Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleA comparative overview of the electrochemical valorization and incorporation of CO2 in industrially relevant compounds
Jef R.
Vanhoof
,
Sander
Spittaels
and
Dirk E.
De Vos
 *
*
Centre for Membrane Separations, Adsorption, Catalysis and Spectroscopy for Sustainable Solutions (cMACS), KU Leuven, Celestijnenlaan 200F P.O. Box 2454, 3001 Leuven, Belgium. E-mail: dirk.devos@kuleuven.be
First published on 16th February 2024
Abstract
Climate change is a critical global challenge that requires urgent action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide (CO2). While essential efforts are being made to reduce emissions by developing new manufacturing processes, it is also crucial to scrutinize sustainable uses for the CO2 that is already produced in excess. The electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (eCO2RR) is a highly promising and versatile approach for converting CO2 into valuable base chemicals and fuels, effectively decarbonizing the chemical industry. New methodologies and electrocatalysts in this area are increasingly being investigated, emphasizing the necessary transition to a more sustainable future. In this review, we focus on the eCO2RR coupled with incorporation in organic or inorganic reactants towards key industrial compounds such as carboxylic acids, ureas and dimethyl carbonate. We provide a broader context by outlining the current industrial synthesis methods of the envisioned compounds. Recent work is summarized in tables for quick comparison while innovations and improvements regarding sustainability and applicability are addressed in more detail.
Broader contextThe unprecedented rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels has emerged as a critical and multifaceted global challenge which extends far beyond environmental science. The elevated greenhouse gas concentrations have set in motion a cascade of climate shifts, heralding an era marked by extreme weather events, altered precipitation patterns, alarming loss of biodiversity and rising global temperatures. As nations grapple with the consequences of these changes, it becomes imperative to develop and implement effective strategies to mitigate CO2 emissions and to valorize CO2 as a valuable resource. The chemical industry plays a pivotal role as a potential driver in reducing CO2 concentrations through technological innovation. Green chemistry, which emphasizes the design of products and processes that minimize environmental impact, is gaining prominence. More specifically, electrochemistry stands as a cornerstone in the pursuit of sustainability, enabling the direct use of renewable electricity to convert the excess CO2 back to industrially relevant building blocks, like carboxylic acids, urea and dimethyl carbonate. As such, CO2 is reintroduced in the production chain, thereby directly addressing the pressing environmental concerns. |
1. Introduction
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a greenhouse gas that is naturally present in the Earth's atmosphere and plays a critical role in regulating the planet's temperature. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation and global industrialization have led to rapid increases of CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere, leading to an anthropogenic climate change and its associated impacts such as sea level rise, more frequent and severe weather events, and shifts in ecosystems and agriculture.1 After 2 years of varying emissions due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the CO2 emissions even reached a new record in 2022 of over 36.8 Gt globally according to the international energy agency,2 highlighting that global warming is a pressing matter. The Paris agreement, signed by nearly 200 countries in 2015, aims to limit global warming to well below 2 °C above pre-industrial levels, with efforts to limit it to 1.5 °C.3 To achieve this goal, countries must reduce their greenhouse gas emissions,4 including CO2, through a variety of measures such as transitioning to renewable energy sources5 and sustainable production processes,6–9 increasing energy efficiency in transportation10–13 and industry,14–17 and implementing carbon capture and storage technologies.18–23 Specifically for the European Union with the introduction of the European Climate Law, EU countries must cut greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions with 55% by 2030, eventually reaching climate neutrality by 2050.1Industrial manufacturing of chemicals is a significant contributor to the global CO2 problem due to the energy-intensive production processes that largely rely on fossil fuels as a source of energy and feedstock. Nevertheless, it has the potential to play a decisive role in realizing the aforementioned necessities by decarbonizing the chemical industry.24–26 Additionally, developing new materials and chemicals that have a lower carbon footprint, as well as recycling and reusing materials to reduce waste and emissions are important aspects towards closing the carbon loop.27–31 A most viable strategy for CO2 valorization is to use it as a building block towards value-added chemicals,32–36 fuels37,38 and construction materials.39,40 This way, a sustainable source of chemicals and materials is provided by introducing generated CO2 back in the production processes as an elementary building block, gradually transforming the typical linear production chain to a more sustainable production loop. Mineralization towards building materials,41–43 biological44–48 and photochemical49–52 conversion of CO2 will not be discussed and can be found elsewhere.
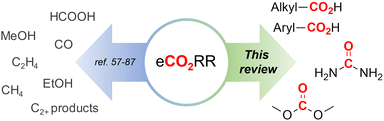
Of particular interest and high potential is the sustainable transformation of CO2 to industrial key chemicals using renewable electricity.53–56 The electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (eCO2RR) is a highly promising approach since a wide variety of desired products are possible, such as carbon monoxide (CO),57–60 formic acid (HCOOH),61–64 methanol (MeOH),65–69 methane (CH4)70–72 and even ethylene,73–76 ethanol (EtOH)77–80 and other C2+ products.81–87 Capturing a reactive intermediate of the eCO2RR with a second substrate creates structural motives ubiquitous in the chemical industry,88–90 expanding the product scope significantly and highlighting the versatility of the eCO2RR. Owing to this large pool of high-value products and the sustainable benefits of eCO2RR, industrial viability is already being thoroughly investigated.91–95
In this comparative review, we present an overview of recent protocols where CO2 is electrochemically coupled with organic and inorganic substrates to form crucial new C–C, C–N or C–O bonds of industrially relevant compounds, such as carboxylic acids, urea and dimethyl carbonate (Fig. 1). For each chapter, the corresponding literature is summarized in tables to facilitate comparisons. Innovations and improvements on the general methodologies will be discussed in more detail, with a focus on sustainability, industrial relevance and applicability and what we think are interesting concepts in general. In addition, some suggestions regarding further investigations will be presented.
2. Carboxylations
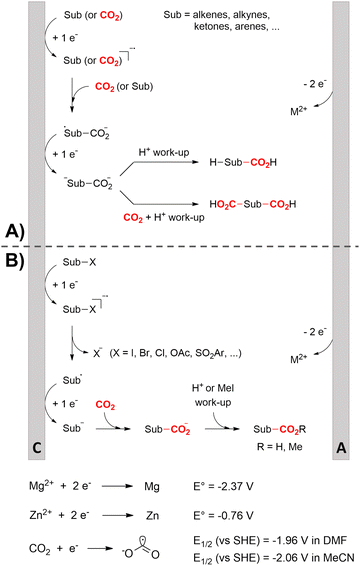
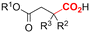
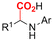
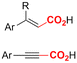
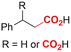
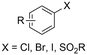
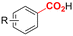
One of the most straightforward uses of CO2 is the formation of carboxylic acids since this amounts only to a decrease in carbon oxidation state from +IV to +III. Carboxylic acids are crucial base chemicals and can be fairly easily derivatized to metal salts, esters, anhydrides and acid chlorides. As such, carboxylic acids are (in)directly involved in numerous applications ranging from pharmaceuticals and food additives to agrochemicals and plastics.96,97 Industrial synthesis still largely relies on oxidation of aldehydes, which themselves are typically generated by the widely employed hydroformylation of alkenes. A second, less frequently used possibility, is the direct hydrocarboxylation of olefins. Both methods exploit the high reactivity of extremely toxic CO gas. An exception is the synthesis of ortho-hydroxycarboxylic acids in the Kolbe–Schmitt reaction where alkali phenolates react under 1–100 bar CO2 atmosphere at temperatures of 120–180 °C.98 Salicylic acid, the precursor for aspirin among others, is produced this way on a global scale of 100.000 metric tons annually.99 Direct incorporation of CO2 in other molecular structures is still a subject of intense research due to the widespread use of carboxylic acids, and the sustainability and safety benefits of using CO2 instead of CO. Recent reviews tackling non-electrified carboxylation protocols using CO2, e.g. metal-catalyzed100–103 and photochemical104–108 ones, can be found elsewhere.109–112Recent electrochemical carboxylation methods are summarized in Table 1. When comparing the different protocols, three aspects immediately catch attention. First of all, the mechanism frequently involves the direct one-electron reduction of either the substrate or of CO2 itself, depending on the respective reduction potentials. Mechanisms of reported electrocarboxylations (EC) can be generalized as in Fig. 2A. In a small variation (Fig. 2B), the starting substrate loses a molecule X. Secondly, sacrificial anodes such as Mg or Zn are frequently used, since the metal ions stabilize the cathodically formed carboxylate ions, promoting the envisioned reactions and diminishing unwanted side reactions. The products are obtained after an acidic workup or by using methyliodide to create the methylester. Since the reduction potentials of Mg and Zn are near or even more positive than that of CO2 (Fig. 2, bottom), it is also possible that in reported reactions, involving the electrogeneration of CO2•− radical anions, these metal ions can be cathodically reduced. While in some cases this results in undesired cathode passivation, this can also advantageously result in the formation of Grignard reagents when for instance halide-containing substrates are used.113 The Grignard reagent can also be formed when an electrogenerated reactive anion of the substrate is associated with a Mg(II) ion. Reaction with CO2 then also produces the carboxylate,114 but overall this increases the complexity in the chemistry. Generally, identifying an appropriate anodic reaction while maintaining high EC selectivity is required to preserve the metal electrodes and preventing ever increasing metal concentrations in the electrolyte, demanding an energy-intensive metal recovery. Finally, most methods use the highly toxic solvents DMF or NMP. These solvents need to be replaced when looking for industrial applications.
| No. | Substrate(s) | Product(s) | Electrodes (+)/(−) | Catalyst + additive | Electrolyte | E or J | Q (F mol−1) | FE (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The free acids are obtained from electrogenerated carboxylates via an acidic work-up. In some cases, a work-up employing methyliodide (MeI) is used, resulting in methyl esters. | |||||||||
| 1 |
|
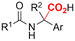
|
Mg or Pt/Pt | TEOA if Pt(+) is used | 0.075 M TBAI/DMF | 10 mA | 5 | <38 | 115 |
| 2 |
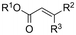
|
|
C/C | TEOA | 0.1 M TEAI/DMF | 10 V (4 h) | 9–15 | <15 | 116 |
| 3 |
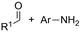
|
|
Pt/GC | — | 0.14 M THAClO4/THF | 12.7 mA cm−2 | 4 | <45 | 117 |
| 4 |
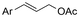
|
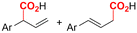
|
Mg/Pt | — | 0.05 M TBABF4/DMF | 5 mA | 4.5 | <44 | 118 |
| 5 |
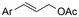
|
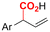
|
Mg/Pt | Pd(OAc)2 + DPPPh + EtOH | 0.07 M TEANOTs/DMF | 8 mA | 3 | <63 | 119 |
| 6 |
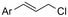
|
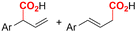
|
Mg/Ni | Co(OAC)2 + PPh3 | 0.05 M TBAPF6/DMF | 10 mA | 9 | <18 | 120 |
| 7 |
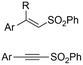
|
|
Mg/Pt | — | 0.05 M TBABF4/DMF | 15 mA | 15 | <13 | 121 |
| 8 |
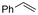
|
|
Mg/Ni | H2O | 0.1 M TBABF4/DMF | 10 mA cm−2 | 0.5 | <89 | 122 |
| 9 |
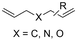
|
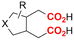
|
Al/Ni | TBD + 5 Å MS | 0.15 M TBAI/NMP | 12.5 mA | 25 | <6 | 123 |
| 10 |
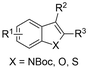
|
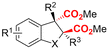
|
Mg/Pt | — | 0.1 M TBAClO4/MeCN | 30 mA | 3 | <65 | 124 |
| 11 |
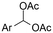
|
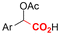
|
Mg or Zn/Pt | — | 0.1 M TBABF4/DMF | 25 mA cm−2 | 3–10 | <62 | 136 |
| 12 |
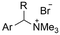
|
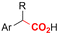
|
Pt/C | — | 0.1 M TBPBF4/DMF | −4.5 V (12 h) | — | ND | 137 |
| 13 |
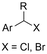
|
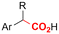
|
SS/Sm | TMSCl | 0.02 M TBAI/MeCN | 100 mA | 7.5 | <26 | 138 |
| 14 |
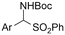
|

|
Mg/Pt | — | 0.1 M TBABF4/DMF | 10 mA cm−2 | 8 | <22 | 139 |
| 15 |
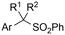
|
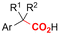
|
Mg/Pt | — | 0.4 M TBAI/DMF | 10 mA | 9 | <22 | 140 |
| 16 |
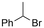
|
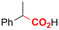
|
Pt/Ag | — | Catholyte: 0.1 M TBAI/MeCN | −1.4 V | 2.5 | <60 | 141 |
| Anolyte: 0.5 M KHCO3/H2O | |||||||||
| 17 |
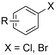
|
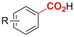
|
GF/Pt | Naphthalene + TBD | 0.05 M TBABF4/DMF | 20 mA | 22 | <9 | 145 |
| 18 |
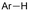
|
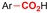
|
GF/GF | — | 0.075 M TEAI/DMF | 20 mA | 25 | <7 | 146 |
| 19 |
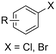
|
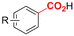
|
Sm/SS | — | 0.01 M TBABF4/DMF | 100 mA | 3 | <53 | 147 |
| 20 |
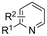
|
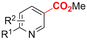
|
Zn/Fe | Cu(OTf)2 + KO-tBu + H2O + O2 | 0.2 M TBAI/NMP | 5 mA | 9 | <17 | 148 |
| 21 |
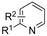
|
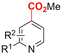
|
Pt/Fe | KO-tBu | 0.2 M TBAI/NMP | 6 mA | 36 | <5 | 148 |
| 22 |
|
|
Zn/C | Ni(acac)2 + dtbbpy + KO-tBu | 0.02 M NaI + MgBr2/NMP | 8 mA | 4–24 | <46 | 149 |
| 23 |
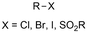
|

|
Zn/C | NiBr2 + dmbpy + CsF | 0.2 M LiClO4/NMP | 8 mA | 14–19 | <11 | 149 |
| 24 |
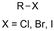
|

|
Pt/Ag | MgBr2 | 0.1 M TBABr/DMF | 20 mA cm−2 | 12 | <13 | 151 |
| 25 |
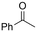
|

|
Mg/GC | — | 0.4 M TBAPF6/MeCN | −2.6 V (12 h) | 0.5 | <72 | 154 |
| 26 |
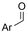
|
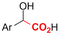
|
G/G | — | 0.3 M TBA/PC | 8 mA cm−2 | 2 | <63 | 154 |
| 27 |
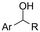
|
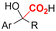
|
GC/Ni | TEMPO + H2O | 0.1 M TEAAc/MeCN | 7 mA cm−2 | 3 | <41 | 155 |
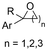
| 28 |
|
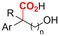
|
Mg/Pt | — | 0.1 M TBAI/DMF | 10 mA | 4.4 | <41 | 157 |
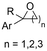
| 29 |
|
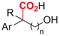
|
Mg/Pt | — | 0.1 M TBABr/DMF | 10 mA | 3.7 | <51 | 158 |
| 30 |
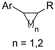
|
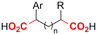
|
Zn/Nb | — | 0.075 M TBABF4/NMP | 15 mA | 22.5 | <9 | 159 |
| 31 |
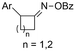
|
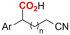
|
Mg/GC | — | 0.1 M TBAI/DMF | 8 mA | 7.5 | <24 | 160 |
| 32 |
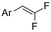
|
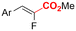
|
Ni/Pt | — | 0.07 M TBAI/DMF | 8 mA | 6.7 | <25 | 161 |
| 33 |
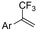
|
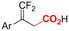
|
Pt/Pt | — | 0.07 M TBAClO4/DMF | 8 mA | 6 | <28 | 162 |
2.1 Carboxylations involving double bonds
In the carboxylations involving double C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C or C
C or C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bonds (Table 1, entries 1–10),115–124 a non-sacrificial Pt115 or C116 anode can be used when triethanolamine (TEOA) is added as a sacrificial reactant (entries 1 and 2, respectively); alternatively, a solvent like THF is used, which itself undergoes anodic oxidation (entry 3).117 However, these methods only shift the problem of identifying an anodic counterreaction and still produce unwanted byproducts. The alkene starting materials in entries 4–6 provide unsaturated carboxylation products, which might be interesting for further derivatization, due to the allylic nature of the reaction products.118–120 It is noteworthy that both the selectivity and faradaic efficiency of two possible products out of the same starting material could be improved by using an electro-active Pd catalyst (entries 4 vs. 5).118,119 Additionally, enantioselective carboxylation with a moderate ee of up to 67% was possible using chiral bidentate triarylphosphine ligands. Although higher ee values are required for applications, asymmetric electrochemistry towards chiral scaffolds is a highly interesting concept gaining increased attention.125–129
N bonds (Table 1, entries 1–10),115–124 a non-sacrificial Pt115 or C116 anode can be used when triethanolamine (TEOA) is added as a sacrificial reactant (entries 1 and 2, respectively); alternatively, a solvent like THF is used, which itself undergoes anodic oxidation (entry 3).117 However, these methods only shift the problem of identifying an anodic counterreaction and still produce unwanted byproducts. The alkene starting materials in entries 4–6 provide unsaturated carboxylation products, which might be interesting for further derivatization, due to the allylic nature of the reaction products.118–120 It is noteworthy that both the selectivity and faradaic efficiency of two possible products out of the same starting material could be improved by using an electro-active Pd catalyst (entries 4 vs. 5).118,119 Additionally, enantioselective carboxylation with a moderate ee of up to 67% was possible using chiral bidentate triarylphosphine ligands. Although higher ee values are required for applications, asymmetric electrochemistry towards chiral scaffolds is a highly interesting concept gaining increased attention.125–129
(Di)carboxylation of simpler alkenes seems more challenging as literature reports are scarce.130 Nam and coworkers (entry 8) reported that even small amounts of water guide the selectivity of styrene carboxylation towards dicarboxylation or β-hydrocarboxylation.122 When using neat DMF as the solvent, highly selective (97%) dicarboxylation of styrene occurred with a FE of 89%, whereas addition of only one equivalent of water relative to styrene shifted the selectivity towards β-hydrocarboxylation (71%) in 65% FE (Fig. 3A). The selectivity for β-hydrocarboxylation over dicarboxylation even reached 96% when 10 equivalents of water were used, albeit with a lower FE of 47% due to competitive H2 and methane formation. It was argued, based on D-labeling experiments and kinetic studies, that the protonation or incorporation of a second CO2 molecule on the benzylic position happened competitively after primary formation of the β-carboxylate intermediate (cf.Fig. 2). Coupling an appropriate anodic reaction with the (di)carboxylation of alkenes, especially aliphatic alkenes, is challenging but would expand the applicability of the alkene (di)carboxylation protocol drastically. Buckley and coworkers employed triethanolamine (TEOA) in combination with Et4NI in DMF.131,132 An interesting strategy can be paired electrosynthesis, which has been demonstrated for butadiene and derivatives in MeCN by our group in the past.133 Extrapolating this paired methodology concept to other abundant alkenes is a most valuable option.
