Retracted Article: Water-soluble multidentate polymers compactly coating Ag2S quantum dots with minimized hydrodynamic size and bright emission tunable from red to second near-infrared region†
Abstract
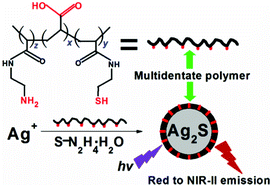
Hydrodynamic size-minimized quantum dots (QDs) have outstanding physicochemical properties for applications in multicolor molecular and cellular imaging at the level of single molecules and nanoparticles. In this study, we have reported the aqueous synthesis of Ag2S QDs by using thiol-based multidentate polymers as capping reagents. By regulating the composition of the precursors (AgNO3 and sulfur–N2H4·H2O complex) and multidentate polymers (poly(acrylic acid)-graft-cysteamine-graft-ethylenediamine), as well as the reaction time, Ag2S QDs (2.6–3.7 nm) are prepared, displaying tunable photoluminescence (PL) emission from red to the second near-infrared region (687–1096 nm). The small hydrodynamic thickness (1.6–1.9 nm) of the multidentate polymers yields a highly compact coating for the QDs, which results in the bright fluorescent QDs with high PL quantum yields (QYs: 14.2–16.4%). Experimental results confirm that the QDs have high PL stability and ultralow cytotoxicity, as well as high PLQYs and small hydrodynamic sizes (4.5–5.6 nm) similar to fluorescent proteins (27–30 kDa), indicating the feasibility of highly effective PL imaging in cells and living animals.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...