 8037–8044 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Tsai, W. Nie, J. C. Blancon, C. C. Stoumpos, R. Asadpour, B. Harutyunyan, A. J. Neukirch, R. Verduzco, J. J. Crochet, S. Tretiak, L. Pedesseau, J. Even, M. A. Alam, G. Gupta, J. Lou, P. M. Ajayan, M. J. Bedzyk and M. G. Kanatzidis, High-efficiency two-dimensional Ruddlesden–Popper perovskite solar cells, Nature, 2016, 536, 312–316 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wang, T. Hisatomi, Z. Wang, J. Song, J. Qu, T. Takata and K. Domen, Core-Shell-Structured LaTaON2 Transformed from LaKNaTaO5 Plates for Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Evolution, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 10666–10670 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Lan, Z. Zhou, R. Wei and J. C. Ho, Two-dimensional perovskite materials: From synthesis to energy-related applications, Mater. Today Energy, 2019, 11, 61–82 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xu, Y. Wang, Q. Guo and X. Wang, Defect engineering of two-dimensional Nb-based oxynitrides for visible-light-driven water splitting to produce H2 and O2, Nanoscale Adv., 2023, 5, 3260–3266 RSC.
- K. Maeda, M. Eguchi, W. J. Youngblood and T. E. Mallouk, Calcium Niobate Nanosheets Prepared by the Polymerized Complex Method as Catalytic Materials for Photochemical Hydrogen Evolution, Chem. Mater., 2009, 21, 3611–3617 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. L. Cen, J. J. Shi, M. Zhang, M. Wu, J. Du, W. H. Guo and Y. H. Zhu, Optimized band gap and fast interlayer charge transfer in two-dimensional perovskite oxynitride Ba2NbO3N and Sr2NbO3/Ba2NbO3N bonded heterostructure visible-light photocatalysts for overall water splitting, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 546, 20–31 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wang, G. Liu and L. Wang, Crystal Facet Engineering of Photoelectrodes for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting, Chem. Rev., 2019, 119, 5192–5247 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Li, F. Zhang, D. Wang, J. Yang, M. Li, J. Zhu, X. Zhou, H. Han and C. Li, Spatial separation of photogenerated electrons and holes among (010) and (110) crystal facets of BiVO4, Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 1432 CrossRef PubMed.
- Z. Pan, V. Nandal, Y. Pihosh, T. Higashi, T. Liu, J. A. Röhr, K. Seki, C. Chu, K. Domen and K. Katayama, Elucidating the Role of Surface Energetics on Charge Separation during Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting, ACS Catal., 2022, 12, 14727–14734 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Luo, S. Suzuki, Z. Wang, K. Yubuta, J. J. M. Vequizo, A. Yamakata, H. Shiiba, T. Hisatomi, K. Domen and K. Teshima, Construction of Spatial Charge Separation Facets on BaTaO2N Crystals by Flux Growth Approach for Visible-Light-Driven H2 Production, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 22264–22271 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2024 |