Themed collection Most popular 2022 physical and theoretical chemistry articles

Modeling titanium dioxide nanostructures for photocatalysis and photovoltaics
The latest findings from theoretical investigations into TiO2 nanoparticles are reviewed, including both realistic models from a bottom-up approach (1–3 nm diameter) and cut from bulk models (>3 nm diameter) in a top-down approach.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 9485-9497
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC02872G
NIR TADF emitters and OLEDs: challenges, progress, and perspectives
This review presents the recent progress of NIR TADF emitters along with their molecular design strategies and photophysical properties, as well as the electroluminescence performance data of the emitters and their OLEDs.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 8906-8923
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC02201J
Data-driven discovery of molecular photoswitches with multioutput Gaussian processes
We present a data-driven discovery pipeline for molecular photoswitches through multitask learning with Gaussian processes. Through subsequent screening, we identify several motifs with separated and red-shifted electronic absorption bands.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 13541-13551
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC04306H
Interrogating the thionium hydrogen bond as a noncovalent stereocontrolling interaction in chiral phosphate catalysis
Transferable selectivity profiles allow data from intermolecular reactions using iminium substrates to be applied to predict intramolecular reactions involving thioniums.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 11065-11073
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC02171D
Molecular mechanism of a large conformational change of the quinone cofactor in the semiquinone intermediate of bacterial copper amine oxidase
The large conformational change of topaquinone in bacterial copper amine oxidase occurs through the TPQ ring rotation and slide, which are essential to stabilize the semiquinone form.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 10923-10938
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01356H
Bare and ligand protected planar hexacoordinate silicon in SiSb3M3+ (M = Ca, Sr, Ba) clusters
The global minimum of SiSb3M3+ (M = Ca, Sr, Ba) is a D3h symmetric structure containing an elusive planar hexacoordinate silicon (phSi) atom. Most importantly, the phSi core remains intact in ligand protected environment as well.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 8045-8051
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01761J
[Cu18H3(S-Adm)12(PPh3)4Cl2]: fusion of Platonic and Johnson solids through a Cu(0) center and its photophysical properties
An example of a butterfly-like [Cu18H3(S-Adm)12(PPh3)4Cl2] cluster with vertex-sharing kernels through a Cu(0) center. Combined experimental and theoretical results correlate its photophysical properties with its unique structural architecture.
![Graphical abstract: [Cu18H3(S-Adm)12(PPh3)4Cl2]: fusion of Platonic and Johnson solids through a Cu(0) center and its photophysical properties](/br/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=D2SC02544B&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2022)
Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 7616-7625
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC02544B
Color-tunable persistent luminescence in 1D zinc–organic halide microcrystals for single-component white light and temperature-gating optical waveguides
1D zinc–organic halide microcrystals exhibiting thermally assisted spectral separation of fluorescence and phosphorescence could be used as single-component standard white-light and temperature-gating active waveguides.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 7429-7436
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01947G
A rechargeable molecular solar thermal system below 0 °C
We demonstrate rationally designed arylazopyrazoles as MOST-PCM that can be circularly charged and discharged below 0 °C with visible light.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 6950-6958
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01873J
Predicting reaction conditions from limited data through active transfer learning
Transfer learning is combined with active learning to discover synthetic reaction conditions in a small-data regime. This strategy is tested on cross-coupling reactions from a high-throughput experimentation dataset and shows promising results.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 6655-6668
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06932B
The oxidation state in low-valent beryllium and magnesium compounds
This article examines the electronic structure of group 2 (E = Be and Mg) ligand stabilized compounds. We elaborate on the donor–acceptor interaction L(0) ⇆ E(0) ⇆ L(0) and diradical L(−1) → E(+2) ← L(−1) pictures to assess the oxidation state of the metal.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 6583-6591
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01401G
Why heterogeneous single-atom catalysts preferentially produce CO in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction
This report discloses a nontrivial role of the CO2 adsorption mode in governing the CO/formate selectivity of single-atom catalysts towards two-electron CO2 reduction.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 6366-6372
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01593E
Non-covalent reconfigurable microgel colloidosomes with a well-defined bilayer shell
Inverse W/O Pickering emulsions and reconfigurable microgelsomes with a well-defined bilayer structure are prepared from octanol-swollen PNIPAM-co-MAA microgels and the combination of binary microgels, which promise wider application of soft colloids.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 6205-6216
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01082H
Prediction and realisation of high mobility and degenerate p-type conductivity in CaCuP thin films
We synthesize air-stable, p-type CaCuP thin films with high hole concentration and high hole mobility as potential p-type transparent conductors. We study their optoelectronic properties in detail by advanced experimental and computational methods.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 5872-5883
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC01538B
Extending conceptual DFT to include external variables: the influence of magnetic fields
An extension of conceptual DFT to include the influence of an external magnetic field is proposed in the context of a program set up to cope with the ever increasing variability of reaction conditions and concomitant reactivity.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 5311-5324
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC07263C
Predicting biomolecule adsorption on MoS2 nanosheets with high structural fidelity
Benchmarked van der Waals density functional theory calculations are used to create a force-field to describe biomolecule interactions at the aqueous MoS2 interface, which can recover interfacial biomolecule adsorption with high structural fidelity.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 5186-5195
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06814H
An open source computational workflow for the discovery of autocatalytic networks in abiotic reactions
We present an open-source chemoinformatic workflow to generate and analyze complex abiological chemical networks to discover novel compounds and autocatalytic processes. We demonstrate this pipeline's capabilities against a well-studied model system.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 4838-4853
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC00256F
Data-driven discovery of cardiolipin-selective small molecules by computational active learning
We present a data-driven approach combining deep learning-enabled active learning with coarse-grained simulations and alchemical free energy calculations to discover small molecules to selectively permeate cardiolipin membranes.
