Supramolecular design as a route to high-performing organic electrodes
Ani N.
Davis
 a,
Kausturi
Parui
a,
Kausturi
Parui
 b,
Megan M.
Butala
b,
Megan M.
Butala
 b and
Austin M.
Evans
b and
Austin M.
Evans
 *ab
*ab
aGeorge and Josephine Butler Polymer Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, USA. E-mail: austinevans@ufl.edu
bDepartment of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611, USA
First published on 15th April 2024
Abstract
Organic electrodes may someday replace transition metals oxides, the current standard in electrochemical energy storage, including those with severe issues of availability, cost, and recyclability. To realize this more sustainable future, a thorough understanding of structure–property relationships and design rules for organic electrodes must be developed. Further, it is imperative that supramolecular interactions between organic species, which are often overlooked, be included in organic electrode design. In this review, we showcase how molecular and polymeric electrodes that host non-covalent interactions outperform materials without these features. Using select examples from the literature, we emphasize how dispersion forces, hydrogen-bonding, and radical pairing can be leveraged to improve the stability, capacity, and energy density of organic electrodes. Throughout this review, we identify potential next-generation designs and opportunities for continued investigation. We hope that this review will serve as a catalyst for collaboration between synthetic chemists and the energy storage community, which we view as a prerequisite to achieving high-performing supramolecular electrode materials.
The coming decades will be defined by a proliferating need for energy storage technologies. Next-generation electrochemical energy storage solutions will address intermittent renewable energy production, empower the deployment of smart grid technologies, improve electric vehicle performance, and enable more complex portable electronics.1–3 New materials and device architectures will be needed to realize this future of energy storage.4 Lithium-ion batteries are the most prominent energy storage technology of the 21st century thus far, being ubiquitous in everyday life. In the simplest sense, lithium-ion battery technologies undergo charging and discharging by shuttling electrons, through an external circuit, and a balancing lithium ion, across an ionically conductive electrolyte and separator membrane, between an anode and cathode (Fig. 1). Commercial lithium-ion batteries currently rely on LiCoO2 or LiNi0.6Mn0.2Co0.2O2 cathodes.5,6 These materials have theoretical capacities of 274 mA h g−1 and 276.5 mA h g−1 with operating voltages of 4.2 V and 4.3 V, respectively. However, demonstrated capacities are often lower; specifically, LiCoO2 has an operating capacity of ≈140 mA h g−1, resulting in a practical energy density of about 600 W h kg−1. The structural stability imparted by partial substitution of Mn and Ni for Co results in even higher energy densities of about 800 W h kg−1 for LiNi0.6Mn0.2Co0.2O2.6–9 These impressive energy densities are accompanied by high cycling stabilities, with these electrodes typically losing less than 25% of their capacity over 1000 cycles. Extracting the cobalt and nickel minerals used for contemporary electrodes causes substantial environmental damage. For instance, mining operations in the Democratic Republic of Congo have led to widespread deforestation, water contamination, and air pollution, negatively affecting the environment and the health of the communities living in them.10–12 Moreover, the political dynamics of areas surrounding cobalt mines often lead to humanitarian conflict in populations near deposits of these metals.13 These unfortunate consequences dramatically offset the benefits of green energy solutions that rely on electrochemical energy storage. This pervasive drawback of existing energy storage solutions also compels continued investigation into alternative energy storage material designs.14
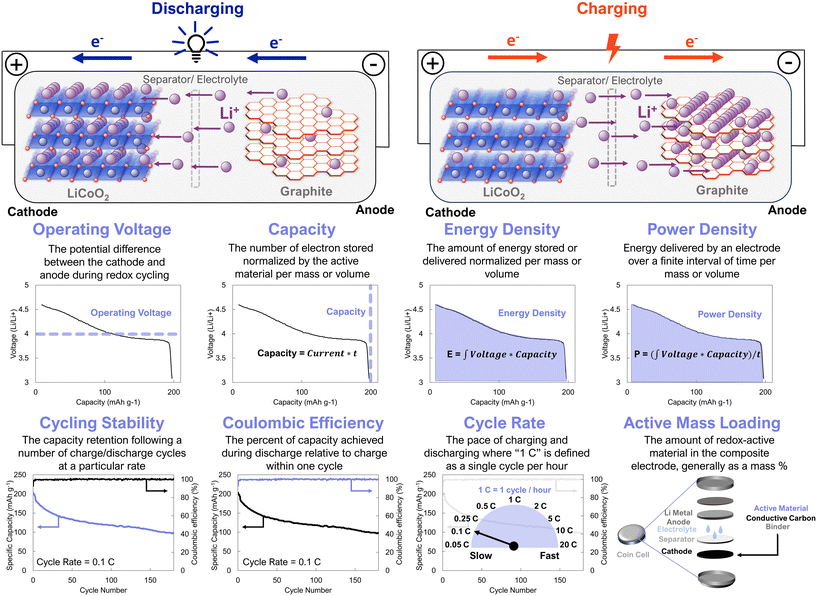 | ||
| Fig. 1 Schematic of battery charging/discharging processes and common performance metrics to evaluate new electrode active materials. Data is for LiCoO2, which was adapted with permissions from ref. 5. Copyright © 2022 Wiley. | ||
Organic electrodes have the potential to circumvent the availability and humanitarian issues of commercial battery electrodes.15 However, for these electrodes to be commercially viable they must meet several performance metrics, which differ based on the precise target application.4,16 For example, gravimetric energy density is paramount for portable energy storage, with a target energy density of 350 W h kg−1 for passenger electric vehicles.17 In contrast, volumetric energy density is a more appropriate consideration for stationary grid-level energy storage. In both applications cycle life, safety, and thermal stability are critical.3 In addition to these performance metrics, it is also critical for battery electrodes to be easily manufactured, at large-scale, for low cost. While it may not be necessary for organic electrodes to surpass their inorganic counterparts on all of these metrics concurrently, we expect that organic cathodes will have to be competitive across these metrics to be commercially viable. Contemporary organic electrode materials fail to suitably address a requisite number of these metrics to be economically competitive. Supramolecular design offers a route to engineer organic electrodes that address this bottleneck.
Organic electrodes are conventionally divided into the broad classes of molecular and polymeric electrodes. Molecular electrodes typically have higher energy densities and are more redox-stable than polymeric electrodes because they are discrete molecular entities with low amounts of redox inactive mass.16 For example, cyclohexanehexanone has an ultra-high capacity of 902 mA h g−1 and an energy density of 1533 W h kg−1 (Fig. 2) However, as is a problem with many small-molecule electrodes, the low molar mass of cyclohexanehaxanone makes it prone to dissolution during cycling, which leads to a loss of electrode active material and poor cycling stability.16,21 In contrast, polymeric electrodes generally have lower solubilities due to their higher molecular masses, which translates to excellent cycling stability. For example, a naphthalene diimide-thiophene co-polymer was found to maintain over 96% capacity after 3000 cycles at a fast-cycling rate (10C), which rivals the stability of commercial cathode materials (Fig. 2).19 However, polymeric electrodes typically have higher amounts of redox inactive mass which decreases their gravimetric energy density.4 Despite the naphthalene diimide-thiophene co-polymer above being quite stable, its gravimetric capacity and energy density are low (54.2 mA h g−1 and 86.2 W h kg−1, respectively) (Fig. 2).19 Moreover, polymers’ electronic heterogeneity (i.e., amorphous nature and chain ends) makes them susceptible to redox degradation.4,21 For both small-molecule and polymer electrodes, it will also be important to consider device-level parameters associated with cost, active material loading, and processability. While molecular engineering has the potential to address these challenges, existing design paradigms have failed to realize commercially-viable organic electrodes.