 | ||
| Fig. 3 (A) Influence of water on the outcome of styrene carboxylation. The anodic reaction is the oxidation of a sacrificial Mg anode. (B) proposed mechanism of the dicarboxylation of skipped dienes. C = cathode. Adapted from ref. 122 and 123, respectively. | ||
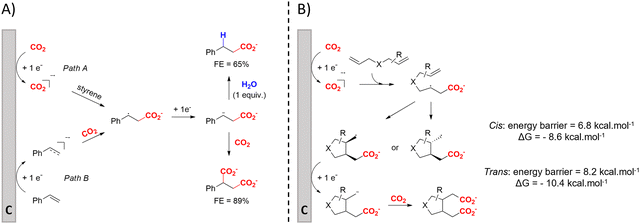
Cyclic adipic acids can be synthesized from unconjugated dienes following the protocol of Yu and coworkers (Fig. 3B).123 Compared to 1,3-dienes, the diminished reactivity of these unactivated alkenes (E < −3.00 V vs. SCE) requires that CO2 is cathodically activated, as confirmed by control experiments. DFT calculations indicate that the carboxylated, secondary radical species favors the 5-exo cyclization with a slight preference for the cis-configuration (free energy barrier of 6.8 kcal mol−1) over the trans-configuration (free energy barrier of 8.2 kcal mol−1), as also observed by experimental results, even if the trans-configuration is thermodynamically more stable. Side reactions like intramolecular 1,4-HAT or 6-endo cyclization involved larger calculated kinetic barriers. Evidence for a carboxylated carbanionic species was found with trapping experiments using different electrophiles like acetone or an isocyanate. Addition of molecular sieves was necessary to trap water and avoid hydrocarboxylation byproducts, as outlined by Nam122 (see above). The desired products are only obtained if Br− or I− are used as the anion of the conducting salt, suggesting that competitive anodic halide oxidation plays a role in the product formation, as is also observed for other EC protocols (see further). Greener solvents or sacrificial anode-free alternatives were not pursued.
Finally, selective formation of trans-configured 2,3-dicarboxylates has been achieved by Mita and coworkers in a dearomatizing dicarboxylation of various N-, O-, or S-heteroaromatics (entry 10).124 Based on DFT calculations and constant potential experiments with their model compound N-boc-indole, they found that the one-electron reduction of CO2 to its CO2˙− radical anion is the preferred mechanism here, leading after radical addition to a carboxylate intermediate at the 2-position rather than at the 3-position. They observed that substrates with reduction potentials between −3.0 V and −2.3 V (vs. SCE) all reacted well in the dicarboxylation protocol. Substrates having a reduction potential lower than −3.0 V possessed too high activation barriers, favoring the reverse decarboxylation and formation of oxalate products after radical–radical coupling of two CO2˙− radical anions. On the other hand, if the reduction potential was more positive than the CO2 reduction potential in MeCN (−2.3 V vs. SCE), the substrate itself undergoes one-electron reduction, potentially lowering the yield of dicarboxylation due to side reactions and decomposition. Analogously as before, addition of four equivalents of water resulted in monocarboxylation, due to protonation of the C3 position in the 2-carboxylate intermediate. In a later study, they found that addition of 1 equivalent of water is also beneficial for the dearomatizing monocarboxylation of electron-deficient naphthalenes with FEs up to 57% for 1,2-dihydronaphthalene derivatives.134
2.2 Benzylic carboxylations
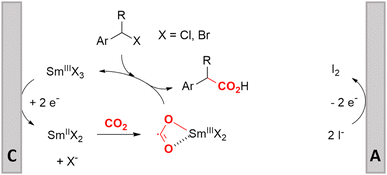
Electrosynthesis of arylacetic acids, which are essential organic synthons,135 has been primarily investigated using starting materials that follow the mechanistic pathway in Fig. 2B (entries 11–16).136–141 When using quaternary ammonium bromide salts as the reactant (entry 12), the bromide anion can be anodically oxidized, making it possible to use a non-sacrificial Pt anode, but this also results in brominated byproducts.137 However, product formation is still observed if BF4− is used as the anion, suggesting that the trimethylamine, which is detached after C–N cleavage in the reactant, can also undergo anodic oxidation, as was observed by CV measurements. This concept, by derivatizing the halide precursors in a fairly easy preparation step to make a tetraalkylammonium halide salt, is able to work under sacrificial anode-free conditions. However, much like with Mg or Zn anodes, stoichiometric byproducts of anodic oxidation are still unavoidable.In an attempt to avoid DMF and to work in the more anodically stable MeCN as the solvent with a non-sacrificial anode, Mellah and coworkers reported the use of an electroactive SmX2 species which generates a coordinated CO2˙− radical anion (Fig. 4).138 This way, CO2 is indirectly activated, followed by a radical substitution on the benzyl halide. This concept can diminish byproduct formation, e.g. dimerization, if the substrate is sensitive to direct electro-activation. After product formation, the produced Sm(III) species is reduced back to Sm(II) to close the catalytic cycle. However, it is not clear what the anodic reaction in this case is; we assume it is halide oxidation since both Cl and I are present in the system. Although the concept of CO2 activation by a redox active metal salt like Sm(II) is interesting, we envision that further improvements regarding practicality are still necessary since a Sm rod is temporarily used as a sacrificial anode to electrogenerate a defined amount of 20 mol% of the Sm(II) species, after which the polarity of the electrodes is switched to start the actual catalytic cycle. Using more common glassy as the cathode or adding a Sm(II) or Sm(III) species as such would circumvent this rather circuitous methodology, but resulted in a large drop in product yield.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Mechanism of the carboxylation of benzyl halides using a Sm(II)/Sm(III) catalyst. C = cathode, A = anode. Adapted from ref. 138. | ||
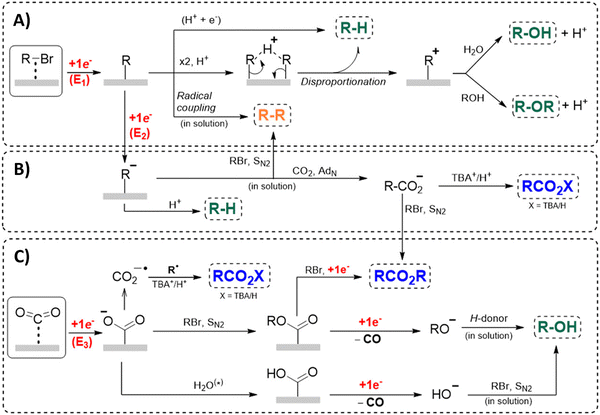
Another approach towards sacrificial anode-free conditions is by employing a divided cell set-up. This way, the envisioned reduction can be coupled with various electrooxidation reactions, even in aqueous anolytes, even if this is less practical than working in an undivided cell. Klinkova and coworkers thoroughly investigated the EC of simple α-methylbenzyl bromide by examining membrane effects, applied potential, total charge, precursor concentration, electrolyte and temperature on the product distribution.141 It was found that an anion-exchange membrane (AEM, with high proton blocking capability based on polyaromatic structure with quaternary ammonium bromide) yielded excellent selectivities and lowest cathode passivation. The authors suggested a detailed reaction mechanism for all observed products in different potential ranges accounting for both protic and aprotic environments. In contrast with the work of Mita,124 the reduction potential of the benzyl bromide here is more positive than that of CO2. The product formation is dependent on the operating potential range, involving either R°, R− without competing CO2 reduction, or R− with competing CO2 reduction, as is summarized in Fig. 5. It was found that the presence of H+ in the catholyte is crucial for the formation of both R–H and R–OR, since these products were not found in experiments employing the AEM at −0.8 V. Additionally, the concentration ratio of CO2/R–Br is an important factor, since CO2 needs to prevent fast formation of R− from reacting with R–Br. However, at potentials <−1.5 V the formation of CO and reaction of the CO2˙− radical anion with R–Br towards CO2R˙, leading to CO2R− and ultimately to ester byproducts, need to be taken into account.
 | ||
| Fig. 5 Overview of the proposed mechanisms and side reactions during the carboxylation of benzyl halides at different potential ranges. (A) E1 > −1.0 V, (B) −1.5 V < E2 < −1.0 V, (C) E3 < −1.5 V. The CO2˙− radical anion can react with CO2, followed by reductive disproportionation to CO and CO32−. Reused from ref. 141. | ||
In a later CV study, a broad scope of metal cathodes were investigated in the reductive transformation of benzylic halides to their radicals and carbanions, which are the common intermediates in the EC reaction (cf.Fig. 2A).142 Potential zones were identified for one- and two-electron reduction of organic halides in MeCN, and a window could be defined in which the electrochemical activation of CO2 does not occur. The onset potentials for benzylic halide reduction were observed to greatly depend on the cathode material. Non-catalytic metals like Fe, Al, Sn, Zn and Ti directly formed the benzylic halide derived anion species due to the high energy input requirements, while for catalytic metals like Ag, Au, Cu, Pt, Pd and in some cases Ni and Pb, the reduction of benzylic bromides to the benzylic anion proceeds in two distinct steps via the benzyl radical species. This radical is formed at potentials between −0.78 V and −1.28 V (vs. SCE) while further reduction to the anion was observed at potentials E < −1.28 V (vs. SCE). In contrast, reduction of benzylic chlorides directly yields the benzyl anion without any observed radical intermediate formation, which most likely correlates with a higher bond dissociation energy of C–Cl bond (∼300 kJ mol−1vs. ∼257 kJ mol−1 for C–Br). It was found that, when working in the ‘radical formation’ zone between −0.78 V and −1.28 V (vs. SCE), no interaction with CO2 occurred and thus no carboxylic acids were formed. Additionally, working at potentials more negative than the CO2 reduction potential resulted in formation of CO and thus in a decrease in FE. This potential gap ΔE between a suitable potential for EC and the potential where CO formation becomes significant is cathode dependent and can be as narrow as <0.3 V for suitable EC metals like Ag. In general, when working at the organohalide reduction peak potentials, the highest FEs for EC of up to 81% were observed for catalytic metals like Au, Cu, Pb and Ag, without any contribution of CO2 reduction. When working under CO2 activation conditions (E < −1.68 V vs. SCE), the highest rates for EC are expected for Ag and Au, followed by Cu, Pt and Pd. It might be of interest to investigate whether electrocatalysts can aid in enlarging the potential gap ΔE to perform selective EC via organohalide reduction, thereby increasing the FE.
2.3 Aromatic carboxylations
Similar to the benzylic carboxylic acids discussed above, aromatic carboxylic acids are key chemicals97,143,144 and recent electrochemical synthesis methods are summarized in Table 1, entries 17–22.145–149 Qiu and coworkers (entry 17) employed the strategy of indirectly activating the starting substrate by using simple naphthalene as a catalyst, which undergoes a single electron reduction at the cathode.145 After a single electron transfer (SET) to the substrate, the mechanism follows a similar pathway as depicted in Fig. 2B, though involvement of CO2˙− radical anions cannot be ruled out. Although the method is a applicable to a wide variety of aryl halides and some alkyl bromides, a drawback is the need for a small excess of TBD (1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene) as a sacrificial reagent; but the TBD makes it possible to employ a cheap graphite felt anode. TBD can also act as a CO2 trapping reagent,150 promoting the envisioned reactions.A real breakthrough followed in 2023 where the same research group could perform a site-selective C–H carboxylation of various simple and polycyclic (hetero)arenes under simple and practical conditions (entry 18).146 The direct reduction of the arene at the cathode is combined with an anodic oxidation of the iodide electrolyte, generating I2 which aids in the rearomatization towards the final product (Fig. 6). This reaction protocol can be considered as a paired electrosynthesis, making it possible to use common graphite felt electrodes as non-sacrificial electrodes. Again, depending on the respective reduction potentials, direct reduction of CO2 to a CO2˙− radical anion cannot be ruled out for some substrates. The regioselectivity originates from the electronic properties of the substrates, where the meta-position addition is the most kinetically favorable, as evidenced by DFT calculations on 1,3-dimethoxybenzene. Nonetheless, the faradaic efficiency (<7%) should be improved for future applications. Attempts to change the DMF solvent to MeCN or DMSO resulted in drastic drops in product yield.
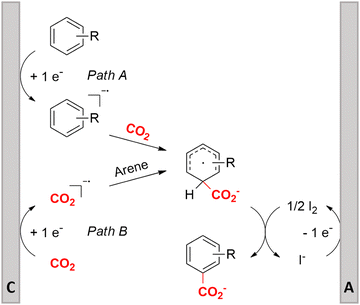 | ||
| Fig. 6 Proposed mechanism of the selective C–H carboxylation of arenes. C = cathode, A = anode. Adapted from ref. 146. | ||
In line with these site-selective aryl C–H carboxylations, Lin and coworkers (entries 20 and 21) reported a protocol for various N-heteroarene substrates, with a strong focus on 2-arylpyridines.148 Remarkably, the site selectivity was dependent on the reactor type: while a divided cell produced C5 carboxylated products, an undivided cell resulted in C4 carboxylations (Fig. 7). Both protocols required the addition of a strong KOtBu base, while optimal conditions for the C5 carboxylations demanded additional Cu(OTf)2, H2O and O2. Cyclic voltammetry experiments revealed the preferential reduction of Cu(II) to metallic Cu on the cathode, altering the electrode surface and thus possibly enhancing the reaction rate. Interestingly, using a Cu cathode without usage of Cu(OTf)2 reduced the selectivity and product yield with more than 20%. Reusing electrode materials is necessary for possible future applications and a functional alternative for this cathode with ever changing surface should be searched for. In addition, a sacrificial Zn anode was used, although it could be replaced by Pt with only a slight decrease in product yield, while obtaining unaltered selectivity levels. Using a Pt anode requires a different anodic reaction, most likely the oxidation of iodide electrolyte. The regioselectivity of the C5 carboxylation in the divided cell originates from the intrinsic electronic properties of the radical intermediate. DFT calculations supported a mechanism in which the C5 position bears the highest electron density after one-electron reduction of the model substrate 2-phenyl-pyridine. Nucleophilic addition of the radical intermediate to CO2 is reversible and slightly endergonic by 8.9 kcal mol−1 (12.3 kcal mol−1 for C4 addition).
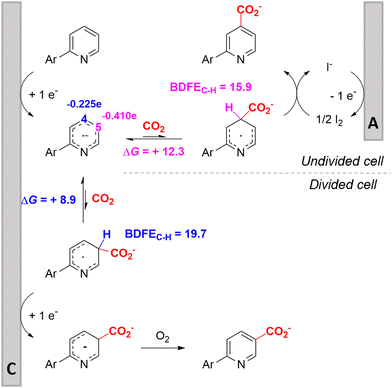 | ||
| Fig. 7 Proposed mechanism of the site selectivity in N-heteroarene carboxylations. BDFEC–H = bond dissociation free energy of the indicated C–H bond. C = cathode, A = anode. Energy values are given in kcal mol−1. Adapted from ref. 148. | ||
However, it was found that the bond dissociation free energy (BDFE) of the C4–H bond is lower than that of the C5–H bond if the CO2 adds on those respective C-atoms. As a consequence, the regioselectivity could be altered if a follow-up irreversible step such as addition of a hydrogen-atom acceptor is included. By changing to an undivided cell setup, the anodically formed I2 served as this H-atom acceptor through direct HAT or proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET), but at the expense of lower FEs due to unproductive reduction of I2 at the cathode. This C4 carboxylation in an undivided cell follows a paired mechanistic pathway very similar to what Qiu and coworkers found in Fig. 6, where anodic oxidation of the iodide electrolyte aids in cathodic product formation.
2.4 Aliphatic carboxylations
Aliphatic carboxylic acids are more arduous targets since starting materials like aliphatic halides are more difficult to be directly reduced at the cathode. One strategy to circumvent this issue is by using an electroactive metal catalyst. Yu and coworkers employed a Ni catalyst to transform unactivated aryl and alkyl halides to the respective carboxylic acids (entries 22 and 23),149 whereby Ni(II) gets cathodically reduced to Ni(0) in order to start the catalytic cycle. Subsequent oxidative addition of the organohalide to form Ni(II), cathodic reduction to Ni(I) and incorporation of CO2 followed by a second cathodic reduction to Ni(0) with release of the product closes the catalytic cycle. When changing the set-up from undivided to divided, the sacrificial Zn anode could be replaced by C while the anodic oxidation reaction was provided by chlorination of toluene. Aromatic substrates yielded similar results in this setup, but the yield for aliphatic substrates dropped drastically with maximum yields up to 45%.The group of Manthiram successfully employed an undivided cell setup to transform alkyl, benzylic and aryl halides to the corresponding carboxylic acids (entry 24) without the use of such a homogeneous electroactive metal catalyst.151 Their sacrificial-anode free method makes use of Mg(II) or Al(III) salts to maintain the selectivity of carboxylation as outlined in the beginning of this chapter. They elucidated a protective property of the carboxylate products towards cathode passivation by removing electrogenerated insoluble carbonates like MgCO3 from the surface; the latter were observed to be formed using a Mg sacrificial anode. In the presence of the protective Mg(II) cation, the main side reaction was the formation of R–H, due to protonation of R−, cathodically formed from the organic halide substrate R–X (cf.Fig. 5). The origin of protonation was due to deprotonation of the solvent (cf. dicarboxylation vs. monocarboxylation as reported by Nam122 and Mita,124 see above). In a follow-up study, this role of the solvent was examined carefully and a strong correlation between the free energy of solvent deprotonation and selectivity was identified (Fig. 8).152 The side reaction of hydrogenolysis appeared to occur via solvent deprotonation rather than hydrogen abstraction. Interestingly, the solvent choice with regard to EC selectivity appeared to be essential for alkyl halides, while it had a less pronounced effect with benzylic halides.
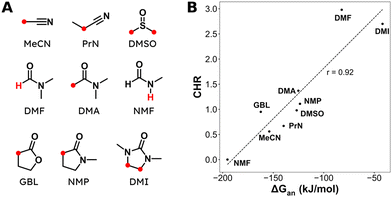 | ||
| Fig. 8 (A) Molecular structures and abbreviations for solvents, where the most acidic protons are indicated in red. (B) Correlation between the deprotonation free energy ΔGan and the carboxylation-to-hydrogenolysis ratio CHR. Dashed line is the best linear fit with a Pearson correlation coefficient of r = 0.92. Experimental details can be found in the corresponding literature. Reused from ref. 152 (open access). | ||
2.5 Hydroxycarboxylic acids
Hydroxycarboxylic acids are an important subclass of carboxylic acids as they are frequently present in nature as metabolic intermediates153 and in pharmaceuticals, but they are also used in pesticides and as plastic monomers.98 Their current industrial synthesis often involves the transformation of an aldehyde or epoxide with the highly toxic HCN to the corresponding α- or β-cyanohydrins, respectively. Hydrolysis of these intermediates yields the hydroxycarboxylic acids. To avoid this dangerous two-step protocol, the direct incorporation of CO2 in both aldehydes/ketones or epoxides seems a most valuable alternative (Table 1, entries 25–29).154–158A sustainable metal-free protocol was developed by Waldvogel and coworkers who reported the sacrificial-anode free synthesis of α-hydroxycarboxylic acids from aryl aldehydes and ketones in a green propylene carbonate solvent, which outperformed the reactions in both DMF and MeCN (Fig. 9A).155 Using a divided cell set-up equipped with two graphite electrodes, yields of up to 63% were achieved. The concentration of the electrolyte was found to be crucial, since a higher amount of tetraalkylammonium cations resulted in higher product yields. It is thought that they stabilize the produced carboxylate ions, similar to what metal ions like Mg(II) tend to do. Finally, the aprotic nature of the solvent is essential to (partially) prevent formation of byproducts such as alcohols and dimers.
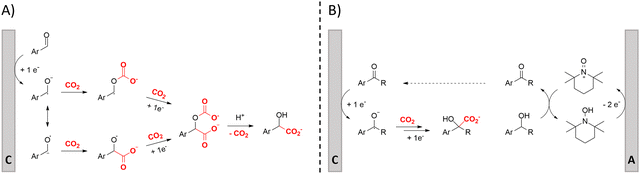 | ||
| Fig. 9 Proposed mechanisms of the carboxylation of aromatic aldehydes/ketones towards α-hydroxycarboxylic acids. Adapted from ref. 155 (A) and 156 (B). Cathodic product formation in B can be envisioned to be similar as in mechanism A. C = cathode, A = anode. | ||
In order to work in a more practical undivided cell, an appropriate anodic reaction should be investigated. Our research group utilized the facile TEMPO-mediated alcohol oxidation to transform benzylic alcohols to α-hydroxycarboxylic acids, providing an elegant paired electrosynthesis in MeCN (Fig. 9B).156 Increasing amounts of a protic impurity like H2O resulted in decreasing carboxylate selectivities. However, a small amount of 0.03 M of H2O proved to be necessary to obtain satisfactory conversions of the aromatic alcohol. Further investigation towards other alcoholic or carbonyl species, especially aliphatic ones, seems to be the logical next step.
Transformation of O-heterocycles like epoxides, oxetanes and tetrahydrofurans to the corresponding β-, γ- and δ-hydroxycarboxylic acids (entries 28–29) has been reported by the groups of Qiu157 and Zhang.158 CV measurements and detection of oxalic acid and formic acid during isotope labeling experiments158 indicate that depending on the respective reduction potentials, CO2 or the substrate preferably undergo one-electron reduction. However, since these reduction potentials are close to each other, both pathways can occur simultaneously. Furthermore, Qiu found that the reduction potential of their model compound styrene oxide underwent a positive shift when Mg(II) or Al(III) was added to the solution, suggesting that the metal ions can serve as a Lewis acid to activate the epoxide.157 In addition, both authors report a racemic product mixture when starting with (R)-styrene oxide, which suggests a benzylic radical intermediate.
Zhang and coworkers studied the mechanism more in depth and noted that this radical intermediate rapidly reacts with CO2 to form a carboxylated radical anion. Deuterium labeling experiments also showed the intermediacy of the α-carbanion, most likely formed via an α-radical intermediate. They performed an additional radical clock control experiment with a similar aromatic epoxide bearing a cyclopropyl substituent at the benzylic position. This substrate did not undergo a radical opening reaction under standard conditions, hinting towards a rapid transformation of the radical carboxylated anion through another one-electron transfer process towards a dianion. This way, CO2 functions both as a carboxylating agent and as a promotor. Additionally, DFT calculations indicate that the single-electron reduction of the carboxylated radical intermediate was more exothermic (26.5 kcal mol−1) than that of the non-carboxylated radical intermediate (9.8 kcal mol−1). Combining all these results, including the activation effect of the metal ion discovered by Qiu and coworkers, they proposed the putative reaction mechanism in Fig. 10. This mechanism is commonly denoted as an ECEC mechanism, where two electrochemical steps (E) are followed by a chemical step (C) towards product formation.
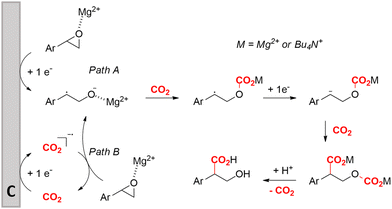 | ||
| Fig. 10 Proposed cathodic reaction mechanism for the carboxylation of O-heterocycles. Adapted from ref. 157 and 158. | ||
Finally, some more distinctive substrates are listed in entries 30–33,159–162 creating products with specific functionalities, such as the gem-difluoroalkene moiety.
3. Urea
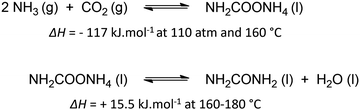
Urea is one of the most crucial chemicals worldwide and its global production reached approximately 180 million metric tonnes in 2022.163,164 More than 90% is destined for fertilization due to the high nitrogen content. Urea is also employed in selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology in cars and other combustion processes in order to reduce NOx pollutants in exhaust gases. Other uses include urea-formaldehyde resins, explosives, energy carriers, textiles, melamine production and pharmaceuticals. As soon as the Haber–Bosch process was established in 1913, industrial urea synthesis involved the reaction between NH3 and CO2 at elevated temperatures and pressures (Bosch–Meiser process following the Basaroff equations, Fig. 11). Thermodynamic limitations on the conversion per pass through the urea reactor, a corrosive ammonium carbamate intermediate, hydrolysis of urea and biuret formation side reactions require specific equipment and precise design of operating and recycling conditions.165,166 In addition, the energetically voracious Haber–Bosch process and the immense urea production scale justify the quest for more sustainable urea synthesis protocols, as nowadays approximately 2% of the annual global energy consumption is attributed to urea synthesis alone.Therefore, other nitrogen sources like NO3−, NO2−, NO and even N2 are increasingly investigated in electrochemical co-reduction with CO2 in aqueous environment. Looking more closely to urea seems to indicate that CO2 does not need to be reduced, as the oxidation state of carbon in both CO2 and urea is +IV. However, partially reducing CO2 is needed to increase reaction rates, making it possible to perform the C–N coupling with an activated N-species, in which process the oxidation state of C increases again. Sluggish C–N bond formation kinetics together with low activity and selectivity based on the reactants are amongst the greatest challenges towards an applicable and sustainable electrocatalytic urea formation protocol. Simultaneous eCO2RR and electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction (eNRR) should occur in close proximity of one another at the catalyst to generate the necessary reactive intermediates in order to form the essential new C–N bonds. Additionally, an effective catalyst should also be able to reduce the coupling barrier between the electrochemically formed C- and N-intermediates, thus minimizing the formation of (incompletely reduced) byproducts from the individual eCO2RR and eNRR such as CO, HCOOH, NO2 and NH3/NH4+, while also suppressing the competitive hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). An optimum in operating potential needs to be found since generally this competition is more intense when the potential is increased below a certain value, ultimately leading to a decrease in FE for urea.
In general, the catalysts can be a variety of transition metals but also metals like In, Te, Ce, Bi and even non-metals like C. Quite often, a combination of two different metals and/or materials is used in order to exploit their synergistic effects towards the individual eCO2RR and eNRR to effectively perform the C–N coupling of the activated intermediates. Notably, structural modifications of the composite material have also been demonstrated to enhance catalytic activity. Examples include introduction of oxygen vacancies or employing nanostructures with increased specific surface areas, such as nanoparticles (NPs), nanotubes (NTs), nanobelts (NBs), multiholes, etc.
When comparing all reported methods, it is clear that a plethora of intermediates have been proposed to ultimately form urea. The combination of control experiments and various (in situ) spectroscopic techniques, supported by DFT calculations, is able to pinpoint some crucial coupling partners and intermediates. However, various pathways to these detected intermediates are possible and are often not all accounted for. In addition, when multiple N-intermediates are observed, two different N-coupling partners can play a role, creating even more possibilities. In order to have a clear overview in the long list of possibilities, we present the following overview (Fig. 12). This roadmap might serve as a guideline when computing a theoretically optimal reaction mechanism, accounting for the discovered intermediates via various spectroscopic techniques. This visual tool can aid in pinpointing which pathway seems more feasible and is ultimately energetically favorable.
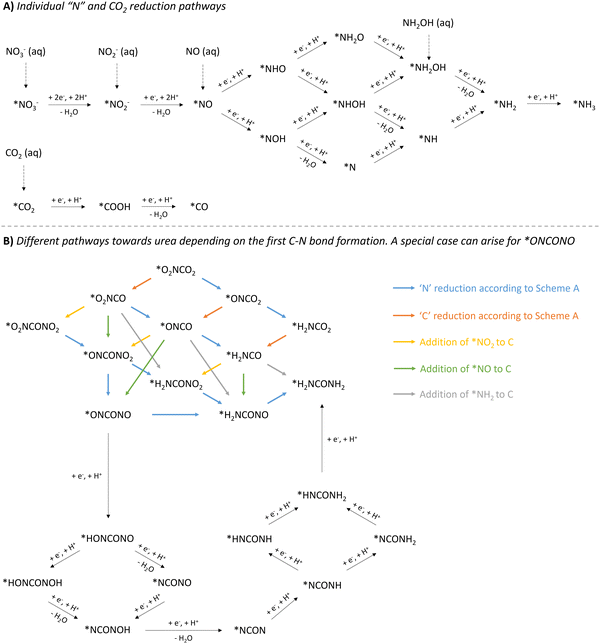 | ||
| Fig. 12 Overview of mechanistic pathways starting from various N-sources and CO2 towards urea. (A) Individual ‘N’ and CO2 reduction pathways. (B) Different pathways towards urea depending on the first C–N bond formation, with a special case for *ONCONO. The asterix * means that the species is adsorbed on the catalyst. Active species like *NH2OH and *COOH have also (rarely) been reported as coupling partners (see Table 2, entries 7 and 23). The net result would be as if *NH2 or *CO2 would be used as the coupling partner, respectively. | ||
The reduction of the described N-containing species to the presumed active species all the way to *NH3 (* means adsorbed on the catalyst), is depicted in Fig. 12A. Based on all reported protocols, it seems that *NO2, *NO and *NH2 are the most plausible N-containing coupling partners. Therefore, in order to avoid overly complex pathways and to keep a clear overview, the intermediates in the *NO reduction towards *NH2 are considered non-reactive towards coupling with any C-containing moiety, also in the second C–N bond formation step. *CO2, if deemed necessary, has a straightforward reduction pathway towards *CO via *COOH. This combination of three active N-species (*NO2, *NO and *NH2) with two active C-species (*CO2 and *CO), results in six possible combinations for the first C–N bond formation: *O2NCO2, *O2NCO, *ONCO2, *ONCO, *H2NCO2 and *H2NCO.
Once the first C–N bond formation occurred, multiple reduction pathways open up, depending on the two coupling partners. The different possibilities, ultimately leading to urea, are closely intertwined via the ‘N’- and ‘C’-reduction pathways and are presented in Fig. 12B. Species like *O2NCO and *ONCO, in which the N atom is already bound to a C atom, are not able to reduce via the *NH2O and *NH2OH pathway. Additionally, C–N coupling with the second N-containing moiety, creating the N–C–N backbone, needs to be taken into account. For instance, if *NH2 and *CO react to form the *H2NCO intermediate, the only possible reaction forward is the coupling of the second N-coupling partner, which can be *NO2, *NO or *NH2. Apart from when *NH2 is the reactive species, which creates urea directly, the produced intermediate needs to be further reduced. However, if the first C–N bond formation step occurs between less reduced N- and C-containing moieties towards e.g. *ONCO, *O2NCO or even *O2NCO2, multiple pathways are possible: (1) reducing the ‘C’ unit, (2) reducing the ‘N’ unit, or (3) coupling of a second N-containing partner. A special case arises when *ONCONO is described as an intermediate. Apart from the complete reduction of one NO-group towards H2NCONO, reduction towards the intermediate *NCON can also be envisioned, where both NO-groups are reduced alternatingly. This tower-like *NCON intermediate is well established, especially in the case where N2 is used as the N-feed (see further).
Recent electrochemical urea synthesis protocols are summarized in Table 2. They are ordered along three levels: first according to the oxidation state of the employed nitrogen source, followed by the key first C–N bond formation step and finally by increasing FEs. In this review, we will compare the various urea synthesis protocols focusing on the mechanistic investigations. Other reviews about this topic can be found elsewhere.167–171
| No. | N-source | Catalyst deposited on cathode | Key C–N coupling intermediates | CO2 saturated electrolyte | E (vs. RHE) | Urea yield rate | FE | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RHE = reversible hydrogen electrode. FE = faradaic efficiency. CNTs = carbon nanotubes. NTs = nanotubes. NPs = nanoparticles. NCs = nanocrystals. RGO = reduced graphene oxide. | ||||||||
| 1 | NO3− | Cu@Zn nanowires@Cu mesh | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.2 M KHCO3 + 0.1 M KNO3 | −1.02 V | 7.29 μmol h−1 cm−2 | 9 | 176 |
| 2 | NO3− | Fe(a)@C–Fe3O4/CNTs@carbon paper | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.65 V | 1341.3 mg h−1 g−1 | 17 | 177 |
| 3 | NO3− | F doped CNT-300 carbon paper | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.65 V | 382.0 mg h−1 g−1 | 78 | 178 |
| 4 | NO3− | Ru@Cu foam | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.1 M NaNO3 | −0.3 V | 151.6 mg h−1 g−1 | 25 | 179 |
| 5 | NO3− | Cu-GS-800@carbon fiber | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.1 M KHCO3 + 0.1 M KNO3 | −1.0 V | 1800 mg h−1 g−1 | 27 | 180 |
| 6 | NO3− | CoPc-COF@TiO2 NTs@carbon paper | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.3 M KHCO3 + 0.2 M KNO3 | −0.6 V | 753.1 mg h−1 g−1 | 49 | 181 |
| 7 | NO3− | Xc72R-AuPd nanoalloy@carbon cloth | *NH2OH + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.075 M KHCO3 + 0.025 M KNO3 | −0.5 V | 204.2 mg h−1 g−1 | 16 | 182 |
| 8 | NO3− | Vo–CeO2-750@carbon paper | *NO + *CO → *ONCO | 0.1 M KHCO3 + 0.05 M KNO3 | −1.6 V | 943.6 mg h−1 g−1 | 1 | 183 |
| 9 | NO3− | Cu–CeO2 nanorods@carbon paper | *NO + *CO → *ONCO | 0.1 M KHCO3 + 0.05 M KNO3 | −1.6 V | 3717.2 mg h−1 g−1 | 5 | 184 |
| 10 | NO3− | Multihole Cu2O@carbon paper | *NO + *CO → *ONCO | 0.1 M KHCO3 + 0.01 M KNO3 | −1.3 V | 1753.8 mg h−1 g−1 | 9 | 185 |
| 11 | NO3− | N–C-1000@carbon paper | *NO + *CO → *ONCO | 0.1 M KHCO3 + 0.1 M KNO3 | −1.5 V | 498.5 mg h−1 g−1 | 9 | 186 |
| 12 | NO3− | Fe(II)–F(III)OOH@BiVO4@carbon paper | *NO + *CO → *ONCO | 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.8 V | 828.8 mg h−1 g−1 | 12 | 187 |
| 13 | NO3− | CuWO4 NPs@carbon paper | *NO2 + *CO → *O2NCO | 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.2 V | 98.5 mg h−1 g−1 | 70 | 188 |
| 14 | NO3− | MoOx NCs@CB@carbon paper | *NO2 + *CO2 → *O2NCO2 | 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.6 V | 1431.5 mg h−1 g−1 | 28 | 189 |
| 15 | NO3− | In(OH)3–S@carbon paper | *NO2 + *CO2 → *O2NCO2 | 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.6 V | 533.1 mg h−1 g−1 | 53 | 190 |
| 16 | NO3− | PdCu NPs@CBC@carbon paper | *NO2 + *CO2 → *O2NCO2 | 0.05 M KNO3 | −0.5 V | 763.8 mg h−1 g−1 | 60 | 191 |
| 17 | NO3− | 3D Zn/Cu hybrid catalyst@carbon paper | *NO2 + *CO2 → *O2NCO2 | 0.1 M KHCO3 + 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.8 V | 3603.6 mg h−1 g−1 | 75 | 192 |
| 18 | NO3− | 6 Å-Cu2O@GDE | Broad investigation | 1 M KOH + 0.1 M KNO3 | −0.41 V | 7541.9 mg h−1 g−1 | 52 | 193 |
| 19 | NO2− | Te-doped Pd NCs@glassy carbon | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.1 M KHCO3 + 0.1 M KNO2 | −1.1 V | Not found | 12 | 194 |
| 20 | NO2− | AuCu SANFs@carbon paper | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.5 M KHCO3 + 0.01 M KNO2 | −1.35 V | 3889.6 mg h−1 g−1 | 25 | 195 |
| 21 | NO2− | Cu–TiO2–VO@carbon paper | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.2 M KHCO3 + 0.02 M KNO2 | −0.4 V | 1249.2 mg h−1 g−1 | 43 | 196 |
| 22 | NO2− | Self-supporting ZnO–V NSs | Not specified | 0.2 M NaHCO3 + 0.1 M NaNO2 | −0.79 V | 16.56 μmol h−1 | 23 | 197 |
| 23 | NO2− | Co–NiOx@graphdiyne | *NH2 + *COOH → *H2NCO2 | 0.1 M NaNO2 | −0.7 V | 913.2 mg h−1 g−1 | 64 | 198 |
| 24 | NO | Zn NBs@GDL | *NH2 + *CO → *H2NCO | 0.2 M KHCO3 | −0.92 V | 908.7 mg h−1 g−1 | 11 | 200 |
| 25 | N2 | Bi2S3/N-glassy carbon | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.5 V | 264.3 mg h−1 g−1 | 8 | 201 |
| 26 | N2 | pdCu@TiO2-400@carbon paper | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.4 V | 201.8 mg h−1 g−1 | 9 | 202 |
| 27 | N2 | SbxBi1−xOy/GO@carbon paper | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.5 M K2SO4 | −0.3 V | 308.0 mg h−1 g−1 | 11 | 203 |
| 28 | N2 | Bi–BiVO4 NPs@carbon cloth | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.4 V | 355.0 mg h−1 g−1 | 13 | 204 |
| 29 | N2 | CoPc–MoS2@carbon paper | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.7 V | 175.6 mg h−1 g−1 | 15 | 205 |
| 30 | N2 | BiFeO3/BiVO4@carbon cloth | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.4 V | 296.7 mg h−1 g−1 | 17 | 206 |
| 31 | N2 | Ni3(BO3)2150@carbon cloth | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.5 V | 582.6 mg h−1 g−1 | 20 | 207 |
| 32 | N2 | InOOH-100 NCs@carbon cloth | *N2 + *CO → *NCON* | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.4 V | 411.4 mg h−1 g−1 | 21 | 208 |
| 33 | N2 | MoP NPs@carbon paper | *HNNH + *CO → *NHCONH | 0.1 M KHCO3 | −0.35 V | 12.4 mg h−1 g−1 | 37 | 209 |
3.1 Urea production starting from nitrate
Nitrate is an enduring contaminant in industrial wastewater and groundwater due to anthropogenic activities like industrial discharge and fertilizer-intensive agriculture, inducing serious environmental and health issues.172,173 Therefore electrochemically transforming both nitrate and CO2 to a valuable chemical such as urea can be considered to be advantageous from a sustainability viewpoint.174,175 However, the overall reduction of these two starting materials to urea involves 16 electrons and 18 protons, resulting in complex chemistry. It is challenging to find the optimal catalyst and reaction conditions to reach high urea selectivities and rates. Therefore, it is useful to elucidate the formation and coupling abilities of key intermediates via various spectroscopic and theoretical techniques.Many reports argue that the coupling of *NH2 (* means: adsorbed on the catalyst), via an almost complete reduction of NO3−, with *CO towards *H2NCO is the crucial first C–N bond formation step (Table 2, entries 1–6).176–181 For instance, Yu and coworkers synthesized Zn covered Cu nanowires (Cu@Zn) which effect an electron transfer from Zn to Cu, as demonstrated by their different work functions (4.30 eV for Zn and 4.63 eV for Cu).176 They calculated a more negative Gibbs free energy for both the individual nitrate reduction and for the coupling of *CO with *NH2 to *H2NCO compared to pristine Cu or Zn materials. Thus, the effective electron transfer from the Zn shell to the Cu core enhances the performance towards formation of the key intermediates and the C–N bond. DEMS measurements showed decreased signal intensities of CO and NH2 when electroreducing the mixture CO2 + NO3− compared to mixtures in the absence of NO3− or CO2, respectively, indicating the competition between eCO2RR and eNRR (Fig. 13A). Additionally, ATR-FTIR measurements at different potentials revealed the formation of *CO (2060 cm−1) and *COOH (1360 and 1210 cm−1) in the individual eCO2RR, and of *NO (1310 cm−1), *NO2 (1210 cm−1) and *NH4 (1140 cm−1) in the individual eNRR (Fig. 13B).176 For the mixture of CO2 + NO3−, ATR-FTIR showed no signal of *CO, while a signal at 1420 cm−1 appeared, characteristic for the C–N bond. Jiang and coworkers performed ATR-FTIR measurements as a function of time (Fig. 13C).181 With increasing time, two new bands of the stretching vibrations of C–O (1101 cm−1) and H–N–H (1171 cm−1) appear. More specifically, the stretching vibration of C–N (1450 cm−1) was only observed after the appearance of the C–O and H–N–H signals, suggesting that *CO and *NH2 are indeed the coupling partners. Urea synthesis is accomplished by reaction of *H2NCO with a second *NH2 intermediate, as indicated by an accompanying drop of free energy in theoretical calculations when comparing the pristine materials with the modified catalysts.
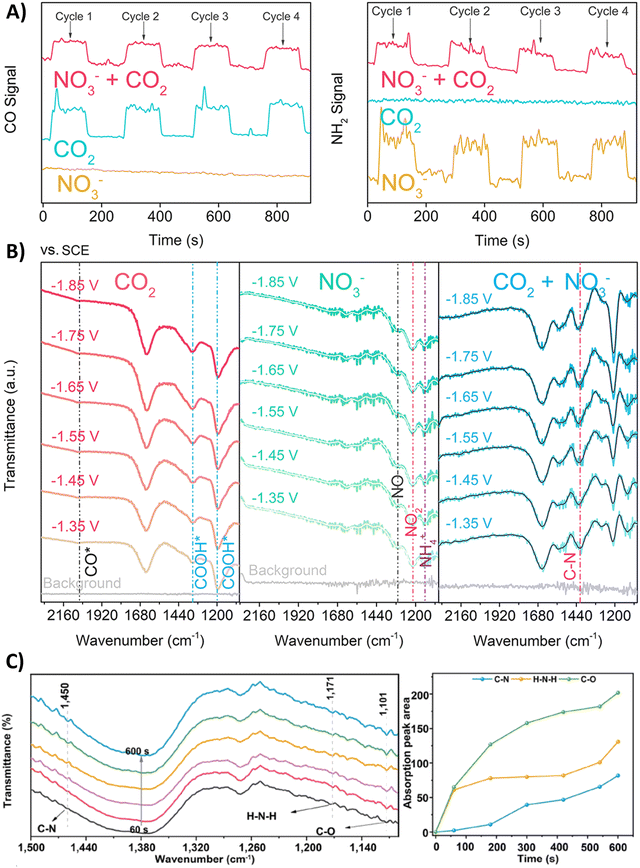 | ||
| Fig. 13 Mechanistic investigations involving the formation of *H2NCO. (A) Online DEMS spectra of CO and NH2 signals over Cu@Zn catalyst in mixtures containing CO2, NO3− or CO2 + NO3−. (B) In situ ATR-FTIR spectra of CO2, NO3− and mixture of CO2 + NO3− electroreduction over Cu@Zn catalyst over different potentials. (C) In situ ATR-FTIR spectra as a function of electrolysis time for CoPc-COF@TiO2 NTs catalyst and the intensity of the signals for C–O, H–N–H and C–N stretching vibrations as a function of electrolysis time. Adapted from ref. 176 (A) and (B) and 181 (C). | ||
However, it might be misleading to consider *NH2 as the only active N-coupling partner when species like *NO2 and *NO are also detected. Li and coworkers discuss whether there is enough experimental and theoretical evidence to support the general claim of an *NH2 intermediate and studied the involvement of the N-intermediates in more detail on their AuPd nanoalloy catalyst (Table 2, entry 7).182 Analogously as for the Cu@Zn catalyst, a slight electron transfer from Au to Pd was found via XPS. The authors exploit the synergism of the metals in this combined material where *CO is easily formed on Pd while eNRR occurs more readily on Au. The combination of Au with Pd was found to also reduce the coupling energy barrier opposed to the pristine Au and Pd materials. Control experiments indicate that both NO2− and NH2OH are formed before urea and NH3, whereas using NH3 or NH4+ did not result in urea formation (Fig. 14). NH2OH seems to be a critical intermediate for urea formation in this case. Urea is also formed when using CO as the C-source, giving experimental indications of *CO as the key C-coupling partner. Additionally, using CO2 resulted in higher urea formation rates compared to CO, indicating that *CO, activated via in situ CO2 reduction is more reactive for coupling with *NH2OH.
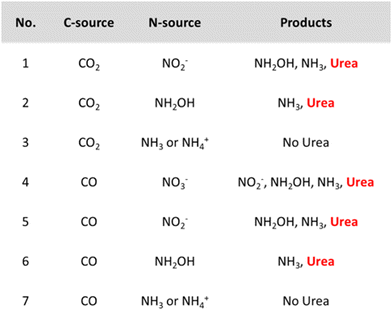 | ||
| Fig. 14 Control experiments for urea formation using different N- and C-sources. Adapted from ref. 182. | ||
A series of catalysts has been developed by Wang and Zhang that perform the C–N coupling at an even earlier stage of reduction, namely the coupling between *CO and *NO towards *ONCO (Table 2, entries 8–12).183–187 For instance, Wang et al. introduced oxygen vacancies in CeO2 nanorods creating coordinatively unsaturated sites that enhance adsorption of both reactants and that stabilize N-intermediates by inhibiting their hydrogenation to NH3.183 Later, they modified the CeO2 nanorods with various metals but only Cu resulted in a significant improvement,184 almost quadrupling the urea formation rate. It was found that the N–O bonds in NO3− are elongated and that the O–C–O bond angle in CO2 changes from 180° to 124.4°, destabilizing its electron cloud. This results in strengthening of the adsorption and activation of both CO2 and NO3−. They postulate that the replacement of certain high-coordinating Ce atoms with low-coordinating Cu induces formation of a unique Cu–O–Ce moiety exhibiting frustrated Lewis acid–base pair properties, a Lewis acid and base sterically prevented from bonding, that enhance the urea synthesis. The Lewis acid site enhances adsorption of the N-containing moiety, while the Lewis base site does the same for the C-containing reactant.
Spectroscopic evidence of *ONCO involvement was found due to the consistent evolution of its infrared band with the evolution of the urea yield rates along the tested potential range with the optimum at −1.6 V (Fig. 15). The appearance of the C–N and NH2 signals follows a similar increase with potential. Control experiments using NO and NH2OH as the N-feed (cf. work of Li, see above), might strengthen their postulated mechanism. However, *NO2 might also be a key intermediate, since Wang confirmed a significantly increased urea yield rate for both the multihole Cu2O185 and N–C-1000 catalyst,186 if NO3− was replaced with a NO2− feed. Even though nitrite is more easily reduced than nitrate176 and that a similar supply of electrons can improve the urea yield rate, this might also suggest that *NO2 plays an important role in the reaction pathway and that *NO2 is not only further reduced to *NO.
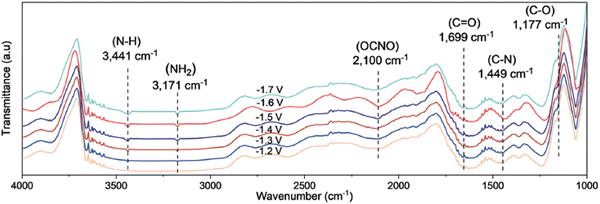 | ||
| Fig. 15 Mechanistic investigations involving the formation of *ONCO using the Cu1–CeO2 catalyst. Operando SR-FTIR spectroscopy measurements at different potentials during electroreduction of CO2 and NO3−. Adapted from ref. 184. | ||
The involvement of *NO2 as a key intermediate was elucidated by Li et al. (Table 2, entry 13).188 They outline that the applied potentials of the reported methods generally range between −0.6 V and −1.5 V vs. RHE, which exceeds the thermodynamic potential for the co-reduction of NO3− and CO2 towards urea (0.48 V vs. RHE). Consequently, such negative potentials increase byproduct formation from the competitive HER and the individual eCO2RR and eNRR, reducing the urea selectivity and FE. Utilizing a high-valence metal center can result in a more positive reaction overpotential since it can decrease the electron density of the adsorbed species. Li et al. combine the advantages of WO3, which has a low *NO2 formation potential, with Cu, which has a low *CO formation potential. Their CuWO4 catalyst can achieve very high FEs of up to 70% with only an applied potential of −0.2 V vs. RHE. Interestingly, *NO2 was the only reduced NO3− intermediate detected using in situ Raman spectroscopy at this applied potential (Fig. 16A). DEMS measurements showed only fluctuations in the signals of CO, NH3, NO, and NO2 with the switching cycles of open circuit and working states, confirming the involvement of *CO and *NO2 (Fig. 16B). Analogously to Li and coworkers,182 the authors performed several control reactions utilizing various C- and N-sources. Only NO2 (apart from nitrate) was capable of forming urea with either CO2 or CO, whereas further reduced N-species, even NO2−, failed to deliver urea (Fig. 16C).
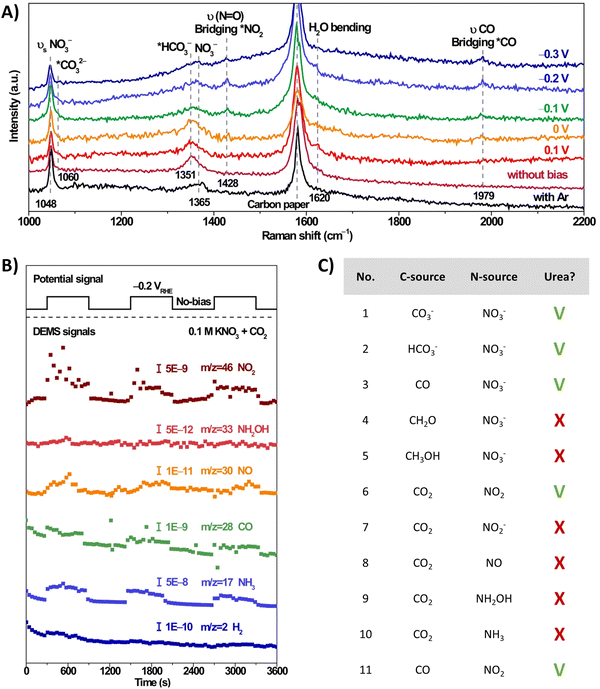 | ||
| Fig. 16 Mechanistic investigations involving the formation of *O2NCO using the CuWO4 catalyst. (A) In situ Raman spectra at different potentials. (B) Online DEMS at −0.2 V vs. RHE. (C) Control experiment with various C- and N-sources. Adapted from ref. 188 (Open Access). | ||
Performing the first C–N coupling at an even earlier stage of the urea synthesis, such as coupling of *CO2 with *NO2, can effectively reduce even the formation of HCOOH and CO byproducts resulting in faradaic efficiencies of up to 75% (Table 2, entries 14–18).189–193 The In(OH)3 catalyst of Yu and coworkers showed facet-dependent activity, where the *NO2 and *CO2 intermediates are preferably coupled on the {100} facets rather than on the {110} facets.190 Remarkably, the only byproduct observed during the co-reduction is NH3, meaning that the C-selectivity for urea synthesis is near 100%; HCOOH or CO are not detected. Control experiments indicate that CO2 promotes nitrate reduction with increased FE and significantly suppresses HER, even though the individual eCO2RR, which otherwise competes with HER, is not involved here. To further investigate this phenomenon, the authors performed Mott–Schottky (M–S) measurements (Fig. 17A). Under Ar atmosphere, a positive slope in the M–S plot indicates intrinsic n-type semiconductor behavior. When CO2 is introduced, p-type semiconductor behavior is observed as well. In addition, the electron concentration in n-type In(OH)3 decreases in the CO2 atmosphere since the slope, which is inversely proportional to the carrier concentration, increases. These results demonstrate that a hole accumulation layer on the surface of the catalyst is formed due to the capture of electrons by CO2, effectively repelling protons to approach the catalyst and impeding the HER (Fig. 17B). A similar advantageous effect of CO2 in diminishing side reactions like HER and eNRR was also observed by Zhao et al. for their PdCU catalyst.191 In addition, the electron transfer between Cu and Pd resulted in a change of the electronic states of the d-band centers. The PdCu nanoalloy can provide more d-bands, favoring adsorption and activation of the reactants, compared to monometallic Pd or Cu. Operando Raman spectroscopy191 as a function of time and in situ ATR-FTIR189 or SR-FTIR190,191 spectroscopy at various potentials provided experimental evidence for some intermediates like the well-known *H2NCO, formed after consecutive ‘N’- and ‘C’-reductions of *O2NCO2.
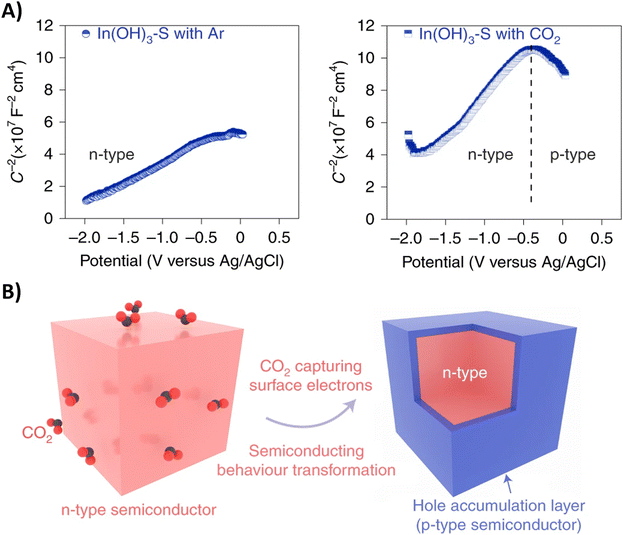 | ||
| Fig. 17 Semiconductor type analysis of the In(OH)3–S catalyst. (A) Mott–Schottky plots measured in Ar and CO2. (B) Schematic illustration of the n–p transformation process. Adapted from ref. 190. | ||
Sargent and coworkers studied both the formation of *O2NCO2 and its further reduction in more detail.192 Initially, they screened various metals, such as Cu, Bi, Zn, Ag and Sn, which are known to prefer both eCO2RR and eNRR over HER. Already decent FEs for urea of <20% were obtained. When constructing a hybrid Zn/Cu (or Zn/Ag) material, the FE for urea improved drastically to 50% and 75% using 100 ppm and 1000 ppm NO3−, respectively. These results indicate that both Zn and Cu are used for their advantageous C–N bond formation and reducing properties, respectively. They performed in situ infrared reflection–absorption spectroscopy (IRRAS) across a potential range (Fig. 18A). The C–N bond in urea appears at 1417 cm−1 but diminishes at higher overpotentials due to more competitive side reactions. The band at 1694 cm−1 is assigned to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O in *H2NCO2H, and diminishes to near zero at −1.2 V. Additionally, the band at 1403 cm−1 followed a similar increase-decrease trend with increasing potential and is ascribed to OCO vibrational band of *H2NCO2. This suggests that indeed the protonation of *H2NCO2 to *H2NCO2H is a crucial step in urea formation. Furthermore, they compared these results with similar measurements on single-component Zn or Cu catalysts. On Zn, the weak band for *H2NCO arises, but no signal for *H2NCO2H is found, which suggests that the rate-determining step on Zn is this protonation step. On the other hand, neither signals were found on Cu, suggesting that the initial C–N bond formation step is rate-determining here (Fig. 18B). Additional in situ surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) measurements compared with ammonium carbamate + KHCO3 as a reference, also indicated that Zn indeed helps to form *H2NCO2 and thus initially *O2NCO2 (Fig. 18C).
O in *H2NCO2H, and diminishes to near zero at −1.2 V. Additionally, the band at 1403 cm−1 followed a similar increase-decrease trend with increasing potential and is ascribed to OCO vibrational band of *H2NCO2. This suggests that indeed the protonation of *H2NCO2 to *H2NCO2H is a crucial step in urea formation. Furthermore, they compared these results with similar measurements on single-component Zn or Cu catalysts. On Zn, the weak band for *H2NCO arises, but no signal for *H2NCO2H is found, which suggests that the rate-determining step on Zn is this protonation step. On the other hand, neither signals were found on Cu, suggesting that the initial C–N bond formation step is rate-determining here (Fig. 18B). Additional in situ surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) measurements compared with ammonium carbamate + KHCO3 as a reference, also indicated that Zn indeed helps to form *H2NCO2 and thus initially *O2NCO2 (Fig. 18C).
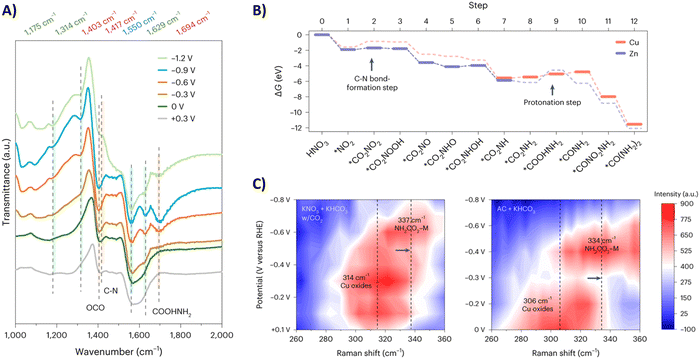 | ||
| Fig. 18 Mechanistic investigations involving the formation of *O2NCO2 using the Zn/Cu hybrid catalyst. (A) In situ IRRAS measurements at different potentials. (B) Free energy diagram towards urea. (C) In situ SERS measurements at different potentials. Adapted from ref. 192. | ||
3.2 Urea production starting from nitrite and nitric oxide
Using nitrite, which equally is a pollutant due to anthropogenic ativities, as the N-coupling partner would obviously show great similarities to the reactions with nitrate in terms of materials and active sites. Overall, employing nitrite results in analogous faradaic efficiencies and urea formation rates (Table 2, entries 19–23).194–198 Li and coworkers characterized in depth their Co–NiOx@GDY catalyst, which comprises in situ grown graphdyine (GDY) on the surface of Co–Ni mixed oxides (entry 23).198 Graphdiyne is an upcoming carbon material consisting of sp/sp2-cohybridized carbon atoms. It exhibits uneven surface charge distribution, uniform pores, a highly conjugated π-system and excellent stability, making it an interesting material for applications in photocatalysis, electrocatalysis, gas separation and energy conversion.199 The synthesized superhydrophilic catalyst displays an incomplete charge-transfer between the GDY (donor) and the mixed metal oxide (acceptor). AFM measurements revealed the superposition of a 1.5 nm Co–NiOx layer and a 1.8 nm GDY layer, connected via ‘C–O–metal’ structures. The enhanced CO2 uptake ability at 298 K (3.86 cm3 g−1) and a specific surface area of 13.7 m2 g−1 indicate the presence of numerous active sites. The combination of mesoporous character and highly mixed valence state of the material leads to performance enhancement and ultimately to a FE for urea of 64%. Advanced operando SR-FTIR measurements at different potentials revealed the presence *NH2. Additionally, the intermediate *CO2NH2 was faintly visible (1200 cm−1), suggesting that *NH2 couples with *CO2 or *COOH to create the first C–N bond (1419 cm−1).Using nitric oxide as N-source occurs less frequently, but Zhang and coworkers (Table 2, entry 24) note that employing NO results in a less complex reaction mechanism (cf. 16e− reduction when using NO3−).200 Additionally, NO (or *NO) is often postulated as an important intermediate, thus it is reasonable to expect urea formation when working with a NO-feed. Out of 10 commercial bulk metals, Zn foil was found to be the best cathode material in terms of urea yield rate when operating at a potential of −0.92 V, with Cu and Fe foil also exhibiting relatively good activity. They argue that the high activity of Zn is due to the inhibition of dimerization side reactions. In order to enhance the catalytic performance, they switched to Zn nanobelts, which results in a relatively low FE of 11.3% but at a fairly high current density of 40 mA cm−2. The combination of DEMS, ATR-FTIR (Fig. 19A and B) and DFT calculations reveal that *NO is reduced to *NH2 (or further towards NH3) via the *NHO, *NHOH and *NH2OH intermediates (cf.Fig. 12A). The successful control experiment with NH2OH as the N-feed confirmed this claim.
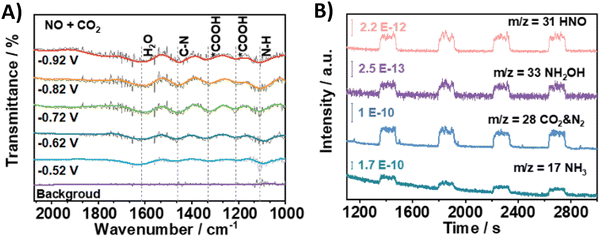 | ||
| Fig. 19 Mechanistic investigations involving the formation of *H2NCO using the Zn NBs catalyst. (A) In situ ATR-FTIR spectra at different potentials with NO + CO2 as the feed gas. (B) Online DEMS measurements. Adapted from ref. 200. | ||
3.3 Urea production starting from dinitrogen
Using N2 as the nitrogen source for urea production poses obvious challenges due to the enormous dissociation energy of the nitrogen triple bond (941 kJ mol−1) and poor solubility in water (0.02 v/v, 298 K, 1 atm).187–189 However, the reaction towards urea requires only 6 electrons, compared to 16 when using nitrate, suggesting less complexity in the total reaction pathway. It is imperative that the inert N2 (and CO2) are sufficiently adsorbed on the catalytic surface in order to start the reduction process. The reported protocols (Table 2, entries 25–33) attempt to enhance the chemisorption of both gases (CO2 and N2) on the catalyst.201–209 Temperature-dependent desorption (TPD) measurements (amount of N2) and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller adsorption–desorption isotherms (specific surface area) are very useful tools in identifying suitable catalyst candidates. In terms of mechanism, almost all protocols report the formation of the intermediate *NCON after reaction between *N2 and *CO. Subsequent hydrogenation steps lead to urea (cf.Fig. 12B). Generally, formation of *NCON is more favorable than reduction of *N2 to an intermediate like *NNH before the C–N coupling. Again, various spectroscopic techniques, supported by DFT calculations, on the different catalyst systems are required to confirm this. Some extensive and purely theoretical reports modeling various catalytic systems for urea formation are also available and can be found elsewhere.210–217Understanding how the inert N2 gets adsorbed and activated is paramount for rational design of an efficient catalyst. In general, a donor–acceptor process is operational, where the occupied σ orbitals of N2 donate electrons to the catalyst, which in turn donates electrons to the empty π* orbitals of N2, reducing the N–N bond order. One often employed catalyst material is Bi, due to its known CO2218 and N2219 reduction capabilities and its relative inertness towards protons. Guo and coworkers modified BiOx clusters with Sb, leading to formation of Bi(II) with unsaturated coordination rather than Bi(0) under reductive conditions, as revealed by XAS measurements.203 They noticed using calculations and Raman spectroscopy that CO2 binds with its C-atom to the catalyst surface rather than via O-mediated adsorption due to the introduction of Sb (Fig. 20A). In the Raman spectra of pure BiOx clusters with applied reduction potentials, an extra peak at 537 cm−1 appeared, corresponding to the out-of-plane swaying vibration of *OCO− (O-bonded). This is an intermediate ultimately leading to HCOOH formation. Using their SbxBi1−xOy clusters, this peak is not observed. However, two other signals at 1046 cm−1 and 2041 cm−1 emerged, indicating the stretching vibration of *COO− (C-bonded) and *CO.
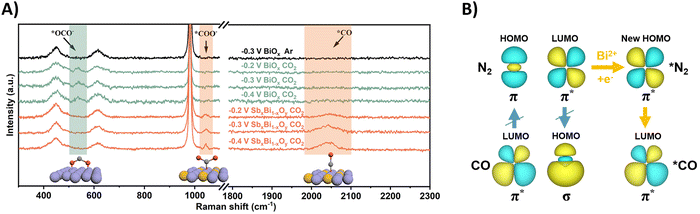 | ||
| Fig. 20 Mechanistic investigations regarding CO2 and N2 activation using the SbxBi1−xOy catalyst. (A) In situ Raman spectra at different potentials. (B) The C–N coupling mechanism regulated by the symmetry matching between the HOMO of *N2 and the LUMO of *CO. Adapted from ref. 203. | ||
Effective urea formation requires C–N coupling of *CO with *N2, which is acknowledged to be a rate limiting step due to the inertness of N2. The authors argue that the mismatch of the symmetry between the molecular orbitals of *CO and *N2 is responsible for this arduous, yet essential C–N bond formation step. The HOMO of *N2 does not match the LUMO of *CO, inhibiting electron injection. Calculations show that Bi(II) can inject electrons into the LUMO of *N2, leading to a modified HOMO now matching the symmetry of the LUMO of *CO and C–N bond formation becomes more feasible towards the *NCON intermediate (Fig. 20B). Thus, Bi(II) effectively decreases the free-energy change of the C–N coupling reaction. DFT calculations and experimental evidence for *NCON and further reduced intermediates were not pursued.
Other Bi-containing materials are reported by Zhang and coworkers, exploiting local charge redistributions of the heterointerfaces that create local electrophilic and nucleophilic regions, responsible for the enhanced targeted adsorption of N2 and CO2, respectively.204,206 Notably, the reduction of *CO2 to *CO is facilitated when *N2 is adsorbed in close proximity due to a lower calculated ΔG. The same research group also exploited the concept of frustrated Lewis pairs to act synergistically towards the targeted capture of N2 and CO2 (Fig. 21A). The InOOH208 and Ni3(BO3)2-150207 catalysts under study comprise coordinatively unsaturated metal sites and neighboring surface hydroxyl groups, creating the Lewis acid and base sites, respectively. For instance, N2 donates electrons via σ orbitals to the empty d orbitals of the Lewis acid metal site, while the lone pair electrons in the filled p orbital of the Lewis base hydroxyl site donates electrons to the π* orbitals of N2. This results in polarization of the N2 molecule with elongation of the chemical bond.
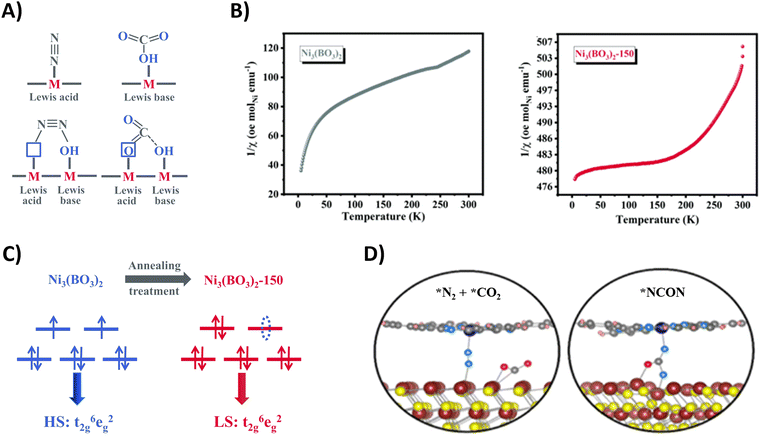 | ||
| Fig. 21 Mechanistic investigations regarding CO2 and N2 activation using the Ni3(BO3)2-150 (A)–(C) and CoPc–MoS2 catalyst (D). (A) Schematic illustration of adsorption of CO2 and N2 on frustrated Lewis pairs. (B) Temperature-dependent inverse susceptibility 1/χ plots for pristine Ni3(BO3)2 and Ni3(BO3)2-150 catalyst. (C) Schematic illustration of the spin-state regulation of Ni3(BO3)2 after annealing treatment. (D) Schematic illustration of N2 and CO2 activation (left) and *NCON formation (right) on the CoPc–MoS2 catalyst. Adapted from ref. 207 (A)–(C) and 205 (D), respectively. | ||
Additionally, these frustrated Lewis pairs aid in the C–N bond formation step towards the crucial *NCON intermediate, as indicated by theoretical calculations. For the Ni3(BO3)2-150 catalyst (150 indicates an annealing temperature of 150 °C), this reaction step is studied in more detail (Fig. 21B).207 The emergence of a newly empty eg orbital after annealing that participates in a so-called σ-orbital carbonylation to couple *N2 with *CO towards *NCON was revealed. More specifically, *N2 is now able to donate σ orbital electrons in this empty eg orbital of Ni, after which *CO is capable of injecting its σ orbital electrons into *N2 (Fig. 21C). Without this annealing treatment, the fully occupied eg orbitals of Ni would cause strong electrostatic repulsion between the occupied σ orbital electrons of both *CO and *N2 if they wanted to react, thus preventing their coupling to *NCON. The presence of *NCON was also verified by SR-FTIR where the Ni3(BO3)2-150 catalyst showed a significant characteristic signal at 1449 cm−1 that was absent in the pristine Ni3(BO3)2 material under identical potential conditions. Overall, the combination of frustrated Lewis pairs with low-spin Ni2+ sites results in one of the highest FE and urea yield rates using CO2 and N2 so far reported (Table 2).
Ghorai and coworkers exploited the donor–acceptor mechanism using the dual metal sites in their CoPc–MoS2 catalyst (Pc = phthalocyanine), where the CoPc is embedded on MoS2 nanosheets.205 Both Mo and Co use their empty d orbitals to pull at a lone pair at the end of N2 while filled d orbitals feed electrons back to N2 antibonding orbitals, effectively elongating the N–N bond from 1.130 Å to 1.196 Å. The N2 can be envisioned to be positioned in between the CoPc and MoS2 nanosheets, anchored to both metal centers, inducing spatial distribution of the charge and effectively polarizing and activating N2 (Fig. 21D). Thermodynamically spontaneous reaction with formed *CO again results in *NCON.
Chen and coworkers also utilized Mo, this time in combination with P (Table 2, entry 33).209 Due to the slightly larger electronegativity of P (2.1 vs. 1.8 for Mo), a small electron transfer from Mo to P creates moderate coupling between Mo-4d and P-3p orbitals. Theoretical calculations also indicated that the 4dz2 orbital of Mo is empty, while the other 4d orbitals are occupied. These filled and empty orbitals can enable the abovementioned donor–acceptor mechanism, where the empty d orbitals accept electrons from both CO2 and N2 while the filled d orbitals donate electrons to the anti-bonding orbitals of CO2 and N2. Again, this results in enhanced adsorption and activation. The N–N bond is elongated to 1.20 Å while the O–C–O bond angle is significantly bent at about 47°. Theoretical calculations suggest that *NNH is preferentially formed over the coupling of *N2 with *CO and that the coupling takes place between *HNNH and *CO. However, when reduction of *N2 is necessary before C–N bond formation, it might also be insightful to investigate the occurrence and origin of byproducts like NH3 and hydrazine. Chen and coworkers report that the computed limiting potential for ammonia synthesis is −0.86 V, which is more negative that the value of −0.27 V for urea, suggesting good selectivity for urea synthesis with an experimental FE of 37%. In situ spectroscopic investigations would be useful to strengthen the claim for this rather unusual reaction mechanism.
4. Dimethyl carbonate
Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) is a carbonate ester of methanol with various applications. Its high polarity enables the dissolution of high concentrations of lithium ions, making it an ideal solvent for lithium batteries which are widely used in household portable devices and even transportation.220 Due to the high oxygen content and low vapor pressure it is used as a fuel additive in order to minimize the production of soot, while it can also aid in the reduction of CO, SOx and NOx emissions due to its significant blending octane number.221 Additionally, DMC is considered environmentally friendly and can be labelled as a green solvent; it can be used as an alternative in industrial paint applications.222 Finally, the greenness of DMC makes it an attractive organic building block. For instance, it is a sustainable substitute for methyl iodide and dimethyl sulfate in methylation reactions of various compounds like phenols, anilines, thiols, amides and heterocyclic compounds. Additionally, DMC can be used in carboxymethylation reactions, replacing hazardous phosgene.223 One of the most important applications of this reaction is the carboxymethylation of phenol, which is used in the production of polycarbonate via a diphenyl carbonate intermediate.220,223Besides the oxidative carbonylation of methanol with a copper catalyst and the phosgenation of methanol, the majority of the DMC worldwide is produced by the transesterification of ethylene or propylene carbonate, using tetravalent Lewis acidic catalysts such as ZrCl4 or Ti(acac)2.224,225 The cyclic ethylene or propylene carbonate themselves are obtained from the reaction between the corresponding epoxide with CO2.225,226 These synthetic pathways have some disadvantages, due to the use of toxic chemicals (e.g. phosgene or CO), costly processing, high temperature and pressure, and the use of explosive compounds (e.g. ethylene oxide).226 A promising and sustainable alternative is to capture a reactive intermediate of the eCO2RR with methanol.
A lot of research concerning the direct electrochemical conversion of CO2 and methanol to DMC employs imidazolium-based ionic liquids with a BF4− anion.227,228 These ILs are preferred due to their remarkable capacity to dissolve CO2, which surpasses that of conventional solvents, creating CO2˙− as the reactive species at the cathode. The main drawback of these systems with costly ionic liquids is that methyl iodide, a highly toxic and carcinogenic compound, is needed as methylating agent for the CH3OCO2− intermediate. An alternative method starts by reducing CO2 to CO in situ, followed by the carbonylation of methanol. This is a redox-neutral process, as the oxidation number of the central carbon atom remains the same before and after the reaction, since CO2(+IV) is first reduced to CO(+II) and afterwards oxidized to DMC(+IV), making it necessary to couple both half-reactions in the electrolytic cell. Additionally, using more common solvents would be advantageous from a practical point of view. Recent reports are summarized in Table 3.
| No. | Catalysts | Electrodes (+)/(−) | Solvent | Electrolyte | E (vs. RHE) | FE (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA = single atom. RHE = reversible hydrogen electrode. FE = faradaic efficiency. | |||||||
| 1 | — | Pt/Cu | MeCN | 0.1 M Et4NBF4 | −1.4 V | — | 229 |
| 2 | Pd/C and Br− | GC/Au | MeOH | 0.1 M NaBr | −1.1 V | 60 | 230 |
| 3 | Pd/C and Br− | CC/Ni SAs-OMMNC@CC | MeOH | 0.1 M KBr | −0.6 V | 80 | 231 |
Figueiredo and coworkers confirmed with in situ FTIR that CO was the responsible species in the electrocarbonylation reaction with methanol instead of CO2˙− in an MeCN solvent.229 DMC could not be directly identified and the main observed product was an alkyl ammonium methyl carbonate. However, it was noticed that DMC decomposes under these strongly reducing conditions (−1.4 V) to the same alkyl ammonium methyl carbonate. They hypothesize that it is indeed possible to synthesize DMC from methanol and CO2 electrochemically, but it is not stable under the studied conditions.
Nam and coworkers developed a mediated pathway using MeOH as both reactant and solvent (Table 3, entry 2).230 Pd- and Cu-based catalysts are known for DMC synthesis. Therefore, Pd/C, PdBr2, Cu/C and CuBr2 were screened and Pd/C showed the best performance with a total FE of 60%. The proposed mechanism starts with simultaneous activation of CO2 and methanol to CO and methoxide (Fig. 22A). Next, CO and 2 methoxide ions bind to the Pd catalyst and through a catalytic cycle, DMC is formed (Fig. 22B). This reduces the Pd(II) to Pd(0). The employed halide mediator allows for electrochemical re-oxidation of the metal catalyst. All three halides proved effective, with Br− exhibiting the highest FE of 57%, in comparison to Cl− (51%) and I − (33%). This is because I2 has a relatively low oxidizing power compared to Cl2 and Br2, and Br2 has a higher solubility in methanol compared to Cl2. Direct oxidation of the metal catalyst was also tested by the addition of redox inactive electrolytes (e.g. NaClO4), but this resulted in a very low FE (8%). The high activity for halide oxidation on the GC cathode suppresses side reactions such as metal dissolution and the formation of dimethoxymethane through methanol oxidation. Ag and Au were tested as cathode materials due to their known CO selectivity in CO2 electroreduction. Cyclic voltammetry was used to determine the onset potential for CO formation which was −1.1 V vs. Ag/Ag+. Also, the optimal current density for CO production was determined to be 12 mA cm−2, which is the same optimal value for the production of DMC, indicating that the production of CO is the determining factor for DMC synthesis. Extrapolating this reaction protocol to diethyl carbonate using ethanol resulted in a moderate yield of 18%.
 | ||
| Fig. 22 Mechanism for the Pd-catalyzed carbonylation of methanol with in situ electrogenerated CO from CO2. (A) General mechanism. (B) Detailed Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle. A = anode, C = cathode. Adapted from ref. 230. | ||
Zhu and coworkers were able to further improve the system. They introduced single atom catalysts (SAC) dispersed on carbon supports as a cathode.231 These individual metal atoms function as active sites due to their distinctive electronic structures and coordination environments, features that have been extensively proven to result in high activity and selectivity for eCO2RR. Different variations of the catalyst were screened (Ni-free, N-free, varying pore content) and the catalyst denoted as Ni SAs/OMMNC was found to give the highest FE.231 This is a pentacoordinated Ni SAC with an asymmetric charge distribution, believed to enhance the activation of the reactants. This catalyst had a FE of 99% for CO and a FE of 80% for DMC. Also, an overpotential of only −0.6 V was needed, which is substantially less in comparison to previous work and can aid in preventing DMC decomposition.229
5. Conclusions and outlook
Electrochemical CO2 reduction offers a sustainable tool to produce numerous crucial products under mild and safe conditions. In this review, we highlight the electrochemical valorization of CO2 towards value-added chemicals like carboxylic acids, urea and dimethyl carbonate with focus on sustainability and mechanistic insight. Carboxylic acids have been prepared starting from a wide variety of organic chemicals. Important aspects for the future that are increasingly being addressed are sacrificial-anode free processes, more benign solvents and regio- and chemoselective C(sp3)–H carboxylations, other than allylic and benzylic. Also, the electrochemical asymmetric insertion of CO2 is an important upcoming field. Mechanistic investigations revealed the importance of water for the reaction outcome. Additionally, a suitable cathode is of utmost importance to activate either CO2 or the substrate without causing run-off reactions. Ag seems a promising candidate for this type of reactions. Together with the potential dependent studies described in Section 2.2, in depth mechanistic investigations with modern techniques such as DEMS and time-resolved electron paramagnetic resonance might elucidate paramount information and ultimately lead to fastened discoveries and improvements towards new catalytic systems with enhanced FEs.Besides the need for developing appropriate operating techniques for large-scale applications, the scope of starting materials should be expanded to abundant industrial chemicals to facilitate the incorporation of eCO2RR in industry. Especially the transformation of unbiased aliphatic alkenes is underdeveloped. Additionally, maintaining the olefinic character during carboxylation of these unactivated alkenes would create much more valuable building blocks. For instance, synthesis of acrylic acid from ethylene and methacrylic acid from propylene are very interesting and relevant syntheses to be investigated.110,232
Electrochemical synthesis of urea from CO2 and abundant N-sources (NO3−, NO2−, NO and N2) offers huge sustainable benefits over its current industrial counterpart. Being an ongoing challenge, the reported research is greatly focused at elucidating and characterizing a stable and efficient electrocatalyst deposited on the cathode while also deeply investigating the mechanistic reduction pathways in order to determine the key intermediates and their correlation with the catalyst. Several analysis techniques are useful tools to identify the active coupling species. Control experiments with different N-containing feeds combined with isotope-labeled characterization techniques and TPD measurements can give initial leads regarding the intermediates. Advanced spectroscopic measurements such as in situ Raman and ATR-FTIR/SR-FTIR spectroscopy measured at different potentials or as a function of time can give valuable mechanistic insights due to the increase and decrease of certain signals, hinting towards certain active species. Online DEMS measurements, where one hunts for certain m/z values of possible intermediates, can give additional information. Our mechanistic roadmap (Fig. 12) can quickly visualize the link between the observed intermediates and can guide DFT calculations to support the experimental findings. Combined, these experimental and theoretical results lead to an in depth understanding of the formation and stability of intermediates that are pivotal in the rational design of an appropriate catalyst. Experimental evidence for the second C–N bond formation step is scarce and highly challenging but might give valuable insights in the total urea synthesis pathway.
There is always some trade-off between FE and current density leading to the highest urea production rate, when often a more negative potential results in an increased urea yield rate, but lower FE. This highlights the main obstacle, namely highly competitive side reactions and HER, which need to be suppressed. Generally, it seems from Table 2 that an early C–N bond formation step, e.g. coupling of *CO2 or *CO with *NO2, results in higher FEs for urea up to 75%, although higher FEs are still required for commercialization. On the other hand, achieving a high urea production rate with unavoidable but selective formation of useful byproducts like NH3, and thus a relatively low FE for urea, might also be interesting for applications. Investigating and controlling the microenvironment (electrolyte, local pH, electrical double layer, electric field distribution, …) is often overlooked, but is an important aspect regarding diffusion, adsorption, selectivity and activity of the catalyst next to the intrinsic properties of the active sites.233
Cu appears to be a highly promising catalyst leading to the highest FEs when using nitrate or nitrite, while other metals such as Mo, Co and In are also encouraging, even when working with N2 (Table 2). Since two different species, i.e. CO2 and “N”, need to be activated, a dual-site catalyst is often employed to exploit its synergistic effect,233 as extensively outlined in Section 3. An additional advantage of incorporating a second material can be in preventing byproduct formation, since for instance neighbouring Cu-sites are more likely to form C–C coupled byproducts.188 In addition, introducing nanostructures, surface vacancies and maximizing the number of active sites enhance the specific surface area and the catalytic performance. Moreover, innovative conductive supports like CBC191 and graphdiyne198 seem to have a positive influence on urea synthesis due to enhanced interactions. It is noteworthy that relatively cheap and expensive metal-free catalysts generate decent FEs and urea production rates. A cheap, simple, robust and easily mass-produced catalyst is essential for large-scale applications and will be an important aspect in regulating the current mismatch of the economics between the industrial urea synthesis and the electrochemical route.167 The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the materials genome initiative can accelerate the material discovery and prediction of target materials.234,235
The few reports that electrochemically generate DMC from CO2 and methanol are already capable of achieving high FEs up to 80% with some advanced catalysts.230,231 However, further research can be performed to increase the FE of the system even more. Alternatives for the halide-assisted metal reoxidation can be investigated, even towards direct metal reoxidation at the anode.236–238 Furthermore, a lot of electrochemical protocols for DMC synthesis starting from CO as carbon source have been published.228 Additionally, the electrochemical transformation of CO2 to CO is also well established, with electrocatalysts analogously deposited on the cathode. Combining the literature regarding these two synthetic strategies can open new possibilities towards DMC starting from CO2. This has the potential to reduce the usage of the toxic CO while simultaneously increasing the utilization of CO2.
In summary, this review demonstrates the versatility and potential of electrochemical processes in transforming CO2 into valuable compounds, contributing to both environmental remediation and the development of economically viable chemical pathways. Through the sustainable valorization of CO2, electrochemistry offers a promising avenue for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a circular carbon economy. It is essential to address challenges such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, practicality, sustainability and the identification of optimal catalysts for specific reactions. As research in this field progresses, technological innovation and interdisciplinary collaborative efforts are imperative to unlock the full potential of electrochemical CO2 valorization in shaping the future of sustainable chemical manufacturing.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.References
- Climate Action, https://climate.ec.europa.eu/index_en, (accessed 9 October 2023).
- CO2 Emissions in 2022 – Analysis, https://www.iea.org/reports/co2-emissions-in-2022, (accessed 7 October 2023).
- The Paris Agreement | UNFCCC, https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement, (accessed 9 October 2023).
- L. Yao, S. Tan and Z. Xu, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2022, 30, 20570–20589 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Twidell, Renewable energy resources, Routledge, New York, 4th edn, 2021 Search PubMed.
- J. Gu, H. Kim and H. Lim, Energy Convers. Manage, 2022, 270, 116256 CrossRef CAS.
- M. He, Y. Sun and B. Han, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202112835 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. B. Zimmerman, P. T. Anastas, H. C. Erythropel and W. Leitner, Science, 2020, 367, 397–400 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Sartal, R. Bellas, A. M. Mejías and A. García-Collado, Adv. Mech. Eng., 2020, 12, 168781402092523 CrossRef.
- P. Miklautsch and M. Woschank, J. Cleaner. Prod., 2022, 366, 132883 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Letnik, M. Marksel, G. Luppino, A. Bardi and S. Božičnik, Energy, 2018, 163, 245–257 CrossRef.
- N. V. Martyushev, B. V. Malozyomov, I. H. Khalikov, V. A. Kukartsev, V. V. Kukartsev, V. S. Tynchenko, Y. A. Tynchenko and M. Qi, Energies, 2023, 16, 729 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Brenna, V. Bucci, M. C. Falvo, F. Foiadelli, A. Ruvio, G. Sulligoi and A. Vicenzutti, Energies, 2020, 13, 2378 CrossRef.
- A. Talaei, M. Ahiduzzaman and A. Kumar, Energy, 2018, 153, 231–247 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Johansson, N. Mardan, E. Cornelis, O. Kimura and P. Thollander, Energies, 2019, 12, 1338 CrossRef.
- G. Nota, F. D. Nota, D. Peluso and A. Toro Lazo, Sustainability, 2020, 12, 6631 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Matsunaga, V. Zytkowski, P. Valle and F. Deschamps, J. Energy Resour. Technol., 2022, 144, 102104 CrossRef.
- O. Gutiérrez-Sánchez, B. Bohlen, N. Daems, M. Bulut, D. Pant and T. Breugelmans, ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9, e202101540 CrossRef.
- S. Budinis, S. Krevor, N. M. Dowell, N. Brandon and A. Hawkes, Energy Strategy Rev., 2018, 22, 61–81 CrossRef.
- M. Van Der Spek, S. Roussanaly and E. S. Rubin, Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control, 2019, 83, 91–104 CrossRef.
- M. Bui, C. S. Adjiman, A. Bardow, E. J. Anthony, A. Boston, S. Brown, P. S. Fennell, S. Fuss, A. Galindo, L. A. Hackett, J. P. Hallett, H. J. Herzog, G. Jackson, J. Kemper, S. Krevor, G. C. Maitland, M. Matuszewski, I. S. Metcalfe, C. Petit, G. Puxty, J. Reimer, D. M. Reiner, E. S. Rubin, S. A. Scott, N. Shah, B. Smit, J. P. M. Trusler, P. Webley, J. Wilcox and N. Mac Dowell, Energy Environ. Sci., 2018, 11, 1062–1176 RSC.
- N. Bahman, M. Al-Khalifa, S. Al Baharna, Z. Abdulmohsen and E. Khan, Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol., 2023, 22, 451–470 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Rosa, D. L. Sanchez, G. Realmonte, D. Baldocchi and P. D’Odorico, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2021, 138, 110511 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Chung, J. Kim, B. K. Sovacool, S. Griffiths, M. Bazilian and M. Yang, Energy Res. Soc. Sci., 2023, 96, 102955 CrossRef.
- D. S. Mallapragada, Y. Dvorkin, M. A. Modestino, D. V. Esposito, W. A. Smith, B.-M. Hodge, M. P. Harold, V. M. Donnelly, A. Nuz, C. Bloomquist, K. Baker, L. C. Grabow, Y. Yan, N. N. Rajput, R. L. Hartman, E. J. Biddinger, E. S. Aydil and A. D. Taylor, Joule, 2023, 7, 23–41 CrossRef CAS.
- M. H. Barecka and J. W. Ager, Energy Adv., 2023, 2, 268–279 RSC.
- M. Y. Khalid, Z. U. Arif, W. Ahmed and H. Arshad, Sustainable Mater. Technol., 2022, 31, e00382 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Keßler, S. A. Matlin and K. Kümmerer, Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem., 2021, 32, 100535 CrossRef.
- S. Kheirabadi and A. Sheikhi, Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem., 2022, 38, 100695 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T.-D. Bui, J.-W. Tseng, M.-L. Tseng and M. K. Lim, Resour., Conserv. Recycl., 2022, 177, 105968 CrossRef.
- A. E. Krauklis, C. W. Karl, A. I. Gagani and J. K. Jørgensen, J. Compos. Sci., 2021, 5, 28 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Das, CO2 as a building block in organic synthesis, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2020 Search PubMed.
- A. D. N. Kamkeng, M. Wang, J. Hu, W. Du and F. Qian, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 409, 128138 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Vanhoof, R. Dirix and D. E. De Vos, Green Chem., 2023, 25, 978–985 RSC.
- V. Lemmens, T. Vanbergen, G. O’Rourke, C. Marquez and D. E. De Vos, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2023, 6, 9153–9158 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Matthessen, J. Fransaer, K. Binnemans and D. E. D. Vos, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 4634 RSC.
- Carbon Dioxide Utilization to Sustainable Energy and Fuels, ed. Inamuddin, R. Boddula, M. I. Ahamed and A. Khan, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2022 Search PubMed.
- C. G. Okoye-Chine, K. Otun, N. Shiba, C. Rashama, S. N. Ugwu, H. Onyeaka and C. T. Okeke, J. CO2 Util., 2022, 62, 102099 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Li, L. Mo and C. Unluer, J. CO2 Util., 2022, 65, 102237 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Lippiatt, T.-C. Ling and S.-Y. Pan, J. Build. Eng., 2020, 28, 101062 CrossRef.
- L. Li, Q. Liu, T. Huang and W. Peng, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2022, 298, 121512 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zajac, J. Skocek, M. Ben Haha and J. Deja, Energies, 2022, 15, 3597 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Hanifa, R. Agarwal, U. Sharma, P. C. Thapliyal and L. P. Singh, J. CO2 Util., 2023, 67, 102292 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Qian, X. Yu, T. Zheng and Y. Chen, J. CO2 Util., 2022, 55, 101849 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Nisar, S. Khan, M. Hameed, A. Nisar, H. Ahmad and S. A. Mehmood, Microbiol. Res., 2021, 251, 126813 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Gupta, A. Mishra, Y. Thirupathaiah and A. K. Chandel, Biomass Convers. Biorefinery, 2024, 14, 3007–3030 CrossRef CAS.
- K. R. Choi, Y.-J. Ahn and S. Y. Lee, J. CO2 Util., 2022, 58, 101929 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Salehizadeh, N. Yan and R. Farnood, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 390, 124584 CrossRef CAS.
- S. C. Shit, I. Shown, R. Paul, K.-H. Chen, J. Mondal and L.-C. Chen, Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 23301–23332 RSC.
- R. Cauwenbergh and S. Das, Green Chem., 2021, 23, 2553–2574 RSC.
- G. H. Han, J. Bang, G. Park, S. Choe, Y. J. Jang, H. W. Jang, S. Y. Kim and S. H. Ahn, Small, 2023, 19, 2205765 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Khalil, J. Gunlazuardi, T. A. Ivandini and A. Umar, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2019, 113, 109246 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Senocrate and C. Battaglia, J. Energy Storage, 2021, 36, 102373 CrossRef.
- J. Zhang, W. Cai, F. X. Hu, H. Yang and B. Liu, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 6800–6819 RSC.
- in Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide: Fundamentals and Technologies, ed. J. Qiao, Y. Liu and J. Zhang, CRC Press, 2016 Search PubMed.
- S. Overa, B. H. Ko, Y. Zhao and F. Jiao, Acc. Chem. Res., 2022, 55, 638–648 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. C. Poon, W. Y. Wan, H. Su and H. Sato, RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 22703–22721 RSC.
- S. Jin, Z. Hao, K. Zhang, Z. Yan and J. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 20627–20648 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Liang, L. Huang, Y. Gao, Q. Wang and B. Liu, Adv. Sci., 2021, 8, 2102886 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. U. Nielsen, X.-M. Hu, K. Daasbjerg and T. Skrydstrup, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 244–254 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Duarah, D. Haldar, V. Yadav and M. K. Purkait, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9, 106394 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Ewis, M. Arsalan, M. Khaled, D. Pant, M. M. Ba-Abbad, A. Amhamed and M. H. El-Naas, Sep. Purif. Technol., 2023, 316, 123811 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Fan, C. Xia, P. Zhu, Y. Lu and H. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 3633 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. A. Al-Tamreh, M. H. Ibrahim, M. H. El-Naas, J. Vaes, D. Pant, A. Benamor and A. Amhamed, ChemElectroChem, 2021, 8, 3207–3220 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, F. Li, X. Zhang and X. Ji, Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem., 2020, 23, 10–17 CrossRef.
- E. Boutin and M. Robert, Trends Chem., 2021, 3, 359–372 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wiranarongkorn, K. Eamsiri, Y.-S. Chen and A. Arpornwichanop, J. CO2 Util., 2023, 71, 102477 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Roy, H. S. Jadhav, S. J. Park and J. G. Seo, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 887, 161449 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Hussain, H. Alasiri, W. Ullah Khan and K. Alhooshani, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2023, 482, 215081 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Umeda, Y. Niitsuma, T. Horikawa, S. Matsuda and M. Osawa, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 1119–1127 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Cai, Q. Zhao, W.-Y. Hsu, C. Choi, Y. Liu, J. M. P. Martirez, C. Chen, J. Huang, E. A. Carter and Y. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 9136–9143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Cai, J. Fu, Y. Zhou, Y.-C. Chang, Q. Min, J.-J. Zhu, Y. Lin and W. Zhu, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 586 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Ajmal, G. Yasin, A. Kumar, M. Tabish, S. Ibraheem, K. A. Sammed, M. A. Mushtaq, A. Saad, Z. Mo and W. Zhao, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2023, 485, 215099 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Chen, Y. Zhao, J. Han and Y. Bu, ChemPlusChem, 2023, 88, e202200370 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. R. Pappijn, M. Ruitenbeek, M.-F. Reyniers and K. M. Van Geem, Front. Energy Res., 2020, 8, 557466 Search PubMed.
- H. H. Khoo, I. Halim and A. D. Handoko, J. CO2 Util., 2020, 41, 101229 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Du, P. Zhang and H. Liu, Chem. – Asian J., 2021, 16, 588–603 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, L. Bian, H. Tian, Y. Liu, Y. Bando, Y. Yamauchi and Z. Wang, Small, 2022, 18, 2107450 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Dongare, N. Singh, H. Bhunia, P. K. Bajpai and A. K. Das, ChemistrySelect, 2021, 6, 11603–11629 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Wang, T. Kou, S. E. Baker, E. B. Duoss and Y. Li, Adv. Energy Sustainable Res., 2022, 3, 2100131 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Zhang, C. Guo, S. Fang, X. Zhao, L. Li, H. Jiang, Z. Liu, Z. Fan, W. Xu, J. Xiao and M. Zhong, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 1298 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Ye, X. Guo and T. Ma, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 414, 128825 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Zhao and X. Quan, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 2076–2097 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Xue, Y. Guo, H. Cui and Z. Zhou, Small Methods, 2021, 5, 2100736 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Xiao and J. Zhang, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 7975–8000 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z.-Z. Niu, L.-P. Chi, Z.-Z. Wu, P.-P. Yang, M.-H. Fan and M.-R. Gao, Natl. Sci. Open, 2023, 2, 20220044 CrossRef.
- P.-P. Yang, X.-L. Zhang, P. Liu, D. J. Kelly, Z.-Z. Niu, Y. Kong, L. Shi, Y.-R. Zheng, M.-H. Fan, H.-J. Wang and M.-R. Gao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 8714 CAS.
- W. Zhong, W. Huang, S. Ruan, Q. Zhang, Y. Wang and S. Xie, Chem. – Eur. J., 2023, 29, e202203228 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. V. Medvedeva, J. J. Medvedev and A. Klinkova, Adv. Energy Sustainable Res., 2021, 2, 2100001 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Song, S. Jia, L. Xu, J. Feng, L. He, X. Sun and B. Han, Mater. Today Sustain., 2022, 19, 100179 CrossRef.
- D. Xu, K. Li, B. Jia, W. Sun, W. Zhang, X. Liu and T. Ma, Carbon Energy, 2023, 5, e230 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Somoza-Tornos, O. J. Guerra, A. M. Crow, W. A. Smith and B.-M. Hodge, iScience, 2021, 24, 102813 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Park, D. T. Wijaya, J. Na and C. W. Lee, Catalysts, 2021, 11, 253 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yang and F. Li, Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem., 2021, 27, 100419 CrossRef CAS.
- S. C. Perry, Electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction, Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin, Boston, 2021 Search PubMed.
- J. Kubitschke, H. Lange and H. Strutz, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2014, pp. 1–18 Search PubMed.
- F. Röhrscheid, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Wiley, 1st edn, 2000 Search PubMed.
- E. Ritzer and R. Sundermann, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Wiley, 1st edn, 2000 Search PubMed.
- R. and M. ltd, Salicylic Acid Market by Application, https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5561173/salicylic-acid-market-by-application-global, (accessed 18 October 2023).
- S. Saini, P. K. Prajapati and S. L. Jain, Catal. Rev., 2022, 64, 631–677 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Song, Y. Zhang, Z. Chen and X. Wu, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2022, 11, e202200237 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zhang and E.-Q. Gao, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2023, 486, 215138 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Cauwenbergh, V. Goyal, R. Maiti, K. Natte and S. Das, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51, 9371–9423 RSC.
- S. Nandi and R. Jana, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2022, 11, e202200356 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-H. Ye, T. Ju, H. Huang, L.-L. Liao and D.-G. Yu, Acc. Chem. Res., 2021, 54, 2518–2531 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, J.-H. Ye, T. Ju, L.-L. Liao, H. Huang, Y.-Y. Gui, W.-J. Zhou and D.-G. Yu, ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 10871–10885 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Fan, Z. Zhang and C. Xi, ChemSusChem, 2020, 13, 6201–6218 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Huang, J. Lin, F. Deng and H. Zhong, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2022, 11, e202200220 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Pradhan and S. Das, Synlett, 2023, 1327–1342 CAS.
- L. Faba, P. Rapado and S. Ordóñez, Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol., 2023, 13, 227–244 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Davies, J. R. Lyonnet, D. P. Zimin and R. Martin, Chem, 2021, 7, 2927–2942 CAS.
- J. Hong, M. Li, J. Zhang, B. Sun and F. Mo, ChemSusChem, 2019, 12, 6–39 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Seyferth, Organometallics, 2009, 28, 1598–1605 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Kobayashi and Y. Kondo, Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 2035–2037 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Zhang, X.-F. Liu, W.-Z. Zhang, W.-M. Ren and X.-B. Lu, Org. Lett., 2022, 24, 3565–3569 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Sheta, A. Alkayal, M. A. Mashaly, S. B. Said, S. S. Elmorsy, A. V. Malkov and B. R. Buckley, Angew. Chem., 2021, 133, 22003–22008 CrossRef.
- Y. Naito, Y. Nakamura, N. Shida, H. Senboku, K. Tanaka and M. Atobe, J. Org. Chem., 2021, 86, 15953–15960 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Zhao, Z. Lin, I. Maksso, J. Struwe and L. Ackermann, ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9, e202200989 CrossRef CAS.
- K.-J. Jiao, Z.-M. Li, X.-T. Xu, L.-P. Zhang, Y.-Q. Li, K. Zhang and T.-S. Mei, Org. Chem. Front., 2018, 5, 2244–2248 RSC.
- N. W. J. Ang, J. C. A. Oliveira and L. Ackermann, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 12842–12847 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z.-X. Yang, L. Lai, J. Chen, H. Yan, K.-Y. Ye and F.-E. Chen, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2023, 34, 107956 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Kim, G. D. Park, M. Balamurugan, J. Seo, B. K. Min and K. T. Nam, Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 1900137 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Zhang, L. Liao, L. Li, Y. Liu, L. Dai, G. Sun, C. Ran, J. Ye, Y. Lan and D. Yu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202301892 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. You, W. Kanna, H. Takano, H. Hayashi, S. Maeda and T. Mita, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 3685–3695 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Chakraborty, R. Mandal, N. Garg and B. Sundararaju, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 444, 214065 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Chang, Q. Zhang and C. Guo, Angew. Chem., 2020, 132, 12712–12722 CrossRef.
- K.-J. Jiao, Z.-H. Wang, C. Ma, H.-L. Liu, B. Cheng and T.-S. Mei, Chem. Catal., 2022, 2, 3019–3047 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Margarita and H. Lundberg, Catalysts, 2020, 10, 982 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zheng, Y. Tao, W. Ma and Q. Lu, Synthesis, 2023, 2896–2910 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Matthessen, J. Fransaer, K. Binnemans and D. E. De Vos, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2014, 10, 2484–2500 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Alkayal, V. Tabas, S. Montanaro, I. A. Wright, A. V. Malkov and B. R. Buckley, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 1780–1785 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Sheta, M. A. Mashaly, S. B. Said, S. S. Elmorsy, A. V. Malkov and B. R. Buckley, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 9109–9114 RSC.
- R. Matthessen, J. Fransaer, K. Binnemans and D. E. De Vos, ChemElectroChem, 2015, 2, 73–76 CrossRef CAS.
- V. K. Rawat, H. Hayashi, H. Katsuyama, S. R. Mangaonkar and T. Mita, Org. Lett., 2023, 25, 4231–4235 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yang, X. Sheng, L. Zhang, J. Yu and D. Huang, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2020, 9, 23–41 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Senboku, K. Sakai, A. Fukui, Y. Sato and Y. Yamauchi, ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6, 4158–4164 CrossRef CAS.
- D.-T. Yang, M. Zhu, Z. J. Schiffer, K. Williams, X. Song, X. Liu and K. Manthiram, ACS Catal., 2019, 9, 4699–4705 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Bazzi, E. Schulz and M. Mellah, Org. Lett., 2019, 21, 10033–10037 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Senboku, Y. Minemura, Y. Suzuki, H. Matsuno and M. Takakuwa, J. Org. Chem., 2021, 86, 16077–16083 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-S. Zhong, Z.-X. Yang, C.-L. Ding, Y.-F. Huang, Y. Zhao, H. Yan and K.-Y. Ye, J. Org. Chem., 2021, 86, 16162–16170 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. J. Medvedev, X. V. Medvedeva, F. Li, T. A. Zienchuk and A. Klinkova, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 19631–19639 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. Medvedev, X. V. Medvedeva, H. Engelhardt and A. Klinkova, Electrochim. Acta, 2021, 387, 138528 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Rawat, S. Dhakla, P. Lama and T. K. Pal, J. CO2 Util., 2022, 59, 101939 CrossRef CAS.
- X.-Q. Hu, Z.-K. Liu, Y.-X. Hou and Y. Gao, iScience, 2020, 23, 101266 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, Z. Zhao, D. Pan, S. Wang, K. Jia, D. Ma, G. Yang, X. Xue and Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem., 2022, 134, e202210201 CrossRef.
- Z. Zhao, Y. Liu, S. Wang, S. Tang, D. Ma, Z. Zhu, C. Guo and Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem., 2023, 135, e202214710 CrossRef.
- S. Bazzi, G. Le Duc, E. Schulz, C. Gosmini and M. Mellah, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 8546–8550 RSC.
- G.-Q. Sun, P. Yu, W. Zhang, W. Zhang, Y. Wang, L.-L. Liao, Z. Zhang, L. Li, Z. Lu, D.-G. Yu and S. Lin, Nature, 2023, 615, 67–72 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G.-Q. Sun, W. Zhang, L.-L. Liao, L. Li, Z.-H. Nie, J.-G. Wu, Z. Zhang and D.-G. Yu, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 7086 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhou, S. Mu, B.-H. Ren, R. Zhang and X.-B. Lu, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 991–994 RSC.
- N. Corbin, D.-T. Yang, N. Lazouski, K. Steinberg and K. Manthiram, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 12365–12376 RSC.
- N. Corbin, G. P. Junor, T. N. Ton, R. J. Baker and K. Manthiram, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145, 1740–1748 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Miltenberger, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Wiley, 1st edn, 2000 Search PubMed.
- M. A. Stalcup, C. K. Nilles, H.-J. Lee, B. Subramaniam, J. D. Blakemore and K. C. Leonard, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2021, 9, 10431–10436 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Seidler, A. Roth, L. Vieira and S. R. Waldvogel, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2023, 11, 390–398 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Muchez, D. E. De Vos and M. Kim, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 15860–15864 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, S. Tang, G. Yang, S. Wang, D. Ma and Y. Qiu, Angew. Chem., 2022, 134, e202207746 CrossRef.
- K. Zhang, B. Ren, X. Liu, L. Wang, M. Zhang, W. Ren, X. Lu and W. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2022, 61, e202207660 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L.-L. Liao, Z.-H. Wang, K.-G. Cao, G.-Q. Sun, W. Zhang, C.-K. Ran, Y. Li, L. Chen, G.-M. Cao and D.-G. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 2062–2068 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-F. Liu, K. Zhang, L.-L. Wang, H. Wang, J. Huang, X.-T. Zhang, X.-B. Lu and W.-Z. Zhang, J. Org. Chem., 2023, 88, 5212–5219 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-L. Xie, X.-T. Gao, H.-H. Wu, F. Zhou and J. Zhou, Org. Lett., 2020, 22, 8424–8429 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X.-T. Gao, Z. Zhang, X. Wang, J.-S. Tian, S.-L. Xie, F. Zhou and J. Zhou, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 10414–10420 RSC.
- The Institute of Export and International Trade, https://www.export.org.uk, (accessed 20 October 2023).
- Public Summary – Medium-Term Fertilizer Outlook 2023-2027, https://www.fertilizer.org/resource/public-summary-medium-term-fertilizer-outlook-2023-2027/, (accessed 20 October 2023).
- J. H. Meessen, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2010, p. a27_333.pub2 Search PubMed.
- M. Brouwer, Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, Kirk-Othmer, Wiley, 1st edn, 2019, pp. 1–19 Search PubMed.
- M. Jiang, M. Zhu, M. Wang, Y. He, X. Luo, C. Wu, L. Zhang and Z. Jin, ACS Nano, 2023, 17, 3209–3224 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Peng, L. Zeng, D. Wang, Z. Liu, Y. Li, Z. Li, B. Yang, L. Lei, L. Dai and Y. Hou, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2023, 52, 2193–2237 RSC.
- S. Liu, M. Wang, Q. Cheng, Y. He, J. Ni, J. Liu, C. Yan and T. Qian, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 17911–17930 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Tao, C. L. Rooney, Y. Liang and H. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 19630–19642 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Mei, Y. Zhou, W. Lv, S. Tong, X. Yang, L. Chen and N. Zhang, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10, 12477–12496 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Abascal, L. Gómez-Coma, I. Ortiz and A. Ortiz, Sci. Total Environ., 2022, 810, 152233 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Priya, S. Kumar, C. Verma, S. Sarkar and P. K. Maji, J. Water Process Eng., 2022, 49, 103159 CrossRef.
- S. Garcia-Segura, M. Lanzarini-Lopes, K. Hristovski and P. Westerhoff, Appl. Catal., B, 2018, 236, 546–568 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Meng, Y. Ling, M. Yang, X. Zhao, A. I. Osman, A. H. Al-Muhtaseb, D. W. Rooney and P.-S. Yap, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2023, 11, 109418 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Meng, X. Ma, C. Wang, Y. Wang, R. Yang, J. Shao, Y. Huang, Y. Xu, B. Zhang and Y. Yu, ACS Nano, 2022, 16, 9095–9104 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Geng, S. Ji, M. Jin, C. Zhang, M. Xu, G. Wang, C. Liang and H. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202210958 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, P. V. Kumar, Q. Chen, L. Zhao, F. Ye, X. Ma, D. Liu, X. Chen, L. Dai and C. Hu, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 316, 121618 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Qin, N. Liu, L. Chen, K. Wu, Q. Zhao, B. Liu and Z. Ye, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2022, 10, 15869–15875 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Leverett, T. Tran-Phu, J. A. Yuwono, P. Kumar, C. Kim, Q. Zhai, C. Han, J. Qu, J. Cairney, A. N. Simonov, R. K. Hocking, L. Dai, R. Daiyan and R. Amal, Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12, 2201500 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Li, H. Gao, Z. Liu, Q. Zhi, B. Li, L. Gong, B. Chen, T. Yang, K. Wang, P. Jin and J. Jiang, Sci. China: Chem., 2023, 66, 1417–1424 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Wang, Y. Jiang, S. Li, F. Gou, X. Liu, Y. Jiang, W. Luo, W. Shen, R. He and M. Li, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 318, 121819 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Wei, X. Wen, Y. Liu, C. Chen, C. Xie, D. Wang, M. Qiu, N. He, P. Zhou, W. Chen, J. Cheng, H. Lin, J. Jia, X.-Z. Fu and S. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 11530–11535 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wei, Y. Liu, X. Zhu, S. Bo, L. Xiao, C. Chen, T. T. T. Nga, Y. He, M. Qiu, C. Xie, D. Wang, Q. Liu, F. Dong, C. Dong, X. Fu and S. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2023, 35, 2300020 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Qiu, X. Zhu, S. Bo, K. Cheng, N. He, K. Gu, D. Song, C. Chen, X. Wei, D. Wang, Y. Liu, S. Li, X. Tu, Y. Li, Q. Liu, C. Li and S. Wang, CCS Chem., 2023, 1–11 CAS.
- C. Chen, S. Li, X. Zhu, S. Bo, K. Cheng, N. He, M. Qiu, C. Xie, D. Song, Y. Liu, W. Chen, Y. Li, Q. Liu, C. Li and S. Wang, Carbon Energy, 2023, e345 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-Q. Yin, Z.-S. Sun, Q.-P. Zhao, L.-L. Yang, T.-B. Lu and Z.-M. Zhang, J. Energy Chem., 2023, 84, 385–393 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Zhao, Y. Ding, W. Li, C. Liu, Y. Li, Z. Zhao, Y. Shan, F. Li, L. Sun and F. Li, Nat. Commun., 2023, 14, 4491 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Sun, G. Wu, J. Jiang, Y. Yang, A. Du, L. Dai, X. Mao and Q. Qin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202301957 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Lv, L. Zhong, H. Liu, Z. Fang, C. Yan, M. Chen, Y. Kong, C. Lee, D. Liu, S. Li, J. Liu, L. Song, G. Chen, Q. Yan and G. Yu, Nat. Sustain., 2021, 4, 868–876 CrossRef.
- S. Zhang, J. Geng, Z. Zhao, M. Jin, W. Li, Y. Ye, K. Li, G. Wang, Y. Zhang, H. Yin, H. Zhang and H. Zhao, EES Catal., 2023, 1, 45–53 RSC.
- Y. Luo, K. Xie, P. Ou, C. Lavallais, T. Peng, Z. Chen, Z. Zhang, N. Wang, X.-Y. Li, I. Grigioni, B. Liu, D. Sinton, J. B. Dunn and E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal., 2023, 6, 939–948 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Shin, S. Sultan, Z.-X. Chen, H. Lee, H. Choi, T.-U. Wi, C. Park, T. Kim, C. Lee, J. Jeong, H. Shin, T.-H. Kim, H. Ju, H. C. Yoon, H.-K. Song, H.-W. Lee, M.-J. Cheng and Y. Kwon, Energy Environ. Sci., 2023, 16, 2003–2013 RSC.
- Y. Feng, H. Yang, Y. Zhang, X. Huang, L. Li, T. Cheng and Q. Shao, Nano Lett., 2020, 20, 8282–8289 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Liu, S. Yin, Z. Wang, Y. Xu, X. Li, L. Wang and H. Wang, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci., 2022, 3, 100869 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Cao, Y. Quan, A. Guan, C. Yang, Y. Ji, L. Zhang and G. Zheng, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2020, 577, 109–114 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Meng, Y. Huang, Y. Liu, Y. Yu and B. Zhang, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci., 2021, 2, 100378 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zhang, Y. Xue, X. Zheng, C. Zhang and Y. Li, Natl. Sci. Rev., 2023, 10, nwac209 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Gao, H. Liu, D. Wang and J. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 908–936 RSC.
- Y. Huang, R. Yang, C. Wang, N. Meng, Y. Shi, Y. Yu and B. Zhang, ACS Energy Lett., 2022, 7, 284–291 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Xing, S. Wei, Y. Zhang, X. Chen, L. Dai and Y. Wang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15, 22101–22111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Chen, X. Zhu, X. Wen, Y. Zhou, L. Zhou, H. Li, L. Tao, Q. Li, S. Du, T. Liu, D. Yan, C. Xie, Y. Zou, Y. Wang, R. Chen, J. Huo, Y. Li, J. Cheng, H. Su, X. Zhao, W. Cheng, Q. Liu, H. Lin, J. Luo, J. Chen, M. Dong, K. Cheng, C. Li and S. Wang, Nat. Chem., 2020, 12, 717–724 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Chen, S. Lv, J. Kang, Z. Wang, T. Guo, Y. Wang, G. Teobaldi, L.-M. Liu and L. Guo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2023, 120, e2306841120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Yuan, J. Chen, Y. Bai, Z. Liu, J. Zhang, T. Zhao, Q. Wang, S. Li, H. He and G. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 10910–10918 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Paul, S. Sarkar, A. Adalder, A. Banerjee and U. K. Ghorai, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 13249–13254 RSC.
- M. Yuan, J. Chen, Y. Bai, Z. Liu, J. Zhang, T. Zhao, Q. Shi, S. Li, X. Wang and G. Zhang, Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 6048–6058 RSC.
- M. Yuan, J. Chen, Y. Xu, R. Liu, T. Zhao, J. Zhang, Z. Ren, Z. Liu, C. Streb, H. He, C. Yang, S. Zhang and G. Zhang, Energy Environ. Sci., 2021, 14, 6605–6615 RSC.
- M. Yuan, H. Zhang, Y. Xu, R. Liu, R. Wang, T. Zhao, J. Zhang, Z. Liu, H. He, C. Yang, S. Zhang and G. Zhang, Chem. Catal., 2022, 2, 309–320 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Jiao, Y. Dong, X. Cui, Q. Cai, C. R. Cabrera, J. Zhao and Z. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 232–240 RSC.
- D. Jiao, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, Q. Cai, J. Zhao, C. R. Cabrera and Z. Chen, Energy Environ. Mater., 2024 DOI:10.1002/eem2.12496.
- Z. Ma, Y. Luo, P. Wu, J. Zhong, C. Ling, Y. Yu, X. Xia, B. Song, L. Ning and Y. Huang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33, 2302475 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yang, J. Peng, Z. Shi, P. Zhang, A. Arramel and N. Li, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11, 6428–6439 RSC.
- X. Zhu, X. Zhou, Y. Jing and Y. Li, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 4080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Xiong, Y. Xiao and C. Shen, Chem. Mater., 2022, 34, 9402–9413 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Kong, D. Jiao, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Shang, L. Yin, Q. Cai and J. Zhao, Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 451, 138885 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Li, Y. Wang, J. Lu, W. Ding, F. Huo, H. He and S. Zhang, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci., 2023, 4, 101435 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Zhu, Y. Geng, X. Yao, G. Zhu, Z. Su and M. Zhang, Small Methods, 2023, 7, 2201331 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Li, B. Sun, D. Xiao, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, Z. Zheng, P. Wang, Y. Dai, H. Cheng and B. Huang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2023, 62, e202217569 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y.-C. Hao, Y. Guo, L.-W. Chen, M. Shu, X.-Y. Wang, T.-A. Bu, W.-Y. Gao, N. Zhang, X. Su, X. Feng, J.-W. Zhou, B. Wang, C.-W. Hu, A.-X. Yin, R. Si, Y.-W. Zhang and C.-H. Yan, Nat. Catal., 2019, 2, 448–456 CrossRef CAS.
- A. H. Tamboli, A. A. Chaugule and H. Kim, Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 323, 530–544 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Tundo and M. Selva, Acc. Chem. Res., 2002, 35, 706–716 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Aricò and P. Tundo, Russ. Chem. Rev., 2010, 79, 479–489 CrossRef.
- M. Selva and A. Perosa, Green Chem., 2008, 10, 457–464 RSC.
- H.-J. Buysch, Carbonic Esters, Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2000, DOI:10.1002/14356007.a05_197.
- H. Offermanns, K. Schulz, E. Brandes and T. Schendler, Substance properties of methanol, 2014 Search PubMed.
- A. Raza, M. Ikram, S. Guo, A. Baiker and G. Li, Adv. Sustainable Syst., 2022, 6, 1–29 Search PubMed.
- M. Alvarez-Guerra, J. Albo, E. Alvarez-Guerra and A. Irabien, Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8, 2574–2599 RSC.
- D. Anastasiadou, E. J. M. Hensen and M. C. Figueiredo, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 13082–13092 RSC.
- M. C. Figueiredo, V. Trieu and M. T. M. Koper, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 10716–10723 CrossRef CAS.
- K. M. Lee, J. H. Jang, M. Balamurugan, J. E. Kim, Y. I. Jo and K. T. Nam, Nat. Energy, 2021, 6, 733–741 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Li, S. G. Han, W. Wu, K. Zhang, B. Chen, S. H. Zhou, D. D. Ma, W. Wei, X. T. Wu, R. Zou and Q. L. Zhu, Energy Environ. Sci., 2022, 16, 502–512 RSC.
- X. Wang, H. Wang and Y. Sun, Chem, 2017, 3, 211–228 CAS.
- J. Fu, Y. Yang and J.-S. Hu, ACS Mater. Lett., 2021, 3, 1468–1476 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. De Pablo, N. E. Jackson, M. A. Webb, L.-Q. Chen, J. E. Moore, D. Morgan, R. Jacobs, T. Pollock, D. G. Schlom, E. S. Toberer, J. Analytis, I. Dabo, D. M. DeLongchamp, G. A. Fiete, G. M. Grason, G. Hautier, Y. Mo, K. Rajan, E. J. Reed, E. Rodriguez, V. Stevanovic, J. Suntivich, K. Thornton and J.-C. Zhao, npj Comput. Mater., 2019, 5, 41 CrossRef.
- Y. Liu, C. Niu, Z. Wang, Y. Gan, Y. Zhu, S. Sun and T. Shen, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2020, 57, 113–122 CrossRef.
- F. Franco, C. Rettenmaier, H. S. Jeon and B. Roldan Cuenya, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 6884–6946 RSC.
- P. K. Baroliya, M. Dhaker, S. Panja, S. A. Al-Thabaiti, S. M. Albukhari, Q. A. Alsulami, A. Dutta and D. Maiti, ChemSusChem, 2023, 16, e202202201 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. A. Malapit, M. B. Prater, J. R. Cabrera-Pardo, M. Li, T. D. Pham, T. P. McFadden, S. Blank and S. D. Minteer, Chem. Rev., 2022, 122, 3180–3218 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |