Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Total syntheses of spiroviolene and spirograterpene A: a structural reassignment with biosynthetic implications†
Hyung Min
Chi‡
 ,
Charles J. F.
Cole
,
Charles J. F.
Cole
 ,
Pengfei
Hu
,
Pengfei
Hu
 ,
Cooper A.
Taylor
,
Cooper A.
Taylor
 and
Scott A.
Snyder
and
Scott A.
Snyder
 *
*
Department of Chemistry, University of Chicago, 5735 S. Ellis Avenue, Chicago, IL 60637, USA. E-mail: sasnyder@uchicago.edu
First published on 30th September 2020
Abstract
The recent natural product isolates spiroviolene and spirograterpene A are two relatively non-functionalized linear triquinane terpenes with a large number of structural homologies. Nevertheless, three significant areas of structural disparity exist based on their original assignments, one of which implies a key stereochemical divergence early in their respective biosyntheses. Herein, using two known bicyclic ketone intermediates, a core Pd-catalyzed Heck cyclization sequence, and several chemoselective transformations, we describe concise total syntheses of both natural product targets and propose that the structure of spiroviolene should be reassigned. As a result, these natural products possess greater homology than previously anticipated.
Introduction
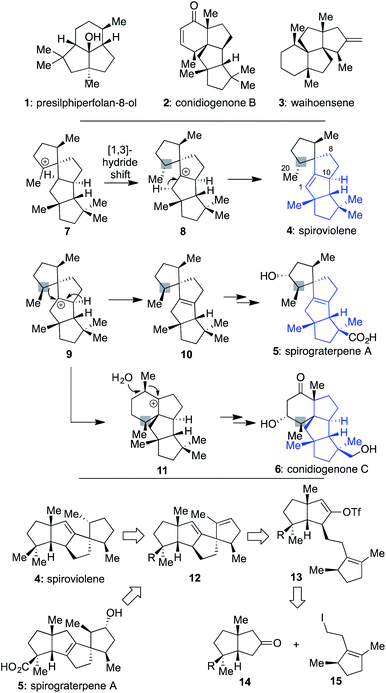
In recent years, chemists have devoted much attention to addressing the synthetic challenges posed by terpenes, such as 1–3 (Scheme 1), which possess a modicum of traditionally reactive functional groups.1–4 Indeed, efforts with such molecules have suggested that since functional groups are typically required to forge C–C bonds, they should be chosen strategically and used for multiple purposes to limit step counts since they often are target superfluous.5 In addition, when multiple quaternary centers are present,6 they should be used as an essential part of retrosynthetic planning, focused on the question of how the presence of one might assist in the formation of others.2bIt was against this backdrop that we became interested in the structures of spiroviolene (4)7 and spirograterpene A (5),8 two recently disclosed linear triquinanes characterized largely on the basis of NMR data. The first of these was isolated by Dickschat and co-workers from the treatment of a terpene cyclase analog (termed spiroviolene synthase, SvS) with geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP).7 The other was obtained by the Yang group from Penicillium granulatum MCCC 3A00475 and was shown to possess modest anti-allergic activity.8 From a structural perspective, these molecules possess a high degree of structural homology, with both containing the same core carbon skeleton comprised of 4 rings and 3 all-carbon quaternary centers. However, they also have three main differences: their overall oxidation level, with 5 possessing an additional hydroxyl and carboxylic acid group as opposed to the saturated hydrocarbon units of 4, the specific placement of their central alkene, and the stereochemical disposition of a methyl group at the highlighted position. It was the latter of these differences that especially caught our attention since its accuracy would require a divergence in how those chiral centers were originally set as part of their respective biosyntheses. Indeed, in the Dickschat work7 it was postulated that this key stereocenter might arise from intermediate 7via a facially selective 1,3-hydride shift to produce 8; deuterium-labelling studies supported that stereochemical assessment, assuming that all stereocenters were set as drawn in the initial cyclization of linear GGPP leading to this polycycle.9 Subsequent proton elimination would then afford spiroviolene (4).10 By contrast, as postulated by Yang,8 if diastereomer 9 could also be obtained from a cyclization process involving GGPP, then loss of an alternate hydride could afford the distinctive alkene of 10, ultimately leading to spirograterpene A (5) through further oxidations. Herein, we delineate a unified approach capable of achieving the expeditious total synthesis of both natural products. As a result, we also provide a body of evidence implicating that the structure of spiroviolene is in error and has a stereochemical disposition of its highlighted chiral center which matches that of spirograterpene A.
