DOI:
10.1039/D4NR00680A
(Review Article)
Nanoscale, 2024,
16, 12820-12856
Advances in engineered nanosystems: immunomodulatory interactions for therapeutic applications
Received
17th February 2024
, Accepted 27th May 2024
First published on 18th June 2024
Abstract
Advances in nanotechnology have led to significant progress in the design and fabrication of nanoparticles (NPs) with improved therapeutic properties. NPs have been explored for modulating the immune system, serving as carriers for drug delivery or vaccine adjuvants, or acting as therapeutics themselves against a wide range of deadly diseases. The combination of NPs with immune system-targeting moieties has facilitated the development of improved targeted immune therapies. Targeted delivery of therapeutic agents using NPs specifically to the disease-affected cells, distinguishing them from other host cells, offers the major advantage of concentrating the therapeutic effect and reducing systemic side effects. Furthermore, the properties of NPs, including size, shape, surface charge, and surface modifications, influence their interactions with the targeted biological components. This review aims to provide insights into these diverse emerging and innovative approaches that are being developed and utilized for modulating the immune system using NPs. We reviewed various types of NPs composed of different materials and their specific application for modulating the immune system. Furthermore, we focused on the mechanistic effects of these therapeutic NPs on primary immune components, including T cells, B cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and complement systems. Additionally, a recent overview of clinically approved immunomodulatory nanomedicines and potential future perspectives, offering new paradigms of this field, is also highlighted.
1. Introduction
The immune system plays a crucial role in the surveillance of our body. The system consists of specialized cells, tissues, and organs working together to encounter the threats posed by deadly diseases, including influenza, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), SARS-CoV-2 infections, atherosclerosis, cancers, multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), diabetes, etc. Conventionally, the immune system is divided into two components, referred to as (a) innate and (b) adaptive components. The innate immune system consists of phagocytes (dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages) and granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells), contributing to the formation of the first line of defence in the body. DCs and macrophages, as well as other host cells, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells, play primary roles in the recognition of pathogens during the innate immune response. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) via pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and get activated quickly to recruit themselves to the assault sites (infected, inflamed, and damaged tissues).1 The classical, lectin, and alternative pathways of the complement system are the additional components of the innate immune system. The classical pathway is activated by antigen–antibody interaction; the lectin pathway via microbial molecules (mannose residues) by soluble mannose-binding lectins; and the alternative pathway by any recognizing surfaces.2 On the other hand, the adaptive immune component governs the activities of T cells and B cells that together confer “specificity” and “memory” to the immune responses. In response to pathogenic changes in the body, the innate and adaptive immune cells collectively drive immunological responses and restore normal physiological activities. Aberrant immune implications can result in either immune suppression or overactivation of immune components. In many cases, the hyperactive cellular and molecular components of the immune system play pathogenic roles, thereby promoting disease progression, while individuals also suffer from immunosuppressive diseases due to the compromised activities of T cells, B cells, macrophages, DCs, and other immune components. Importantly, it has been observed that even different phenotypes of a specific immune cell are also engaged in different sets of diseases. For instance, M1 phenotype macrophages play proinflammatory roles (implicated in autoimmune disorders), while M2 phenotypes are associated with anti-inflammatory responses (implicated in immunosuppressive disorders). Thus, understanding the functionalities of the immune system and clinically harnessing the modulation of immune components are imperative in the fight against a variety of immune disorders.
Advances in science and nanotechnology now allow us to manipulate cellular and molecular immune components. Progress in biomedical science has led to the development of engineered nanostructured materials for therapeutic delivery. Due to their high surface area-to-volume ratio, nanoparticles (NPs) exert greater biological interaction with respect to their bulk counterparts.3 This enhanced biological interaction thereby augments better therapeutic efficacy by concentrating the therapeutic cargo at pathogenic sites. In combination with specific therapeutic agents, NPs can be employed in both activation as well as suppression of immune responses. To achieve immune-specific therapeutic delivery, the surface of NPs can be functionalized with antibodies, peptides, oligosaccharides, antigens, etc.4–6 The clinical and preclinical data also suggest that immunotherapeutic nanomedicines are rapidly emerging and promising novel therapeutic platforms for targeting diseases characterized by aberrant immune functions. This review discusses, in detail, the fundamental properties of various types of NPs and their interaction with physiological and immune components, as well as their contribution in targeting immune components for therapeutic applications. Furthermore, we illustrate how these therapeutic nanomedicines mechanistically act on different components of the immune system, including T cells, B cells, DCs, macrophages, and complement systems. We also provided a current update on clinically approved nanomedicines with their immunomodulatory properties. Furthermore, a comprehensive overview of the challenges in the field and future perspectives is presented, elucidating avenues for further research and development.
2. The interplay between fundamental morphological features of NPs and immune systems
The interactions between fundamental morphological features of NPs and the immune components, including size, shape, surface charge, and modifications, are crucial in determining their responses within biological systems (Fig. 1). Understanding fundamental features of different NPs and their interactions with immune components is essential in order to rationally design nanomedicines for optimized therapeutic outcomes.
 |
| | Fig. 1 Schematic illustration depicting immune components and fundamental attributes of nanosystems in modulating immune response for immunotherapy. Image created with BioRender.com. | |
2.1. Size
Size is a key factor that governs the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic behavior of therapeutic NPs. Particles smaller than 5 nm undergo either rapid renal clearance or get cleared by the extravasation process.7,8 Increasing the size of NPs beyond a certain limit leads to their accumulation and deposition in multiple organs and tissues. The particles greater than 200 nm in diameter activate and provoke the complement system, which can lead to rapid removal of the NPs from circulatory systems and accumulation in organs like the liver and spleen.9–11 Although the cellular uptake of NP depends on cell types, it has been observed that particles of 50 nm in size get internalized by the cells with higher efficiency at a greater uptake rate.12 100–200 nm rigid and spherical NPs exhibit prolonged circulation time, avoid hepatic uptake, and are also protected from being engulfed by the spleen cells.13 The NPs of 20–200 nm in size exhibit greater accumulation in tumor tissues by avoiding the reticuloendothelial system and renal filtration, which helps in achieving greater therapeutic concentration at the tumor site.14,15 Therefore, variations in particle size trigger immune responses differentially depending on the immune cell types. In comparison with small particles, large particles induce greater immune responses by locating themselves in immune cells and delivering therapeutic payloads.16 On the other hand, the smaller particles have also been reported to trigger potent immune responses by modulating helper T-cell subtypes compared with the larger NPs.17 Thus, multiple studies suggest that 20–200 nm is the most effective size range that can be considered in the development of nanotherapeutics.18
2.2. Shape
The variation in shape governs different cellular uptake patterns of NPs by mammalian cells and influences their systemic circulation and binding affinity behavior. Cell membranes exhibit different sets of cellular responses with particle shape alterations due to changes in membrane integrity.19 Hence, altering the shape of NPs can improve their therapeutic outcomes.20 In particular, in vitro cellular study based on a macrophage cell line, RAW264.7, revealed that the uptake efficiency of triangular particles is greater than that of rod and star-shaped particles.21 The rod-shaped and spherical particles can also induce different sub-populations of helper T cells. In vivo results depicted that spherical particles favor the helper T cell 1 (Th-1) subtypes, while rod-shaped particles promote Th-2 cell-induced immune responses.17 The shape variations have significant effects on adjuvanticity and cytokine production. The specific adjuvant engineered on gold nanorods and nanospheres provoked the release of different levels of inflammatory cytokines. In comparison with nanospheres, the nanorods displayed a greater ability to potentiate the adjuvanticity of chemical species with minimal inflammatory cytokine production.22 Even at the same therapeutic doses, the antibody-coated nanorod exerts multi-fold greater therapeutic efficacy against breast cancer cells than the nanospheres.23 Contradictory to these results, a recent study also demonstrated that the mammalian cell studied with spherical gold NP exhibited better uptake efficacy in comparison with rod-shaped NPs.24
2.3. Surface charge
The charge on surface of the NP is very crucial for its bioactivity, and its variation induces different sets of biological responses. NPs with a positive charge show more rapid cellular uptake than neutral and negatively charged NPs.25,26 Negatively charged cell membranes promote the cellular internalization of positively charged NPs.12 However, positive charge also affects the structural integrity of the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, and greater charge density leads to disordering of the phospholipid bilayer structure.27 The positive and negative charges of the NPs also reflect their mode of entry into the cells. Positively charged particles follow the macropinocytosis mode of entry, while negatively charged particles make their entry into the cell via the clathrin- or caveolae-independent endocytosis pathway.28 Differently charged particles with similar size and shape provoke varied immune responses. Positively charged NPs show a greater influence on the activation of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) like DCs and macrophages than uncharged particles. Thus, the loading of an anionic species like nucleic acids or other polymers can mask the extent of positive charge of the particles that slackens the undesirable immunogenic outputs.29,30 The positively charged gold NPs (AuNPs) stimulated the monocyte cells of immune systems at a significant level by inducing the expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokine (IL-1β) and anti-inflammatory cytokine (TGF-β), while the negatively charged AuNPs promoted pro-inflammatory (TNF-α) expression.31 The deleterious immune responses that are produced by cationic charges can be advantageous in immunotherapeutic applications. Recent studies suggested that the positive charge can play beneficial roles in the development of vaccines where the cationic surface moieties can potentiate the therapeutic efficacies of adjuvants like ovalbumin (OVA) via complement activation, T-cell activation, enhanced antibody production, and cytokine secretion.32
2.4. Surface modification
The surface modification of NPs is carried out to improve biocompatibility and blood circulation time, targeting the disease pathology, and achieving greater therapeutic retention in desired sites with minimal toxicity hazards.33 In achieving specific nano–bio interaction as well as targeted delivery of therapeutics, the NP surface can be modified with a variety of ligands such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyethyleneimine (PEI), cell-penetrating peptides, targeting antibodies, antigens, etc.34–37 PEG is a chemically inert hydrophilic polymer widely used for surface modification, which helps in preventing direct exposure of the NP surface to the biosystems and inhibits particle aggregation, opsonization, and phagocytosis.38 The phagocytosis of NPs by macrophages is considered one of the major clinical limitations that occurs in the development of therapeutics. Surface modification with antibodies has proved to be an excellent strategy to target immune components and prevent macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. Besides PEG, CD47 antibody conjugation with NPs can selectively block the signal regulatory protein-α (SIRP-α), which is found on macrophages. The CD47-SIRP-α coupling interaction and subsequent blocking of SIRP-α target protein with CD47 antibody-modified nanoplatforms prevents macrophagic phagocytosis of the NPs.37 CD11c monoclonal antibody has also been used as a surface-modifying agent to bind to DCs via specific intercellular adhesion molecules, such as 3-grabbing-non-integrin (SIGN) surface proteins.39 Hence, CD11c antibody modification of NPs loaded with immunosuppressive agents can deliver therapeutic cargo to DCs by specifically targeting the DC-SIGN.39 Tailoring the surface of NPs with antigen molecules is a key strategy in the development of nano-vaccines. OVA, the model antigen, can be attached to the NP surface, and the delivery of OVA-conjugated nano-vaccine showed antigen-induced immunological responses.40 Furthermore, the modification of NPs with amine functional groups enables the OVA-loaded nano-vaccines to activate the complement systems at a significant level.32 Recently, cytokine modifications have been made in the surface engineering of NPs to target specific components of the immune system. Interleukin-2 receptors (IL-2R) that are expressed on the surface of T cells can be targeted to deliver therapeutics precisely and specifically. In this regard, the IL-2 cytokine can be used as a surface-modifying ligand to mediate IL-2R-dependent T-cell targeting and delivery of immunotherapeutic agents.41 Chemical species such as hyaluronic acid, folic acid, and biotins have been engineered onto the NP surface to specifically bind with the respective CD44 and biotin receptors that are overexpressed in cancer cells. Thus, modifying the particle surfaces with these ligands can selectively eliminate the cancer cells while minimally affecting the normal and healthy cell population.42–44 The surface modifying agents employed in the fabrication of various types of NPs for target-specific immune activities are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 List of surface modifying agents used to fabricate NPs for target-specific immune activities
| Nanoparticle involved |
Surface-modifying agent |
Method of modification |
Target receptor |
Purpose of modification |
Ref. |
| LNPs |
Murine anti-DEC205 single chain antibody (scFv) |
Thiol-maleimide chemical attachment |
DEC205 receptors on DCs |
DC-targeted siRNA delivery for immunosuppression |
45
|
| Carboxylated polystyrene NPs |
PEG, CD47 antibody |
EDC-NHS coupling reaction |
SIRPα on macrophages |
Macrophage targeting in the prevention of phagocytosis |
37
|
| Silicon NPs |
Anti-CD11c/anti-DC-SIGN antibodies |
Direct conjugation of periodate oxidized mAb |
CD11c/DC-SIGN |
DC-specific drug delivery |
39
|
| SPIONs (superparamagnetic iron oxide NPs) |
IL-2 (interleukin-2) cytokine |
Biotin–streptavidin non-covalent interaction |
IL-2R on T-cells |
T-cell targeted immunotherapy |
41
|
| Chitosan NPs |
Mannose |
Electrostatic interaction |
Mannose receptors on immature DCs |
DC-targeting in tumor immunotherapy |
46
|
| Gold NPs |
Shikimoyl-ligand |
Covalent attachment via 6-amino hexane thiol spacer |
Mannose receptors on DCs |
DC-targeted genetic immunization |
47 and 48 |
| Gold NPs |
HIV Gag p17 and CMV pp65 peptides |
EDC-NHS coupling |
DC-SIGN receptors |
DC-targeting in anti-HIV therapy |
49
|
| Polystyrene NPs |
CD200 glycoprotein |
Attachment via streptavidin rDNA technique |
CD200R on macrophages |
CD200R targeting, preventing the phagocytosis and inflammatory cytokines |
50
|
| PLGA NPs |
M2pep peptide |
Tannic acid-Fe3+ complexation |
CD206R on macrophages |
M2-phenotype macrophage targeting in tumor immunotherapy |
51
|
| PLGA-b-PEG NPs |
Herceptin® antibody/trastuzumab |
NHS-PEG-alkyne linker mediated NHS-esterification |
HER2+ receptors on cancer cells |
Targeting the HER2+ breast cancer cells |
52
|
| Iron oxide NPs |
Neu antibody/trastuzumab |
Thiol-maleimide reaction |
HER2+ receptors on cancer cell |
HER2+ anti-cancer immunotherapy |
6
|
| PLGA NPs |
Anti-CD8a F(ab′)2 obtained from IgG antibody |
Thiol-maleimide reaction |
CD8a receptors on T-cells |
CD8+ T-cell targeting in cancer immunotherapy |
53
|
| Lipid-dendrimer-calcium phosphate NPs |
SP94 peptide |
Thiol-maleimide reaction |
PD1 (programmed cell death protein 1)-receptors on T-cells |
Targeted delivery of drugs in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy |
54
|
| Liposome |
IL-2-Fc, anti-CD137 Fab2 protein |
Thiol-maleimide reaction |
IL-2, CD137 receptors on CD8+ T-cells |
T-cell, NK-cell activation in tumor immunotherapy |
55
|
| LNPs |
Anti-human CD45RO primary antibody |
Biotin–streptavidin non-covalent interaction |
CD45RO on memory T-cells (Tm) cells |
CD8+ Tm-cell targeting in lupus nephritis therapy |
56
|
| ZIF-8 metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) |
Anti-CD16/32 antibody |
Electrostatic adsorption |
CD16/32 on M1-macrophages |
M1-macrophage targeted drug delivery in osteoarthritis therapy |
57
|
| PLGA-b-PEG NPs |
Anti-CD19, anti-CD220 mAbs |
EDC-NHS coupling |
CD19, B220 (CD45R) on B-cells |
B-cell targeted drug delivery |
58
|
3. Types of NPs and their immunotherapeutic applications
NPs are broadly classified into polymeric, metallic, ceramic, carbon-based, lipid-based, and other types.59 Another class of NPs that has gained great attention in therapeutic application is biological NPs. The category includes viral components, exosomes, ferritin, lipoproteins, and magnetite, all of which are utilized for therapeutic delivery purposes.60 Different types of such NPs, along with their immunotherapeutic applications, are discussed below.
3.1. Polymeric NPs
Polymeric NPs are crucial for therapeutic delivery due to their stability, biocompatibility, biodegradability, and water-soluble properties.61 As the by-products are relatively less toxic, polymers of both natural and synthetic origin are preferred for the fabrication of NPs.62 The polymeric NPs are mainly divided into two forms: nanocapsules and nanospheres. The nanocapsules possess a reservoir-like structure, and the nanospheres provide a solid matrix structure where the therapeutics are loaded by entrapment and adsorption mechanisms.63,64 These two large categories of polymeric NPs are further sub-categorised into different shapes like dendrimers, polymerosomes, and micelles.61 Dendrimers are hyperbranched synthetic polymeric 3D nanostructures bearing multiple functional groups that help in the binding of various therapeutics.65,66 Polymerosomes are stable polymeric amphiphilic vesicles capable of encapsulating both hydrophilic and hydrophobic therapeutic agents while maintaining their stability during the delivery process.67 Micelles are generally spherical self-assembled NPs composed of amphiphilic block co-polymers characterized by hydrophobic core (accommodate hydrophobic drugs) and hydrophilic shell structures in an aqueous medium.68 A variety of hydrophobic chemotherapeutic agents can be accommodated within polymeric micelles for their active and passive delivery.69 Naturally derived polymers, such as proteins and polysaccharides, are extensively utilized in nanomedicine development. Polysaccharide-based NPs are favored for their biocompatibility and biodegradability, serving in various therapeutic roles, including cancer immunotherapy, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) therapy, atherosclerosis treatment, vaccine delivery, macrophage polarization, and arthritis management.70–74 Similarly, various protein-based NPs are also used in immune modulation and therapeutic delivery in the treatment of various diseases such as acute pancreatitis, gastritis, cancer, arthritis, etc.73,75–77 Besides natural polymeric NPs, synthetic polymer-based NPs are pivotal in immunotherapy, offering promise due to their distinct characteristics like weak functional groups, chemical inertness, and tunable mechanical properties.78–82 The detail of polymer-based NPs are listed in following Table 2.
Table 2 List of natural and synthetic polymers used for fabrication of NPs for immunotherapeutic applications
| Polymer source |
Properties |
Immunotherapeutic applications of fabricated NPs |
Ref. |
|
Natural polymers
|
| Chitosan |
U.S. FDA-approved, cationic, highly basic, polysaccharide, biocompatible. |
Anti-cancer immunotherapy. |
74 and 83 |
| Hyaluronic acid |
Poly-anionic, non-sulphated polysaccharide, non-toxic, biocompatible, biodegradable. |
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) therapy, anti-inflammatory activities in atherosclerosis. |
70 and 84 |
| Gelatin |
Protein obtained from collagen, biodegradable, biocompatible, non-antigenic. |
Antigen delivery for immune stimulation, delivery of immunostimulant CpG oligonucleotides. |
85 and 86 |
| Silk fibroin |
Protein obtained from skin cocoons or larvae, excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low immunogenicity. |
Immune system modulating drug delivery for cancer therapy, macrophage modulation, immunosuppressive therapeutic delivery in acute pancreatitis. |
87–89
|
| Albumin |
Plasma protein, high biocompatibility, biodegradability, non-immunogenicity. |
Immunomodulation in glioblastoma therapy, immune system activation and sonodynamic anti-tumor therapy, macrophage modulation in treatment of gastritis, checkpoint blockade-based metastatic pancreatic cancer immunotherapy, neutrophil-targeted drug delivery in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). |
75–77,90 and 91
|
| Cyclodextrin |
Amphiphilic cyclic oligosaccharide, excellent biocompatibility. |
Anti-inflammatory activity in treatment of Atherosclerosis, immune checkpoint blockade-based cancer immunotherapy. |
71 and 92 |
| Alginate |
Anionic polysaccharide, good biodegradability, biocompatibility, non-toxic. |
Antigen delivery for eliciting immune response against influenza, therapeutic delivery targeting macrophage polarization in treatment of RA, dendritic cell-targeted antigen delivery in cancer immunotherapy. |
4,72 and 73 |
|
Synthetic polymers
|
| PLA-poly(lactic acid)/polylactide |
Aliphatic polyester molecule, biocompatible, low toxicity, controlled hydrolytic degradation. |
Macrophage cell-mediated anticancer drug delivery, hepatitis B vaccine delivery for cell-mediated immunity, improving immunogenicity of polysaccharide antigens and vaccine delivery, DC-targeted mRNA vaccine delivery. |
78 and 93–95 |
| PLGA-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) |
Copolymer of PLA and PGA, FDA-approved, biocompatible, tunable mechanical property, a wide range of erosion times. |
Macrophage-stimulated immune modulation and drug delivery, immune induction and therapeutic delivery. |
79 and 96–98 |
| Poly(caprolactone) |
Polyester molecule, FDA-approved, biocompatible, non-toxic. |
pH-responsive antigen delivery for humoral immune induction, vaccine delivery, immunity induction, immune modulation and anti-inflammatory drug delivery. |
80,99 and 100 |
| Polyanhydrides |
Excellent biocompatibility, sustained drug delivery. |
Protective and sustained immunisation, oral antigen delivery. |
82 and 101 |
| Polyorthoesters |
Biocompatible, non-toxic, sustained release of drugs. |
Immune cell-targeted antigen delivery. |
81
|
3.2. Metallic NPs
The metallic NPs have emerged as potential carriers of therapeutics due to their unique optical, magnetic, catalytic, and photocatalytic properties.102 The metallic NPs can be categorized into pure metallic NPs, metal oxide NPs, doped metal/metal oxide/metal NPs, metal sulfides, and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs).103 Among pure metal NPs, gold NPs (AuNPs) with different shapes, like nanorods, nanostars, and nanoclusters, are most widely used for immunotherapeutic applications. Previous studies also demonstrated that bare metal NPs without any therapeutic agents can stimulate the immune system for the induction of effective immune responses against viral infections.104 In the treatment of viral disease, the metallic NPs were observed to deliver specific nucleic acid cargos in hosts where subsequent expression of nucleic acid elicits potent anti-viral immune responses.105 Cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells are the emerging choice of therapeutic cells in the development of cell-drug therapy against cancer. The metallic NPs have shown the ability to form CIK cell-mediated cell-drug nanotherapeutics for exhibiting anti-tumor immune responses.106,107 Silver NP (AgNP) is a metallic category of NPs known for its pronounced antimicrobial properties, and researchers are exploiting AgNPs for immunotherapeutic purposes. In vivo animal studies provided several insights into the immunotherapeutic role played by AgNPs, and polyphenol-modified AgNPs exert immune protection against the highly infectious herpes simplex virus-2.108 The cell death of distant and deep-tissue tumors is quite challenging to target, and therefore researchers have successfully designed an immunogenic cell death therapy using palladium NPs for efficient deep-tissue tumor cell targeting. The Pd-based nanotherapeutic system triggers the release of “danger” signaling molecules that recruit T cells of immune systems in tumor tissues and efficiently arrest tumor growth.109
3.3. Ceramic NPs
The ceramic NPs are considered promising therapeutic delivery vehicles due to their high heat resistance, mechanical integrity, stability, and chemical inertness. They are involved in the delivery of drugs, genes, proteins, peptides etc.110,111 Ceramic NPs are composed of oxides, carbides, carbonates, phosphates of different metals, and metalloids.110 Iron oxide NPs (IONPs) are one of the most popular and promising NPs that are employed in numerous immunotherapeutic applications. Starting from immunosuppressive drugs to various antigens, a wide range of therapeutics can be delivered with the help of IONPs.112,113 Due to their elemental compositions, the IONPs are involved in neutrophil modulation in the therapy of iron-deficiency disorders.114 The superior thermal conductivity of IONPs makes them a perfect candidate for photoimmunotherapy. In combination with other therapeutic agents, IONPs modulated anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotypes into tumor-suppressive proinflammatory macrophages, which facilitated immunotherapeutic restriction of tumor progression.115 Similarly, a variety of other ceramic NPs, such as silica NPs, hydroxyapatite NPs, titanium oxide, zinc oxide, and copper oxide NPs are also harnessed in multiple immunotherapeutic applications.
3.4. Carbon NPs
Carbon-based NPs are widely used nanostructured vehicles that have great potential for the delivery of therapeutics. The carbon family of NPs exhibits several characteristic features, such as high mechanical integrity, excellent thermal conductivity, and great optical and magnetic properties. Therapeutic agents such as anti-cancer drugs, therapeutic peptides, genetic materials, antioxidants, protective agents, etc., are either encapsulated or conjugated for their effective delivery.116 Among multiple subtypes, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), nanodiamonds (ND), carbon dots (CD), and graphene are the most used carbon NPs. The CNTs are sp2 hybridized NPs, which are further divided into two types: single-walled CNT (SWCNT) and multi-walled CNT (MWCNT). The use of CNTs in near-infrared light-triggered conductive nanomaterial-assisted photothermal therapy (PTT) for cancer cell ablation has gained attention. Conjugating checkpoint blockers to CNTs enhances their anti-tumor immunotherapeutic efficacy, making CNT-led PTT more efficient.117 CNTs have also been used to deliver various immune-stimulating agents to provoke the immune components and to fight against cancer pathologies.118–120 Additionally, in the context of cancer vaccines, CNTs have been used to develop nanocomposite vaccines, such as by combining NY-ESO-1 antigen and CpG-ODN (TLR9 agonist) adjuvant molecule. NY-ESO-1, a cancer-testis antigen found in various cancers such as lung cancer, melanoma, and prostate cancer, elicits effective T-cell responses due to its potential immunogenicity, making it a promising vaccine candidate.121 Early phase clinical trials have shown that immunotherapy using NY-ESO-1could lead to the mitigation of cancers. The addition of a vaccine adjuvant molecule to NY-ESO-1 ameliorated the immunological responses against cancer. The nanovaccine exhibited rapid internalisation by DCs, and elicited strong antitumor immunological responses by promoting humoral and cellular (CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses).121 In the manipulation of immune components to treat cancer, other carbon-based nanomaterials such as carbon dots and graphene are also employed to promote T-cell infiltration, modulation of DCs, and polarization of macrophages that suppress the disease pathologies.122–128 The immunotherapeutic applications of different types of NPs are listed in Table 3.
Table 3 List of different types of nanoparticles synthesized for immunotherapeutic applications
| Types of NPs |
Therapeutic payload |
Application |
Ref. |
|
Metallic NPs
|
| Gold nanorod (AuNR) |
ssRNA |
Antiviral therapy against pandemic influenza. |
104
|
| None |
Immune stimulation and inhibition of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). |
105
|
| Immunoadjuvant imiquimod (R837) |
Immunotherapy in melanoma |
129
|
| Gold nanostar (AuNS) |
Cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells |
Anticancer immunotherapy |
106
|
| Gold nanocluster (AuNC) |
CIK cells |
Anticancer immunotherapy |
107
|
| Antigenic peptide, cytosine-phosphate-guanine (CpG) oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) |
Vaccine-mediated immune stimulation |
130
|
| Technetium-99 m, lutecium-177 |
Cancer radio-immunotherapy |
131
|
| Silver NP (AgNP) |
None |
Enhances immune protection against Herpes simplex virus-2 (HSV-2) infection. |
108
|
| None |
Immune stimulation in cancer immunotherapy. |
132
|
| None |
Immune modulation for cancer therapy |
133
|
| Palladium NP (PdNP) |
Doxorubicin (DOX) |
Anticancer chemoimmunotherapy |
109
|
|
Ceramic NPs
|
| Iron oxide NP (IONP) |
Ovalbumin (OVA) |
Anti-tumor vaccine immunotherapy |
112
|
| Mycophenolic acid |
Immunosuppressive drug delivery. |
113
|
| None |
Neutrophil modulation in iron deficient anaemia. |
114
|
| Sulfasalazine |
Anti-cancer immunotherapy |
115
|
| DOX, polyinosinic: polycytidylic acid (poly (I:C)) |
Anti-cancer immunotherapy |
134
|
| Ferumoxytol |
Immune activation in cancer immunotherapy |
135
|
| Poly (I:C) |
Vaccine delivery to lymph nodes. |
136
|
| Silica-based NP (SiNP) |
Nucleic acid and DOX |
Co-delivery of therapeutics for immune stimulation and cancer cell targeting. |
137
|
| Peptide neoantigen, CpG oligodeoxynucleotide |
Anticancer immunotherapy. |
138
|
| anti-PD1 antibody |
Anticancer immunotherapy. |
139
|
| Gardiquimod |
Anticancer photoimmunotherapy. |
140
|
| Cyclic diguanylate monophosphate(cdGMP) |
Dysregulated APCs specific drug delivery in glioblastoma immunotherapy. |
141
|
| Peptide antigen B2T |
Vaccine delivery |
142
|
| Hydroxyapatite NP (HApNP) |
Methylprednisolone acetate |
Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory drug delivery in RA. |
143
|
| Lactoferrin |
Immunomodulation for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. |
144
|
| OVA |
Immune stimulation, anti-cancer immunity |
145
|
| Bacterial lipopolysaccharide |
Macrophage modulation and immune stimulation |
146
|
| Titanium oxide (TiO) NP |
Chito-oligosaccharides |
Anticancer immunotherapy |
147
|
| None |
Anticancer immunotherapy |
148
|
| None |
DC and helper T-cell modulation |
149
|
| Zinc oxide (ZnO) NP |
DOX |
DOX-induced macrophage polarization in cancer immunotherapy |
150
|
| None |
T-cell differentiation, immune modulation |
151
|
| Copper oxide (CuO) NP |
Chitosan |
Macrophage activation in cancer immunotherapy |
152
|
| None |
Immunomodulation in the treatment of inflammatory ulcerative colitis. |
153
|
|
Carbon-based NPs
|
| CNTs (SWCNT and MWCNT) |
Anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
Immune stimulation in anti-tumor therapy |
117
|
| CpG, OVA and anti-CD40 Ig (α CD40) |
Adjuvant delivery for immune induction for cancer therapy |
118
|
| None |
Immune cell recruitment for anticancer therapy |
119
|
| CpG |
Macrophage activation and immune stimulation against glioblastoma. |
120
|
| Indolicidin |
Immune activation and modulation in the treatment against antibiotic resistance. |
154
|
| None |
Immunomodulation in bone remodelling |
155
|
| Nanodiamonds (NDs) |
None |
Immune cell induction for anti-tumor immunotherapy |
156
|
| Octadecylamine, dexamethasone |
Macrophage-specific immunomodulation in the treatment of RA. |
157 and 158 |
| Carbon dots (CDs) |
Fe ion, DOX, and Losartan |
T-cell infiltration, chemoimmunotherapy against cancer |
122
|
| None |
DC-targeted danger signal-specific anti-cancer immunotherapy |
123
|
| None |
Induction of CD8+ T cells, mature macrophages, and natural killer cells for anti-cancer immunotherapy |
124
|
| None |
Immunotherapy against melanoma |
125
|
| Graphene-nanoplatform |
None |
Anticancer immunotherapy |
126–128
|
3.5. Lipid-based NPs (LNPs)
LNPs belong to the most important class of NPs that are receiving growing clinical approvals due to their suitable physicochemical properties, payload flexibility, greater bioavailability, superior biocompatibility, biodegradability, and facile mode of fabrication. The LNPs can be either natural or synthetic in origin. The polar hydrophilic head and non-polar hydrophobic tails of the lipid molecules are assembled to give rise to a variety of LNPs. A wide range of lipid materials, such as triglycerides, mixtures of triglycerides, waxes, hard fats, and other lipids, are harnessed in the fabrication of LNPs. Additional components like emulsifiers and/or co-emulsifiers are also used for the fabrication of LNPs. Based on the lipid assembly features, the LNPs are further classified into liposomes, cationic LNPs, solid-lipid NPs (SLNs), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs), non-lamellar LNPs, ethosomes, cubosomes, etc. Within the aqueous interior, hydrophilic therapeutic agents can be loaded while maintaining drug stability, whereas hydrophobic drugs can be entrapped in the non-polar hydrophobic chains of the lipid components. LNPs can be functionally modified with a variety of agents, such as monoclonal antibodies, peptides, small molecule ligands, etc., for the targeted delivery of therapeutic cargo.159 Liposomes were developed in the earliest phases and were considered the simplest drug delivery vehicle to target and modulate the components of immune systems. For anti-cancer immunotherapy, the liposomes were loaded with various therapeutic agents that aimed at modulating the activities of macrophages, DCs, T cells, and NK cells residing in the tumor microenvironment (TME).160–163 In addition to anti-inflammatory drugs, therapeutic RNAs have also been delivered usingliposomes for the treatment of diseases such as atherosclerosis, bacterial infections, and RA.164–166 Immune cell-specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) delivery and downregulation of gene expression of pathogenic stimulatory molecules are attractive ways to regulate the hyperactive immune systems. Hence, protective and targeted delivery of siRNA without further provoking the immune cells is quite challenging and demanding. In this regard, cationic LNPs were heralded as safe and potent nanocarriers of immune system-targeted therapeutic siRNA delivery that results in a reduction of hyperactive, dysregulated immune responses.45 Preventing the premature release of cargo siRNA in systemic circulation promoted greater accumulation of the therapeutic in the TME. Hence, a higher level of therapeutic siRNA at the TME raised the pH of the acidic TME by silencing the specific gene, which consequently decreased the number of immunosuppressive cells, promoted T-cell infiltration, and restored immune activities to retard the growth of tumor tissues.167 Other types of LNPs, such as SLNs, NLCs, ethosomes, and cubosomes, are widely used as drug-delivery vehicles to modulate the immune components in several diseases. The immunotherapeutic applications of diffrent types of LNPs are listed in Table 4.
Table 4 List of LNPs used for immunotherapy of various diseases
| Types of LNPs |
Lipid composition |
Therapeutic payload |
Applications |
Ref. |
| Abbreviation: SPC, soybean phosphatidylcholine; DSPE-PEG2000, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000]; HSPC, hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine; DSPC, distearoylphosphatidylcholine; DPPE, 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; DMPC, dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine; DOTAP, 1,2-dioleoyl-3-(trimethylammonium)propane; DC8,9PC, 1,2-bis(10,12-tricosadiynoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; DOPE, dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine; DLinDMA, 1,2-dilinoleyloxy-3-dimethylaminopropane; DSPE-PEG-MAL, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-[maleimide(polyethylene glycol)-2000]; PEG200-DMG, polyethylene glycol-2000-dimyristoyl glycerol. |
| Liposomes |
SPC, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG2000 |
Honokiol and disulfiram-copper complex |
Activation of macrophage, DCs, T cells, NK cells, immunogenic cell death, anti-tumor immunotherapy against glioblastoma. |
162
|
| Phosphatidylcholine, DSPE-PEG carboxy, CSF1R-inhibiting amphiphile |
Anti-PDL1 and BLZ945 (CSF1R-inhibitor) |
Anti-cancer immunotherapy |
160
|
| HSPC, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG2000 |
Ursolic acid |
Immunomodulation and anti-cancer immunotherapy |
161
|
| Cholesterol, phosphatidylcholine, DPPE, rhodamine red-labelled DPPE |
siRNA |
NK cell-targeted anti-tumor therapy |
163
|
| DSPE |
Methotrexate |
Anti-inflammatory drug delivery in the treatment of atherosclerosis |
164
|
| DOTAP, DMPC, DSPE-PEG |
siRNA |
Macrophage modulation, immunogene therapy against staphylococcus infection |
166
|
| (DC8,9PC), DSPE-PEG2000 |
Dexamethasone |
Anti-inflammatory drug delivery in the treatment of RA |
165
|
| Cationic LNPs |
DSPC, DLinDMA, cholesterol, DSPE-PEG-MAL |
siRNA |
DC-targeted siRNA delivery |
45
|
| DOTAP, PEG5000-block-PLGA11000 |
siRNA |
T-cell modulation and anti-cancer immunotherapy |
167
|
| AMPA-O16B, DOPE, DSPE-PEG2000, cholesterol |
Shigella bacteria-derived effector OspF |
Macrophage modulation in anti-cancer therapy |
168
|
| Amino lipid (lipid D), cholesterol, DSPC, DMG-PEG2000 |
Dengue envelope proteins (DEN-80E) |
Vaccine delivery and immunostimulation against dengue |
169
|
| DODMA, DSPC, DMG-PEG |
mRNA |
Immunomodulation |
170
|
| SLNs and NLCs |
Stearic acid, lecithin, poloxomer-188 |
Paclitaxel |
Immunomodulation in melanoma |
171
|
| Naringenin and linolenic acid |
Cyclosporin |
Immunosuppressive drug delivery in psoriasis |
172
|
| Cetyl palmitate, polysorbate-60 (Tween-60), miglyol-812 |
Resveratrol |
DC-targeted anti-inflammatory drug delivery and immunomodulation |
173
|
| DOTAP, Span, Tween-80, Squalene, dynasan114 |
Zika virus antigen encoding viral RNA |
Zika vaccine delivery |
174
|
| Ethosomes |
Lecithin, cholesterol, octadecyl amine |
Tyrosinase-related protein-2 (TRP-2), CpG, mRNA, siRNA delivery |
DC stimulation in tumor immunotherapy |
175 and 176 |
| Cubosomes |
Phytantriol, propylene glycol, Pluronic F127 |
Immunostimulant polysaccharide (PS) obtained from Ganoderma lucidum |
DC activation, T-cell modulation |
177
|
|
Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide (ABS), Monooleate, Pluronic F127 |
ABPs delivery |
Immunomodulation |
178
|
3.6. Biologic NPs (BNPs)
The BNPs are naturally obtained NPs that are formed in various biological systems. These BNPs are composed of different organic and inorganic materials and can be intracellular as well as extracellular in origin. Among the different BNPs, exosomes, viruses and virus-like particles (VLPs), ferritin, magnetite, etc., are widely used in the delivery of therapeutics (Table 5). The structural uniformity, immune system encompassing capability, and lower level of toxicity make them a suitable candidate for drug delivery applications.60 Exosome nanovesicles are secreted by most cells (endothelial cells, adipocytes, B cells, DCs, neurons, mast cells, tumor cells, etc.) and are also found in several bodily fluids such as saliva, plasma, breast milk, amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, etc.179,180 Individual exosomes can elicit both positive and negative immune responses. Particularly in multiple cases of cancer immunotherapies, the exosome-based nanomedicines have greatly evolved. The chimeric antigen receptor-T cell (CAR-T) cell-derived CAR-exosomes are known to express cytotoxic signal molecules that can be useful in triggering anticancer immune responses. Unlike CAR-T cells used in CAR-T therapy, the CAR-exosome nanovesicle does not possess programmed cell death protein (PD1) and is relatively safe to use. Thus, the use of CAR-exosome reduces the risk of slackening of anti-tumor efficacy during recombinant programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) therapy of cancer.181 DC-targeted exosome-based vaccines represent a novel strategy in immunogenic cell death therapy. The surface-modified exosomes loaded with antigen and adjuvant exhibit promising results in DC activation and subsequent modulation of the tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells.182 Exosome nanovesicles of different cellular origins display bystander activities on macrophage polarization. Repolarizing the tumor-associated macrophages by macrophage-derived exosomes has become a new tool in antitumor immunotherapy. M2 macrophages assist in tumor progression by releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines and angiogenic factors. Thus, macrophage transition from the M2 to M1 phenotype is essential to release proinflammatory cytokines, thereby eliciting anti-tumor immune responses. In this regard, M1 proinflammatory macrophage-derived exosome NPs were successfully used as a therapeutic agent to repolarize the M2 macrophage into the M1 phenotype that effectively restricts tumor progression.183 On the other hand, it is interesting that exosomes from olfactory ensheathing cells have also been shown to suppress proinflammatory macrophages.184 Thus, the specific-cell-derived exosome repolarizes the M1 macrophage into an anti-inflammatory M2-phenotype and plays excellent immunomodulatory roles in the therapy of neuroinflammation. In the prevention of autoimmune uveitis, specific circulatory exosomes were used as direct anti-inflammatory nanotherapeutics to reduce the disease-relevant inflammatory immune mediators.185 Viruses and VLPs are nanostructured non-pathogenic BNPs that are resistant to temperature and pH and have emerged as highly efficient vaccine delivery tools. The non-pathogenic viruses and genetic material-free viral capsid protein-based VLPs possess a striking ability to elicit immune responses. Particularly, these BNPs act as engineered nanovaccines in cancer immunotherapy, where they can solely or in association with therapeutic immunogens provoke anti-tumor immune responses by recruiting immune cells and elevating the level of cytokines.186–188 Ferritin BNPs are protein nanocages found in the biological systems of eukaryotes, bacteria, and archaea that have evolved mainly to store iron species. Recent studies claimed that ferritin BNPs could meet the need for novel antiviral vaccines. The ferritin NPs obtained from diverse viral and bacterial sources exhibited antiviral immune responses against the pandemic SARS-CoV-2 virus.189 Moreover, the ferritin BNPs are also found to act as potential vaccine delivery agents against viral infections caused by hepatitis virus C, HIV-1, and other viruses.190,191
Table 5 List of BNPs used for immunotherapeutic applications
| Types of BNPs |
Source of origin |
Therapeutic payload |
Therapeutic application |
Ref. |
| Exosomes |
Serum of hypopharyngeal cancer patients |
|
CD8+ T-cell suppression, hypopharyngeal cancer immunotherapy. |
192
|
| Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells |
Ag/anti-CD64 antibody complex |
Suppression of polymorphonuclear neutrophils in the treatment of asthma. |
193
|
| Cancer cells |
Chlorin e6 |
Immune stimulation in cancer immunotherapy. |
194
|
| Dendritic cells |
TGF-β1 cytokine |
Immunomodulation in the treatment of inflammatory lung diseases. |
195
|
| Olfactory ensheathing cells |
|
Pro-inflammatory macrophage suppression, immunomodulation in treatment of spinal cord injury. |
184
|
| Viruses and VLPs |
Alfalfa mosaic virus |
|
Immune stimulation via recruitment of immune cells and increasing cytokine level in cancer immunotherapy. |
187
|
| Cowpea mosaic virus |
|
Anti-tumor immunotherapy. |
186
|
| Hepatitis B virus |
OVA-antigen, gp100-antigen |
DC maturation, T-cell stimulation in anticancer immunotherapy. |
188
|
| Ferritin |
SARS-CoV-2 Spike-protein(S), S1, and RBD domain |
|
Immunization against SARS-CoV-2 virus. |
189
|
| Engineered human ferritin |
CpG ODNs |
Tumor-associated M2 macrophage-targeted therapeutic delivery for cancer immunotherapy. |
196
|
|
Helicobacter pylori-derived ferritin |
Recombinant soluble E2 subunit |
Immunization against hepatitis C virus. |
190
|
|
Heliobacter pylori-derived ferritin |
HIV-1 envelope proteins |
Immunization against HIV-1 virus. |
191
|
4. Key immune components and their modulation with therapeutic nanoplatforms
As the immune system plays a complex role in the pathogenesis of several diseases like allergic rhinitis (AR), RA, cancer, multiple sclerosis, HIV, and other viral infections, significant attention has been paid to the discovery of novel immunotherapeutic nanomedicines to restore physiological normalcy. In various human disorders, T cells, B cells, DCs, macrophages, and complement components of the immune system play bystander roles where aberrant immune activities are directly associated with poor disease prognosis. Hence, various immunomodulators (activators and suppressors) can be delivered to re-establish optimal immune responses by selectively targeting the immune components using novel nanomedicines. Specifically, in the treatment of autoimmune diseases like RA, type-1 diabetes mellitus, and allergic inflammation, the autoreactive immune cells can be suppressed, while therapeutic NPs have also been used to activate the immune cell responses during the treatment of cancer and other immunosuppressive diseases.
4.1 Nanotherapeutics for targeting T cells
T cells are one of the centrally important cells of the immune system and play critical roles in regulating normal immune responses. This dynamic effector cell coordinates with other immune components for the detection and encounter of antigens and other foreign invaders. Researchers have been manipulating T cells to eradicate several immune disorders. The engineered NPs are either conjugated or encapsulated with therapeutic agents that are delivered to T cells by targeting T-cell receptors (TCRs). Modulating T cells has therapeutic consequences, leading to the remission of immune disorders.
4.1.1. Nanotherapeutics in activation and recruitment of T cells.
Multiple immune disorders, ranging from viral to cancer, are characterized by diminished activity of T cells. Hence, activation of T cells is necessary to deal with suppressed or compromised immunity and is a key strategy for the restoration of effective immune activities. For instance, in cancer, T cells are greatly affected due to the presence of different inhibitory signals in the TME. The reasons behind poor T-cell activities are inhibitory receptors present on abnormal T cells, inhibitory cells in the TME, immunosuppressive mediators, etc. Specific activation of T cells represents a targeted and precise modality in the clinical settings of antitumor immunotherapy. Activation of T cells directly, or supply of genetically modified engineered T cells from an external source pave the way for the restoration of T-cell functionalities.197,198 PD1 and its predominant form, PDL1, are the immune checkpoints associated with the phenomenon of tumor-immune tolerance. The induction of immunological tolerance leads to poor infiltration of cytotoxic T cells, causing the TME to be immunosuppressive in nature, which subsequently results in the failure of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. Blocking the PD-1/PDL1 protein with an anti-PDL1 antibody and subsequent elicitation of antigen-induced recruitment of T cells in tumor tissues has become an effective approach for fighting against cancers.199 The anti-PDL1 antibody assembled NPs was developed to achieve T-cell targeted therapeutic cargo delivery. The engineered antibody nanoplatforms, loaded with TME-responsive peptides and antigen-generating species, abrogate immunological tolerance and accelerate greater T-cell infiltration in the TME to deplete the cancer cells.199 The surface of T cells expresses the costimulatory receptor OX40 and PD-1 receptor, which can be significant targets for activation of T cells.200 Administration of agonistic antibodies aOX40 and aPD-1 individually or in combination showed activation of T cells but at a sub-optimal level. Hence, dual antibody (aOX40 and aPD-1) delivery is necessary to synergistically activate a large population of T cells. With the help of thiol-maleimide chemistry, conjugating the aOX40 and aPD-1 antibodies on the surface of poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG-PLGA) NPs provided the formation of stable antibody co-delivery nanoplatforms that confer greater T-cell activation, improved therapeutic efficacy, and immunological memory.200 Apart from OX40 receptor modulation, the stimulation of Toll-Like receptors 7/8 (TLR7/8) receptors in T cells by external agonists is a key strategy to activate the T-cell population. PD-1 positive T cells are also characterized by immunosuppressive TGFβ cell signalling, and their blockade prevents the establishment of an immune-deficient cold TME. Hence, the co-administration of a TGFβ inhibitor (SD-208) and a TLR7/8 receptor agonist (R848 or resquimod) via antibody-modified NPs enables precise targeting and activation of T cells.53 The anti-PD-1 F(ab′)2 antibody fragment-modified PEG-PLGA NPs loaded with SD-208 and R848 significantly target the PD-1-positive T cells. The T-cell-specific targeted co-delivery of immunomodulatory agents ensured a higher accumulation of therapeutic cargos that expanded the activation of CD8+ T cells.53 The direct application of therapeutic nanoscale artificial antigen-presenting cells (naAPCs) is a new approach that has been employed in the activation of T cells. Mechanistically, to activate the T cells, aAPCs act on several cellular and molecular components, such as MHC-I/T-cell receptor stimulation, CD80/CD28 costimulatory signaling, and cytokine release. The T-cell activation potential of nano aAPCs is relatively less than that of micro aAPCs, which can be a therapeutic barrier in this strategy. Hence, antigen-based pre-activation of CD8+ T cells and subsequently inducing high redox potential augments the T-cell activation efficacy of nano aAPCs in a size-convertible manner. The pre-activated CD8+ T-cell-mediated redox potential converted the nano aAPCs into highly efficient micro aAPCs at the tumor site and significantly activated the CD8+ T cells201 (Fig. 2). The poor efficacy of triggering T-cell activation in the regression of tumor growth is observed in vaccine-monotherapy treatment modalities. Thus, vaccine efficiency can be accelerated by promoting the activation of T cells by employing adjuvant nanotherapeutics. In combination with vaccine antigen, the polymeric cationic NPs act as adjuvants to increase the immunogenicity of the administered vaccine, thereby recruiting a greater population of tumor-associated antigen-specific CD8+ T cells.202 Since specific surface antigen receptors expressed by cancer cells are recognized by the TCRs that aid in directing T cells toward specific cancer cells, the insufficient expression of cancer cell-recognizing receptors fails to effectively eliminate the cancer cells. Hence, CAR T-cell therapy has emerged as a tremendous strategy to target cancer cells by modulating the activity of T cells. The gene encoding the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) can be successfully transported to the T cells by NPs, where specific releases of cargo genes express CARs on T cells and enable them to reach cancer cells for effective elimination. Smith et al. employed biocompatible and biodegradable poly(β-amino ester) NPs in the delivery of CAR genes to T cells.203 To achieve T-cell-specific therapeutic cargo gene delivery, the NPs were surface-modified with anti-CD3eF(ab′)2 antibody fragments by means of electrostatic interaction. Furthermore, the modification with microtubule-associated sequence and nuclear localization signals conferred microtubule-mediated uptake and nuclear transport of genetic cargo to T cells, respectively.203 Similarly, in an alternative approach, NP-based bispecific T-cell engagers, or nanoBiTEs, were developed as nanotherapeutic platforms that interplay between T cells and cancer cells for better T-cell recruitment.204 The liposomal NPs were decorated with anti-CD3 antibodies for T-cell-specific binding and conjugated with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to bind to tumor-associated antigens (TAAs). Thus, the nanoBiTEs with dual functionality served as a linker or engager to redirect the T cells toward the antigen-displaying cancer cells. Despite being great tools for targeted activation and recruitment of T cells, nanoBiTEs and CAR-T therapeutic strategies are facing several limitations. The cancer cells might express multiple TAAs, where only targeting the monotypic antigen is a major limitation associated with both CAR-T and nanoBiTEs therapies. To overcome the limitations associated with CAR-T and nanoBiTEs therapies, the researchers have developed NP-based multi-specific T-cell engagers (nanoMuTEs).204 First, nanoliposomes were decorated with a variety of mAbs to bind with multi-antigenic receptors present on cancer cells, and then further modification of the liposomes with mAbs (anti-CD3) governed T-cell binding. Thus, target-specific multiple antibody-conjugated nanoMuTEs not only targeted multi-antigenic cancer cells, but also inhibited the progression of antigen-less tumors. Hence, the novel nanotherapeutic system showed higher activation of CD4+/CD8+ T cells and could be a potential solution in clinical settings of cancer immunotherapy.204
 |
| | Fig. 2 Schematic illustration demonstrating nanosized artificial antigen-presenting cells (naAPCs) for immunotherapy. (a) Nanoparticles (NPs) self-assembled from copolymer PEG-PDMA-PDPA could elicit host immunity in EG7-OVA tumor-bearing mice. NP encapsulated with OVA DOX, or HPPH (NP-drug) acts as nano-vaccines. This NP-drug induces immunogenic cell death (ICD), promotes maturation of dendritic cells (DCs), antigen processing, and T-cell presentation. This ultimately leads to activation of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells and infiltration into tumor tissue. (b) Scheme representing formation of IL-2-loaded size-transformable naAPCs through self-assembly of copolymer biotin-PEG-PHPMA(-SH)-PDMA. The surface of naAPCs is decorated with peptide-loaded MHC (pMHC) monomer and αCD28. High redox potential on preactivated antigen-specific T-cell surface results in cleavage of disulfide bonds of naAPCs into thiols. As a consequence, conversion of naAPC from nanosize to microsize leads to the formation of an aggregate in tumor tissue due to its large size, while secreting IL-2 to enhance immune response. Reproduced with permission from ref. 201, Copyright 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science. Abbreviations used: PEG-PDMA-PDPA polyethylene glycol-block-poly(2-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate)-block-poly(2-diisopropylaminoethyl methacrylate). | |
Modulation of immune components has become an urgent survival option for an individual suffering from the COVID-19 viral infection. Activation of different T-cell subsets and eliciting strong immune responses against COVID-19 by specific antigens could be an immune-protective, life-saving strategy. Engineered mRNA-loaded LNPs were chosen as novel nanotherapeutic vaccines to provoke strong immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 infection.205 The safe and well-tolerated LNPs precisely delivered genetic information encoded within the mRNA cargo. The released mRNA expressed receptor-binding domains of the COVID-19 viral spike protein, which subsequently activated CD4+, CD8+, and favourable helper type-1 T-cell (Th1) subsets. Hence, the activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells facilitated the establishment of prolonged immunological memory, which helped in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 viral disease.205
CD8+ T cells are superior immune cells that ensure protective immunity against viral diseases caused by the zika virus (ZIKV), dengue virus (DENV), and others. Although various antibody-inducing vaccines are used in immunotherapeutic paradigms, their suboptimal antibody response necessitates alternative and more potent immunotherapeutic platforms. Activating the CD8+ T cells with nanovaccines is one of the major strategies to fight against these deadly viruses. Recent study revealed that the NP-based delivery of antigen-expressing replicon RNA induced CD8+ T cells significantly and prevented the fatality caused by ZIKV infection.206 Activation and expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) have shown great clinical significance in controlling autoimmune diseases. Since autoreactive T cells play pathogenic roles with deleterious outcomes against the body's own immune system, targeting the vicinity of autoreactive T cells could be an effective approach for halting disease progression. Ligating the TCRs present on cognate T cells with an external peptide-based major histocompatibility complex (pMHC) can result in the activation and expansion of immunoregulatory Tregs via TCR-pMHC interaction. Considering this molecular event, the administration of pMHC-decorated NPs showed promising results in the differentiation of disease-driving autoreactive T cells into Tregs.207 Other than TCRs, aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AhRs) are highly expressed by several immune cells and could be a potential target to promote a greater Treg population. This could be achieved by antigen-specific immune tolerance induction and the promotion of AhR signaling. The co-delivery of AhR agonist ligand and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)35–55-derived T-cell epitope led to myelin-specific T-cell modulation and facilitated anti-inflammatory tolerogenic gene expression. However, the biodegradation and clearance of therapeutic agents limit the treatment efficacy when co-administered freely. Hence, LNPs were successfully deployed in the protective delivery of therapeutic AhR-agonist and (MOG)35–55 T-cell epitopes at a time when the concurrent delivery of encapsulated therapeutic cargos exhibited a greater number of Forkhead box protein P3 (Foxp3+) Tregs and type-1 Tregs.208 Thus, the nanomedicine-assisted activation and expansion of Tregs could be a life-saving approach for the treatment of autoimmune disorders.208 Foxp3+ Tregs also play pivotal roles in maintaining atheroprotection; therefore, elevating the level of Tregs could be a therapeutic option in the regimen of cardiovascular immunotherapy.209 The modulation of vitamin D nuclear receptor (VDR) in tolerogenic DCs is a potential therapeutic target to promote greater proliferation of Tregs. In this context, the application of synthetic anti-inflammatory drugs to modulate VDR has been explored to induce disease-preventing Tregs. However, a lower therapeutic index is a major limiting factor associated with systemic administration of these agents, which ultimately fails to recruit an efficient level of Tregs. Hence, micelle NPs have been engaged in the delivery of VDR-modulating anti-inflammatory drugs to obtain a greater therapeutic index. The micelle-assisted sustained delivery of immunomodulatory drugs maintained high levels of Foxp3+ Tregs in atherosclerotic lesions as well as in lymphoid organs, and enhanced cardioprotectivity.209
4.1.2. Nanotherapeutics in T-cell suppression.
The autoimmune diseases are characterized by hyperactivation of the body's own effector T cells that leads to loss of self-tolerance, and self-organ and tissue damage. Inhibiting the autoreactive CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses could be a beneficial therapeutic approach for inducing immunological tolerance. Several antigen-specific immunotherapies have been followed to modulate T-cell activities, but exacerbation of already existing inflammatory events is a potential risk associated with antigen-based immunotherapy. Thus, the development of tolerogenic NP-based therapeutics with the ability to co-deliver antigen and immunosuppressive agents can dampen the risk factors associated with antigen-based immunotherapies. The application of tolerogenic NPs has shown excellent ability to inhibit activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells as well as suppress anti-drug antibody responses, which can prevent autoimmune diseases.210 Leveraging the fact that immune cells possess preferential uptake of NPs, the T-cell favoured the preferential uptake of PEG-modified antioxidant hydrophilic carbon nanoclusters (PEG-HCC) and showed therapeutic efficacy in the management of autoimmune encephalomyelitis.211 The antigen-mediated pre-stimulation of T cells showed preferential internalization of antioxidant carbon NPs, which in turn promoted ROS-species scavenging and reversibly inhibited T-cell proliferation.211 The autoimmune CD8+ T cells are known to have β-cell destructive properties that lead to severe pathogenicity in type-1 diabetes mellitus. Thus, the inhibition of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells is necessary to halt the disease progression. The cocktail of HLA-A*02:01-restricted epitopes decorated on NPs exhibited clinical induction of antigen-specific immune tolerance.212 The epitope peptide carrying therapeutic NPs introduced T-cell tolerance mainly by promoting the activity of Tregs like CD4+CD25+, CD4+Foxp3+, and the release of anti-inflammatory IL-10 cytokines that collectively ablate cytotoxic T-cell proliferation.212 Similarly, autoimmune CD4+ T cells are also found to be involved in the pathogenicity of type-1 diabetes and could be potentially targeted for the induction of immune tolerance. In the induction of tolerogenic responses, the hybrid insulin antigen-loaded tolerogenic NP has gained attention due to its impaired ability to inhibit T-cell activities. The tolerogenic NPs act on Tregs to foster their proliferation. As a result, in comparison with cytotoxic IFN-γ+ effector T cells, a greater population of immunoregulatory Foxp3+ Tregs was inducted by tolerogenic NPs.213
Primary biliary cholangitis is an autoimmune disease where CD8+ T cells play pathogenic roles and essentially need to be suppressed to prevent disease severity. The effective delivery and subsequent cross-presentation of peptide auto-antigens to MHC-I complexes that are expressed on cholangiocyte cells could be an effective approach for aborting the infiltration of pathogenic T cells in the liver. The ovalbumin peptide SIINFEKL antigen-modified NPs were successfully used to deliver the tolerogenic peptide antigen to liver cells that were consequently cross-presented by the MHC-I complex.214 As a result, the antigen–peptide nano-assembly downregulated the infiltration of autoreactive T cells into the liver, thereby protecting the liver from being damaged by cytotoxic T cells214 (Fig. 3A & B). A greater population of T cells has also been implicated in hypersensitive allergic contact dermatitis. Previous studies revealed that the topical application of negatively charged SiNPs can alleviate inflammatory allergic dermatitis by reducing the high level of CD3+ and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. Hence, the low-dose topical application of negatively charged SiNPs acts as an immunomodulator and decreases cytotoxic T-cell infiltration and inflammatory cytokine production.215 The helper T-17 (Th-17) cells are another subset of T cells that play pathogenic roles in the development of chronic inflammatory psoriasis. The enhanced differentiation of native CD4+ T cells into pro-inflammatory cytokine (IL-17) producing helper T-17 cells drives strong inflammatory responses. Particularly, intracellular ROS-species-mediated stress conditions in skin keratinocytes promote high differentiation of native CD4+ T cells into helper T-17. Hence, halting the differentiation and proliferation of IL-17-producing Th-17 cells from their native T cells could be an effective strategy in the management of psoriasis. Endogenous bilirubin-based NPs have shown the potential to scavenge intracellular ROS species, therefore reducing intracellular stress levels. Thus, topical administration of PEG-modified bilirubin NPs (BRNPs) acted as an immunomodulator that dampened the activity of pathogenic Th-17 cells and attenuated the proinflammatory events216 (Fig. 3C). The hyperactivity of pathogenic Th-17 cells is also directly linked with the progression of RA. Therefore, suppressing the IL-17-releasing Th-17 cells can also provide beneficial effects for the treatment of RA. The researchers claimed that targeting the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signalling pathway by delivering antioxidant CoQ10 or ubiquinone can block the inflammatory activities of Th-17 cells.217 Hence, the immunotherapeutic hybrid NP-loaded CoQ10 delivery downregulates the IL-17 level and reduces Th-17 cell-mediated inflammation.217 SLE is a fatal autoimmune disorder characterized by higher infiltration of pathogenic T cells, autoreactive antibody production, and loss of self-tolerance. Altered Ca2+ signalling has also been implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE, where elevated Ca2+ levels affect T-cell receptor signalling with deleterious autoimmune responses.56 The voltage-gated potassium Kv 1.3 channels that are greatly expressed by activated effector Tm cells play a crucial role in maintaining Ca2+ balance via regulation of membrane potential. Targeted depletion of potassium Kv 1.3 channels with therapeutic NPs enables the correction of autoreactive immune responses in the treatment of SLE. Khodoun et al. developed a novel nanoplatform that disrupts Ca2+ signalling by selectively downregulating the potassium Kv 1.3 channels of CD8+ effector Tm cells. Thus, targeted depletion of potassium ion channels shows an effective reduction in Ca2+-mediated T-cell stimulation, CD40L, and IFN-γ levels that collectively alleviate the disease progression.56
 |
| | Fig. 3 (A) Pictorial representation of SIINFEKL-decorated nanoparticle (NP) and its cellular uptake: (a) Illustration of SIINFEKL peptides covalently conjugated to NP, having a monodisperse iron oxide or quantum dot core of about 7 nm diameter; (b) NP uptake in liver sinusoids (red fluorescent quantum dot core) at t = 0 min and 5 min post-tail vein injection. Images captured and assessed by intravital microscopy. (B) SIINFEKL peptide-loaded NP prevents CD8+-mediated autoimmune cholangitis in K14-OVAp mice; (a) percentage change in body weight at day 5 compared with weight at the time of OT-1 T-cell transfer; (b) Severity of autoimmune cholangitis at day 5; (c and d) Serum levels of liver enzymes: alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST); (e) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of CD45.1+ liver-infiltrating OT-1 cells (pink fluorescence) and CK19+ cholangiocytes (green fluorescence) shows reduced infiltration of autoreactive T cells. Reproduced with permission from ref. 214, Copyright 2021, John Wiley & Sons. (C) Schematic representation of PEGylated bilirubin nanoparticles (BRNPs) and their proposed mechanism of action in psoriasis. Oxidative stress, due to redox imbalance, leads to production of ROS and inflammatory mediators and autoantigens mediated through epidermal keratinocytes. This increases the recruitment and maturation of APCs, which further activates differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells to Th1 and Th17 cells in skin lesions and lymphoid organs. Subsequent release of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) or IL-17 results in aberrant proliferation of keratinocytes. The use of BRNPs helps in mitigating the ROS production and activation of APCs through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory action. Reproduced with permission from ref. 216, Copyright 2020, Elsevier. | |
4.2. B-cell targeting nanotherapeutics
B cells are the antibody-producing lymphocytes that serve humoral immunity in the body. To maintain an appropriate immune balance, the activity of B cells can be harnessed in different ways. In the treatment of several immune disorders, B cells need to be activated, while in other cases, B-cell activities are essentially required to be downregulated.
4.2.1. B-cell activation.
The activation of B cells and the generation of effective broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs) is one of the central strategies for developing vaccines against multiple diseases. The use of NPs offers several advantages in the design and development of effective vaccines that can target the immune system and facilitate the activity of B cells. Hence, researchers are striving to develop effective nano-vaccines by loading different immunogens in NPs. Depending on the properties of loaded immunogens and nanomaterials, therapeutic nano-vaccines exhibit varied levels of B-cell stimulation to trigger antibody responses. Following the fact that disease-relevant antigen species can activate B cells, several approaches have been made for developing anti-HIV vaccines. The HIV-1 envelope trimeric protein fragments are considered as strong immunogens to induce antibody responses by activating B cells.218 The administration of free and soluble protein antigens often fails to provoke significant B-cell activation. To overcome this limitation, Ni2+ ion-bound liposomal NPs surface tethered with histidine-tagged HIV-1 spike protein trimers were developed as novel nano-vaccines that strikingly stimulate B cells.218 As a result, a strong elevation in neutralizing antibody (nAb) level was generated by the stable VLP nano-vaccines as compared with their bare protein antigen counterpart (Fig. 4). Hence, controlling the stability of trimeric antigens displayed on liposomal NPs is crucial for their immunological impacts on the host. The covalent attachment of viral immunogen spike protein onto the NP surface provides higher stability to the immunogens and, therefore, helps in obtaining the long-term clinical efficacy of the nano-vaccine. Besides antigen, the sphingomyelin constituents of the LNPs also contribute to immunogenicity and can synergize the activity of nano-vaccines to stimulate germinal center B-cell response and antibody production to encounter HIV strains.219 Similarly, a study has been carried out with HIV envelope protein-conjugated ferritin NPs that also demonstrated the anti-retroviral efficacy of particulate nano-vaccines over the soluble free-form of antigens.220 In another study, Moyer et al. demonstrated direct activation of B cells and production of bnAb with the help of modified HIV envelope protein-decorated NPs.221 The engineered eOD immunogen (outer domain of the HIV-1 glycoprotein-120), tethered on the surface of NPs, promoted direct internalization by B cells, thereby displaying better antigen processing, antigen presentation, and enhanced activation efficiency of B cells.221
 |
| | Fig. 4 (A) Pictorial representation of liposomes decorated with HIV-1 trimer spike. Magnified part illustrates binding of the 6-histidine repeats (His6 tag) present as a fusion on the C terminus of each protomer within each trimer to the Ni + 2 chelated at the hydrophilic head group of the DGS-NTA(Ni) polar lipid. (B) Schematic representation of activation of B cell using liposome decorated with HIV-1 trimer spike. Liposome conjugated with HIV-1 trimer spike leads to enhanced B-cell activation as compared with soluble factor. Reproduced with permission from ref. 218, Copyright 2016, Elsevier. | |
The activation of B cells and subsequent release of bnAbs could be the same method of molecular intervention for protection against deadly strains of influenza. The immunogenic properties of multiple viral protein fragments are harnessed to develop nano-vaccines with the ability to activate B cells and trigger the generation of bnAbs. Previous studies demonstrated that the extracellular domain of ion channel matrix membrane protein 2 (M2e) of influenza virus A exhibits immunogenic properties but has limited efficacy in inducing significant immunological responses. The combination of soluble adjuvant CpG oligonucleotide and M2e-peptide antigen produces a several-fold increase in immune stimulation by eliciting greater antibody responses. Thus, the AuNPs arrayed with M2e-peptide and CpG adjuvant on their surface offered superior activation of B cells, therefore producing broad-spectrum antibody responses against several strains of influenza, such as H1N1, H5N1, and H3N2.222 Targeting the B-cell receptors (BCRs) with ligand antigens is another advanced strategy employed in the activation of B cells. Haemagglutinin (HA) antigen fragment obtained from the influenza virus acts as an immunogenic ligand that binds to sialic acid residues of BCRs. The coupling interaction between ligand-HA and sialic acid target residues of BCRs leads to significant activation of B cells.223 Thus, several novel approaches have been attempted for developing HA-displaying NPs that can recognize the BCRs and exhibit strong antigen-specific immune responses against influenza infection. Following this rationale, recombinant gene-expressed HA-arrayed ferritin NPs have emerged as novel nano-vaccine candidates for protection against influenza. The highly ordered intact HA-ferritin nano-vaccine showed strong germinal center stimulation as well as direct activation of B cells via receptor ligand coupling interaction.224 The effective stimulation of BCRs consequently results in a higher level of nAb production. However, instead of displaying homotypic HA antigens, the colocalization of heterotypic antigens confers superior qualitative and quantitative B-cell activation and broad antibody responses. The engineered gene construct-encoded mosaic heterotypic HA-decorated immunotherapeutic ferritin NPs showed excellent cross-reactive antibody production. Hence, the multipronged immunogenicity of mosaic NPs shows significant neutralization of the H1N1 strain of influenza virus.225 Formation of germinal centers (GC) and activation of B cells are necessary for a robust antibody response in protective immunity against hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The surface protein originated in the preS1-domain of HBV and is known for its immunogenic properties that can be utilized to activate B cells in anti-HBV immunotherapy. Recent studies revealed that the concurrent delivery of antigen into DCs and lymphatic macrophages strikingly enhanced B-cell activation in coordination with follicular helper T cells.226 Hence, the ferritin NPs displaying preS1 surface functionalization targeted dual cells and elicited a robust antibody response against HBV.226
4.2.2. B-cell suppression.
Malfunctioning of B cells often leads to the initiation and progression of diseases ranging from autoimmune to inflammatory disorders. To protect the internal organs and tissues of the body, autoreactive B-cell-driven activities need to be downregulated. Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) characterized by pathogenic expressions of BCRs. Inhibition of BCRs is of great clinical significance for halting B-cell lymphoma progression.227 CD38 is a BCR found to be overexpressed on MCL B-cells and is correlated with the expansion of B-cell malignancy. Targeting CD38 receptors with anti-CD38 antibodies holds great promise for the remission of B-cell lymphomas. Previous clinical trials with anti-CD38 mAb have also demonstrated the therapeutic efficacy of anti-CD38 mAb, which is quite promising against multiple myeloma cells.228 Therefore, arraying the surface of NPs with anti-CD38 mAbs helps in developing therapeutic nanoplatforms that can be useful in targeting CD38-expressing B cells. Furthermore, to enhance the immunotherapeutic efficacy against MCL B-cells, the mAb-conjugated, therapeutic siRNA entrapped NPs are successfully used to downregulate tumorigenic cyclin D1 biomarkers (overexpressed in MCL).229 Targeting the CD20 receptors of NHL B-cells with clinically approved mAbs like Rituximab (anti-CD20 antibody) often shows antibody resistance. To overcome this therapeutic barrier, Li et al. developed novel NPs conjugated with distinct anti-CD20 mAbs that efficiently target CD20+ B cells.230 The NPs bearing both type I anti-CD20 mAb Rituximab and type II mAb 11B8 led to significant depletion of antibody-resistant B-cell lymphomas230 (Fig. 5A). Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most frequent form of NHL and exhibits greater levels of CXCR4 receptor expression, which could be a potential target for aberrant B-cell depletion. The T22-GFP-H6 protein nano-carrier is known for its selective CXCR4+ B-cell targeting potential. The conjugation of microtubule-targeting agents such as monomethyl auristatin E with T22-GFP-H6 forms a strong nano-assembly that selectively targets the B cells and reduces the disease progression.231 The dysregulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) intracellular signalling cascades often leads to B-cell malignancies. CD19 is an immunoglobulin family-based transmembrane glycoprotein receptor that is strongly expressed by B cells in almost all stages of their maturation. In response to molecular signals, the CD19 receptors establish communication between lymphoid B cells and microenvironments. Selective targeting of CD-19 receptors and subsequent inhibition of MAPK signalling represents an excellent approach for suppressing leukemic B cells. The anti-CD19 antibody-modified NPs, loaded with bacterial lethal factor toxin (MAPK inhibitor), have shown the targeted delivery of cargo toxins to CD19+ B cells and effectively abrogate leukemic B cells232 (Fig. 5B). By secreting autoantibodies and rheumatoid factors, the autoreactive B cells play pathogenic roles in the development of RA. Being an APC, the B cell also promotes the activation of T cells that promote inflammatory cytokine release in the joints of the body. Thus, selective targeting of autoreactive B cells is essential in the treatment of RA. The earlier research findings suggested that the B-cell activating factor receptor (BAFF-R) plays a constructive role in regulating the growth and maturation of B cells. In targeted downregulation of BAFF-R to reduce the population of B cells, RNA interference has become a successful tool in the management of arthritis. Hence, Wu et al. demonstrated that BAFF-R siRNA encapsulated therapeutic NPs protectively deliver cargo into B cells. As a result, the suppression of B cells showed immunomodulation and inhibition of inflammatory symptoms in RA.233 Researchers also found that autoantibodies specific for citrullinated proteins (ACPA) are produced by autoreactive B cells that display pathogenic activities in the development of RA. Hence, ACPA-producing B cells could be another potential target in the prevention of RA. In this regard, therapeutic NPs having both autoreactive B-cell selectivity and B-cell targeted complement-mediated cytotoxic properties can potentially eliminate pathogenic B cells. Fibrin-derived β60-74cit synthetic peptide modification on NPs acts as a specific ligand in recognizing the B cells, while another peptide (derived from gp120 of HIV-1) drives complement-mediated cytotoxicity to eliminate autoreactive B cells. Therefore, dual peptide-modified NPs can be specifically engaged in B-cell-targeted immunotherapies. Activating the complement system of the immune system accelerates the attenuation efficacy of B cells. In this regard, the modified effector peptide gp120 can be used to activate the complement component. Therefore, administration of NPs conjugated with multiple copies of the β60-74cit and gp120 peptides significantly exhibits the targeted depletion of B cells via activation of C5b-9 membrane attack complex.234 Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a non-receptor protein molecule that is critically required by B cells for their growth and development. In several aberrant B-cell immune diseases, the BTK plays pathogenic roles that lead to poor disease prognosis. Some BTK-inhibitor therapeutics are already clinically approved, while others are undergoing clinical trials. To facilitate the efficacy of these BTK inhibitors, researchers are developing smart and targeted nanomedicines that specifically deliver these approved drugs. Thus, dysregulated B-cell targeting and precise delivery of BTK inhibitors have become possible by employing antibody-modified NPs. A recent study demonstrated that different BCR-targeted BTK inhibitors delivered by antibody-modified NPs significantly kill dysregulated B cells. The anti-CD19-modified, drug-loaded NPs bind to CD19 receptors and then deliver the therapeutic cargo intracellularly, while anti-B220-coupled NPs recognize B220 receptors and mediate surface localization of loaded BTK-inhibitors.58
 |
| | Fig. 5 (A) Fabrication and characterization of anti-CD20 nanocluster (ACNC). (a and b) Schematic depiction of nanoclusters; (c) 3 proposed major pathways through which ACNC causes B-cell depletion are complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and induction of programmed cell death (PCD). These effective mechanisms cause suppression of rituximab-resistant non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Reproduced with permission from ref. 230, Copyright 2016, Elsevier. (B) Scheme representing the steps involved in the design and production of the immunoliposome. Lethal factor (LF)-loaded immunoliposome was internalized the cell by the surface receptor CD19 followed by blocked phosphorylation of MAPK pathway. Reproduced with permission from ref. 232, Copyright 2021, Elsevier. | |
4.3. Macrophage-targeting nanotherapeutics
Macrophages exhibit diverse phenotypic variations; generally, two common types of macrophage (M1 and M2) play significant roles during immune surveillance. M1 macrophages are known to have pro-inflammatory responses, while M2 macrophages exhibit anti-inflammatory responses. Upon stimulation, M0 macrophages (resting macrophages) give rise to M1 and M2 macrophages by a process called macrophage polarization.235 Different molecular stimuli influence the specific mood of macrophage polarization, which is ultimately reflected in either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory immune responses.236–238 Thus, targeting the event of macrophage polarization eases the advance of therapeutic intervention against several immune disorders.239
4.3.1. Macrophage activation.
The tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are predominantly present in the TME, where they preferably express into M2-phenotype macrophages. Being anti-inflammatory in nature, the M2 macrophage forms an immunosuppressive TME and promotes the cancer pathology to progress further.238 The greater expressions of TAMs into M2-macrophages resist several anti-tumor immunotherapies, thereby necessitating novel strategies that target the TAMs and polarize them into M1 macrophages. Stimulation of immune cells with clinically approved NPs is considered safe to use in disease therapy. Ferumoxytol, an iron oxide NP formulation, has been approved by the US FDA in the therapy of iron-deficient anemia.135 Previous studies demonstrated that ferumoxytol can modulate and activate TAMs into the pro-inflammatory tumor-suppressive M1 phenotype.135 Particularly, the selective targeting of immunosuppressive TAMs and polarizing into M1 phenotype has always been in demand. CD206, or macrophage mannose receptor 1, is a transmembrane receptor found to be highly expressed in TAMs and could be heralded as a prime target in the specific delivery of therapeutics. Currently, targeted NPs carrying synthetic mRNA drugs have been considered as emerging classes of new therapeutics with superior ability to modulate the activities of M2-directing TAMs without any systemic toxicity concerns. Studies demonstrated that di-mannose-targeting ligand-decorated and in vitro-transcribed synthetic mRNA-loaded therapeutic NPs specifically target the TAMs.240 Hence, targeted intracellular delivery of engineered mRNA expresses interferon regulatory factor 5 and IKK-β kinase proteins that cooperatively modulate the TAMs to convert into anti-tumor M1 phenotypes.240 The SIRP-α receptor on macrophages interacts with the “don't eat me” signal receptor CD47 of cancer cells, thereby inhibiting macrophage-based phagocytosis. Hybrid extracellular nanovesicles (hNVs) characterized by SIRP-α receptor variants showed greater affinity for binding to CD47 receptors and blocked the immunosuppressive CD47–SIRP-α interaction. In combination with a stimulator of interferon gene (STING) agonist, the hNVs disrupted the CD47–SIRP-α interaction axis and activated M1 macrophages by modulating the TAMs, which resulted in the reduction of the immunosuppressive nature of the TME235 (Fig. 6A).
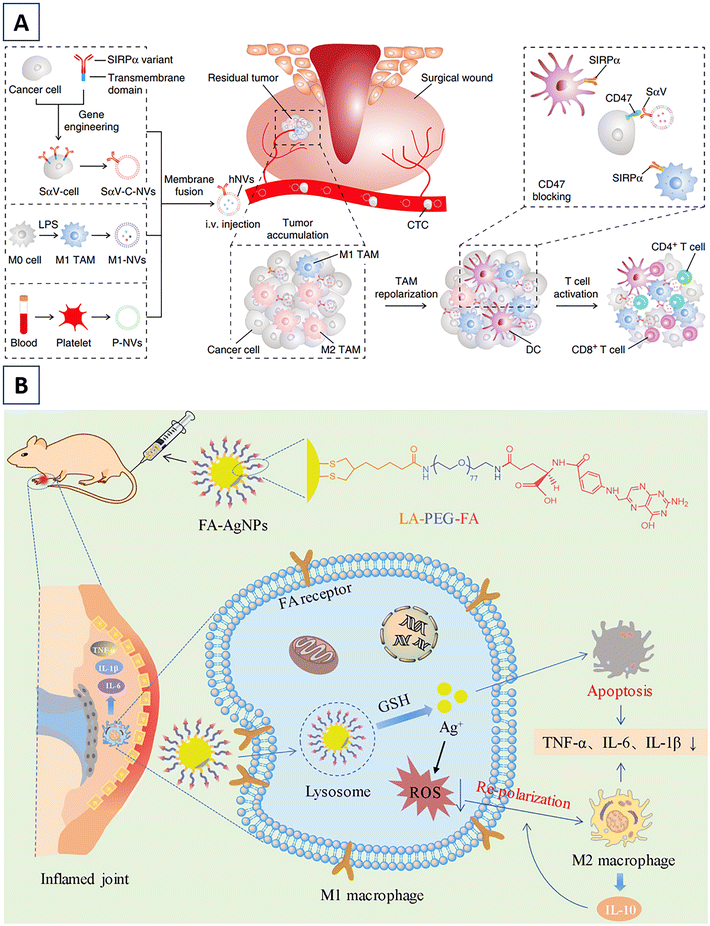 |
| | Fig. 6 (A) Schematic illustration of the hybrid cell membrane nanovesicles (hNVs) comprising engineered cancer cell-derived nanovesicles overexpressing signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα), platelet-derived nanovesicles and M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles. The engineered hNVs, on interaction with circulating tumor cells, accumulate in the post-surgical tumor bed, repolarize tumor-associated macrophages towards M1 phenotype, and block the CD47-SIRPα ‘don't eat me’ pathway for effectively enhancing macrophage-based phagocytosis of cancer cells, as well as promote antitumor T-cell immunity. Reproduced with permission from ref. 235, Copyright 2020, Springer Nature. (B) Scheme representing the mechanism of action of folic acid-modified silver nanoparticles (FA-AgNPs) against rheumatoid arthritis. In response to the intracellular GSH, the developed FA-AgNPs release Ag+ to synergistically induce apoptosis of M1 macrophages and scavenge reactive oxygen species to promote M2 macrophage polarization in inflamed synovial joints. Reproduced with permission from ref. 246, Copyright 2021 Elsevier. | |
The imbalance between two phenotypic macrophages and the higher number of colon-resident M1 phenotypes drives prolonged local tissue inflammation due to its proinflammatory activities. Ulcerative colitis (UC) is an inflammatory disease where higher levels of M1-phenotypic macrophages are associated with local tissue inflammation. Although traditional therapeutics are used to treat UC, the non-specific drug delivery leads to poor therapeutic outcomes. Activation and polarization of anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes in local inflammatory tissues is an effective approach for treating UC. Macrophage membrane-coated biomimetic nanomedicines entrapped with synthetic drugs significantly polarized and activated the M2 phenotype from M1 macrophages.241 β-CD NPs loaded with rosiglitazone exhibited ROS-responsive drug release in epithelial cells of the colon, where inflammation-mediated cellular stress is elevated. Moreover, the macrophage coating on NPs not only mimics to enable infiltration into the inflammatory vicinity, but also absorbs inflammatory cytokines to abolish pathogenic inflammation.241 Activation of macrophages has also been observed in the augmentation of osteogenic differentiation. Mechanistically, stimulating the macrophages releases Oncostatin M (OSM), which acts as a potential inducer of osteoblast differentiation. In this regard, Hirata et al. have illustrated that activating the monocyte-derived macrophages with carbon nanohorns (CNHs) promoted OSM expression and enhanced matrix mineralization by modulating the STAT3 signalling pathway.242 As a result, a greater level of alkaline phosphatase, an osteoblast differentiation marker, has been observed. Hence, CNH-based macrophage activation and release of osteoinductive factors can promote the development of potential regenerative nanomedicines.242
The regenerative or pro-healing properties of M2 phenotypes have been explored in treatment for wound healing. On exposure to external magnetic fields, the superparamagnetic iron oxide NPs (SPIONS) catalyzed M2 macrophage polarization from M1 phenotypes, which resulted in enhanced regeneration and self-healing of wounds.243 Mechanistically, the SPION-based magnetic field-driven M2-macrophage activation promoted better organization of actin filaments and enlargement in cellular topology, therefore enhancing the regenerative functionality of the wounded tissues.243 Immunosuppressed individuals are more prone to fungal infections. Hence, polarization and activation of proinflammatory M1 macrophages could be clinically beneficial for the prevention of fungal infection. Targeting the activation of TLR-4 receptors on macrophages and re-programming the M2 phenotypes into M1 phenotypes can result in significant stimulation of the immune system that provides protective immunity. Recently, Gao et al. developed a novel therapeutic nanoplatform that targets several molecular pathways to polarize the M1 macrophage from its M2 phenotypes.244 Therapeutic NPs coated with mannosylated chitosan polymer specifically activated TLR-4 receptors, where TLR agonist chitosan promoted the M2 to M1 macrophage transition. The mannose modification of NPs confers mannose receptor-mediated selective uptake of imatinib-loaded nanotherapeutics by macrophages. Hence, targeted delivery of imatinib drugs blocked STAT6 signalling and reduced the immunosuppressive M2-macrophage population. Thus, the use of multifunctional NPs accelerated M1-macrophage functionalities and, therefore, stimulated the immune system to fight against fungal infection caused by Candida albicans.244 Previous studies also demonstrated that the internalization of antigen-loaded NPs can greatly activate macrophages and trigger the release of immunostimulatory cytokines. Polymerosome NPs co-loaded with OVA antigen and MPLA adjuvant stimulated macrophage cells. The activation of immune macrophages by dual immunogens triggered the release of potent immune stimulatory IL-6 and TNF-α cytokines that helped in generating strong Ag-specific antibody responses.245
4.3.2. Macrophage suppression.
In some treatment strategies, M1 macrophages need to be abolished to avoid pro-inflammatory immune responses, while suppressing the M2 phenotype leads to immune stimulation in the treatment of immunosuppressive conditions. Although polarizing the TAMs towards M1 macrophages with nanomedicines prevents the immune-suppressive environment found in the TME, direct inhibition of TAMs is another key strategy in re-establishing the immune balance in the TME. Displaying “eat me” signals on the surface of NPs attracts the TAMs for phagocytosis, and this event can be useful in the design of nanotherapeutics to target and deplete the pathogenic TAMs specifically.247 Negatively charged phospholipid phosphatidylserine (PS) naturally acts as an “eat me” signal during apoptosis, and was engineered onto the surface of dasatinib-loaded NPs to promote phagocytosis by macrophages via PS receptor. The internalization of PS-modified nanomedicines by TAMs resulted in the delivery of cargo dasatinib within the macrophages, leading to the depletion of TAMs.247 Local macrophage accumulation and proliferation are observed in the inflammatory pathogenic plaque of atherosclerosis, where mid and large-size arteries are generally affected.248 Additionally, ablation of the macrophages without recruiting monocytes could be an appealing strategy to prevent the prevalence of atherosclerosis. Specifically, delivering statin drugs to atherosclerotic plaque-forming macrophages can help to reduce the inflammatory activities exerted by local macrophages. The administration of biomimetic high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-based NPs loaded with HMG-Co-A reductase inhibitor simvastatin restrained the proliferation of local macrophages by halting the mevalonate metabolic pathway without attracting the blood monocytes.248 Moreover, in combination with oral statin delivery, the administration of simvastatin-loaded HDL NPs prolonged macrophage suppression and curtailed the disease pathology.248
Greater M1-macrophage infiltration and macrophage-mediated proinflammatory autoimmune responses are observed in RA.246 The highly reactive M1-phenotypic macrophages release several proinflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β cytokines, that together aggravate synovial tissue inflammation. The anti-rheumatic AgNPs with folic acid conjugation selectively target M1 macrophages that are characterized by overexpression of folate receptors.246 The selective uptake and reduced glutathione (GSH)-responsive intracellular liberation of Ag+ ions led to M1-macrophage apoptosis, which consequently reduced the level of inflammatory cytokines. In addition to the M1-macrophage apoptosis, the released Ag+ ion also scavenged reactive oxygen species (ROS) in inflammatory tissues to augment M2-macrophage polarization and ameliorate the inflammatory responses in RA246 (Fig. 6B). Other than inflammatory macrophages, bone-resorbing osteoclast cells (OCs) are found to be greatly associated with the persistent pathogenesis of RA.249 These OCs additionally trigger the release of proinflammatory cytokines and exacerbate synovial inflammation. Moreover, both inflammatory macrophages and OCs are known to express high levels of MMP-9 protease in an inflammatory microenvironment that facilitates the severe progression of the disease. Earlier studies have claimed that the αvβ3 integrin receptors are highly expressed by both macrophages and OCs that play a pathogenic role in the development of RA.249 Thus, selective elimination of inflammatory macrophages and bone-resorptive OCs is essential to attenuate the persistent and advanced form of RA. PEG- and RGD-tripeptide-modified PLGA NPs loaded with cytotoxic agents were demonstrated to eliminate macrophages and OCs selectively by targeting integrin receptors. In the RA microenvironment, MMP-9-responsive PEG cleavage and subsequent internalization of RGD-tagged, drug-loaded PLGA NPs occurred by both macrophages and OCs due to the RGD-αvβ3 integrin interaction. Thus, multifunctional NP-mediated dual-targeted delivery of a cytotoxic agent (celastrol) significantly ablated both inflammatory macrophages and OCs in the prevention of RA.249 Specific targeting of synovial M1 macrophages is believed to reduce the pathogenicity of osteoarthritis (OA), which is considered to be another globally prevalent form of arthritis. The abundance of CD16/32 receptors on M1 macrophages is a potential target for the delivery of therapeutics to suppress the synovial macrophages. Due to metabolic dysregulation, the active M1 macrophage releases inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), which catalyzes the biosynthesis of gaseous nitric oxide (NO).57 In turn, NO affects the intracellular O2 level by interfering with mitochondrial respiratory machinery and introducing mitochondrial stress events, thereby leading to the production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and ROS. Targeted metabolic reprogramming of M1 macrophages and suppressing their activity by inhibiting gaseous inflammatory mediators (NO, H2O2) ameliorated the dominance of synovial macrophages. The anti-CD16/32 antibody-modified ZIF-8 MOF-mediated delivery of therapeutics has successfully been employed in the prevention of NO and H2O2 release.57 Synovial macrophages targeting ZIF-8 NPs simultaneously delivered S-methylisothiourea hemisulfate salt (SMT) and catalase (CAT) to reprogram the metabolic events. Intracellular pH-responsive delivery of SMT from ZIF-8 halted the generation of NO by blocking the iNOS, while CAT neutralized H2O2 and facilitated the production of O2. The released O2 also diminished the activity of the M1-polarizing inducer molecule hypoxia-inducible factor α (HIF-α) and inhibited osteoarthritic pathogenic inflammation.57 Being a prime reservoir of viruses, macrophages are also involved in the further spread of viruses to other cellular compartments. The greater antigen presentation and prolonged viral infectivity of CD4/CD8 T cells via interaction between virus-reserved macrophages and T cells possess immunological implications in HIV infection. Hence, the greater reservation of viruses by macrophages in the pre-infection stage sets therapeutic barriers in the way of antiretroviral therapy. Preventing the viral-reservoir macrophages at the pre-infection stage using nanomedicines has shown beneficial therapeutic outcomes for halting the cell-to-cell spreading of viruses. The 2nd generation carbosilane dendrimer, composed of a silica core surrounded by 16 sulphonate moieties (G2-S16), directly suppressed the viruses within macrophages and also inhibited viral spreading from the macrophage to other immune cells.250 Thus, the therapeutic dendrimer NPs exert the ability to inhibit infected macrophage reservoirs and could be used in antiretroviral therapy. Excessive inflammation and multiorgan failure due to proinflammatory cytokine-mediated cytokine storms can result in fatal consequences in patients suffering from the recent pandemic SARS-CoV-2 virus. Virus-infected cells surrounding macrophages release proinflammatory cytokines like IL-6, IL-1β and recruit other immune cells in the lungs, which together lead to the initiation of cytokine storms. The hyperactive macrophage also stimulates the invaded neutrophils to secrete neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) to exacerbate the cytokine storms with more deleterious effects. Preventing macrophages and abolishing cytokine storms is an essential strategy to alleviate the lethal inflammatory immune responses in COVID-19 infection. A recent study demonstrated that macrophage membrane-coated biomimetic NPs, loaded with antiviral drugs, have great potential to inhibit macrophages and arrest the events of cytokine storms.251 The coating of macrophage membrane on NPs absorbed inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and inhibited the actual macrophage population from being activated. The inhibition of macrophages downregulated the secretion of NETs from neutrophils. Moreover, the macrophage membrane-coated NPs, displaying angiotensin converting 2 (ACE-II) receptors, help in specific binding to spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 and deliver the antiviral therapeutics to encounter the viruses.251 Even after recovery from COVID-19 infection, individuals are always at high risk of pulmonary fibrosis (PF). The transition of monocyte macrophages into alveolar macrophages and the release of inflammatory profibrotic cytokines are known to play pathogenic roles in the progression of PF. Interrupting the profibrogenic macrophage transition and abrogating the cytokine release has been proved to be an effective approach for the alleviation of PF.252 The CD206 receptor-expressed profibrogenic macrophage subpopulation targeted NP-based protective delivery of TGFβ1 siRNA and showed promising results in controlling PF. The mannose ligand-modified therapeutic albumin NPs targeted the CD206+ macrophage subsets and effectively delivered therapeutic cargo siRNA, which downregulated the fibrogenic TGFβ1 level to
prevent lung fibrosis.252
4.5. Nanotherapeutics targeting DCs
DCs are another class of key immune cells that regulate immune functions via a subset of mechanisms like antigen presentation and T-cell modulation and, therefore, play a vital role in controlling immune tolerance and autoimmune responses in an organism. Aberrant DC activities are reported in many diseases, like type 1 diabetes, RA, multiple sclerosis, etc. Furthermore, the DC also governs the acceptance and rejection of transplanted tissues in the host. Thus, tuning the activities of tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs) has central importance in the therapy of diseases.253
4.5.1. DC activation.
Targeting the PPRs on DCs is an emerging approach to activate and mature the DCs to induce potent antitumor responses. The DCs express PRRs that recognise different PAMPs on antigens and promote the antigen presentation to trigger immune responses. TLR4 is one of the PRRs found on DC surfaces and is reported to be a prime target for stimulating the DCs. In this context, Rajput et al. developed antigen-loaded inulin acetate NPs to target DCs and stimulate the TLR4 signalling cascades.254 The developed nano-vaccine significantly modulated the activation and maturation of DCs by acting as TLR4 agonist. Moreover, encapsulation of antigen within the NPs resulted in a strong antibody response and an elevated level of immunomodulatory cytokines.254 The application of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) luminogen-coupled upconversion nanoparticles (AUNPs) in regulating the the ROS level in deep tissues made it feasible to restrict tumor growth.255 The high-intensity NIR irradiation directly kills the tumor cells by generating high levels of ROS, while the low-intensity NIR irradiation-based lower-level ROS promotes activation of DCs that induce immunogenic cell death in solid tumors. The initial high level of ROS generation by high-intensity NIR-exposure ablated the tumor cells and released TAA that eventually gets loaded onto administered UCNPs. The TAA-bound NPs were internalized by DCs, and on exposure to low-intensity NIR light the lower ROS production activated the DCs. Hence, the activation of DCs and antigen-bearing NP cross-presentation promoted CD8+ T cells and effectively inhibited tumor growth255 (Fig. 7A). Stimulating the TLR4 receptors and upregulating the NF-κB signalling pathway in DCs promotes inflammatory cytokine production that helps in greater activation and maturation of DCs, thereby augmenting better antigen processing and inducing anti-tumor immune responses.256 In this context, antigen-expressing therapeutic mRNA nano-vaccines were developed to target DCs and activate them for enhanced antigen presentation as well as recruitment of T cells for immune stimulation. The cationic C1 LNP-based DC-targeted delivery of antigen-expressing mRNA exhibited strong activation of DCs via stimulation of TLR4 receptors and modulation of the NF-κB signalling axis.256 The delivery of C1-mRNA nano-vaccines also resulted in greater expression of costimulatory CD80, CD86, and CD40 molecules on DCs that collectively elicited potent inflammatory responses toward immune-cold tumors.256 The cytosolic and endosomal PRRs of DCs are considered to be prime targets in the induction of innate as well as adaptive immunity. The NP-based antigen-expressing mRNA delivery to DCs and PRR-triggered induction of a strong immune response ease the way for the discovery of vaccines against infectious diseases caused by the HIV virus. Following this rationale, Coolen et al. developed mRNA nano-vaccines to stimulate the PRRs of DCs.95 The PLA-NPs, decorated with cell-penetrating peptide and therapeutic mRNA, were efficiently internalized by DCs through phagocytosis and clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathways, facilitating the delivery of Gag protein antigen-encoding cargo mRNA. The recognition of mRNA sequences by PRRs and simultaneous antigen expression of mRNA aided in the activation of PRRs. Specifically, the expression of Gag protein antigens significantly stimulated the endosomal TLR3 as well as DDX58 or RIG-I PRRs in DCs, thereby eliciting both innate and adaptive immune responses against retroviral infection95 (Fig. 7B). Activation of lung-specific DCs and antigen cross-presentation are associated with stimulation of T cells that play a protective role in the prevention of bacterial and fungal infection. The intranasal administration of several vaccines is cited as having adverse immune reactions, and applications are restricted due to poor compliance.257 Recently, adjuvant-free pEα antigen-loaded self-assembled Q11-peptide nano-vaccine has been demonstrated to activate lung DCs with minimal inflammatory response. In particular, the intranasal delivery of nano-vaccine activated lung CD11b+ and CD103+ DCs that are essentially required for effector CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell responses, respectively.257 Moreover, the nanofiber EαQ11 vaccine stimulated the DCs and preferentially modulated the CD4+ T-cell functionality to secrete the IL-17 cytokine, which is known for offering immune protective activities in the respiratory mucosa of the lungs. Thus, intranasal delivery of nano-vaccine provided protective immunity against bacterial and fungal infections.
 |
| | Fig. 7 (A) Schematic representation of dual-mode reactive oxygen species (ROS)-driven immunotherapy: (i) High-power near-infrared (NIR) light irradiation on the intratumorally injected aggregation-induced emission luminogen (AIE)-coupled upconversion nanoparticles (AUNPs) induces immunogenic cell death, reduces immunosuppressive cells and captures tumor-associated antigens (TAA). Furthermore, the TAA-loaded AUNPs are captured by the dendritic cells in the draining lymph node. Moreover, low-power NIR light promotes dendritic cell function through low-level production of ROS. Overall, this process induces the expansion of CD8+ T cells and inhibits the growth of residual tumor. (ii) Schematic illustration of the mechanism of dendritic cell activation through near-infrared light in draining lymph node. Reproduced with permission from ref. 255. Copyright 2020 American Association for the Advancement of Science. (B) Schematic illustration of the model for trafficking of LAH4-L1/mRNA polyplexes and PLA-NP/LAH4-L1/mRNA nanocomplexes into dendritic cells to induce immune response. Overall, the LAH4-L1/mRNA polyplexes and PLA-NP/LAH4-L1/mRNA nanocomplexes represent a potential platform for ex vivo treatment and mRNA vaccine development. Reproduced with permission from ref. 95. Copyright 2019, Elsevier. Abbreviations used: LAH4-L1: amphipathic cationic peptides and PLA-NP: poly (lactic acid) nanoparticles. | |
4.5.2. DC suppression.
Autoreactive T-cell responses are upregulated due to the greater antigen cross-presentation by DCs that leads to aberrant immune disorders. Thus, suppressing DC-based antigen cross-presentation could be a potential intervention to abolish the induction of robust mixed lymphocytic reaction (MLR). Importantly, the DC-specific targeting and delivery of therapeutics to downregulate MLR is a formidable task for the scientific community. Earlier, Katakowski et al. demonstrated that single-chain antibody fragment-modified LNPs can particularly bind to DEC205+ receptors on DCs and efficiently deliver therapeutic cargos in a target-specific manner.45 The research findings revealed that the delivery of therapeutic siRNA blunted the expression of costimulatory molecules such as CD40, CD80, and CD86 found on DCs, therefore halting the antigen cross-presentation to T cells. As a result, the DC-targeted therapeutic LNPs exerted efficacy in controlling the immunological events implicated in robust MLR.45 The dominance of Th2 has been strongly observed in the pathogenesis of AR, where DCs play a crucial role in enhancing the differentiation of Th2 cells from naïve T lymphocytes. The costimulatory molecules CD80, CD86, and MHC II (I-A/I-E) on mature DCs participate in the differentiation of Th2 cells from the naïve T cells. Specific inhibition of DCs by downregulating the co-stimulator functionalities has shown DC resistance, which can result in the abrogation of Th2 activities. The NGR cyclic peptide ligand-modified therapeutic NPs, loaded with anti-inflammatory xanthatin molecules, exhibited suppression of CD80, CD86, and I-A/I-E costimulatory receptors.258 The NGR-peptide modification of NPs facilitated specific binding to CD13 receptors that are overexpressed on DCs. Hence, DC-targeted anti-inflammatory drug delivery and subsequent resistance of DCs ameliorate the dominance of autoimmune T-cell responses and could be a beneficial modality for controlling AR. The CD40 receptors on DCs also act as a stimulatory signal in the activation of T cells and exhibit deleterious autoreactive responses during tissue or organ transplantation. Blocking the activities of DCs by inhibiting CD40 receptor signalling has great clinical significance in depleting T-cell activities toward the transplanted grafts. Recently, CRISPR-Cas9 molecular scissors were used to target and edit the specific gene that encodes CD40 receptors on DCs and reprogram the DCs by disrupting CD40 molecules.259 PEG-b-PLGA-based cationic lipid-assisted NPs were used to encapsulate and deliver the Cas9 mRNA (mCas9) and CD40 directing guide RNA (gCD40).259 Thus, NP-assisted delivery of the CRISPR/Cas9 tool disrupted CD40 signalling and consequently restricted T-cell-mediated transplant rejection. In multiple sclerosis, autoreactive immune responses are implicated by T-cell priming of DCs after being activated by myelin antigens. The myelin membrane of the central nervous system (CNS) gets affected by myelin-specific pathogenic Th-17 cells, where DCs play a crucial role in generation of Th-17 from CD4+ T cells. Recent studies revealed that ROS promotes the maturation of DCs by modulating several costimulatory receptors that ultimately provoke autoreactive CD4+ T-cell responses.260 Being antioxidant in nature, bilirubin NPs (BLNPs) showed promising therapeutic outcomes in the treatment of MS.260 Specifically, BLNPs abstract ROS and suppress the maturation of DCs, thereby further diminishing the conversion of CD4+ T cells to myelin-specific Th-17 cells. Thus, the use of therapeutic BLNPs could be a preventive strategy for blunting DC maturation and limiting the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into autoreactive effector CD4+ T cells in the management of MS.
4.6. NP-assisted cytokine therapy
A subset of therapeutic cytokines ranging from interferons to interleukins is widely used in the treatment of several immune diseases. The administration of such therapeutic cytokines requires potential carriers for their protective delivery. IL-12 is one of the proinflammatory cytokines that drive antitumor immune responses against the immune-cold TME. Several preclinical studies have also been performed for the successful therapeutic translation of IL-12 in the treatment of cancer.261 Researchers developed nanoplatform-based delivery systems for cytokines to reduce systemic toxicity issues, and that can be successfully employed in antitumor therapy. Mechanistically, the delivery of IL-12 molecules from engineered NPs stimulates the release of INF-γ in a downstream molecular cascade fashion, which in turn potentiates T-cell-mediated antitumor responses.262 Lai et al. described an excellent alternative methodology to deliver the IL-12 cytokine in vivo.263 The IL-12-encoding specific mRNA sequence was delivered by LNPs, and subsequent expression of engineered mRNA to IL-12 stimulated CD44+ CD3+ CD4+ T cells, therefore augmenting the greater production of INF-γ.263 Not only did IL-12 produce monotypic mRNA, but dual cytokine delivery approaches have also been carried out for synergistic tumor immunotherapy.264 Liu et al. have demonstrated the dual delivery of therapeutic mRNAs using LNPs. The IL-12 and IL-27-encoding mRNA-encapsulated LNPs showed striking ability against tumor growth by promoting the infiltration of CD8+ T cells, INF-γ, and TNF-α-secreting NK cells.264 Being a natural endotoxic cytokine, TNF-α is considered to be an excellent therapeutic molecule used in the remission of tumor progression. Encapsulation of TNF-α within porous NPs enables protective delivery, therefore conferring minimal acute toxicities.265 The release of cytokines from NPs preferably interrupted different phases of cell cycles (S/G2/M) and damaged the cancer cells directly to promote the retardation of tumor growth. Addition of cytokines to the therapeutic avenue of chemotherapy is an emerging approach for stimulating immune components that significantly limit the tumor progress. Wu et al. demonstrated that co-delivery of DOX and IL-2 via nanovesicles has a great immunomodulatory influence on the activities of DCs, T cells, and NK cells that confer anti-tumor immune responses.266 The anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties of IL-10 have shown promise in treating degenerative diseases. IL-10-producing exosomes effectively target injured kidney tubular epithelial cells via specific integrin receptors, modulating anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotypes and downregulating the mTOR pathway to maintain mitochondrial integrity. Thus, IL-10-expressing therapeutic exosomes could be a potent nanomedicine for managing acute kidney injuries (Fig. 8A).267 The prevalence of CNS-resident astrocytes and microglial cells has been reported to play a pathogenic role in the development of MS.268 The clinical application of the immunomodulatory cytokine INF-β is a promising choice of therapy. However, the low therapeutic index of the cytokine has always been a concern in the treatment of MS. Recently, González et al. developed INF-β loaded NPs for the intranasal delivery of cytokines to overcome the barriers of systemic administration.269 The efficient delivery of INF-β from the NPs alleviated MS pathogenesis by inhibiting the dominance of astrocytes and microglial cells and also depleting the activities of APCs. Furthermore, the IL-4 cytokine has been widely used in the treatment of several autoimmune diseases because of its anti-inflammatory activities. The IL-4 cytokine shows the ability to polarize the M1 macrophage into M2 phenotypes, thereby conferring a pro-regenerative immune response.270 However, the shorter half-life of IL-4 cytokine necessitates high-dose administration, which eventually causes toxicity issues. IL-4-conjugated AuNPs have been demonstrated to skew macrophage polarization towards the M2 phenotype effectively with minimal toxicity concerns.270 Hence, the NP-assisted delivery of IL-4 could be a novel therapeutic option for tissue regeneration, and is highly relevant in the management of muscle injuries.270 The proinflammatory activities of IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines exhibited deleterious effects in the development of asthmatic lung inflammation.271 In particular, the IL4Rα domain of IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines participated in their cognate receptor interaction during airway inflammation. Hence, targeting and blocking the IL4Rα subunit of these cytokines is a novel strategy for mitigating the symptoms of inflammatory lung diseases. Therapeutic NPs with anti-IL4Rα antibodies tethered to their surface have been demonstrated to block the receptor-triggering activity of IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines, which consequently resulted in suppression of lung inflammation.271 Recent studies identified IL-11 as one of the potent profibrogenic cytokine molecules engaged in several lung fibrotic disorders.272 The binding of IL-11 to its cognate receptors stimulates the fibroblast activation and release of ECM via extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathways. Greater deposition of ECM stiffens the lung tissues and drives fibrotic pathogenesis. Recently, researchers have developed siRNA-loaded therapeutic NPs for targeting the ERK pathways and downregulating IL-11 cytokine functionalities.273 Intranasal administration of siRNA-entrapped NPs diminished fibroblast activation and suppressed ECM deposition by interfering with the ERK and SMAD2 pathways. Thus, NP-mediated delivery of siRNA showed significant abrogation in lung fibrosis and improved pulmonary activities273 (Fig. 8B). The combined pathogenic effect conferred by viruses and inflammatory cytokines is known to have highly deleterious health consequences. However, targeting both viruses and inflammatory cytokines has become challenging for the scientific community. However, recently, Rao et al. developed an engineered novel decoy NP with dual targeting capacity.274 Uniquely, the decoy NPs competed with host cells for virus absorption and also captured inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Thus, the powerful nano-decoy therapeutics show excellent ability to effectively protect individuals from viral infections caused by pseudo-viruses and SARS-CoV-2 virus.274
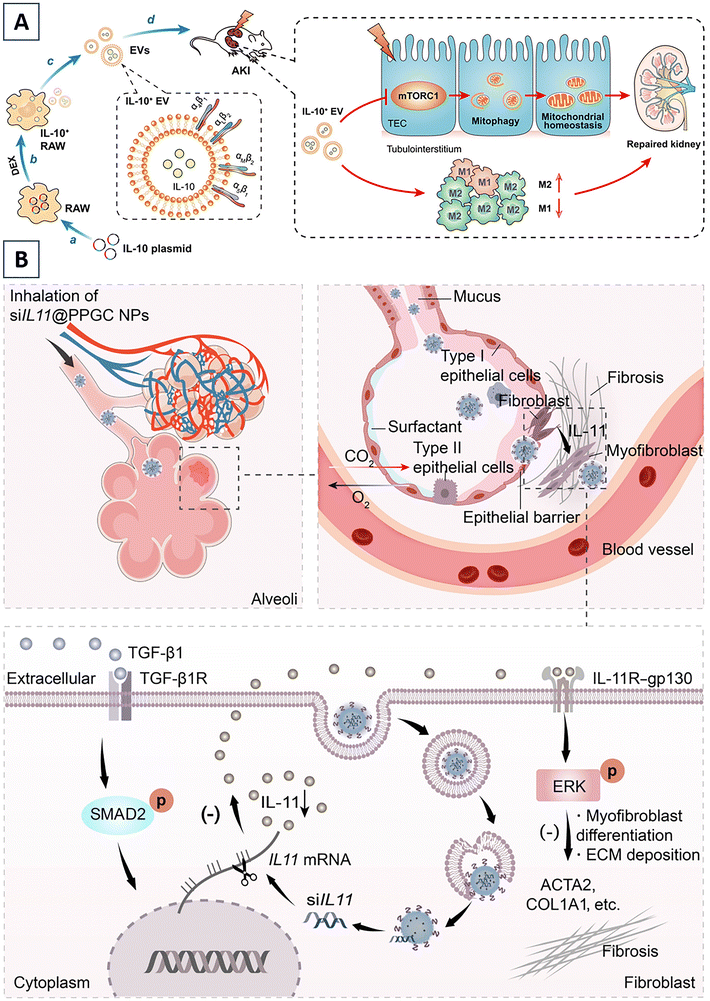 |
| | Fig. 8 (A) Schematic representation of the fabrication of interleukin-10 (IL-10)-loaded extracellular vesicles for the treatment of ischemic acute kidney injury. Reproduced with permission from ref. 267. Copyright 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science. (B) Schematic illustration of the delivery of small interfering RNA encapsulated in self-assembled nanoparticles composed of poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-b-poly (ethylene glycol) (PLGA-PEG) diblock copolymer and cationic lipid-like molecules G0-C14 to mouse lung fibroblasts for the treatment of Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Reproduced with permission from ref. 273. Copyright 2022, American Association for the Advancement of Science. | |
4.7. Nanotherapeutics for targeting complement systems (CS)
The CS is a part of the innate immune system, formed by the assembly of more than 30 small proteins including plasma proteins and cell surface receptors. CS plays a significant role in maintaining homeostasis by critically regulating the balance between different immune components. The specific interplay between antigen receptors, antibodies, and protein components of the CS activates the CS in a molecular cascade mechanism. The activation of the CS results in the formation of C3 convertase, which generates potential anaphylatoxins to encounter the pathogens and mediates multiple immune responses275,276 (Fig. 9A). In most cases, the incorrect activation of the CS results in severe immune complications. The use of nanomedicine for targeting the CS is an emerging treatment modality to restore the normalcy of the CS. NETs serve as a sanctuary for inflammatory IL-17 cytokines; they have autoimmune implications in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.277 The release of IL-17 from NETs occurs via activation of the C5b-9 complement component. Zhang et al. demonstrated that topical administration of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome NPs showed excellent ability to inhibit C5b-9 complement activation and prevent inflammatory IL-17 cytokine release.277 In alleviation of NETosis-driven inflammatory psoriasis, the therapeutic exosome also reduced various side-effects that are observed in traditional drug use. During cell-based therapy, the administration of MSCs into the body provokes the CS to mobilize C5a, which in turn binds to the C5aR receptors present on neutrophils. Thus, escorting neutrophils to the proximity of MSCs by complement activation leads to potential damage to MSC therapeutics. Researchers found that the macrophage membrane exhibits a high expression of C5aR receptors that could be targeted in the development of nanotherapeutics by blunting the C5a-C5aR interaction and preventing the activation of neutrophils.278 Hence, macrophage membrane-coated engineered PLGA NPs were developed that effectively block the C5a-C5aR signalling, thereby preventing the C5a-mediated neutrophil targeting of therapeutic MSCs. Thus, the application of macrophage membrane-wrapped nanotherapeutics holds a promising approach for the regenerative and immunotherapeutic paradigm278 (Fig. 9B). The C3 component of the CS is also considered to be one of the key pathogenic mediators responsible for autoimmune myocarditis. In particular, C3-dependent liver-specific STAT3 signalling drives the pathogenesis of myocarditis and could be a potential target for therapeutic intervention. Avalle et al. demonstrated that liver-specific STAT3/C3-targeting siRNA NPs interfered with STAT3 signalling and complement production, that provided protection against autoimmune cardiomyopathies.279 Autoreactive complement activities have also been reported in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) where the body's C5 complement proteins conduct attacks and lyse the erythrocytes.280 Currently, mAbs are being clinically used to counteract C5-complement protein in the management of PNH. In parallel, researchers have been trying to develop novel nano-vaccines for eliciting strong anti-C5 antibody responses. In this regard, recombinant VLPs are novel choices of nanomaterials for the design and development of complement-inhibiting nano-vaccine candidates. Zhang et al. have developed bacteriophage Qβ plasmid-derived VLPs, surface engineered with C5 peptide epitopes to trigger anti-C5 auto-antibody responses.281 The administration of VLP-C5 nano-vaccine efficiently produced anti-C5 autoantibodies that blocked the haemolytic C5 complement protein and could be an alternative to molecular medicines in the therapy of PNH.
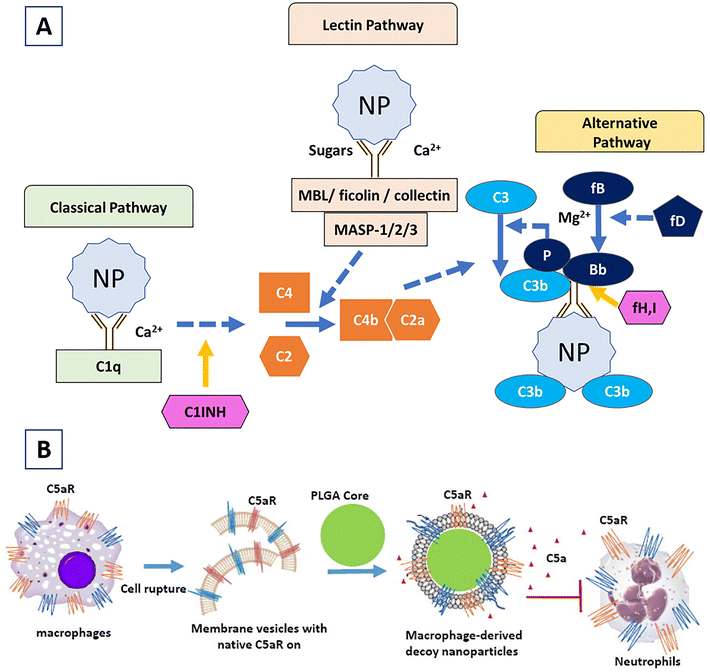 |
| | Fig. 9 (A) Schematic representation of the activation of the upstream part of the complement cascade through nanoparticle-bound immunoglobulins. The three initiating complement pathways include the classical, lectin and alternative pathway. The activation of the classical pathway occurs through C1q binding to the Fc portion of the surface-bound antibodies, the lectin pathway through the binding of the glycosylated regions of the antibodies to MBL/MASP-2 and the alternative pathway through the deposition of antibody-bound C3. The natural inhibitors of the complement cascade are shown in pink with yellow arrows. (B) Schematic illustration of the inhibition of neutrophil activation through C5aR-displaying decoy nanoparticles for improved mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies. Reproduced with permission from ref. 278. Copyright 2019, Elsevier. Abbreviations used: NP-nanoparticles; C1, C2, C3, C4-complement proteins; MBL-mannose-binding lectin; MASP-MBL-associated serine proteases; fB, fD, fI, fH: complement factors. | |
Overall, several treatment strategies discussed have advanced to clinical trials, in some cases, achieved approval for immunotherapeutic applications, as listed in Table 6.
Table 6 List of clinically approved/in clinical trials nanomedicines for immunotherapy
| Type of NPs |
Components |
Name |
Manufacturer |
Therapeutic payload |
Mode of action and effect on immune system |
Application |
NCT number |
| Abbreviation: SM-102, sphingomyelin-102; DSPC, distearoylphosphatidylcholine; PEG200-DMG, polyethylene glycol-2000-dimyristoyl glycerol; HSPC, hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine; PEG2000-DSPE, polyethylene glycol-2000-distearoyl-sn-glycero-phosphoethanolamine; SM, sphingomyelin; MPEG2000-DSPE, methoxy polyethylene glycol 2000-distearoyl-sn-glycero-phosphoethanolamine; DSPG, distearoylphosphatidylglycerol; DMPC, dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine; EPG, esterified propoxylated glycerol; EPC, egg phosphatidylcholine; DOPS, dioleoylphosphatidylcholine; POPC, palmitoyloleoylphosphatidylcholine. |
| Lipid NP |
Ionizable lipid (proprietary), SM-102, cholesterol, DSPC, PEG2000 DMG |
mRNA1273 |
Sponsor: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) |
mRNA |
The mRNA encoded spike (S) protein acts as an immunogen and generates antibodies, which provides immunity against the viral infection. |
Covid-19 vaccine |
NCT04470427 |
| Collaborator: Moderna TX, Inc. |
| Lipid NP |
ALC-0315, ALC-0159, DSPC, cholesterol |
BNT162b2/Tozinameran |
Sponsor: BioNTech |
Nucleoside modified mRNA (modRNA) |
The modRNA-encoded mutated full-length spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 drives immunity by serving as an immunogen. |
Covid-19 vaccine |
NCT04368728 |
| Collaborator: Pfizer |
| Liposome |
Cholesterol, HSPC, PEG2000-DSPE |
Doxil/Caelyx |
Janssen Research & Development, LLC |
Doxorubicin (DOX) |
Primarily, DOX acts as a chemotherapeutic agent. |
Anti-cancer |
NCT00103506 |
| In association with monoclonal antibody (Pembrolizumab), DOX can contribute to immunotherapy against sarcoma. |
| Liposome |
Cholesterol, DSPC |
DaunoXome |
Sponsor: Nexstar Pharmaceuticals |
Daunorubicin |
Primarily, it acts as DNA topoisomerase-II poison. |
Anti-cancer |
NCT00002093 |
| It induces cGAS-dependent innate immune response to suppress Hepatitis B virus production. |
| Protein NP |
Human albumin protein |
Abraxane |
Sponsor: Celgene |
Paclitaxel (PTX) |
It inhibits dissociation of microtubules, assembles tubulin into microtubules, thus, arresting cancer cell growth. |
Anti-cancer |
NCT02027428 |
| PTX also possesses tumor immunotherapy by regulating the activities of T cells, DCs, NK cells, Tregs and Macrophages. |
| Liposome |
Soybean oil, egg lecithin, glycerol |
Diprivan® |
Sponsor: R-Pharm |
Propofol |
Propofol mainly acts as GABA-receptor agonist. It also augments NK cell functions, inhibits PGE2 and COX-2 in postoperative immune protection. |
Anaesthetic |
NCT03669484 |
| Collaborator: Synergy Research, Inc. |
| Liposome |
Cholesterol, HSPC, DSPG |
AmBisome |
Sponsor: Drugs for Neglected Diseases |
Amphotericin B (Amp-B) |
Amp-B binds to Ergosterol of the fungal cell membrane and creates pores and cells die eventually. |
Antifungal, Antiparasitic |
NCT01122771 |
| Collaborator: Shaheed Surhawardy Medical College and Hospital |
Amp-B can modulate the immune system but also possess toxicity. |
| International centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh |
|
| Liposome |
DMPC, EPG |
Visudyne |
Sponsor: QLT Inc. |
Verteporfin |
Verteporfin exerts its activity via light-induced PDT. |
In treatment of eye diseases caused by age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other pathological conditions. |
NCT00121407 |
| Verteporfin inhibits PD-L1 and exerts antitumor efficacy. |
| (Non-PEGylated) |
DOPS, POPC |
MEPACT |
Sponsor: UNICANCER |
Mifamurtide |
Increased production of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, and others) for cancer immunotherapy |
For the treatment of osteosarcoma |
NCT03643133 |
| Liposome (Non-PEGylated) |
EPC, cholesterol |
Myocet |
Sponsor: Sopherion Therapeutics |
Doxorubicin |
DNA intercalating agent |
For the treatment of breast cancer |
NCT00294996 |
| Hafnium oxide NP |
Hafnium oxide |
NBTXR3 |
Sponsor: Nanobiotix |
|
Radiation-induced cancer cell killing and immune stimulation-based immunogenic cell death (ICD) |
Radiotherapy for solid tumor |
NCT04892173 |
| Fe-dextran colloid |
Iron(III)-hydroxide, dextran |
CosmoFer®/INFeD® |
Sponsor: Pharmacosmos A/S |
Fe |
Overcomes iron deficiency |
In the treatment of congestive heart failure |
NCT00537186 |
| Fe-sucrose colloid |
Iron, sucrose |
Venofer |
Sponsor: American Regent, Inc. |
Fe |
Replacement of iron |
In the treatment of anemia with chronic kidney disease |
NCT00236938 |
| Fe-gluconate colloid |
Iron, gluconate |
Ferrlecit® |
Sponsor: Watson Pharmaceuticals |
Fe |
Replacement of iron |
In the treatment of anemia with chronic kidney disease |
NCT00224003 |
| Fe-carboxymaltose colloid |
Iron, carboxymaltose |
Ferinject® |
Sponsor: Vifor Pharma |
Fe |
Replacement of iron |
Chronic heart failure and iron deficiency |
NCT00520780 |
| Collaborator: Syneos Health |
| ClinStar, LLC |
5. Challenges and future perspectives
NPs and immune cells form a unique physico-chemical environment that can be impacted by several factors of NPs, including source, variable catalysis residues, storage conditions, variability in synthesis, and endotoxin contamination.282 Successful translation necessitates a meticulously streamlined synthesis protocol, standardized experimental tools and in vitro assays, and rigorous validation, including nanosafety assessment of endotoxins. Furthermore, NPs fabricated from specific materials, including metals, polymers, and ceramics, may show different levels of immunotoxicity that raise potential concerns over their usage. One effective strategy to mitigate material-mediated toxicity involves the utilization of inert materials that can serve as a protective coating, suppressing immune toxicity by preventing the formation of a protein corona. In addition, instead of targeting a single antigenic receptor, dual or more receptor targeting could be one of the advanced strategies for precise therapeutic intervention. NPs decorated with multiple ligands against multi-antigenic receptors can significantly reduce the associated off-target nano-immune toxicity concerns. The encapsulation of multiple therapeutic agents within a single nanocarrier and the subsequent co-delivery strategy represents a synergistic approach for achieving higher therapeutic efficacy and effectively overcoming multidrug resistance. Several practical challenges limit the clinical availability of these nanoparticle-based technologies in the market. These include scalability, reproducibility, prolonged regulatory approval processes, and patient heterogeneity.283,284 Several clinical data indicate that developed nanomedicines may only be effective in certain sub-populations of patients. Therefore, effective clinical implementation of these therapeutics depends on exploring strategies for patient stratification and treatment identification for trials. The selection of patient-specific immunological biomarkers can be a crucial step in advancing biomarker-guided nano-immunotherapeutic interventions. Moreover, the integration of existing knowledge of targeted regulation and stimuli-responsive release with advanced scientific theories from different fields, such as artificial intelligence, big data analysis, bioinformatics, and 3D printing, presents new opportunities for further advancement in this field. This integration holds significant potential to provide multi-immunoreceptor-targeted, micro-environment-responsive controlled delivery of drugs with minimal immunotoxicity hazards.
6. Conclusion
The increasing prevalence of life-threatening immune diseases necessitates the development of novel therapeutic platforms. The frequency and intricacy of such diseases have raised major concerns about the efficacy of traditional therapeutic regimens. In many cases, conventional therapeutic strategies have failed to deal with disease pathology for multiple reasons, such as non-specific disease targeting, low therapeutic index, rapid clearance of therapeutics, difficulty in bypassing several physiological barriers, and immune toxicities. Therapeutic NPs display better payload flexibility that helps to overcome the therapeutic limitations of traditional medications. The specific immune receptor-targeted drug-delivery strategy provides breakthroughs in target-specific modulation of pathogenic T cells, B cells, macrophages, and DCs. The combinations of engineered nanostructured vehicles and therapeutic payloads have produced several nanomedicines that can easily target these specific immune components. While some limitations exist for their clinical applications, the therapeutic efficiency of immunomodulatory NPs can be enhanced through further research and design of safer nanocarriers. The advancements in the field necessitate multidisciplinary collaboration among researchers, scientists, healthcare professionals, engineers, and regulatory experts to adapt immunomodulatory NPs to meet market demands. Such collaboration can transform health care by improving immune targeting precision and facilitating the successful clinical translation of immunomodulatory nanomedicines.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
B. B. M. acknowledges the funding support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India. R. K., B. B., S. D. and V. J. acknowledge the Ministry of Education (MoE), Government of India, for providing fellowship. C. J. acknowledges the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India for fellowship.
References
- K. C. Ma, E. J. Schenck, M. A. Pabon and A. M. K. Choi, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 2018, 197, 300–309 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Afshar-Kharghan, J. Clin. Invest., 2017, 127, 780–789 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Bantz, O. Koshkina, T. Lang, H. J. Galla, C. J. Kirkpatrick, R. H. Stauber and M. Maskos, Beilstein J. Nanotechnol., 2014, 5, 1774–1786 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Zhang, G. Shi, J. Zhang, H. Song, J. Niu, S. Shi, P. Huang, Y. Wang, W. Wang, C. Li and D. Kong, J. Controlled Release, 2017, 256, 170–181 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Conde, C. Bao, Y. Tan, D. Cui, E. R. Edelman, H. S. Azevedo, H. J. Byrne, N. Artzi and F. Tian, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25, 4183–4194 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Korangath, J. D. Barnett, A. Sharma, E. T. Henderson, J. Stewart, S. H. Yu, S. K. Kandala, C. T. Yang, J. S. Caserto, M. Hedayati, T. D. Armstrong, E. Jaffee, C. Gruettner, X. C. Zhou, W. Fu, C. Hu, S. Sukumar, B. W. Simons and R. Ivkov, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eaay1601 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. S. Choi, W. Liu, P. Misra, E. Tanaka, J. P. Zimmer, B. I. Ipe, M. G. Bawendi and J. V. Frangioni, Nat. Biotechnol., 2007, 25, 1165–1170 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. V. Vinogradov, T. K. Bronich and A. V. Kabanov, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2002, 54, 135–147 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. L. B. de Barros, A. Tsourkas, B. Saboury, V. N. Cardoso and A. Alavi, EJNMMI Res., 2012, 2, 1–15 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. A. Kulkarni and S. S. Feng, Pharm. Res., 2013, 30, 2512–2522 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. H. Faraji and P. Wipf, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2009, 17, 2950–2962 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Foroozandeh and A. A. Aziz, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2018, 13, 1–12 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. A. Petros and J. M. Desimone, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2010, 9, 615–627 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Ernsting, M. Murakami, A. Roy and S. D. Li, J. Controlled Release, 2013, 172, 782–794 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Wu, L. Luo, Y. Wang, Q. Wu, H. B. Dai, J. S. Li, C. Durkan, N. Wang and G. X. Wang, Theranostics, 2018, 8, 3038–3058 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kang, S. Ahn, J. Lee, J. Y. Kim, M. Choi, V. Gujrati, H. Kim, J. Kim, E. C. Shin and S. Jon, J. Controlled Release, 2017, 256, 56–67 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kumar, A. C. Anselmo, A. Banerjee, M. Zakrewsky and S. Mitragotri, J. Controlled Release, 2015, 220, 141–148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. F. Bachmann and G. T. Jennings, Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2010, 10, 787–796 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Graf, D. Nordmeyer, C. Sengstock, S. Ahlberg, J. Diendorf, J. Raabe, M. Epple, M. Köller, J. Lademann, A. Vogt, F. Rancan and E. Rühl, Langmuir, 2018, 34, 1506–1519 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Toy, P. M. Peiris, K. B. Ghaghada and E. Karathanasis, Nanomedicine, 2014, 9, 121–134 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Xie, J. Liao, X. Shao, Q. Li and Y. Lin, Sci. Rep., 2017, 7, 1–9 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Tazaki, K. Tabata, A. Ainai, Y. Ohara, S. Kobayashi, T. Ninomiya, Y. Orba, H. Mitomo, T. Nakano, H. Hasegawa, K. Ijiro, H. Sawa, T. Suzuki and K. Niikura, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 16527–16536 RSC.
- S. Barua, J. W. Yoo, P. Kolhar, A. Wakankar, Y. R. Gokarn and S. Mitragotri, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2013, 110, 3270–3275 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. D. Chithrani, A. A. Ghazani and W. C. W. Chan, Nano Lett., 2006, 6, 662–668 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. L. J. Thorek and A. Tsourkas, Biomaterials, 2008, 29, 3583–3590 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Slowing, B. G. Trewyn and V. S. Y. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 14792–14793 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Behzadi, V. Serpooshan, W. Tao, M. A. Hamaly, M. Y. Alkawareek, E. C. Dreaden, D. Brown, A. M. Alkilany, O. C. Farokhzad and M. Mahmoudi, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 4218–4244 RSC.
- J. Dausend, A. Musyanovych, M. Dass, P. Walther, H. Schrezenmeier, K. Landfester and V. Mailänder, Macromol. Biosci., 2008, 8, 1135–1143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Liu, F. Cao, X. Liu, H. Wang, C. Zhang, H. Sun, C. Wang, X. Leng, C. Song, D. Kong and G. Ma, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 11969–11979 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. K. Dey, A. Nougarède, F. Clément, C. Fournier, E. Jouvin-Marche, M. Escudé, D. Jary, F. P. Navarro and P. N. Marche, Front. Immunol., 2021, 12, 722411 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Srijampa, S. Buddhisa, S. Ngernpimai, C. Leelayuwat, S. Proungvitaya, A. Chompoosor and P. Tippayawat, Bioconjugate Chem., 2020, 31, 1133–1143 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Pan, Y. Qi, N. Shao, A. C. Tadle and Y. Huang, Biomacromolecules, 2019, 20, 3575–3583 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Shreffler, J. E. Pullan, K. M. Dailey, S. Mallik and A. E. Brooks, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2019, 20, 6056 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Patsula, D. Horák, J. Kučka, H. Macková, V. Lobaz, P. Francová, V. Herynek, T. Heizer, P. Páral and L. Šefc, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, 1–12 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Feng, Y. Liu, J. Huang, K. Chen, J. Huang and K. Xiao, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, 1–13 CAS.
- V. Juang, C.-H. Chang, C.-S. Wang, H.-E. Wang, Y.-L. Lo, V. Juang, C.-H. Chang, C.-S. Wang, Y.-L. Lo and H.-E. Wang, Small, 2019, 15, 1903296 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Qie, H. Yuan, C. A. Von Roemeling, Y. Chen, X. Liu, K. D. Shih, J. A. Knight, H. W. Tun, R. E. Wharen, W. Jiang and B. Y. S. Kim, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 1–11 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. S. Suk, Q. Xu, N. Kim, J. Hanes and L. M. Ensign, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2016, 99, 28–51 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. O. Stead, S. Kireta, S. J. P. McInnes, F. D. Kette, K. N. Sivanathan, J. Kim, E. J. Cueto-Diaz, F. Cunin, J. O. Durand, C. J. Drogemuller, R. P. Carroll, N. H. Voelcker and P. T. Coates, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 6637–6647 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Xiang, L. Xu, H. Gong, W. Zhu, C. Wang, J. Xu, L. Feng, L. Cheng, R. Peng and Z. Liu, ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 6401–6411 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. S. S. A. Ayyadevara, A. Ahmadi and K. H. Roh, Bioconjugate Chem., 2021, 32, 1675–1687 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Jing, S. Shao, Y. Wang, Y. Yang, X. Yue and Z. Dai, Theranostics, 2016, 6, 40–53 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gangrade and B. B. Mandal, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2019, 5, 2365–2381 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Luo, X. Meng, J. Su, H. Ma, W. Wang, L. Fang, H. Zheng, Y. Qin and T. Chen, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2018, 66, 9219–9230 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. A. Katakowski, G. Mukherjee, S. E. Wilner, K. E. Maier, M. T. Harrison, T. P. Di Lorenzo, M. Levy and D. Palliser, Mol. Ther., 2016, 24, 146–155 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. N. Shi, C. N. Zhang, R. Xu, J. F. Niu, H. J. Song, X. Y. Zhang, W. W. Wang, Y. M. Wang, C. Li, X. Q. Wei and D. L. Kong, Biomaterials, 2017, 113, 191–202 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. K. Gulla, B. R. Rao, G. Moku, S. Jinka, N. V. Nimmu, S. Khalid, C. R. Patra and A. Chaudhuri, Biomater. Sci., 2019, 7, 773–788 RSC.
- R. R. Meka, S. Mukherjee, C. R. Patra and A. Chaudhuri, Nanoscale, 2019, 11, 7931–7943 RSC.
- N. Climent, I. García, M. Marradi, F. Chiodo, L. Miralles, M. J. Maleno, J. M. Gatell, F. García, S. Penadés and M. Plana, Nanomedicine, 2018, 14, 339–351 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhang and C. A. Peng, Sci. Rep., 2020, 10, 1–13 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Pang, Y. Pei, G. Uzunalli, H. Hyun, L. T. Lyle and Y. Yeo, Pharm. Res., 2019, 36, 65 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Badkas, E. Frank, Z. Zhou, M. Jafari, H. Chandra, V. Sriram, J. Y. Lee and J. S. Yadav, Colloids Surf., B, 2018, 162, 271–278 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Schmid, C. G. Park, C. A. Hartl, N. Subedi, A. N. Cartwright, R. B. Puerto, Y. Zheng, J. Maiarana, G. J. Freeman, K. W. Wucherpfennig, D. J. Irvine and M. S. Goldberg, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 1–12 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. W. Huang, F. F. Hsu, J. T. Qiu, G. J. Chern, Y. A. Lee, C. C. Chang, Y. T. Huang, Y. C. Sung, C. C. Chiang, R. L. Huang, C. C. Lin, T. K. Dinh, H. C. Huang, Y. C. Shih, D. Alson, C. Y. Lin, Y. C. Lin, P. C. Chang, S. Y. Lin and Y. Chen, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eaax5032 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, N. Li, H. Suh and D. J. Irvine, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 1–15 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Khodoun, A. A. Chimote, F. Z. Ilyas, H. J. Duncan, H. Moncrieffe, K. S. Kant and L. Conforti, Sci. Adv., 2021, 6, eabd1471 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Zhou, J. Mei, S. Yang, X. Han, H. Li, Z. Yu, H. Qiao and T. Tang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 2009–2022 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. N. Khan, P. Han, R. Chaudhury, S. Bickerton, J. S. Lee, B. Calderon, A. Pellowe, A. Gonzalez and T. Fahmy, Mol. Pharm., 2021, 18, 850–861 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Khan, K. Saeed and I. Khan, Arabian J. Chem., 2019, 12, 908–931 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Stanley, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol, 2014, 28, 69–74 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Mitchell, M. M. Billingsley, R. M. Haley, M. E. Wechsler, N. A. Peppas and R. Langer, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2021, 20, 101–124 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Taghipour-Sabzevar, T. Sharifi and M. M. Moghaddam, Ther. Delivery, 2019, 10, 527–550 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Kumar, N. Dilbaghi, R. Saharan and G. Bhanjana, BioNanoScience, 2012, 4, 227–250 CrossRef.
- I. R. Khalil, A. T. H. Burns, I. Radecka, M. Kowalczuk, T. Khalaf, G. Adamus, B. Johnston and M. P. Khechara, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2017, 18, 313 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. P. Sherje, M. Jadhav, B. R. Dravyakar and D. Kadam, Int. J. Pharm., 2018, 548, 707–720 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. C. Lee, J. A. MacKay, J. M. J. Fréchet and F. C. Szoka, Nat. Biotechnol., 2005, 23, 1517–1526 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Anajafi and S. Mallik, Ther. Deliv., 2015, 6, 521–534 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Majumder, N. G. Das and S. K. Das, Ther. Deliv., 2020, 11, 613–635 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Varela-Moreira, Y. Shi, M. H. A.
M. Fens, T. Lammers, W. E. Hennink and R. M. Schiffelers, Mater. Chem. Front., 2017, 1, 1485–1501 RSC.
- Y. Lee, K. Sugihara, M. G. Gillilland, S. Jon, N. Kamada and J. J. Moon, Nat. Mater., 2020, 19, 118–126 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, L. Li, W. Zhao, Y. Dou, H. An, H. Tao, X. Xu, Y. Jia, S. Lu, J. Zhang and H. Hu, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 8943–8960 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Dehghan, M. T. Kheiri, K. Abnous, M. Eskandari and M. Tafaghodi, Microb. Pathog., 2018, 115, 74–85 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jain, T. H. Tran and M. Amiji, Biomaterials, 2015, 61, 162–177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. D. Han, Y. Byeon, J. H. Jang, H. N. Jeon, G. H. Kim, M. G. Kim, C. G. Pack, T. H. Kang, I. D. Jung, Y. T. Lim, Y. J. Lee, J. W. Lee, B. C. Shin, H. J. Ahn, A. K. Sood and Y. M. Park, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 1–13 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Wu, J. Gu, S. Zhang, Y. Gu, J. Ma, Y. Wang, L. W. Zhang and Y. Wang, Anal. Chem., 2021, 93, 6414–6420 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Yu, X. Tang, W. Zhao, Y. Qiu, J. He, D. Wan, J. Li, X. Wang, X. He, Y. Liu, M. Li, Z. Zhang and Q. He, Acta Biomater., 2021, 133, 244–256 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Lyu, L. Wang, X. Bai, X. Du, J. Wei, J. Wang, Y. Lin, Z. Chen, Z. Liu, J. Wu and Z. Zhong, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 266–276 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Xie, Y. Su, G. B. Kim, E. Selvi, C. Ma, V. Aragon-Sanabria, J. T. Hsieh, C. Dong and J. Yang, Small, 2017, 13, 1603121 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Tukulula, R. Hayeshi, P. Fonteh, D. Meyer, A. Ndamase, M. T. Madziva, V. Khumalo, P. Lubuschagne, B. Naicker, H. Swai and A. Dube, Pharm. Res., 2015, 32, 2713–2726 CAS.
- S. Vemireddy, P. P. Madhurantakam, M. N. Talati and H. M. S. Kumar, ACS Appl. Bio Mater., 2019, 2, 4837–4846 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Xing, Z. Xu, T. Liu, L. Shi, D. Kohane and S. Guo, Angew. Chem., 2020, 132, 7302–7306 CrossRef.
- A. Thukral, K. Ross, C. Hansen, Y. Phanse, B. Narasimhan, H. Steinberg and A. M. Talaat, npj Vaccines, 2020, 5, 1–10 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Walter, E. Winter, S. Rahn, J. Heidland, S. Meier, A. M. Struzek, M. Lettau, L. M. Philipp, S. Beckinger, L. Otto, J. L. Möller, O. Helm, D. Wesch, R. Scherließ and S. Sebens, PLoS One, 2020, 15, e0239369 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. J. Beldman, M. L. Senders, A. Alaarg, C. Pérez-Medina, J. Tang, Y. Zhao, F. Fay, J. Deichmöller, B. Born, E. Desclos, N. N. Van Der Wel, R. A. Hoebe, F. Kohen, E. Kartvelishvily, M. Neeman, T. Reiner, C. Calcagno, Z. A. Fayad, M. P. J. De Winther, E. Lutgens, W. J. M. Mulder and E. Kluza, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 5785–5799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. F. Lin, P. L. Jiang, J. S. Tsai, Y. Y. Huang, S. Y. Lin, J. H. Lin and D. Z. Liu, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B, 2019, 107, 1228–1237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Zwiorek, C. Bourquin, J. Battiany, G. Winter, S. Endres, G. Hartmann and C. Coester, Pharm. Res., 2008, 25, 551–562 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Bourquin, Chimia, 2019, 73, 69–72 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. D. Totten, T. Wongpinyochit, J. Carrola, I. F. Duarte and F. P. Seib, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 14515–14525 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Hassanzadeh, E. Arbabi and F. Rostami, Life Sci., 2021, 281, 119772 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Ji, J. Si, Y. Xu, W. Zhang, Y. Yang, X. He, H. Xu, X. Mou, H. Ren and H. Guo, Theranostics, 2021, 11, 8587 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. V. Gregory, P. Kadiyala, R. Doherty, M. Cadena, S. Habeel, E. Ruoslahti, P. R. Lowenstein, M. G. Castro and J. Lahann, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 1–15 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Sun, Y. Zou, L. Song, S. Han, H. Yang, D. Chu, Y. Dai, J. Ma, C. M. O'Driscoll, Z. Yu and J. Guo, Acta Pharm. Sin. B, 2022, 12, 378–393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Thomas, A. Rawat, L. Hope-Weeks and F. Ahsan, Mol. Pharm., 2011, 8, 405–415 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Meena, R. Kumar, M. Singh, A. Ahmed and A. K. Panda, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 2020, 152, 270–281 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. L. Coolen, C. Lacroix, P. Mercier-Gouy, E. Delaune, C. Monge, J. Y. Exposito and B. Verrier, Biomaterials, 2019, 195, 23–37 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Boltnarova, J. Kubackova, J. Skoda, A. Stefela, M. Smekalova, P. Svacinova, I. Pavkova, M. Dittrich, D. Scherman, J. Zbytovska, P. Pavek and O. Holas, Nanomaterials, 2021, 11, 749 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kaur, J. Rathee, R. Kanwar, D. Kaushik, D. B. Salunke and S. K. Mehta, Colloids Surf., A, 2022, 647, 129084 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Igartua, R. M. Hernández, A. Esquisabel, A. R. Gascón, M. B. Calvo and J. L. Pedraz, J. Controlled Release, 1998, 56, 63–73 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Bansal, M. Kumar, A. Bhardwaj, H. G. Brahmne and H. Singh, Vaccine, 2015, 33, 5623–5632 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Ahmad, E. Fauzia, M. Kumar, R. K. Mishra, A. Kumar, M. A. Khan, S. S. Raza and R. Khan, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2019, 5, 683–695 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. H. Salman, J. M. Irache and C. Gamazo, Vaccine, 2009, 27, 4784–4790 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. H. Huynh, X. H. Pham, J. Kim, S. H. Lee, H. Chang, W. Y. Rho and B. H. Jun, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21, 1–29 Search PubMed.
- A. A. Yaqoob, H. Ahmad, T. Parveen, A. Ahmad, M. Oves, I. M. I. Ismail, H. A. Qari, K. Umar and M. N. M. Ibrahim, Front. Chem., 2020, 8, 528583 Search PubMed.
- K. V Chakravarthy, A. C. Bonoiu, W. G. Davis, P. Ranjan, H. Ding, R. Hu, J. B. Bowzard, E. J. Bergey, J. M. Katz, P. R. Knight, S. Sambhara and P. N. Prasad, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2010, 107, 10172–10177 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. S. Bawage, P. M. Tiwari, A. Singh, S. Dixit, S. R. Pillai, V. A. Dennis and S. R. Singh, Nanomedicine, 2016, 12, 2299–2310 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Liang, M. Sun, Y. Lu, S. Shi, Y. Yang, Y. Lin, C. Feng, J. Liu and C. Dong, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8, 8368–8382 RSC.
- F. Xia, W. Hou, Y. Liu, W. Wang, Y. Han, M. Yang, X. Zhi, C. Li, D. Qi, T. Li, J. M. de la Fuente, C. Zhang, J. Song and D. Cui, Biomaterials, 2018, 170, 1–11 CAS.
- P. Orłowski, A. Kowalczyk, E. Tomaszewska, K. Ranoszek-Soliwoda, A. Węgrzyn, J. Grzesiak, G. Celichowski, J. Grobelny, K. Eriksson and M. Krzyzowska, Viruses, 2018, 10, 524 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Wen, X. Chen, X. Zhu, Y. Gong, G. Yuan, X. Qin and J. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 43393–43408 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Thomas, B. S. P. Harshita, P. Mishra and S. Talegaonkar, Curr. Pharm. Des., 2015, 21, 6165–6188 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Singh, P. Dubey, M. Pradhan and M. R. Singh, Expert Opin. Drug Delivery, 2013, 10, 241–259 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhao, X. Zhao, Y. Cheng, X. Guo and W. Yuan, Mol. Pharm., 2018, 15, 1791–1799 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Hwang, E. Lee, J. Kim, Y. Seo, K. H. Lee, J. W. Hong, A. A. Gilad, H. Park and J. Choi, Colloids Surf., B, 2016, 142, 290–296 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Garcia, M. H. Kim, V. A. Morikis and S. I. Simon, Front. Immunol., 2020, 11, 571489 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Jiang, K. Wang, X. Zhang, B. Ouyang, H. Liu, Z. Pang and W. Yang, Small, 2020, 16, 2001704 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Mohajeri, B. Behnam and A. Sahebkar, J. Cell Physiol., 2018, 234, 298–319 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. McKernan, N. A. Virani, G. N. F. Faria, C. G. Karch, R. P. Silvy, D. E. Resasco, L. F. Thompson and R. G. Harrison, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2021, 16, 1–9 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. A. F. M. Hassan, L. Smyth, J. T. W. Wang, P. M. Costa, K. Ratnasothy, S. S. Diebold, G. Lombardi and K. T. Al-Jamal, Biomaterials, 2016, 104, 310–322 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. M. Radzi, N. A. Johari, W. F. A. W. M. Zawawi, N. A. Zawawi, N. A. Latiff, N. A. N. N. Malek, A. A. Wahab, M. I. Salim and K. Jemon, Biomater. Adv., 2022, 134, 112586 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Alizadeh, E. E. White, T. C. Sanchez, S. Liu, L. Zhang, B. Badie and J. M. Berlin, Bioconjugate Chem., 2018, 29, 1659–1668 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. C. B. D. Faria, L. I. D. Santos, J. P. Coelho, H. B. Ribeiro, M. A. Pimenta, L. O. Ladeira, D. A. Gomes, C. A. Furtado and R. T. Gazzinelli, Nano Lett., 2014, 14, 5458–5470 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Hou, D. Chen, R. Wang, R. Wang, H. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Z. Nie and S. Lu, Angew. Chem., 2021, 133, 6655–6666 CrossRef.
- Q. Zhou, N. Gong, D. Zhang, J. Li, X. Han, J. Dou, J. Huang, K. Zhu, P. Liang, X. Liang and J. Yu, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 2920–2932 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. H. Kim, J. Seo and K. Na, Mol. Pharm., 2020, 17, 2532–2545 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. H. Horst, C. V. d. S. Rodrigues, P. H. P. R. Carvalho, A. M. Leite, R. B. Azevedo, B. A. D. Neto, J. R. Corrêa, M. P. Garcia, S. Alotaibi, M. Henini, S. B. Chaves and M. O. Rodrigues, RSC Adv., 2021, 11, 6346–6352 RSC.
- X. Zhang, H. Li, C. Yi, G. Chen, Y. Li, Y. Zhou, G. Chen, Y. Li, Y. He and D. Yu, Int. J. Nanomed., 2020, 15, 9627 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Lategan, H. Alghadi, M. Bayati, M. F. de Cortalezzi and E. Pool, Nanomaterials, 2018, 8, 125 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. J. Feito, R. Diez-Orejas, M. Cicuéndez, L. Casarrubios, J. M. Rojo and M. T. Portolés, Colloids Surf., B, 2019, 176, 96–105 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Zhou, J. Song, M. Wang, X. Wang, J. Wang, E. W. Howard, F. Zhou, J. Qu and W. R. Chen, Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 21640–21647 RSC.
- Y. Tao, Y. Zhang, E. Ju, H. Ren and J. Ren, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 12419–12426 RSC.
- P. Pei, W. Shen, H. Zhou, Y. Sun, J. Zhong, T. Liu and K. Yang, Nano Today, 2021, 38, 101144 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Chakraborty, R. Pal, M. Ali, L. M. Singh, D. S. Rahman, S. K. Ghosh and M. Sengupta, Cell. Mol. Immunol., 2015, 13, 191–205 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Vuković, Ž. Cvetić, K. Bendelja, R. Barbir, M. Milić, B. Dobrošević, V. Šerić and I. V. Vrček, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2021, 26, 817–831 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Mu, G. Lin, M. Jeon, H. Wang, F. C. Chang, R. A. Revia, J. Yu and M. Zhang, Mater. Today, 2021, 50, 149–169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zanganeh, G. Hutter, R. Spitler, O. Lenkov, M. Mahmoudi, A. Shaw, J. S. Pajarinen, H. Nejadnik, S. Goodman, M. Moseley, L. M. Coussens and H. E. Daldrup-Link, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2016, 11, 986 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Cobaleda-Siles, M. Henriksen-Lacey, A. R. De Angulo, A. Bernecker, V. G. Vallejo, B. Szczupak, J. Llop, G. Pastor, S. Plaza-Garcia, M. Jauregui-Osoro, L. K. Meszaros and J. C. Mareque-Rivas, Small, 2014, 10, 5054–5067 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Juneja, H. Vadarevu, J. Halman, M. Tarannum, L. Rackley, J. Dobbs, J. Marquez, M. Chandler, K. Afonin and J. L. Vivero-Escoto, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 38873–38886 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Xu, J. Nam, H. Hong, Y. Xu and J. J. Moon, ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 12148–12161 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Zhao, L. Qiu, S. Zhou, L. Li, Z. Qian and H. Zhang, Int. J. Nanomed., 2021, 16, 2107 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Seth, H. G. Derami, P. Gupta, Z. Wang, P. Rathi, R. Gupta, T. Cao, J. J. Morrissey and S. Singamaneni, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 42499 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. A. Bielecki, M. E. Lorkowski, W. M. Becicka, P. U. Atukorale, T. J. Moon, Y. Zhang, M. Wiese, G. Covarrubias, S. Ravichandran and E. Karathanasis, Nanoscale Horiz., 2021, 6, 156–167 RSC.
- W. An, S. Defaus, D. Andreu and P. Rivera-Gil, Front. Immunol., 2021, 12, 684612 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jafari, N. Maleki-Dizaji, J. Barar, M. Barzegar-Jalali, M. Rameshrad and K. Adibkia, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 2016, 91, 225–235 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Fulgione, N. Nocerino, M. Iannaccone, S. Roperto, F. Capuano, N. Roveri, M. Lelli, A. Crasto, A. Calogero, A. P. Pilloni and R. Capparelli, PLoS One, 2016, 11, e0158646 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Wang, X. Li, A. Ito, Y. Watanabe and N. M. Tsuji, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 7078–7081 RSC.
- Y. Hua, J. Wu, H. Wu, C. Su, X. Li, Q. Ao, Q. Zeng, X. Zhu and X. Zhang, Acta Biomater., 2021, 135, 650–662 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, W. Sha, X. Zhang, M. Cheng, Q. Wu, W. Wang and Z. Yuan, Biomater. Sci., 2019, 7, 5027–5034 RSC.
- F. Zhao, C. Wang, Q. Yang, S. Han, Q. Hu and Z. Fu, Life Sci., 2018, 202, 44–51 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. C. Schanen, S. Das, C. M. Reilly, W. L. Warren, W. T. Self, S. Seal and D. R. Drake, PLoS One, 2013, 8, e62816 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wang, J. S. Lee, D. Kim and L. Zhu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 39971–39984 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Moratin, P. Ickrath, A. Scherzad, T. J. Meyer, S. Naczenski, R. Hagen and S. Hackenberg, Nanomaterials, 2021, 11, 629 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Dey, S. Manna, S. Kumar, S. Chattopadhyay, B. Saha and S. Roy, Cytokine, 2020, 127, 154958 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. K. Mishra, A. Selim, V. Gowri, A. Ahmad, A. Nadeem, N. Siddiqui, S. S. Raza, G. Jayamurugan and R. Khan, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2022, 8, 2088–2095 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Sur, B. Pradhan, A. Banerjee and P. Aich, PLoS One, 2015, 10, e0123905 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Li, D. He, X. Xiao, G. Yu, G. Hu, W. Zhang, X. Wen, Y. Lin, X. Li, H. Lin, Y. Diao and Y. Tang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 25290–25305 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. P. Suarez-Kelly, A. R. Campbell, I. V. Rampersaud, A. Bumb, M. S. Wang, J. P. Butchar, S. Tridandapani, L. Yu, A. A. Rampersaud and W. E. Carson, Nanomedicine, 2017, 13, 909–920 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Pentecost, C. E. Witherel, Y. Gogotsi and K. L. Spiller, Biomater. Sci., 2017, 5, 2131 RSC.
- A. Pentecost, M. J. Kim, S. Jeon, Y. J. Ko, I. C. Kwon, Y. Gogotsi, K. Kim and K. L. Spiller, Regen. Biomater., 2019, 6, 163–174 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Tenchov, R. Bird, A. E. Curtze and Q. Zhou, ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 16982–17015 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Ramesh, V. Malik, H. A. Ranjani, H. Smith and A. A. Kulkarni, Drug Deliv. Transl. Res., 2021, 11, 2317–2327 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Zhang, S. Liu, S. Shi, Y. Chen, F. Xu, X. Wei and Y. Xu, J. Controlled Release, 2020, 320, 168–178 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zheng, J. Zhang, J. Jiang, Y. He, W. Zhang, X. Mo, X. Kang, Q. Xu, B. Wang and Y. Huang, J. Immunother. Cancer., 2020, 8, e000207 CrossRef PubMed.
- G. Biber, B. Sabag, A. Raiff, A. Ben-Shmuel, A. Puthenveetil, J. I. C. Benichou, T. Jubany, M. Levy, S. Killner and M. Barda-Saad, EMBO Mol. Med., 2021, 14, e14073 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. Di Francesco, D. Gurgone, R. Palomba, M. F. M. M. Ferreira, T. Catelani, A. Cervadoro, P. Maffia and P. Decuzzi, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 37943–37956 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wang, L. He, D. Fan, W. Liang and J. Fang, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8, 1841–1851 RSC.
- B. Kim, H. B. Pang, J. Kang, J. H. Park, E. Ruoslahti and M. J. Sailor, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 1–13 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. X. Zhang, Y. Y. Zhao, J. Shen, X. Sun, Y. Liu, H. Liu, Y. Wang and J. Wang, Nano Lett., 2019, 19, 2774–2783 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Yang, Q. Tang, L. Chen, J. Chang, T. Jiang, J. Zhao, M. Wang and P. R. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 18087–18094 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Swaminathan, E. A. Thoryk, K. S. Cox, J. S. Smith, J. J. Wolf, M. E. Gindy, D. R. Casimiro and A. J. Bett, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 1–17 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. S. Nogueira, A. Schlegel, K. Maxeiner, B. Weber, M. Barz, M. A. Schroer, C. E. Blanchet, D. I. Svergun, S. Ramishetti, D. Peer, P. Langguth, U. Sahin and H. Haas, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2020, 3, 10634–10645 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Banerjee, M. De, G. Dey, R. Bharti, S. Chattopadhyay, N. Ali, P. Chakrabarti, R. L. Reis, S. C. Kundu and M. Mandal, Biomater. Sci., 2019, 7, 1161–1178 RSC.
- S. Trombino, C. Servidio, A. S. Laganà, F. Conforti, M. Marrelli and R. Cassano, Molecules, 2020, 25, 3535 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Barbosa, A. R. Neves, A. M. Silva, M. A. Barbosa, M. S. Reis and S. G. Santos, Int. J. Nanomed., 2016, 11, 3501 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. H. Erasmus, A. P. Khandhar, J. Guderian, B. Granger, J. Archer, M. Archer, E. Gage, J. Fuerte-Stone, E. Larson, S. Lin, R. Kramer, R. N. Coler, C. B. Fox, D. T. Stinchcomb, S. G. Reed and N. Van Hoeven, Mol. Ther., 2018, 26, 2507 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Song, Y. Jiang, W. Zhang, G. Elfawal, K. Wang, D. Jiang, H. Hong, J. Wu, C. He, X. Mo and H. Wang, Acta Biomater., 2022, 140, 247–260 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Wang, X. Wang, D. Jiang, Y. Pei, Z. Wang, X. Zhou, J. Wu, X. Mo and H. Wang, Compos. B Eng., 2022, 233, 109648 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Liu, L. Luo, S. Zheng, Y. Niu, R. Bo, Y. Huang, J. Xing, Z. Li and D. Wang, Int. J. Nanomed., 2016, 11, 3571 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Ou, Y. Sun, S. Zhou, P. Gu, Z. Liu, R. Bo, Y. Hu, J. Liu and D. Wang, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 109, 748–760 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Kibria, E. K. Ramos, Y. Wan, D. R. Gius and H. Liu, Mol. Pharm., 2018, 15, 3625–3633 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liang, L. Duan, J. Lu and J. Xia, Theranostics, 2021, 11, 3183 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Fu, C. Lei, S. Liu, Y. Cui, C. Wang, K. Qian, T. Li, Y. Shen, X. Fan, F. Lin, M. Ding, M. Pan, X. Ye, Y. Yang and S. Hu, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Huang, Y. Rong, X. Tang, K. Yi, P. Qi, J. Hou, W. Liu, Y. He, X. Gao, C. Yuan and F. Wang, Mol. Cancer, 2022, 21, 1–19 Search PubMed.
- Y. W. Choo, M. Kang, H. Y. Kim, J. Han, S. Kang, J. R. Lee, G. J. Jeong, S. P. Kwon, S. Y. Song, S. Go, M. Jung, J. Hong and B. S. Kim, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 8977–8993 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Fan, Z. Chen, H. Bin Tang, L. Q. Shan, Z. Y. Chen, X. H. Wang, D. G. Huang, S. C. Liu, X. Chen, H. Yang and D. Hao, Bioeng. Transl. Med., 2022, 7, e10287 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Jiang, J. Yun, H. J. Kaplan, Y. Zhao, D. Sun and H. Shao, Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol., 2021, 49, 1069–1077 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. E. Boone, C. Wang, M. A. Lopez-Ramirez, V. Beiss, S. Shukla, P. L. Chariou, D. Kupor, R. Rueda, J. Wang and N. F. Steinmetz, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2020, 3, 8037–8051 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Shahgolzari, M. Pazhouhandeh, M. Milani, S. Fiering and A. Y. Khosroushahi, Nanomedicine, 2021, 16, 97–107 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Cheng, T. Du, Y. Li, Y. Qi, H. Min, Y. Wang, Q. Zhang, C. Wang, Y. Zhou, L. Li, S. Ye, X. Zhou, S. Bi, J. Yang and L. Ren, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 53682–53690 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. M. Joyce, W.-H. Chen, R. S. Sankhala, M. Rao, N. L. Michael, K. Modjarrad, M. Gordon Joyce, A. Hajduczki, P. V. Thomas, M. Choe, E. J. Martinez, W. C. Chang, C. E. Peterson, E. B. Morrison, C. Smith, R. E. Chen, A. Ahmed, L. Wieczorek, A. Anderson, J. Brett Case, Y. Li, T. Oertel, L. Rosado, A. Ganesh, C. Whalen, J. M. Carmen, L. Mendez-Rivera, C. P. Karch, N. Gohain, Z. Villar, D. McCurdy, Z. Beck, J. Kim, S. Shrivastava, O. Jobe, V. Dussupt, S. Molnar, U. Tran, C. B. Kannadka, S. Soman, C. Kuklis, M. Zemil, H. Khanh, W. Wu, M. A. Cole, D. K. Duso, L. W. Kummer, T. J. Lang, S. E. Muncil, J. R. Currier, S. J. Krebs, V. R. Polonis, S. Rajan, P. M. McTamney, M. T. Esser, W. W. Reiley, M. Rolland, N. de Val, M. S. Diamond, G. D. Gromowski, G. R. Matyas, M. Rao, N. L. Michael and K. Modjarrad, Cell Rep., 2021, 37, 110143 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Yan, X. Wang, P. Lou, Z. Hu, P. Qu, D. Li, Q. Li, Y. Xu, J. Niu, Y. He, J. Zhong and Z. Huang, J. Infect. Dis., 2020, 221, 1304–1314 CAS.
- A. A. Murji, J. S. Qin, T. Hermanus, L. Morris and I. S. Georgiev, Viruses, 2021, 13, 1296 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Gao, H. T. Liu, Y. Q. Xu, L. Zhang, Y. R. Liu, Q. Ren, J. P. Sheng and Z. X. Zhang, Cancer Cell Int., 2021, 21, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Z. Zhao, Y. Li, H. Y. Han, L. H. Mo, G. Yang, Z. Q. Liu, C. Ma, P. C. Yang and S. Liu, Mol. Immunol., 2021, 129, 103–111 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Jang, H. Kim, S. Yoon, H. Lee, J. Hwang, J. Jung, J. H. Chang, J. Choi and H. Kim, J. Controlled Release, 2021, 330, 293–304 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Elashiry, R. Elsayed, M. M. Elashiry, M. H. Rashid, R. Ara, A. S. Arbab, A. R. Elawady, M. Hamrick, Y. Liu, W. Zhi, R. Lucas, J. Vazquez and C. W. Cutler, Front. Immunol., 2021, 12, 636222 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Shan, W. Dou, Y. Zhang and M. Qi, Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 22268–22280 RSC.
- A. Xia, Y. Zhang, J. Xu, T. Yin and X. J. Lu, Front. Immunol., 2019, 10, 1719 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. K. Singh and J. P. McGuirk, Lancet Oncol., 2020, 21, e168–e178 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Wang, T. Wang, H. Yu, B. Feng, L. Zhou, F. Zhou, B. Hou, H. Zhang, M. Luo and Y. Li, Sci. Immunol., 2019, 4, eaau6584 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Mi, C. C. Smith, F. Yang, Y. Qi, K. C. Roche, J. S. Serody, B. G. Vincent and A. Z. Wang, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1706098 CrossRef PubMed.
- W. Yang, H. Deng, S. Zhu, J. Lau, R. Tian, S. Wang, Z. Zhou, G. Yu, L. Rao, L. He, Y. Ma and X. Chen, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eabb2712 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Smith, E. I. Wafa, S. M. Geary, K. Ebeid, S. O. Alhaj-Suliman and A. K. Salem, Sci. Adv., 2022, 8, 3150 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. T. Smith, S. B. Stephan, H. F. Moffett, L. E. McKnight, W. Ji, D. Reiman, E. Bonagofski, M. E. Wohlfahrt, S. P. S. Pillai and M. T. Stephan, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12, 813–822 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Alhallak, J. Sun, K. Wasden, N. Guenthner, J. O'Neal, B. Muz, J. King, D. Kohnen, R. Vij, S. Achilefu, J. F. DiPersio and A. K. Azab, Leukemia, 2021, 35, 2346–2357 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. Sahin, A. Muik, E. Derhovanessian, I. Vogler, L. M. Kranz, M. Vormehr, A. Baum, K. Pascal, J. Quandt, D. Maurus, S. Brachtendorf, V. Lörks, J. Sikorski, R. Hilker, D. Becker, A. K. Eller, J. Grützner, C. Boesler, C. Rosenbaum, M. C. Kühnle, U. Luxemburger, A. Kemmer-Brück, D. Langer, M. Bexon, S. Bolte, K. Karikó, T. Palanche, B. Fischer, A. Schultz, P. Y. Shi, C. Fontes-Garfias, J. L. Perez, K. A. Swanson, J. Loschko, I. L. Scully, M. Cutler, W. Kalina, C. A. Kyratsous, D. Cooper, P. R. Dormitzer, K. U. Jansen and Ö. Türeci, Nature, 2020, 586, 594–599 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. E. Ngono, T. Syed, A. V. Nguyen, J. A. Regla-Nava, M. Susantono, D. Spasova, A. Aguilar, M. West, J. Sparks, A. Gonzalez, E. Branche, J. L. DeHart, J. B. Vega, P. P. Karmali, P. Chivukula, K. Kamrud, P. Aliahmad, N. Wang and S. Shresta, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eabb2154 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Singha, K. Shao, Y. Yang, X. Clemente-Casares, P. Solé, A. Clemente, J. Blanco, Q. Dai, F. Song, S. W. Liu, J. Yamanouchi, C. S. Umeshappa, R. H. Nanjundappa, P. Detampel, M. Amrein, C. Fandos, R. Tanguay, S. Newbigging, P. Serra, A. Khadra, W. C. W. Chan and P. Santamaria, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12, 701–710 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. E. Kenison, A. Jhaveri, Z. Li, N. Khadse, E. Tjon, S. Tezza, D. Nowakowska, A. Plasencia, V. P. Stanton, D. H. Sherr and F. J. Quintana, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2020, 117, 32017–32028 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Yi, N. B. Karabin, J. Zhu, S. Bobbala, H. Lyu, S. Li, Y. Liu, M. Frey, M. Vincent and E. A. Scott, Front. bioeng. biotechnol., 2020, 8, 544669 Search PubMed.
- R. A. Maldonado, R. A. LaMothe, J. D. Ferrari, A. H. Zhang, R. J. Rossi, P. N. Kolte, A. P. Griset, C. O'Neil, D. H. Altreuter, E. Browning, L. Johnston, O. C. Farokhzad, R. Langer, D. W. Scott, U. H. Von Andrian and T. K. Kishimoto, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2015, 112, E156–E165 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Huq, E. L. G. Samuel, W. K. A. Sikkema, L. G. Nilewski, T. Lee, M. R. Tanner, F. S. Khan, P. C. Porter, R. B. Tajhya, R. S. Patel, T. Inoue, R. G. Pautler, D. B. Corry, J. M. Tour and C. Beeton, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 1–15 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Xu, L. Bian, M. Shen, X. Li, J. Zhu, S. Chen, L. Xiao, Q. Zhang, H. Chen, K. Xu and T. Yang, Diabetologia, 2017, 60, 2418–2431 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. L. Jamison, T. Neef, A. Goodspeed, B. Bradley, R. L. Baker, S. D. Miller and K. Haskins, J. Immunol., 2019, 203, 48–57 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Carambia, C. Gottwick, D. Schwinge, S. Stein, R. Digigow, M. Şeleci, D. Mungalpara, M. Heine, F. A. Schuran, C. Corban, A. W. Lohse, C. Schramm, J. Heeren and J. Herkel, Immunology, 2021, 162, 452–463 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. C. Palmer, S. Jatana, S. J. Phelan-Dickinson and L. A. DeLouise, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, 1–11 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Keum, T. W. Kim, Y. Kim, C. Seo, Y. Son, J. Kim, D. Kim, W. Jung, C. H. Whang and S. Jon, J. Controlled Release, 2020, 325, 359–369 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Jhun, J. Moon, J. Ryu, Y. Shin, S. Lee, K. H. Cho, T. Kang, M. La Cho and S. H. Park, PLoS One, 2020, 15, e0241080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Ingale, A. Stano, J. Guenaga, S. K. Sharma, D. Nemazee, M. B. Zwick and R. T. Wyatt, Cell Rep., 2016, 15, 1986–1999 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Tokatlian, D. W. Kulp, A. A. Mutafyan, C. A. Jones, S. Menis, E. Georgeson, M. Kubitz, M. H. Zhang, M. B. Melo, M. Silva, D. S. Yun, W. R. Schief and D. J. Irvine, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, 1–13 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Sliepen, G. Ozorowski, J. A. Burger, T. Van Montfort, M. Stunnenberg, C. LaBranche, D. C. Montefiori, J. P. Moore, A. B. Ward and R. W. Sanders, Retrovirology, 2015, 12, 1–5 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. J. Moyer, Y. Kato, W. Abraham, J. Y. H. Chang, D. W. Kulp, N. Watson, H. L. Turner, S. Menis, R. K. Abbott, J. N. Bhiman, M. B. Melo, H. A. Simon, S. Herrera-De la Mata, S. Liang, G. Seumois, Y. Agarwal, N. Li, D. R. Burton, A. B. Ward, W. R. Schief, S. Crotty and D. J. Irvine, Nat. Med., 2020, 26, 430–440 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Tao, B. L. Hurst, A. K. Shakya, M. J. Uddin, R. S. J. Ingrole, M. Hernandez-Sanabria, R. P. Arya, L. Bimler, S. Paust, E. B. Tarbet and H. S. Gill, Antiviral Res., 2017, 141, 62–72 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. F. Villar, J. Patel, G. C. Weaver, M. Kanekiyo, A. K. Wheatley, H. M. Yassine, C. E. Costello, K. B. Chandler, P. M. McTamney, G. J. Nabel, A. B. McDermott, J. R. Mascola, S. A. Carr and D. Lingwood, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 1–11 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. G. Kelly, H. X. Tan, J. A. Juno, R. Esterbauer, Y. Ju, W. Jiang, V. C. Wimmer, B. C. Duckworth, J. R. Groom, F. Caruso, M. Kanekiyo, S. J. Kent and A. K. Wheatley, JCI Insight, 2020, 5, e136653 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Kanekiyo, M. G. Joyce, R. A. Gillespie, J. R. Gallagher, S. F. Andrews, H. M. Yassine, A. K. Wheatley, B. E. Fisher, D. R. Ambrozak, A. Creanga, K. Leung, E. S. Yang, S. Boyoglu-Barnum, I. S. Georgiev, Y. Tsybovsky, M. S. Prabhakaran, H. Andersen, W. P. Kong, U. Baxa, K. L. Zephir, J. E. Ledgerwood, R. A. Koup, P. D. Kwong, A. K. Harris, A. B. McDermott, J. R. Mascola and B. S. Graham, Nat. Immunol., 2019, 20, 362 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Wang, X. Zhou, Y. Bian, S. Wang, Q. Chai, Z. Guo, Z. Wang, P. Zhu, H. Peng, X. Yan, W. Li, Y. X. Fu and M. Zhu, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2020, 15, 406–416 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Fichtner, M. Dreyling, M. Binder and M. Trepel, J. Hematol. Oncol., 2017, 10, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Phipps, Y. Chen, S. Gopalakrishnan and D. Tan, Ther. Adv. Hematol., 2015, 6, 120 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Weinstein, I. A. Toker, R. Emmanuel, S. Ramishetti, I. Hazan-Halevy, D. Rosenblum, M. Goldsmith, A. Abraham, O. Benjamini, O. Bairey, P. Raanani, A. Nagler, J. Lieberman and D. Peer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2016, 113, E16–E22 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Li, G. Zhang, C. Jiang, F. Zhang, C. Ke, H. Zhao, Y. Sun, M. Zhao, D. Chen, X. Zhu, L. Zhang, B. Li, J. Dai and W. Li, Oncotarget, 2015, 6, 24192–24204 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Falgàs, V. Pallarès, U. Unzueta, Y. Núñez, J. Sierra, A. Gallardo, L. Alba-Castellón, M. A. Mangues, P. Álamo, A. Villaverde, E. Vázquez, R. Mangues and I. Casanova, Int. J. Nanomed., 2021, 16, 1869–1888 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. R. Banihashemi, F. Rahbarizadeh, A. Z. Hosseini, D. Ahmadvand and S. K. Nikkhoi, Int. Immunopharmacol., 2021, 100, 107927 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Wu, S. Su, Y. Wu, Y. Wu, Z. Zhang and Q. Chen, Int. Immunopharmacol., 2020, 88, 106933 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Pozsgay, F. Babos, K. Uray, A. Magyar, G. Gyulai, É. Kiss, G. Nagy, B. Rojkovich, F. Hudecz and G. Sármay, Arthritis Res. Ther., 2016, 18, 1–12 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Rao, L. Wu, Z. Liu, R. Tian, G. Yu, Z. Zhou, K. Yang, H. G. Xiong, A. Zhang and G. T. Yu, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 4909 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. M. K. Tang, D. J. Nikolic-Paterson and H. Y. Lan, Nat. Rev. Nephrol., 2019, 15, 144–158 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Watanabe, M. Alexander, A. V. Misharin and G. R. S. Budinger, J. Clin. Invest., 2019, 129, 2619–2628 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. C. Funes, M. Rios, J. Escobar-Vera and A. M. Kalergis, Immunology, 2018, 154, 186–195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Miao, X. Leng and Q. Zhang, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2017, 18, 336 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Zhang, N. N. Parayath, C. I. Ene, S. B. Stephan, A. L. Koehne, M. E. Coon, E. C. Holland and M. T. Stephan, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1–16 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Sun, C. H. T. Kwong, C. Gao, J. Wei, L. Yue, J. Zhang, R. D. Ye and R. Wang, Theranostics, 2020, 10, 10106–10119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Hirata, E. Miyako, N. Hanagata, N. Ushijima, N. Sakaguchi, J. Russier, M. Yudasaka, S. Iijima, A. Bianco and A. Yokoyama, Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 14514–14522 RSC.
- J. Wu, J. Zhu, Q. Wu, Y. An, K. Wang, T. Xuan, J. Zhang, W. Song, H. He, L. Song, J. Zheng and J. Xiao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 2230–2244 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Gao, J. Zhang, C. Chen, M. Chen, P. Sun, W. Du, S. Zhang, Y. Liu, R. Zhang, M. Bai, C. Fan, J. Wu, T. Men and X. Jiang, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 3980–3990 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Lim, W. Na, H. O. Kim, M. Yeom, A. Kang, G. Park, C. Park, J. Ki, S. Lee, B. Jung, H. H. Jeong, D. Park, D. Song and S. Haam, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8, 5620–5626 RSC.
- Y. Yang, L. Guo, Z. Wang, P. Liu, X. Liu, J. Ding and W. Zhou, Biomaterials, 2021, 264, 120390 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liu, J. Wang, J. Zhang, S. Marbach, W. Xu and L. Zhu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 52402–52414 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Tang, M. E. Lobatto, L. Hassing, S. Van Der Staay, S. M. Van Rijs, C. Calcagno, M. S. Braza, S. Baxter, F. Fay, B. L. Sanchez-Gaytan, R. Duivenvoorden, H. B. Sager, Y. M. Astudillo, W. Leong, S. Ramachandran, G. Storm, C. Pérez-Medina, T. Reiner, D. P. Cormode, G. J. Strijkers, E. S. G. Stroes, F. K. Swirski, M. Nahrendorf, E. A. Fisher, Z. A. Fayad and W. J. M. Mulder, Sci. Adv., 2015, 1, e1400223 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Deng, Q. Zhang, P. He, B. Zhou, K. He, X. Sun, G. Lei, T. Gong and Z. Zhang, Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 1–15 CrossRef PubMed.
- I. Relaño-Rodríguez, M. D. L. S. Espinar-Buitrago, V. Martín-Cañadilla, R. Gómez-Ramírez and M. Á. Muñoz-Fernández, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 8366 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Tan, L. He, X. Meng, W. Wang, H. Pan, W. Yin, T. Zhu, X. Huang and H. Shan, J. Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19, 173 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Singh, S. Chakraborty, S. W. Wong, N. A. Hefner, A. Stuart, A. S. Qadir, A. Mukhopadhyay, K. Bachmaier, J. W. Shin, J. Rehman and A. B. Malik, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2022, 119, e2121098119 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Cifuentes-Rius, A. Desai, D. Yuen, A. P. R. Johnston and N. H. Voelcker, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2021, 16, 37–46 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. K. S. Rajput, S. S. Kesharwani, S. Kumar, P. Muley, S. Narisetty and H. Tummala, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 27589–27602 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Mao, F. Hu, Z. Yi, K. Kenry, S. Xu, S. Yan, Z. Luo, W. Wu, Z. Wang, D. Kong, X. Liu and B. Liu, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eabb2712 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, X. You, X. Wang, L. Cui, Z. Wang, F. Xu, M. Li, Z. Yang, J. Liu, P. Huang, Y. Kang, J. Wu and X. Xia, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2021, 118, e2005191118 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Si, Q. Tian, F. Zhao, S. H. Kelly, L. S. Shores, D. F. Camacho, A. I. Sperling, M. S. Andrade, J. H. Collier and A. S. Chong, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, 995–1002 Search PubMed.
- X. Zheng, C. Sun, R. Yu, X. Chu, J. Xu, C. Liu, M. Zhao, X. Xu, M. Xia and C. Wang, Int. J. Pharm., 2020, 577, 119034 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, S. Shen, G. Zhao, C. F. Xu, H. B. Zhang, Y. L. Luo, Z. T. Cao, J. Shi, Z. Bin Zhao, Z. X. Lian and J. Wang, Biomaterials, 2019, 217, 119302 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. W. Kim, Y. Kim, W. Jung, D. E. Kim, H. Keum, Y. Son and S. Jon, J. Controlled Release, 2021, 331, 74–84 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- U. e. Habiba, M. Rafiq, M. B. Khawar, B. Nazir, G. Haider and N. Nazir, Adv. Cancer Biol.: Metastasis, 2022, 5, 100053 CAS.
- A. E. Barberio, S. G. Smith, S. Correa, C. Nguyen, B. Nhan, M. Melo, T. Tokatlian, H. Suh, D. J. Irvine and P. T. Hammond, ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 11238–11253 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Lai, S. Swaminathan, V. Baylot, A. Mosley, R. Dhanasekaran, M. Gabay and D. W. Felsher, J. Immunother. Cancer, 2018, 6, 1–11 Search PubMed.
- J. Q. Liu, C. Zhang, X. Zhang, J. Yan, C. Zeng, F. Talebian, K. Lynch, W. Zhao, X. Hou, S. Du, D. D. Kang, B. Deng, D. W. McComb, X. F. Bai and Y. Dong, J. Controlled Release, 2022, 345, 306–313 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kienzle, S. Kurch, J. Schlöder, C. Berges, R. Ose, J. Schupp, A. Tuettenberg, H. Weiss, J. Schultze, S. Winzen, M. Schinnerer, K. Koynov, M. Mezger, N. K. Haass, W. Tremel and H. Jonuleit, Adv. Healthc. Mater., 2017, 6, 1700012 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. Wu, Q. Qiao, X. Qin, D. Zhang and Z. Zhang, Nanomedicine, 2019, 18, 66–77 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. T. Tang, B. Wang, M. Wu, Z. L. Li, Y. Feng, J. Y. Cao, D. Yin, H. Liu, R. N. Tang, S. D. Crowley, L. L. Lv and B. C. Liu, Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, 748–760 Search PubMed.
- C. Baecher-Allan, B. J. Kaskow and H. L. Weiner, Neuron, 2018, 97, 742–768 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. F. González, E. Acuña, G. Arellano, P. Morales, P. Sotomayor, F. Oyarzun-Ampuero and R. Naves, J. Controlled Release, 2021, 331, 443–459 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. M. Raimondo and D. J. Mooney, Sci. Adv., 2021, 7, 3693–3716 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Halwani, A. S. Shaik, E. Ratemi, S. Afzal, R. Kenana, S. Al-Muhsen and A. Al Faraj, Exp. Mol. Med., 2016, 48, e262 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Ng, J. Dong, G. D'Agostino, S. Viswanathan, A. A. Widjaja, W. W. Lim, N. S. J. Ko, J. Tan, S. P. Chothani, B. Huang, C. Xie, C. J. Pua, A. M. Chacko, N. Guimarães-Camboa, S. M. Evans, A. J. Byrne, T. M. Maher, J. Liang, D. Jiang, P. W. Noble, S. Schafer and S. A. Cook, Sci. Transl. Med., 2019, 11, 1237 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Bai, G. Zhao, Q. Chen, Z. Li, M. Gao, W. Ho, X. Xu and X. Q. Zhang, Sci. Adv., 2022, 8, 7162 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Rao, S. Xia, W. Xu, R. Tian, G. Yu, C. Gu, P. Pan, Q. F. Meng, X. Cai, D. Qu, L. Lu, Y. Xie, S. Jiang and X. Chen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2020, 117, 27141–27147 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Zarantonello, H. Pedersen, N. S. Laursen and G. R. Andersen, Biomolecules, 2021, 11, 1–24 CrossRef PubMed.
- N. Maisha, T. Coombs and E. Lavik, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng., 2020, 6, 4903–4915 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Zhang, R. C. Lai, W. K. Sim, A. B. H. Choo, E. B. Lane and S. K. Lim, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 1–13 Search PubMed.
- Y. Li and F. Lin, Acta Biomater., 2019, 99, 330–338 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Avalle, F. Marino, A. Camporeale, C. Guglielmi, D. Viavattene, S. Bandini, L. Conti, J. Cimino, M. Forni, C. Zanini, A. Ghigo, R. L. Bogorad, F. Cavallo, P. Provero, V. Koteliansky and V. Poli, Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev., 2020, 18, 62–72 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. A. Colden, S. Kumar, B. Munkhbileg and D. V. Babushok, Front. Immunol., 2022, 12, 830172 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Zhang, W. Qiu, S. Crooke, Y. Li, A. Abid, B. Xu, M. G. Finn and F. Lin, ACS Chem. Biol., 2017, 12, 539–547 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. F. Jones and D. W. Grainger, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2009, 61, 438–456 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wahab, M. Ghazwani, U. Hani, A. R. Hakami, A. A. Almehizia, W. Ahmad, M. Z. Ahmad, P. Alam and S. Annadurai, Molecules, 2023, 28, 1216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. M. Metselaar and T. Lammers, Drug Delivery Transl. Res., 2020, 10, 721–725 CrossRef PubMed.
Footnote |
| † These authors contributed equally. |
|
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |
Click here to see how this site uses Cookies. View our privacy policy here.  a,
Bibrita
Bhar†
a,
Souradeep
Dey
a,
Bibrita
Bhar†
a,
Souradeep
Dey
 b,
Chitra
Jaiswal
a,
Victoria
J
a and
Biman B.
Mandal
b,
Chitra
Jaiswal
a,
Victoria
J
a and
Biman B.
Mandal
 *abc
*abc









