Synthesis of nitrogen-doped activated graphene aerogel/gold nanoparticles and its application for electrochemical detection of hydroquinone and o-dihydroxybenzene†
Abstract
Graphene aerogel materials have attracted increasing attention owing to their large specific surface area, high conductivity and electronic interactions. Here, we report for the first time a novel strategy for the synthesis of nitrogen-doped activated graphene aerogel/gold nanoparticles (N-doped AGA/GNs). First, the mixture of graphite oxide, 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzaldehyde, urea and potassium hydroxide was dispersed in water and subsequently heated to form a graphene oxide hydrogel. Then, the hydrogel was dried by freeze-drying and reduced by thermal annealing in an Ar/H2 environment in sequence. Finally, GNs were adsorbed on the surface of the N-doped AGA. The resulting N-doped AGA/GNs offers excellent electronic conductivity (2.8 × 103 S m−1), specific surface area (1258 m2 g−1), well-defined 3D hierarchical porous structure and apparent heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (40.78 ± 0.15 cm s−1), which are notably better than that of previous graphene aerogel materials. Moreover, the N-doped AGA/GNs was used as a new sensing material for the electrochemical detection of hydroquinone (HQ) and o-dihydroxybenzene (DHB). Owing to the greatly enhanced electron transfer and mass transport, the sensor displays ultrasensitive electrochemical response to HQ and DHB. Its differential pulse voltammetric peak current linearly increases with the increase of HQ and DHB in the range of 5.0 × 10−8 to 1.8 × 10−4 M for HQ and 1 × 10−8 to 2.0 × 10−4 M for DHB. The detection limit is 1.5 × 10−8 M for HQ and 3.3 × 10−9 M for DHB (S/N = 3). This method provides the advantage of sensitivity, repeatability and stability compared with other HQ and DHB sensors. The sensor has been successfully applied to detection of HQ and DHB in real water samples with the spiked recovery in the range of 96.8–103.2%. The study also provides a promising approach for the fabrication of various graphene aerogel materials with improved electrochemical performances, which can be potentially applied in biosensors, electrocatalysis, and energy storage/conversion devices.
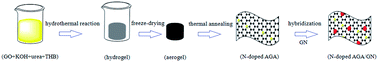
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...