Results and discussion
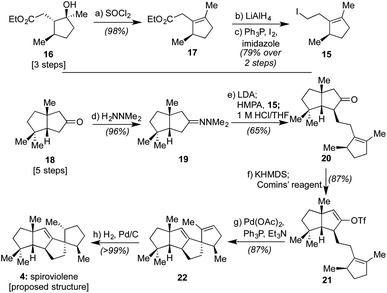
Given that we had already synthesized several members of the conidiogenones as single enantiomers and verified their absolute configuration in the process, including 2 and 6,2b we surmised that the stereochemical assignments for spirograterpene A (5) were likely accurate given that it was co-isolated with 6 and other members of the class. Biosynthetically, what was required to obtain these conidiogenone architectures from 9 was a 1,2-alkyl shift, instead of a β-hydride elimination, to afford reactive intermediate 11. That material, following a further 1,2-alkyl shift and attack by water, could afford most of the structural elements of 6.8 As such, to determine whether or not 4 and 5 were accurately assigned, we developed the retrosynthetic approach shown in the bottom of Scheme 1; the structures of 4 and 5 have been rotated here from their initial presentation. Our hope was that intermediates of type 12, differing solely in terms of their R group, could afford the means to access both targets and address any stereochemical ambiguities. In that regard, we assumed that the central alkene within 12 could be isomerized to that of its tetrasubstituted variant in spirograterpene A under thermodynamic control, and that the distal alkene could be chemoselectively functionalized through hydrogenation or hydroboration, respectively, to afford the final patterning of both natural products. We hoped that the latter of these functionalizations could be effected without complete facial control to provide access to both diastereomers to aid in structural assignments. In turn, the key quaternary spirocyclic stereocenter within 12 was anticipated to arise via a Heck cyclization11 from vinyl triflate 13, itself prepared from the regiospecific merger of bicyclic ketone 14 and alkyl iodide 15. These final steps would mirror operations used in our syntheses of both 1 and 2,1,2b commencing from an intermediate set (14) already in hand and used as part of our conidiogenone syntheses;2b as such, these bicyclic ketones could be envisioned as common intermediates leading to several different classes of natural products if successfully advanced to 4 and 5.As shown in Scheme 2, our efforts commenced with the preparation of enantioenriched 15. Using a procedure developed by Piva and co-workers,12 we were able to access γ-hydroxy ester 16 in 3 steps and in ∼90% ee. From here, subsequent regioselective elimination, as promoted by SOCl2, led to β,γ-unsaturated ester 17 in near quantitative yield. The desired alkyl iodide was then completed by reduction of the ester to a primary alcohol using LiAlH4 followed by an Appel reaction; these operations afforded 15 in 79% overall yield.
Next, following the conversion of known bicyclic ketone 18 to its corresponding hydrazone derivative (19), a subsequent regiospecific alkylation with 15 was achieved through the action of LDA and HMPA, using an acidic treatment (1 M HCl/THF) to cleave the hydrazone and afford ketone 20 in 65% isolated yield. In this event, the quaternary center uniting the two five-membered rings is presumed to afford sufficient steric bulk to drive its regioselectivity.2b From here, treatment with KHMDS and Comins' reagent led to the regiospecific formation of vinyl triflate 21, setting the stage for a stereospecific Heck cyclization leading to the requisite 1,3-trans stereochemical arrangement of substituents in tetracycle 22.11 These operations proceeded in 87% overall yield. At this point, all that remained was controlled reduction of one of its two alkenes to reach the putative structure of spiroviolene (i.e.4). Given that exploration of molecular models suggested standard hydrogenation might afford the undesired diastereomer preferentially, initial attempts focused on hydrogen atom transfer (HAT)-processes in a radical-type manifold.13 However, all efforts under such a regime failed. As such, an attempt was made under more standard conditions using a H2 atmosphere with Pd/C in EtOH. To our surprise, this event led to the smooth formation of a single product in near quantitative yield (98%). Its spectral properties (1H and 13C NMR) and optical rotation fully matched those reported by Dickschat and co-workers.7 Unclear, however, was the identity of the new chiral center within this synthetic material as the face of addition could not be confirmed.