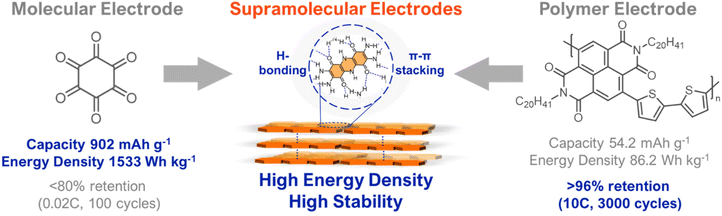 | ||
| Fig. 2 Comparison of molecular and polymeric electrodes and their desirable features, which can be mutually accessed using supramolecular designs. Data for representative molecular, polymeric, and supramolecular electrodes were selected from ref. 18, 19 and 20, respectively. | ||
Contemporary organic electrode designs have focused on manipulating the covalent (macro-)molecular structure but have neglected to consider how supramolecular design elements might also impact performance.22 Manipulating these ubiquitous non-covalent interactions is a promising approach to realizing high-performing organic electrodes. As one demonstration of the importance of non-covalent interactions, graphite – the most common anode material in lithium-ion batteries – is held together by van der Waals interactions that lead to electric and ionic conductivity.23–25 Compared to covalent bonds, non-covalent interactions have small bond energies. In this report, we explore a variety of non-covalent interactions, including electrostatic interactions (1 to 20 kcal mol−1),26 hydrogen bonding (1 to 8 kcal mol−1),27 radical–radical pairing (4 to 7 kcal mol−1),28 π–π stacking (0 to 10 kcal mol−1),29 and dispersion forces (0 to 3 kcal mol−1).27 While these interactions have bond energies that are significantly lower than covalent bonds, the cumulative nature of supramolecular forces generates an outsized impact on performance in all organic electrochemical energy storage devices.
Beyond controlling the solubility of species, non-covalent interactions also impact the electrical conductivity, ionic conduction pathways, manufacturability, and stability of these systems.30 However, the versatility of these supramolecular interactions as a design feature has not yet been widely leveraged by the organic electrode community.
In this review, we summarize how different types of non-covalent interactions, whether coincidentally present or intentionally installed, influence electrode performance. We also expect that supramolecular interactions can give new functionality to organic electrodes, such as self-healing or switchability, that may be valuable in emerging energy storage applications.31 For the sake of clarity, we focus our discussion on lithium-ion batteries. However, similar design principles could be extended to organic electrodes for other metal-ion (e.g. Na-ion or Mg-ion) batteries, which we consider an exciting frontier in organic energy storage materials. We also constrain our discussion entirely to electrochemical energy storage applications, but the design considerations we outline here could be useful in other electrochemical devices such as sensors, neuromorphic computers, electrochemical transistors, or electrocatalysts.32 We structure our discussion based on the different types of supramolecular interactions that are most prominent in organic materials and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each. While we divide these interactions for the sake of clarity, it should be understood that supramolecular interactions operate concurrently, and it can be challenging to holistically assign performance to a single non-covalent interaction. Throughout our discussion, we focus on the potential for future supramolecular synthetic designs to yield high-performance organic electrodes.
Dispersion forces, π–π bonding, and van der Waals interactions
Dispersion forces are attractive interactions that arise due to temporary fluctuations in electron distributions (Fig. 3).25 While these interactions are weak individually, they can have a profound impact on cumulative material behavior. When these electrons are located within aromatic systems, these interactions are sometimes referred to as π-interactions (Fig. 3). Because most redox-active organic systems include aromatic cores, these dispersion forces feature prevalently in organic electrodes even if they are not intentionally designed to host these interactions. For example, Carter, Ji, and coworkers showed how a simple polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, coronene, which is stabilized by π–π interactions, functions as an organic cathode, with a 92% capacity retention after 960 cycles (0.5C).34 The authors claim that the molecular coronene structure is more flexible than a chemically similar graphite electrode, which leads to a 500 mV lower operating potential (4 V vs. Li+/Li) without ionic liquids or electrolyte additives. In addition to driving insolubility and generating ion percolation pathways, these dispersion forces can also improve the electrical conductivity and the resultant redox accessibility in organic electrodes. Despite these desirable features, the coronene-based electrodes hosted a low capacity of 40 mA h g−1 (45% of theoretical capacity), which suggests that not all of the coronenes are redox-accessible under the investigated cycling conditions. Presumably, this limitation could be improved by increasing the redox activity of future polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.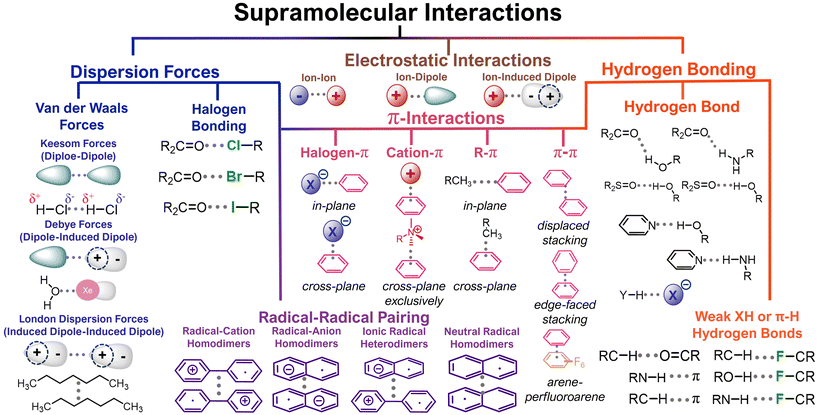 | ||
| Fig. 3 Supramolecular interactions present in in organic molecules electrodes. Adapted from Roman A. Valiulin Copyright © 2020 adapted with permissions from ref. 33. Copyright © 2021 Springer Nature Limited. | ||
The most immediate benefit of dispersion forces is the decreased dissolution or decomposition of the active species in the electrolyte. However, adding redox inactive mass to optimize these supramolecular interactions will necessarily reduce the gravimetric capacity of organic electrodes. Bieker, Esser, and coworkers addressed this challenge by synthesizing poly(3-vinyl-N-methylphenothiazine) electrodes that were stabilized by π–π interactions between redox-active units (Fig. 4).35 This is advantageous because it increased the cycling stability of the resultant electrodes (93% capacity retention after 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles at a 10C scan rate (Fig. 4)) while maintaining a moderate capacity of 56 mA h g−1 at a 1C rate. In addition to stabilizing the redox-active electrodes, the strong π–π interactions (and radical–radical pairing, vide infra) produce a hole-transport pathway that facilitates rapid charge-transport between redox-active sites, which led to the high-rate capability of these electrodes (Fig. 4). This report demonstrates that moderate strength π–π interactions can lead to improved stability and electrochemical performance.
000 cycles at a 10C scan rate (Fig. 4)) while maintaining a moderate capacity of 56 mA h g−1 at a 1C rate. In addition to stabilizing the redox-active electrodes, the strong π–π interactions (and radical–radical pairing, vide infra) produce a hole-transport pathway that facilitates rapid charge-transport between redox-active sites, which led to the high-rate capability of these electrodes (Fig. 4). This report demonstrates that moderate strength π–π interactions can lead to improved stability and electrochemical performance.
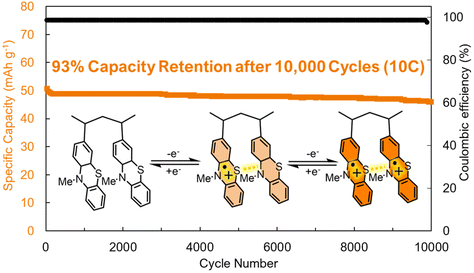 | ||
| Fig. 4 Cycling performance of poly(3-vinyl-N-methylphenothiazine) at a 10C rate. Structure depicted visualizes the π–π interactions between the monomer units during different stages of charge/discharge. Adapted with permissions from ref. 35. Copyright © 2017 Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
Building off of this study, Esser, Kolek and coworkers explored how suppressing π–π interactions with sterically demanding side-chains guides poly(3-vinyl-N-methylphenothiazine) electrode performance.36 After confirming a significant decrease in π–π interactions between redox-active methylphenothiazine by spectroscopic methods, the authors found that these electrodes showed reduced performance when compared to the poly(3-vinyl-N-methylphenothiazine) material previously studied.35 The newly formed materials with more limited π–π interactions were found to have a capacity of 51 mA h g−1 (65% of theoretical capacity) and only retained 19% capacity after 50 cycles at a 1C rate. This reduced capacity is partially due to the increase in redox-inactive mass. However, the lower accessible capacity suggests that suppressing supramolecular interactions also decreases electrode performance.
Rylene diimides are well-studied organic electrode materials, both as small molecules and as polymeric materials. Within this class, perylene diimides (PDIs) and naphthalene diimides (NDIs) are known to host significant supramolecular interactions. For example, Chen and coworkers explored a 1,4,5,8-naphthalenediimide cathode under a variety of electrolyte conditions with the goal of optimizing electrode performance.37 Ultimately, these authors report that a LiTFSI- or LiClO4-based electrolyte in dioxolane![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) dimethoxyethane (vol 1
dimethoxyethane (vol 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) facilitated a near theoretical electrode capacity of 200 mA h g−1 with 96% capacity retention after 400 cycles at a 1C cycling rate. The authors attribute this to this electrolyte condition not disturbing the supramolecular π–π stacking interactions and H-bonding interactions that stabilize these electrodes. However, the authors identified that the terminal N–H bond of the imide was susceptible to electrochemical degradation over long periods of time in carbonate-based electrolyte. This paper highlights the important impact that electrolyte conditions play on modulating supramolecular interactions. As these non-covalent designs are explored in more detail, we expect resolving the impacts of electrolyte-electrode and electrode–electrode interactions will be extremely important.38
1) facilitated a near theoretical electrode capacity of 200 mA h g−1 with 96% capacity retention after 400 cycles at a 1C cycling rate. The authors attribute this to this electrolyte condition not disturbing the supramolecular π–π stacking interactions and H-bonding interactions that stabilize these electrodes. However, the authors identified that the terminal N–H bond of the imide was susceptible to electrochemical degradation over long periods of time in carbonate-based electrolyte. This paper highlights the important impact that electrolyte conditions play on modulating supramolecular interactions. As these non-covalent designs are explored in more detail, we expect resolving the impacts of electrolyte-electrode and electrode–electrode interactions will be extremely important.38
To address the stability concerns of small molecule rylene diimides, several groups have prepared diimide oligomers and polymers. For example, Yang, Nuckolls, and coworkers recently reported PDI nanoribbons, hPDI[n], where n is the number of PDIs annulatively fused in series (Fig. 5a).39 In addition to being more electrochemically stable, these hPDI[n] oligomers were found to be more electrically and ionically conductive than the parent PDI. The authors ascribe both advantageous features to the π–π interactions (and H-bonding) between the non-planar PDI oligomers (Fig. 5c). The unique geometry and non-covalent interactions between the longest PDI nanoribbon, hPDI[6], led to an exceptionally high power density (28 kW kg−1), with long-term cycling stability (>75% capacity retention over 3000 cycles), at high mass loadings (5 mg cm−2), which allowed the authors to power a commercial LED fan using these energy storage materials in a pouch cell configuration (Fig. 5b). These results demonstrate that more complex molecular designs that facilitate intensive supramolecular interactions may improve organic electrode performance.
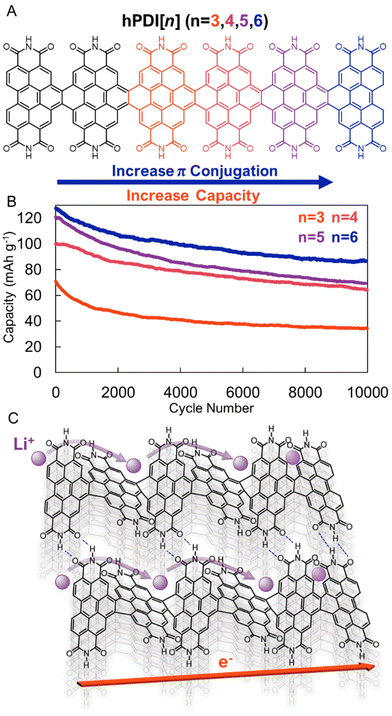 | ||
Fig. 5 (A). Helical PDI nanoribbons (hPDI[n]). (B). Cycling performance of hPDI[n]-based electrodes at 7.7C over 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles. (C). Graphical depiction of contorted PDI nanoribbon with high ionic and electronic conductivities. Adapted with permissions from ref. 39. Copyright © 2022 American Chemical Society. 000 cycles. (C). Graphical depiction of contorted PDI nanoribbon with high ionic and electronic conductivities. Adapted with permissions from ref. 39. Copyright © 2022 American Chemical Society. | ||
Chemical design and processing are not typically explored synergistically for organic electrodes. However, the integration of active material with conductive additives and binders during electrode preparation can greatly influence performance. Liu, Su, and coworkers explored the influence of the non-covalent interactions between composite electrode components on measured performance by comparing PDI polymers that were mechanically mixed with carbon black (conductive additive) against PDI polymers produced in the presence of carbon black (Fig. 6).40 In all cases, the electrodes produced by polymerizing perylene diimides in the presence of carbon black led to higher performance than physically mixing the two species. The authors attribute this enhancement to higher density π–π interactions between the conductive carbon black and the redox-active PDI polymer. This enabled these composite electrodes to achieve a reversible capacity of 100 mA h g−1 with a high current density of 50C, which was 1.3× higher than the capacity achieved by post-polymerization blending of the conductive additive and active material. Future explorations in supramolecular electrode design would benefit from a more thorough understanding of how non-covalent interactions between electrode active materials and electrode additives impact energy storage performance.
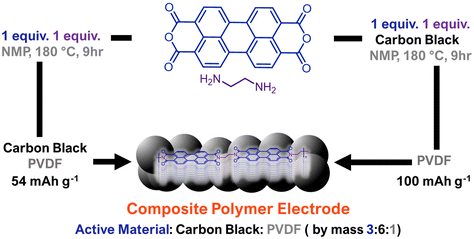 | ||
| Fig. 6 Comparative approach to generate composite polymer electrodes where polymerization is done either separate from or in the presence of conductive carbon additive. Polymerizing in the presence of carbon additive leads to higher measured capacities at fast charge/discharge rates. Adapted with permissions from ref. 40. Copyright © 2018 Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
New material designs have recently emerged that have enhanced supramolecular interactions.42,43 For instance, by polymerizing multitopic planar monomers, permanently porous two-dimensional polymer sheets can be generated that then stack to yield a three-dimensional material.44,45 Wang, Lee, Zhang and coworkers exploited this approach to produce a truxenone-containing β-ketoenamine-linked 2D polymer (Fig. 7).41 The crystalline material generated through this approach leads to a Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area of 150 m2 g−1, which led to the moderate rate performance of these batteries. Moreover, the non-covalent π–π interactions facilitated high redox-accessibility of the 2D polymer, with an experimental capacity of 268 mA h g−1, which was retained over 100 cycles at a 0.1C cycling rate (Fig. 7). While this report demonstrates that moderate performance can be achieved using these new polymer architectures, the inherent insolubility of these species may complicate their processing and manufacturing in real devices.46,47 Nonetheless, the crystalline structure, permanent porosity, and strong supramolecular interactions in these systems make them an exciting test bed to explore fundamental concepts in organic electrode design.48,49
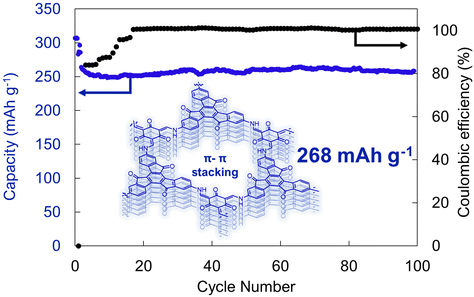 | ||
| Fig. 7 Electrochemical cycling of a truxenone-based 2D polymer at 0.1C rate. Structure depicted showcases the π–π interactions between the different layers of the 2D polymer. Adapted with permissions from ref. 41. Copyright © 2020 Wiley Online Library. | ||
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding (H-bonding) attractions are driven by the intermolecular interaction between a hydrogen atom and other electronegative units, which are most commonly nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine (Fig. 3). These interactions are stronger than van der Waals forces, but weaker than covalent bonds.50 However, similar to dispersion interactions, when these interactions act in a cumulative way across many hydrogen bond acceptors and donors, they can surpass the strength of covalent bonding.H-bonding can greatly reduce the solubility of electrode active materials in electrolyte. Vlad, Poizot, and coworkers exploited this in benzoquinone-based electrodes.51 Specifically, these researchers compared the performance of a 2,5-diamino-1,4-benzoquinone which is reinforced by intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds and an unfunctionalized 1,4-benzoquinone that does not benefit from such interactions (Fig. 8b and d). They found that H-bonding yielded low solubility, higher thermal stability, and high redox cycling stability (>99%). In contrast, in the absence of H-bonding interactions the electrode quickly dissolved upon cycling and exhibited much lower stabilities (<150 °C T95 as evaluated by thermogravimetric analysis) (Fig. 8c). Because the added mass of the H-bonding functionality is low, the functionalized benzoquinone derivatives still maintained a notable capacity of >350 mA h g−1 (Fig. 8a). This work demonstrates that cooperative H-bonds can lead to improved electrochemical performance by stabilizing organic electrodes. We expect that more complex H-bonding environments in other electrode designs could achieve similar aims.
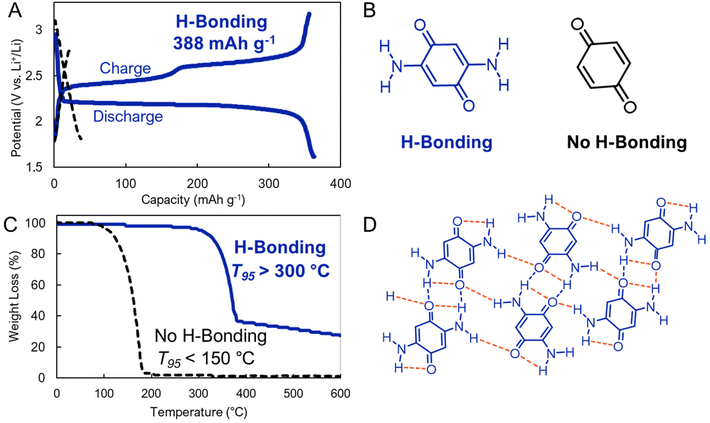 | ||
| Fig. 8 (A). Electrochemical cycling of (B). molecular electrodes that host (blue) or do not host (black) hydrogen bonding interactions. (C). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) the electrodes. (D). Supramolecular interactions present in electrode hosting H-bonding interactions (2,5-diamino-1,4-benzoquinone). Adapted with permissions from ref. 51. Copyright © 2018 Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
When H-bond interactions act in concert, they can be used to engineer the crystalline structure of redox-active units. For example, Wuest and coworkers demonstrated how various redox-active benzene tetramine isomers crystalize.52 They found that they could direct the resultant crystalline structure of these salts by engineering the H-bonding environment. Later, Wuest and coworkers showed how more complex benzoquinone-hydroquinone cocrystals could be generated by synergistic hydrogen bonds between these redox-active units.53 By exploring several quinonoid compounds, the authors show how the charge-transfer behavior of these materials was related to their H-bonding. These efforts demonstrate how careful tuning of hydrogen bond interactions can be used to control multi-length scale structure and prevent dissolution of organic electrodes. Presumably, crystalline engineering by supramolecular interactions will yield more precise fundamental understanding and potentially more direct routes to electrode performance improvement than what is possible in amorphous systems.
Synergistic H-bonding between multivalent H-bond acceptors and donors on an aza-phenazine derivative were explored by Zhang and coworkers and found to have improved lithium-ion battery performance over species that were not reinforced by H-bonding.54 Specifically, they found that the close-packed 2D structure of an aza-phenazine containing four hydrogen bond donors and acceptors had a discharge capacity of 145 mA h g−1 at 2C with an 82% capacity retention over 1000 cycles. The authors attribute the enhanced performance to the stabilization that is facilitated by H-bonding, which was validated by 2D and variable-temperature nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy with van't Hoff analysis. Continued investigation into the fundamental nature of supramolecular interactions during electrode operation will be critical to the continued development of these synthetic designs.
Simplified device processing can also emerge when supramolecular interactions are included in organic cathode design. Organic electrodes are typically resistive and require carbon additives to increase electronic accessibility of the redox-active centers. To ensure a homogenous mixture between the active material and the conductive additive, binders are also added. These additions to the electrode material reduce the energy density of the composite electrode. Supramolecular interactions can increase conductivity of organic electrodes, enabling the casting of a neat electrode, or an electrode without any additives.
Dincǎ and coworkers recently synthesized bis-tetraaminobenzoquinones (TAQ), a fused aromatic molecule that forms an insoluble layered organic cathode material upon casting from an ethanol slurry.20 Strong non-covalent interactions make TAQ insoluble in common battery electrolytes and highly conductive, which enabled these authors to explore how TAQ performed as a near-standalone electrode. It was identified that extended conjugation and hydrogen bonding promoted long-term cycling stabilities and high capacities, with TAQ retaining 88% of its initial 256 mA h g−1 capacity after 1000 cycles at 5C. The same authors explored the performance of TAQ-based materials as a pseudocapacitor electrodes with moderate specific capacities (>200 mA h g−1) and rapid discharging times (<100 s). This material also achieved >90% capacity retention over 60![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles.55 These investigations highlight how supramolecular interactions can be used to achieve high-performance electrodes when supramolecular design and device processing are synergized.
000 cycles.55 These investigations highlight how supramolecular interactions can be used to achieve high-performance electrodes when supramolecular design and device processing are synergized.
H-bonding can also lead to tighter intermolecular packing, that positively impacts the electronic characteristics of redox-active materials. Yang, Loh, and coworkers synthesized a quinoxaline-based cathode that had a high capacity of 372 mA h g−1 at a 1C cycle rate with a capacity retention of >70% over 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 cycles at a 20C cycling rate (Fig. 9a).56 The large number of supramolecular interactions (including π–π interactions and H-bonding) helped to stabilize these materials during electrochemical cycling. Moreover, the large number of directional supramolecular interactions allowed for single-crystal X-ray structures to be collected for these materials, which demonstrated that the intermolecular spacing between redox-centers is small (3.3 Å). Ex situ15N solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and density functional calculations of a different quinoxaline derivative demonstrates that multiple nitrogen atoms participate in the redox-cycling upon lithiation/delithiation (Fig. 9b). Presumably, interactions between multiple quinoxaline sites in close proximity facilitate the ease of this electrochemical transformation. Future supramolecular designs will leverage this structural control to enhance the electronic performance of organic electrode systems.
000 cycles at a 20C cycling rate (Fig. 9a).56 The large number of supramolecular interactions (including π–π interactions and H-bonding) helped to stabilize these materials during electrochemical cycling. Moreover, the large number of directional supramolecular interactions allowed for single-crystal X-ray structures to be collected for these materials, which demonstrated that the intermolecular spacing between redox-centers is small (3.3 Å). Ex situ15N solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and density functional calculations of a different quinoxaline derivative demonstrates that multiple nitrogen atoms participate in the redox-cycling upon lithiation/delithiation (Fig. 9b). Presumably, interactions between multiple quinoxaline sites in close proximity facilitate the ease of this electrochemical transformation. Future supramolecular designs will leverage this structural control to enhance the electronic performance of organic electrode systems.
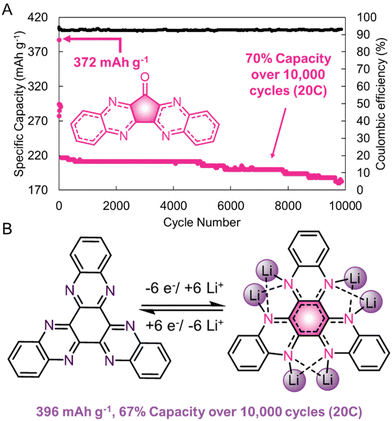 | ||
| Fig. 9 (A). Performance of a quinoxaline-based cathode at a 20C rate. (B). Structure of a quinoxaline-based electrode in its fully lithiated state. Adapted with permissions from ref. 56. Copyright © 2017 Springer Nature Limited. | ||
A nascent feature of supramolecular interactions is that they can be reversibly broken and reformed under ambient conditions. This can lead to highly elastic and self-healable materials that are reinforced by non-covalent interactions. While this has not yet been widely explored for organic electrodes, H-bonded electrolytes have been shown to combine the desirable ionic conductivities and mechanical properties needed for electrochemical energy storage. For example, a multidentate H-bonding motif, ureidopyrimidinone, was appended to a poly(ethylene glycol) and explored by Zhou, Xue, and coworkers as a supramolecular cross-link in lithium-ion battery electrolytes (Fig. 10a).57 These authors found that the electrolyte could be damaged and self-healed with near pristine performance (<3% loss in capacity, Fig. 10b). Presumably, similar designs could be realized in electrode materials, though electronic conductivity would also be required, which would open the door to flexible or deformable organic electrodes that are useful in bioelectronic devices.
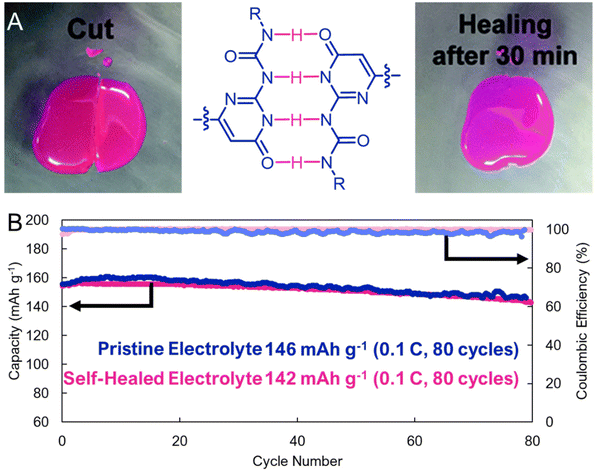 | ||
| Fig. 10 (A). Optical images showing the self-healing process of the ureidopurimidinone-based electrolyte. (Left) The sample was cut into two pieces and (Right) after 30 minutes at 60 °C self-healing was observed. (B). Cycling stability comparing a cell containing pristine electrolyte, and electrolyte that has been cut, and then self-healed. Adapted with permissions from ref. 57. Copyright © 2018 Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
Radical–radical pairing
It has recently become apparent that radical-pairing interactions between conjugated organic π-radicals are an important addition to the supramolecular chemistry library.33 In radical–radical pairing interactions a non-covalent bond is generated by unpaired electrons in two singly occupied molecular orbitals that dimerize to give a diamagnetic radical dimer (Fig. 3).33 While this phenomenon was identified fifty years ago, it has only recently come into focus as a tailorable supramolecular motif.58 In the context of organic electrodes, radical-pairing interactions are particularly appealing because in the process of reduction or oxidation, organic radicals are generated. Moreover, in high energy density electrodes these unpaired electrons will likely be proximal to one another. For this reason, we find the continued exploration of radical–radical pairing to be a promising design motif to generate high-performing organic electrodes.Radical dense materials are known to have moderate electrochemical energy storage performance.59 For instance, Lutkenhaus and coworkers found that by mixing a polyacid with a polyaniline, they were able to access a fully oxidized pernigraniline salt form of polyaniline (Fig. 11).60 Previously, polyaniline-based electrodes were overlooked because of the large capacity drop associated with irreversible degradation during cycling. However, with the addition of a polyacid, the electrode capacity was maintained >200 mA h g−1 over 800 cycles at a 50C cycling rate (Fig. 11). Evaluating whether radical dense electrodes maintain their high cycling stability under slower cycling rates, where degradation is more apparent would be a useful next step in radical-dense electrode design. We expect that in addition to stabilizing H-bonding and electrostatic interactions, radical–radical pairing likely also contributes to the desirable energy storage performance metrics observed in this study.
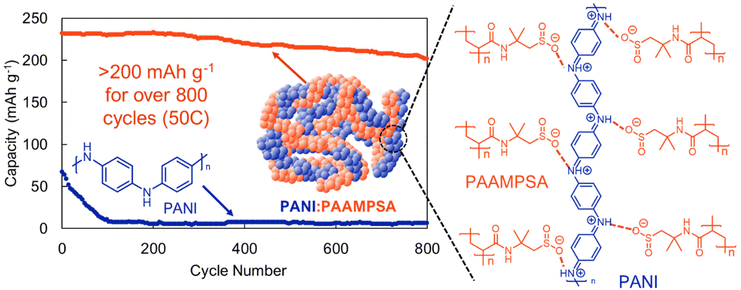 | ||
| Fig. 11 Cycling of a pernigraline-polyaninline with a polyacid stabilizer (PANI:PAAMPSA) (orange) compared to pure polyaniline (PANI) (blue) at a 50C rate. Adapted with permissions from ref. 57. Copyright © 2013 Royal Society of Chemistry. | ||
Another prominent motif that exhibits radical–radical pairing is tetrathiafulvalene (TTF). Becher and coworkers studied a tethered TTF to explore radical dimerization, which they characterized by optical absorption spectroscopy.61 These systematic characterizations of radical-pairing strengths and the features that influence these interaction strengths will be critical as these interactions are utilized in supramolecular electrodes. Chen, Tong, and coworkers leveraged a carboxylate-functionalized TTF as organic cathodes.62 They found that both di- and tetra-carboxylate TTF were stable over 120 cycles with specific capacities of 250 mA h g−1 and 150 mA h g−1, respectively. This was partially attributed to the extremely low solubility of these TTF electrodes in the electrolyte. We expect that this is partially driven by the dense radical–radical pairing interactions that emerge upon electrochemical cycling. Moreover, we expect that the high-rate performance of this material is partially facilitated by the high electrical conductivity that is also achieved by radical-dimerization between TTF materials. In the future, it will be useful to explore how radical dimerization influences the material properties (e.g. solubility, conductivity) of organic electrode systems. To achieve this aim, it will be useful to develop in operando analytical techniques to evaluate non-covalent interactions during battery cycling.
Electrostatic interactions
Charged species can interact attractively or repulsively through ionic electrostatic interactions (Fig. 3). The fact that charged species are ubiquitously generated during electrochemical cycling of organic electrodes leads us to conclude that understanding and controlling these interactions will be paramount for consideration of supramolecular organic electrode design. However, to-date, these interactions have not yet been holistically considered in the context of organic electrode cycling. Additionally, the ubiquity of these interactions makes it challenging to meaningfully engineer them for improved electrode performance. For this reason, we omit a more thorough discussion of these interactions here. Going forward, we expect that even straightforward studies on the impact of electrostatic interactions on conductivity, redox-activity, and solubility of typical organic electrode motifs would be valuable for future supramolecular electrode designs.Conclusions
Despite their promise, the realization of organic electrodes remains constrained by the materials properties that can be accessed by contemporary synthetic design. Ubiquitous non-covalent interactions remain a powerful yet underexplored design consideration for organic energy storage materials. It is still unknown whether there is an advantage to enhancing one supramolecular interaction over another in organic electrode design. It is also unclear how the cumulative nature of non-covalent interactions can be leveraged to enhance particular performance metrics, such as energy density, power density, or cycling stability. Presumably, strong supramolecular interactions can decrease the solubility of electrode active materials and enhance electronic communication between redox centers, both of which might enhance the capacity and cycling stability of organic electrodes. However, if supramolecular interactions are too strong it might restrain ion mobility within these materials, which could lead to a reduction in electrode power density. This example highlights how incorporating many weak supramolecular interactions may allow chemists to decouple the trade-offs that might be inherent to purely covalent design. Going forward, it will be critical to identify how individual non-covalent interactions collectively influence electrode performance. We encourage researchers in this field to explore and value the fundamental molecular structure–property design rules for electrode performance without the constraint of optimizing a particular performance metric (e.g., gravimetric capacity).Supramolecular interactions are attractive because molecular-scale engineering can be used to control structure and properties across nano-, micro-, and macro-scales. However, realizing this future of organic electrode design will require an intimate understanding of how a variety of supramolecular interactions between multiple electrode components (active materials, conductive additives, binders, etc.) together to define performance.
To better understand how supramolecular design can be leveraged in organic electrodes it is imperative that investigations of non-covalent interactions are performed in device-like conditions, e.g., in electrolytes. Once static non-covalent interactions are understood in typical battery configurations, it will also be necessary to characterize how these interactions evolve during battery cycling via ex situ, in situ, and operando methods. Currently, comparing disparate organic electrodes is challenging because there are many experimental parameters during battery testing, such as electrode preparation, electrolyte conditions, electrochemical potential range, and cycling rate that vary between studies. This variability makes comparison of active material properties difficult. Future organic electrode designs will benefit from a more systematic consideration of these parameters. We anticipate that computational insight, high-throughput experimentation, and data science approaches will expedite the exploration of this nearly infinite design space.
In spite of the apparent simplicity of supramolecular materials design, significant complexity arises because the outcomes of these designs are intimately tied to their processing history and environment. While the dynamic nature of organic electrode design and testing may appear daunting, it is also possible that the reversibility of non-covalent interactions can yield responsive or self-healing electrodes that are straightforward to manufacture and recycle. This could be particularly important for emerging energy storage needs, such as grid-level stationary storage or flexible bio-interfaced batteries, which have different performance requirements than portable lithium-ion batteries for mobile applications. We see the design of supramolecular electrodes for these emerging energy storage applications as a fruitful area of exploration with large potential for real world impact.
Current supramolecular structure–property relationships cannot yet be used to predict the electronic, mechanical, or thermal properties relevant for organic electrodes. For this reason, more focused efforts into connecting supramolecular chemistry to materials properties and device performance should be an immediate research goal. This aim will be complemented by developing electrolytes and additives (conductive additives and binders) for organic electrodes rather than relying on designs that were empirically optimized for inorganic electrodes. Realizing the promise of supramolecular electrodes will require interdisciplinary engagement between chemists, materials scientists, and device engineers. We hope the perspective outlined here will help catalyze this multi-disciplinary effort.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.References
- M. Li, J. Lu, Z. Chen and K. Amine, 30 Years of Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(33), 1800561 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Arbabzadeh, R. Sioshansi, J. X. Johnson and G. A. Keoleian, The role of energy storage in deep decarbonization of electricity production, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 3413 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Tian, G. Zeng, A. Rutt, T. Shi, H. Kim, J. Wang, J. Koettgen, Y. Sun, B. Ouyang, T. Chen, Z. Lun, Z. Rong, K. Persson and G. Ceder, Promises and Challenges of Next-Generation “Beyond Li-ion” Batteries for Electric Vehicles and Grid Decarbonization, Chem. Rev., 2021, 121(3), 1623–1669 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Lu and J. Chen, Prospects of organic electrode materials for practical lithium batteries, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2020, 4(3), 127–142 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Mao, Z. Shen, W. Zhang, Q. Wu, Z. Wang and Y. Lu, Outside-In Nanostructure Fabricated on LiCoO2 Surface for High-Voltage Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Mater., 2022, 9(11), 2104841 CAS.
- J. Qian, L. Liu, J. Yang, S. Li, X. Wang, H. L. Zhuang and Y. Lu, Electrochemical surface passivation of LiCoO2 particles at ultrahigh voltage and its applications in lithium-based batteries, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 4918 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Xie and Y.-C. Lu, A retrospective on lithium-ion batteries, Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 2499 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. R. Tallman, G. P. Wheeler, C. J. Kern, E. Stavitski, X. Tong, K. J. Takeuchi, A. C. Marschilok, D. C. Bock and E. S. Takeuchi, Nickel-rich Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC622) Cathode Lithiation Mechanism and Extended Cycling Effects Using Operando X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125(1), 58–73 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Li, L. M. Housel, G. P. Wheeler, D. C. Bock, K. J. Takeuchi, E. S. Takeuchi and A. C. Marschilok, Thermodynamic Analysis of LiNi0.6Mn0.2Co0.2O2 (NMC622) Voltage Hysteresis Induced through High Voltage Charge, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2021, 4(11), 12067–12073 CrossRef CAS.
- C. B. L. Nkulu, L. Casas, V. Haufroid, T. De Putter, N. D. Saenen, T. Kayembe-Kitenge, P. M. Obadia, D. K. Wa Mukoma, J.-M. L. Ilunga, T. S. Nawrot, O. L. Numbi, E. Smolders and B. Nemery, Sustainability of artisanal mining of cobalt in DR Congo, Nat. Sustain., 2018, 1(9), 495–504 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. Davey, Earth.Org, https://earth.org/cobalt-mining-in-congo (accessed January 2024) Search PubMed.
- The National Institute for Occupational Saftey and Health, https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/cobalt/default.html, (accessed January 2024).
- M. F. Lawson, The DRC Mining Industry: Child Labor and Formalization of Small-Scale Mining, in Africa Up Close, Wilson Center, Washington, DC, Onubogu, 2021, vol. 2024 Search PubMed.
- M. Armand and J. M. Tarascon, Building better batteries, Nature, 2008, 451(7179), 652–657 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liang and Y. Yao, Positioning Organic Electrode Materials in the Battery Landscape, Joule, 2018, 2(9), 1690–1706 CrossRef CAS.
- J. J. Shea and C. Luo, Organic Electrode Materials for Metal Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(5), 5361–5380 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Deng, C. Bae, A. Denlinger and T. Miller, Electric Vehicles Batteries: Requirements and Challenges, Joule, 2020, 4(3), 511–515 CrossRef.
- Y. Lu, X. Hou, L. Miao, L. Li, R. Shi, L. Liu and J. Chen, Cyclohexanehexone with Ultrahigh Capacity as Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2019, 58(21), 7020–7024 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Liang, Z. Chen, Y. Jing, Y. Rong, A. Facchetti and Y. Yao, Heavily n-Dopable π-Conjugated Redox Polymers with Ultrafast Energy Storage Capability, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(15), 4956–4959 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Chen, H. Banda, J. Wang, J. J. Oppenheim, A. Franceschi and M. Dincǎ, A Layered Organic Cathode for High-Energy, Fast-Charging, and Long-Lasting Li-Ion Batteries, ACS Cent. Sci., 2024, 10(3), 569–578 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Du, X. Du, M. Ma, S. Huang, X. Sun and L. Xiong, Polymer Electrode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(21), 2110871 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Wang, W. Zhang, J. Yang, Y. Gong, J. Zhang, M. Fang, Q.-H. Yang and Z. Li, The key role of molecular aggregation in rechargeable organic cathodes, Matter, 2022, 5(12), 4467–4479 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Frisenda, Y. Niu, P. Gant, M. Muñoz and A. Castellanos-Gomez, Naturally occurring van der Waals materials, npj 2D Mater. Appl., 2020, 4(1), 38 CrossRef.
- F. Bonaccorso, L. Colombo, G. Yu, M. Stoller, V. Tozzini, A. C. Ferrari, R. S. Ruoff and V. Pellegrini, Graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, and hybrid systems for energy conversion and storage, Science, 2015, 347(6217), 1246501 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Meirzadeh, A. M. Evans, M. Rezaee, M. Milich, C. J. Dionne, T. P. Darlington, S. T. Bao, A. K. Bartholomew, T. Handa, D. J. Rizzo, R. A. Wiscons, M. Reza, A. Zangiabadi, N. Fardian-Melamed, A. C. Crowther, P. J. Schuck, D. N. Basov, X. Zhu, A. Giri, P. E. Hopkins, P. Kim, M. L. Steigerwald, J. Yang, C. Nuckolls and X. Roy, A few-layer covalent network of fullerenes, Nature, 2023, 613(7942), 71–76 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Biedermann and H.-J. Schneider, Experimental Binding Energies in Supramolecular Complexes, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(9), 5216–5300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. F. Lodish, Molecular cell biology, Macmillan Learning, Austin, 9th edn, 2021, p 1 volume (various pagings) Search PubMed.
- C. Cheng, T. Cheng, H. Xiao, M. D. Krzyaniak, Y. Wang, P. R. McGonigal, M. Frasconi, J. C. Barnes, A. C. Fahrenbach, M. R. Wasielewski, W. A. Goddard and J. F. Stoddart III, Influence of Constitution and Charge on Radical Pairing Interactions in Tris-radical Tricationic Complexes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(26), 8288–8300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. O. Sinnokrot, E. F. Valeev and C. D. Sherrill, Estimates of the Ab Initio Limit for π−π Interactions: The Benzene Dimer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002, 124(36), 10887–10893 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Strauss, I. Hwang, A. M. Evans, A. Natraj, X. Aguilar-Enriquez, I. Castano, E. K. Roesner, J. W. Choi and W. R. Dichtel, Lithium-Conducting Self-Assembled Organic Nanotubes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(42), 17655–17665 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Huang, S. Li, E. Y. Kim, L. Cheng, G.-L. Xu, K. Amine, C. Wang and C. Luo, A Self-Healing Chemistry-Enabled Organic Cathode for Sustainable and Stable Sodium-Ion Batteries, Small Struct., 2023, 4(12), 2300211 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Schaack, A. M. Evans, F. Ng, M. L. Steigerwald and C. Nuckolls, High-Performance Organic Electronic Materials by Contorting Perylene Diimides, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(1), 42–51 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Cai, L. Zhang, R. D. Astumian and J. F. Stoddart, Radical-pairing-induced molecular assembly and motion, Nat. Rev. Chem., 2021, 5(7), 447–465 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. A. Rodríguez-Pérez, Z. Jian, P. K. Waldenmaier, J. W. Palmisano, R. S. Chandrabose, X. Wang, M. M. Lerner, R. G. Carter and X. Ji, A Hydrocarbon Cathode for Dual-Ion Batteries, ACS Energy Lett., 2016, 1(4), 719–723 CrossRef.
- M. Kolek, F. Otteny, P. Schmidt, C. Mück-Lichtenfeld, C. Einholz, J. Becking, E. Schleicher, M. Winter, P. Bieker and B. Esser, Ultra-high cycling stability of poly(vinylphenothiazine) as a battery cathode material resulting from π–π interactions, Energy Environ. Sci., 2017, 10(11), 2334–2341 RSC.
- F. Otteny, V. Perner, C. Einholz, G. Desmaizieres, E. Schleicher, M. Kolek, P. Bieker, M. Winter and B. Esser, Bridging the Gap between Small Molecular π-Interactions and Their Effect on Phenothiazine-Based Redox Polymers in Organic Batteries, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2021, 4(8), 7622–7631 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Shi, H. Tang, S. Jiang, L. V. Kayser, M. Li, F. Liu, F. Ji, D. J. Lipomi, S. P. Ong and Z. Chen, Understanding the Electrochemical Properties of Naphthalene Diimide: Implication for Stable and High-Rate Lithium-Ion Battery Electrodes, Chem. Mater., 2018, 30(10), 3508–3517 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Perner, D. Diddens, F. Otteny, V. Küpers, P. Bieker, B. Esser, M. Winter and M. Kolek, Insights into the Solubility of Poly(vinylphenothiazine) in Carbonate-Based Battery Electrolytes, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(10), 12442–12453 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Jin, Q. Cheng, S. T. Bao, R. Zhang, A. M. Evans, F. Ng, Y. Xu, M. L. Steigerwald, A. E. McDermott, Y. Yang and C. Nuckolls, Iterative Synthesis of Contorted Macromolecular Ladders for Fast-Charging and Long-Life Lithium Batteries, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(30), 13973–13980 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Wu, G. Zhang, D. Lu, L. Ma, Z. Xu, X. Xi, R. Liu, P. Liu and Y. Su, Perylene diimide-diamine/carbon black composites as high performance lithium/sodium ion battery cathodes, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(28), 13613–13618 RSC.
- X. Yang, Y. Hu, N. Dunlap, X. Wang, S. Huang, Z. Su, S. Sharma, Y. Jin, F. Huang, X. Wang, S.-h. Lee and W. Zhang, A Truxenone-based Covalent Organic Framework as an All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Battery Cathode with High Capacity, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59(46), 20385–20389 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Jhulki, C. H. Feriante, R. Mysyk, A. M. Evans, A. Magasinski, A. S. Raman, K. Turcheniuk, S. Barlow, W. R. Dichtel, G. Yushin and S. R. Marder, A Naphthalene Diimide Covalent Organic Framework: Comparison of Cathode Performance in Lithium-Ion Batteries with Amorphous Cross-linked and Linear Analogues, and Its Use in Aqueous Lithium-Ion Batteries, ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2021, 4(1), 350–356 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Strauss, A. M. Evans, E. K. Roesner, R. J. Monsky, M. I. Bardot and W. R. Dichtel, Divergent Nanotube Synthesis through Reversible Macrocycle Assembly, Acc. Mater. Res., 2022, 3(9), 935–947 CrossRef CAS.
- A. M. Evans, M. J. Strauss, A. R. Corcos, Z. Hirani, W. Ji, L. S. Hamachi, X. Aguilar-Enriquez, A. D. Chavez, B. J. Smith and W. R. Dichtel, Two-Dimensional Polymers and Polymerizations, Chem. Rev., 2022, 122(1), 442–564 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. S. Xie, G. Skorupskii and M. Dincă, Electrically Conductive Metal–Organic Frameworks, Chem. Rev., 2020, 120(16), 8536–8580 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Evans, N. P. Bradshaw, B. Litchfield, M. J. Strauss, B. Seckman, M. R. Ryder, I. Castano, C. Gilmore, N. C. Gianneschi, C. R. Mulzer, M. C. Hersam and W. R. Dichtel, High-Sensitivity Acoustic Molecular Sensors Based on Large-Area, Spray-Coated 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks, Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(42), 2004205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. W. Burke, C. Sun, I. Castano, N. C. Flanders, A. M. Evans, E. Vitaku, D. C. McLeod, R. H. Lambeth, L. X. Chen, N. C. Gianneschi and W. R. Dichtel, Acid Exfoliation of Imine-linked Covalent Organic Frameworks Enables Solution Processing into Crystalline Thin Films, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 59(13), 5165–5171 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Haldar, A. Schneemann and S. Kaskel, Covalent Organic Frameworks as Model Materials for Fundamental and Mechanistic Understanding of Organic Battery Design Principles, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145(25), 13494–13513 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Jin, Q. Cheng, A. M. Evans, J. Gray, R. Zhang, S. T. Bao, F. Wei, L. Venkataraman, Y. Yang and C. Nuckolls, π-Conjugated redox-active two-dimensional polymers as organic cathode materials, Chem. Sci., 2022, 13(12), 3533–3538 RSC.
- S.-J. Park and M.-K. Seo, Chapter 4 – Solid-Solid Interfaces, in Interface Science and Technology, ed. S.-J. Park and M.-K. Seo, Elsevier, 2011, vol. 18, pp. 253–331 Search PubMed.
- L. Sieuw, A. Jouhara, É. Quarez, C. Auger, J. F. Gohy, P. Poizot and A. Vlad, A H-bond stabilized quinone electrode material for Li-organic batteries: The strength of weak bonds, Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(2), 418–426 RSC.
- J. O. E. Sosoe, T. Maris and J. D. Wuest, Strongly Hydrogen-Bonded Networks Formed by Sulfate and Bisulfate Salts of Benzenetetramines, Cryst. Growth Des., 2023, 23(12), 8865–8874 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Néron, M. Morency, C. Malveau, T. Maris, R. Iftimie and J. D. Wuest, Diphenoquinhydrones and Related Hydrogen-Bonded Charge-Transfer Complexes, J. Org. Chem., 2022, 87(23), 15796–15805 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. R. Tuttle, S. T. Davis and S. Zhang, Synergistic Effect of Hydrogen Bonding and π–π Stacking Enables Long Cycle Life in Organic Electrode Materials, ACS Energy Lett., 2021, 6(2), 643–649 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Chen, H. Banda, L. Yang, J. Li, Y. Zhang, R. Parenti and M. Dincă, High-rate, high-capacity electrochemical energy storage in hydrogen-bonded fused aromatics, Joule, 2023, 7(5), 986–1002 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Peng, G.-H. Ning, J. Su, G. Zhong, W. Tang, B. Tian, C. Su, D. Yu, L. Zu, J. Yang, M.-F. Ng, Y.-S. Hu, Y. Yang, M. Armand and K. P. Loh, Reversible multi-electron redox chemistry of π-conjugated N-containing heteroaromatic molecule-based organic cathodes, Nat. Energy, 2017, 2(7), 17074 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Zhou, D. He, J. Hu, Y. Ye, H. Peng, X. Zhou, X. Xie and Z. Xue, A flexible, self-healing and highly stretchable polymer electrolyte via quadruple hydrogen bonding for lithium-ion batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(25), 11725–11733 RSC.
- E. M. Kosower and J. L. Cotter, Stable Free Radicals. II. The Reduction of 1-Methyl-4-cyanopyridinium Ion to Methylviologen Cation Radical, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1964, 86(24), 5524–5527 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Louie, Y. Zhong, S. T. Bao, C. Schaack, A. Montoya, Z. Jin, N. M. Orchanian, Y. Liu, W. Lei, K. Harrison, J. Hone, A. Angerhofer, A. M. Evans and C. P. Nuckolls, Coaxially Conductive Organic Wires Through Self-Assembly, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2023, 145(9), 4940–4945 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J.-W. Jeon, Y. Ma, J. F. Mike, L. Shao, P. B. Balbuena and J. L. Lutkenhaus, Oxidatively stable polyaniline:polyacid electrodes for electrochemical energy storage, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(24), 9654–9662 RSC.
- H. Spanggaard, J. Prehn, M. B. Nielsen, E. Levillain, M. Allain and J. Becher, Multiple-Bridged Bis-Tetrathiafulvalenes: New Synthetic Protocols and Spectroelectrochemical Investigations, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122(39), 9486–9494 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Hu, N. Chen, D. Chen and B. Tong, Conjugated Tetrathiafulvalene Carboxylates for Stable Organic Lithium Batteries, ChemElectroChem, 2022, 9(6), e202200026 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |