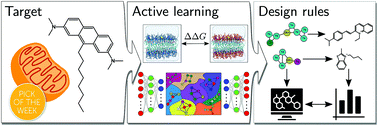
Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 4498-4511
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC00116K
Mining anion–aromatic interactions in the Protein Data Bank
The comprehensive analysis of non-redundant PDB macromolecular structures investigating anion distributions around all aromatic molecules in available biosystems is presented.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 3984-3998
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC00763K
Model agnostic generation of counterfactual explanations for molecules
Generating model agnostic molecular counterfactual explanations to explain model predictions.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 3697-3705
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC05259D
Computationally driven discovery of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors: from design to experimental validation
The dominant binding mode of the QUB-00006-Int-07 main protease inhibitor during absolute binding free energy simulations.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 3674-3687
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC05892D
PIGNet: a physics-informed deep learning model toward generalized drug–target interaction predictions
PIGNet, a deep neural network-based drug–target interaction model guided by physics and extensive data augmentation, shows significantly improved generalization ability and model performance.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 3661-3673
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06946B
A reactivity model for oxidative addition to palladium enables quantitative predictions for catalytic cross-coupling reactions
We report a quantitative model for oxidative addition reactivity in palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling, which is broadly applicable to predict reactivity and selectivity for complex substrates from simple molecular descriptors.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 3477-3488
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC00174H
Synaptotagmin-1 C2B domains cooperatively stabilize the fusion stalk via a master-servant mechanism
Synaptotagmin-1 is a low-affinity Ca2+ sensor that triggers synchronous vesicle fusion.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 3437-3446
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06711G
Generating 3D molecules conditional on receptor binding sites with deep generative models
We generate 3D molecules conditioned on receptor binding sites by training a deep generative model on protein–ligand complexes. Our model uses the conditional receptor information to make chemically relevant changes to the generated molecules.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 2701-2713
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC05976A
Photosensitization mechanisms at the air–water interface of aqueous aerosols
First-principles molecular dynamics simulations of imidazole-2-carboxaldehyde at the air–water interface highlight the role of surfactants in stabilising the reactive triplet state involved in photosensitisation reactions in aqueous aerosols.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 2624-2631
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06866K
Equilibria between conformational states of the Ras oncogene protein revealed by high pressure crystallography
The equilibria between structural states induced by pressure within the crystal structure of Ras are illustrated with different colors corresponding to different Ras substates.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 2001-2010
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC05488K
Low-energy electron distributions from the photoionization of liquid water: a sensitive test of electron mean free paths
Our study reveals the detailed influence of elastic and inelastic mean-free paths on the complete photoelectron spectra of liquid water, including the low-energy electron distributions and the reshaping of the primary photoelectron bands.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 1675-1692
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06741A
Improving machine learning performance on small chemical reaction data with unsupervised contrastive pretraining
Contrastive pretraining of chemical reactions by matching augmented reaction representations to improve machine learning performance on small reaction datasets.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 1446-1458
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06515G
MGraphDTA: deep multiscale graph neural network for explainable drug–target binding affinity prediction
MGraphDTA is designed to capture the local and global structure of a compound simultaneously for drug–target affinity prediction and can provide explanations that are consistent with pharmacologists.

Chem. Sci., 2022,13, 816-833
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC05180F
About this collection
This specially curated collection pulls together some of the most popular articles from 2022 in the field of physical and theoretical chemistry. The collection presents some outstanding contributions to the field, ranging from deep learning models for predicting drug-target interactions, through to investigations into colour-tunable persistent luminescence in low-dimensional zinc-organic halide microcrystals. As with all Chemical Science articles, they are all completely free to access and read. We hope you enjoy browsing through this collection.
If a particular article has inspired you, do feel free to share on social media using the buttons on each article landing page and use our hashtag: #ChemSciMostPopular