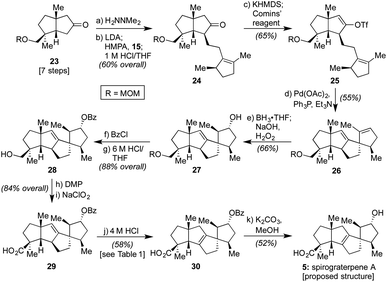
As such, we endeavored next to synthesize spirograterpene A (5, cf.Scheme 1). As indicated in Scheme 3, the initial elements of our route were effected following the same general sequence as for spiroviolene, starting with the MOM-protected 23.2b Alternate modes of protection provided distinct challenges in appending alkyl iodide 15, but with this group in place, that event, as well as subsequent vinyl triflate formation and Heck cyclization, afforded smooth access to tetracycle 26. At this juncture, the remaining major operations consisted of olefin isomerization and a series of oxidative manipulations, events that, in principle, could be conducted in either order. In practice, however, we were unable to effect olefin migration to its arguably more stable tetrasubstituted isomer at this stage as a series of undesired rearrangements were observed under a variety of conditions. As such, we exposed 26 to a standard hydroboration/oxidation protocol. This event afforded a single product in 66% yield, drawn here as 27 to match the stereochemistry proposed for spirograterpene A, though again of unknown configuration at this stage (vide infra).
With this material in hand, efforts were once again made to effect olefin isomerization, but either no transformation or decomposition was observed. As a result, we protected the secondary alcohol as a benzoate ester and adjusted the oxidation state of the other alcohol motif to that of a carboxylic acid over three additional steps to deliver 29.14,15 As shown in Table 1, the alkene within this material proved equally challenging to migrate, with a number of transition metals and photochemical conditions failing to afford any desired product.16 Under acidic conditions, including treatment with p-TsOH or TfOH, we observed the recovery of starting material, even at elevated temperatures. However, when 4 M HCl in 1,4-dioxane was used at 55 °C over the course of 12 h, 15% conversion to the desired product was detected by 1H NMR analysis based on the presence of a diagnostic allylic proton peak. By increasing the temperature (80 °C) and prolonging the reaction time (72 h), the desired alkene could be obtained in 58% isolated yield.17 Finally, methanolysis of the benzoate ester with K2CO3 at 55 °C afforded material which matched both the spectral (1H and 13C NMR) and optical rotation data obtained by the Yang group for spirograterpene A (5).8
| Entry | Conditions | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Pd(CH3CN)4](BF4)2, CH3CN, 23 °C, 12 h | No reaction |
| 2 | [Pd(CH3CN)4](BF4)2, CH3CN, 80 °C, 12 h | No reaction |
| 3 | UV (<365 nm), Et2O, 23 °C, 1 h | No reaction |
| 4 | UV (<365 nm), Et2O, 23 °C, 12 h | Decomposition |
| 5 | p-TsOH, toluene, 100 °C, 12 h | No reaction |
| 6 | p-TsOH, 1,4-dioxane, 100 °C, 12 h | No reaction |
| 7 | TfOH, 1,4-dioxane, 100 °C, 12 h | No reaction |
| 8 | HCl (4 M in 1,4-dioxane), 23 °C, 12 h | No reaction |
| 9 | HCl (4 M in 1,4-dioxane), 55 °C, 12 h | <15% conversion |
| 10 | HCl (4 M in 1,4-dioxane), 80 °C, 72 h | Full conversion (58% yield) |
With both targets in hand, and both events proceeding with a fully facially selective alkene functionalization (i.e. hydrogenation and hydroboration, respectively) on intermediates differing solely by the presence of a remote MOM-protected alcohol in the case of 26 (cf.Scheme 3), our conclusion was that the one of the two natural products was misassigned and that the configuration about their highlighted centers as denoted in Scheme 1 is conserved. Unfortunately, despite multiple efforts encompassing a range of synthetic derivatives, we were unable to obtain suitable material for X-ray diffraction to aid in such a reassignment.18 As such, computational, chemical, and spectroscopic means were explored instead.
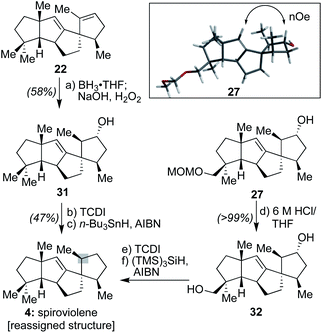
First, DFT transition state analysis for the hydroboration of 26 (see ESI†) revealed that in the potential energy surface for the transformation, there is a difference of 8.0 kcal mol−1 favoring hydroboration from the α-face, thereby supporting the stereochemical outcome originally proposed for spirograterpene A. In addition, NOE experiments with 27 (Scheme 4) revealed an interaction between the vinylic proton and the proton geminal to the hydroxyl group, one that would be possible only had the hydroboration taken place from the indicated, and computationally expected, face. These results are in agreement with the Mosher's ester analysis performed by the isolation team, which indicated that the absolute stereochemistry of the secondary alcohol is as drawn.8
Further, as shown in Scheme 4, to assess whether the MOM-protecting group of 26 played any role in leading to a differential facial preference for functionalization, alkene 22 was subjected to the same hydroboration/oxidation sequence to afford 31. Subsequent treatment with 1,1′-thiocarbonyldiimidazole (TCDI) and subjection of the resultant crude thiocarbamate intermediate to typical Barton–McCombie deoxygenation conditions19 afforded a sample with spectral properties that matched that of spiroviolene. Finally, intermediate 27, following conversion to diol 32 and a similar double Barton–McCombie deoxygenation, also afforded material with spectral properties that matched spiroviolene.20
Finally, we also considered the collated body of spectral data for natural spiroviolene collected by the Dickschat group. In particular, we examined key NOE correlations that served as a core element for the initial structural assignment. Specifically, the observed interaction between H-10 and C-20 (see Scheme 1 for positional numbering) as well as the interaction between H-8α and C-20, would appear to support both the original and revised structures. However, there is an additional interaction, albeit relatively weak, between the H-1 vinyl proton and C-20, one that could only be possible with the relative stereochemistry displayed in the revised structure.
As such, based on this collated evidence, we believe that the structure of spiroviolene should be reassigned to that of structure 4 as drawn within Scheme 4, with stereochemistry at the key center matching that of the originally assigned spirograterpene A. This result would thus suggest that 9 (cf.Scheme 1), not 8, is a likely biosynthetic precursor for 4, with implications for the stereochemical outcome of cyclizations and/or other events starting from GGPP to account for its formation. At what point in that biosynthesis this alteration would occur is unclear, and it may be distinct for the route used to reach 9 for spirograterpene A given that these natural products are produced by bacteria and fungi, respectively.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have achieved concise and enantioselective syntheses of both spiroviolene and spirograterpene A, in 10 and 18 steps, respectively, utilizing previously prepared bicyclic ketone building blocks coupled with a powerful Heck cyclization sequence and other chemoselective transformations. As a result of computational, synthetic, and spectroscopic investigations, we believe that a previously assigned chiral center within spiroviolene is in error, with the two natural products likely sharing an overall biosynthetic pathway despite being produced in different organisms. Efforts to extend several of the findings of this work, including toward the synthesis of other non-functionalized terpenes, are the subject of current endeavors.Author contributions
S. A. S., H. M. C., and P. H. conceived the project. S. A. S. directed the research, and all authors composed the manuscript and the ESI section.† H. M. C. and C. J. F. C. executed the total syntheses and C. A. T. performed the calculations. P. H. provided intellectual contribution for route design.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Antoni Jurkiewicz, Dr Josh Kurutz, and Dr C. Jin Qin for assistance with NMR and mass spectrometry, respectively. We would also like to thank Prof. Jeroen S. Dickschat (Univ. Bonn) for helpful discussions regarding the evidence presented for the structural revision of 4. Support for the calculations performed was completed in part with resources provided by the University of Chicago's Research Computing Center. Financial support for this work came from the University of Chicago, Bristol-Myers Squibb (fellowship to P. H.), and the National Institutes of Health (T32 GM08720, Predoctoral Training Program in Chemistry and Biology, fellowship to C. A. T. and R01-GM132570).Notes and references
- For a total synthesis of presilperfolan-8-ol, see: (a) P. Hu and S. A. Snyder, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 5007 CrossRef CAS . For a review on the class, see: ; (b) A. Y. Yong and B. M. Stoltz, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 5248 CrossRef.
- For total syntheses of the conidiogenones, see: (a) S.-H. Hou, Y.-Q. Tu, S.-H. Wang, C.-C. Xi, F.-M. Zhang, S.-H. Wang, Y.-T. Li and L. Liu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 128, 4532 CrossRef; (b) P. Hu, H. M. Chi, K. C. DeBacker, X. Gong, J. H. Keim, I. T. Hsu and S. A. Snyder, Nature, 2019, 569, 703 CrossRef CAS; (c) B. Xu, W. Xun, S. Su and H. Zhai, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 16475 CrossRef CAS.
- For total syntheses of waihoensene, see: (a) H. Lee, T. Kang and H.-Y. Lee, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 8254 CrossRef CAS; (b) Y. Qu, Z. Wang, Z. Zhang, W. Zhang, J. Huang and Z. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 6511 CrossRef CAS; (c) C. Peng, P. Arya, Z. Zhou and S. A. Snyder, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 13521 CrossRef CAS.
- For selected recent examples, see: (a) A. Mendoza, Y. Ishihara and P. S. Baran, Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 21 CrossRef CAS; (b) S. V. Pronin and R. A. Shenvi, Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 915 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. Y. Hong and B. M. Stoltz, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 9674 CrossRef CAS; (d) Q. Zhang and K. Tiefenbacher, Nat. Chem., 2015, 7, 197 CrossRef CAS; (e) Q. Zhang, J. Rinkel, B. Goldfuss, J. S. Dickshat and K. Tiefenbacher, Nat. Catal., 2018, 1, 609 CrossRef CAS; (f) L.-D. Syntrivanis, I. Némethová, D. Schmid, S. Levi, A. Prescimone, F. Bissegger, D. T. Major and K. Tiefenbacher, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 5894 CrossRef CAS.
- For an early example of this concept from our group, see: S. A. Snyder, D. A. Wespe and J. M. von Hof, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 8850 CrossRef CAS.
- For selected reviews, see: (a) J. Christoffers and A. Baro, Quaternary stereocenters: Challenges and Solutions for Organic Synthesis, Wiley-VCH, 2005 CrossRef; (b) M. Bueschleb, S. Dorich, S. Hanessian, D. Tao, K. B. Schenthal and L. E. Overman, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 4156 CrossRef CAS; (c) G. Mehta and A. Srikrishna, Chem. Rev., 1997, 97, 671 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Rabe, J. Rinkel, E. Dolja, T. Schmitz, B. Nubbemeyer, T. H. Luu and J. S. Dickschat, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 2776 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Niu, Z.-W. Fan, C.-L. Xie, Q. Liu, Z.-H. Luo, G. Liu and X.-W. Yang, J. Nat. Prod., 2017, 80, 2174 CrossRef CAS.
- For examples that could support such an assertion, see: (a) D. E. Cane, J. S. Oliver, P. H. M. Harrison, C. Abell, B. R. Hubbard, C. T. Kane and R. Lattman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1990, 112, 4513 CrossRef CAS; (b) C.-M. Wang, R. Hopson, X. Lin and D. E. Cane, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 8360 CrossRef CAS.
- For reviews on the biosynthesis of similarly derived terpenes, see: (a) J. S. Dickschat, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2016, 33, 87 RSC; (b) J. Rinkel, P. Rabe, P. Garbeva and J. S. Dickschat, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 13593 CrossRef CAS; (c) P. Rabe, J. Rinkel, T. A. Klapschinski, L. Barra and J. S. Dickschat, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016, 14, 158 RSC; (d) J. S. Dickschat, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 15964 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) L. E. Overman, M. M. Abelman, D. J. Kucera, V. D. Tran and D. J. Ricca, Pure Appl. Chem., 1992, 64, 1813 CAS; (b) R. Grigg, J. M. Sansano, V. Santhakumar, V. Sridharan, R. Thangavelanthum, M. Thornton-Pett and D. Wilson, Tetrahedron, 1997, 53, 11803 CrossRef CAS . For a review, see:; (c) R. Grigg and V. J. Sridharan, Organomet. Chem., 1999, 576, 65 CrossRef CAS . For an additional example from our group achieving a unique terminating functionalization, see:; (d) H. Yi, P. Hu and S. A. Snyder, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 2674 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Feuillastre, B. Pelotier and O. Piva, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2014, 8, 1753 CrossRef.
- (a) K. Iwasaki, K. K. Wan, A. Oppedisano, S. W. M. Crossley and R. A. Shenvi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 1300 CrossRef CAS . For a review of metal-mediated HAT reactions, see:; (b) S. W. M. Crossley, C. Obradors, R. M. Martinez and R. A. Shenvi, Chem. Rev., 2016, 115, 8912 CrossRef . For examples of HAT-mediated hydrogenation in total synthesis, see:; (c) C. Bosch, B. Fiser, E. Gómez-Bengoa, B. Bradshaw and J. Bonjoch, Org. Lett., 2015, 17, 5084 CrossRef CAS; (d) S. A. Ruider, T. Sandmeier and E. M. Carreira, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 2378 CrossRef CAS; (e) H.-H. Lu, S. V. Pronin, Y. Antonova-Koch, S. Meister, E. A. Winzeler and R. A. Shenvi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 7268 CrossRef CAS.
- Attempts were made to selectively oxidize the primary alcohol in the presence of the secondary alcohol using some of the methods cited here, but ultimately proved unsuccessful. See: (a) P. L. Anelli, C. B. F. Montanari and S. Quici, J. Org. Chem., 1987, 52, 2559 CrossRef; (b) J. B. Epp and T. S. Widlanski, J. Org. Chem., 1999, 64, 293 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Zhao, J. Li, E. Mano, Z. J. Song, D. M. Tschaen, E. J. J. Grabowski and P. J. Reider, J. Org. Chem., 1999, 64, 2564 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. Zhao, J. Li, E. Mano, Z. J. Song and D. M. Tschaen, Org. Synth., 2004, 81, 195 Search PubMed; (e) M. Shibuya, T. Sato, M. Tmoizawa and Y. Iwabuchi, Chem. Commun., 2009, 1739 RSC.
- The most challenging of these operations was the initial MOM cleavage, as significant decomposition when observed when this operation was conducted on scale in the presence of trace water (such as from p-TsOH·H2O); only 6 M HCl in THF afforded consistent results.
- For examples of metal-mediated olefin isomerization, see: (a) P. A. Greico, M. Nishizawa, N. Marinovic and W. J. Ehmann, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1976, 98, 7102 CrossRef; (b) J. Andrieux, D. H. R. Barton and P. Henri, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1977, 4, 359 RSC; (c) L. A. Paquette, W. E. Fristad, D. S. Dime and T. R. Bailey, J. Org. Chem., 1980, 45, 3017 CrossRef CAS; (d) A. Sen and T.-W. Lai, Inorg. Chem., 1984, 23, 3257 CrossRef CAS; (e) A. Sen, T.-W. Lai and R. T. Thomas, J. Organomet. Chem., 1988, 358, 567 CrossRef CAS.
- This step required strictly anhydrous conditions to avoid hydrolysis of the benzoate, as not only was the resultant free alcohol prone to decomposition, but the resulting benzoic acid by-product proved extremely difficult to remove, often requiring several rounds of preparative TLC.
- To date, several unsuccessful attempts have been made to obtain a crystal of suitable quality under a variety of solvent combinations and crystallization techniques. The compounds used toward this end include 5, S6 (and the tosyl hydrazone derivative thereof), the bis(thionoimidazole) derivative of 32, and S5 (as well as the p-bromobenzoate and ferrocenecarboxylate analogues).
- For the original report of the Barton–McCombie deoxygenation, see: (a) D. H. R. Barton and S. W. McCombie, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 1975, 16, 1574 RSC . For an example of a similar application, see:; (b) W.-C. Liu and C.-C. Liao, Chem. Commun., 1999, 117 RSC.
- In these latter experiments, stereochemical scrambling at the key reassigned center could only have occurred if there was a 1,2-hydrogen shift to form a tertiary radical followed by H˙ capture from the more hindered face (i.e. the opposite face of addition observed from hydrogenation and hydroboration of an alkene at that position). We do not believe such a sequence to be likely.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d0sc04686h |
| ‡ Present address: Department of Chemistry, Pohang University of Science and Technology, South Korea. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2020 |

![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
: