Revealing the reduction process of Cu(ii) by sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide†
Abstract
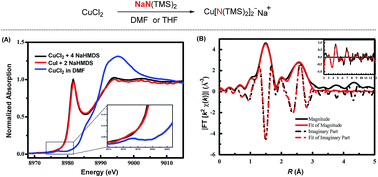
The mechanistic investigation of copper-catalysed transformations has been an important and fundamental task. Herein, we report via XAS and EPR spectroscopy that the sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide could reduce Cu(II) to a Cu(I) species serving as an electron donor. XAS spectroscopy demonstrates that the newly formed Cu(I) species is the Cu[N(TMS)2]2Na ate complex, in which the nitrogen atoms coordinate with copper linearly.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Mechanistic processes in organometallic chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...