Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleStructure and dynamics of concentration fluctuations in a non-equilibrium dense colloidal suspension†
Fabio
Giavazzi
*a,
Giovanni
Savorana
ab,
Alberto
Vailati
b and
Roberto
Cerbino
 a
a
aDipartimento di Biotecnologie Mediche e Medicina Traslazionale, Università degli Studi di Milano, Via Fratelli Cervi 93, 20090 Segrate, Italy. E-mail: fabio.giavazzi@unimi.it
bDipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano, via Celoria 16, 20133 Milano, Italy
First published on 5th July 2016
Abstract
Linearised fluctuating hydrodynamics describes effectively the concentration non-equilibrium fluctuations (NEF) arising during a diffusion process driven by a small concentration gradient. However, fluctuations in the presence of large gradients are not yet fully understood. Here we study the giant concentration NEF arising when a dense aqueous colloidal suspension is allowed to diffuse into an overlying layer of pure water. We use differential dynamic microscopy to determine both the statics and the dynamics of the fluctuations for several values of the wave-vector q. At small q, NEF are quenched by buoyancy, which prevents their full development and sets an upper timescale to their temporal relaxation. At intermediate q, the mean squared amplitude of NEF is characterised by a power law exponent −4, and fluctuations relax diffusively with diffusion coefficient D1. At large q, the amplitude of NEF vanishes and equilibrium concentration fluctuations are recovered, enabling a straightforward determination of the osmotic compressibility of the suspension during diffusion. In this q-range we also find that the relaxation of the fluctuations occurs with a diffusion coefficient D2 significantly different from D1. Both diffusion coefficients exhibit time-dependence with D1 increasing monotonically (by about 15%) and D2 showing the opposite behaviour (about 17% decrease). At equilibrium, the two coefficients coincide as expected. While the decrease of D2 is compatible with a diffusive evolution of the concentration profile, the increase of D1 is still not fully understood and may require considering nonlinearities that are neglected in current theories for highly stressed colloids.
1 Introduction
The correlation properties of a fluid in a non-equilibrium steady state differ dramatically from the equilibrium ones.1,2 For instance, in pure fluids that are kept out-of-equilibrium by a temperature gradient, the coupling between the gradient and the equilibrium velocity fluctuations gives rise to extraordinarily long-ranged (giant) non-equilibrium fluctuations (NEF) of temperature and density. Theories first predicted the existence and the long-range nature of these correlations3–6 and a confirmation was provided by experiments that detected a large excess of scattering at small angles with respect to equilibrium.7,8 It was later shown that, in a similar fashion, when a fluid mixture is subjected to a macroscopic concentration gradient, giant concentration NEF arise, whose correlation properties are akin to those of single component fluids.1,9–11A non-equilibrium case that involves fluid mixtures and that bears particular relevance is represented by isothermal diffusion, the time-dependent, non-equilibrium process by which a macroscopic concentration gradient (obtained for instance by bringing two miscible liquids into contact at time t = 0) relaxes back to an equilibrium state characterised by a uniform concentration everywhere across the sample.12 Macroscopically, diffusion is well described by the well known Fick's law,13 which expresses the proportionality between the diffusive flux and the concentration gradient. However, the presence of a macroscopic concentration gradient causes giant concentration NEF that exist at the mesoscopic scales14,15 during the whole transient toward equilibrium. These NEF do not represent a fine perturbation of an otherwise quiet diffusive process but rather they are its very essence. Indeed, it has been recently proven that in the presence of a concentration gradient the net mass transfer due to the advection by thermal velocity fluctuations (the same mechanism that gives rise to the NEF) coincides with the one predicted by the macroscopic Fick's law,16–18 which implies that there would be no net diffusive flow without the NEF.
On Earth, the size of these NEF is limited by the presence of gravity that quenches their amplitude and sets an upper bound for their relaxation time.14,19–21 In microgravity, the growth of NEF is limited only by the size of the container and long wavelength fluctuations exhibit a dramatically long lifetime, comparable to that of the macroscopic state.22,23 As a result, while in microgravity theoretical models valid for non-equilibrium steady states cannot be used during the transient to equilibrium,24 on Earth the evolution of the macroscopic state is always significantly slower than the maximum relaxation time of the NEF. One can thus assume that the system goes through a sequence of quasi-stationary states, as originally suggested in ref. 15. As a consequence, at every instant during diffusion, the presence of the NEF in fluid mixtures can be detected by small-angle scattering experiments14,15,19–21,25,26 and analyzed with the same theoretical tools that are used to describe non-equilibrium steady states.1,15
While NEF in molecular binary mixtures have been widely investigated, their investigation in soft matter and in particular in colloidal systems has been so far quite limited. On the theoretical side, a model based on fluctuating hydrodynamics,27 describing NEF in a colloidal suspension subjected to a steady-state macroscopic concentration gradient, was developed by Schmitz28 more than twenty years ago. This model provides an analytical expression for the dynamic structure factor S(q,ω) of an arbitrarily dense buoyancy-matched suspension (or equivalently in the absence of gravity). As shown by Li et al.,10 the result obtained by Schmitz coincides in the hydrodynamic limit (qR ≪ 1, where q is the wave-vector of the fluctuations and R is the radius of the colloidal particles) with the previously developed theory for molecular mixtures, if the effect of gravity is neglected in the latter theory. This analogy is somehow expected: even a dense colloidal suspension, when probed over length scales that are much larger than the size of colloidal particles, should not differ from a molecular mixture. It is plausible that this analogy remains valid also when buoyancy is taken into account but this fact remains unchecked.
A very promising theoretical framework for the study of NEF in colloidal suspensions is represented by dynamic density functional theory (DDFT), an extension of the very successful (static) density functional theory (DFT)29 that is aimed at capturing the dynamics of inhomogeneous fluids, in particular when they are in non-equilibrium states.30–32 DDFT can be thought of as a generalized diffusion equation that captures the time-dependent behavior of density in non-equilibrium systems undergoing Brownian dynamics.33 It is thus clear that DDFT has the potential to describe successfully the correlations in non-equilibrium colloidal suspensions,34 especially in view of the recent progress that was made to account for hydrodynamic interactions among the colloidal particles and to clarify the controversy between deterministic and fluctuating DDFT. However, a DDFT-based prediction for the dynamic structure factor or for the intermediate scattering function of a colloidal suspension diffusing across a macroscopic gradient is, to the best of our knowledge, not yet available even though encouraging steps have been recently made.35,36
Experiments on NEF have been focused mostly on polymer suspensions and other macromolecular solutions in non-equilibrium steady states,10,11,22 during diffusion25,26 and also during the transient to a steady state.24 A surprisingly small number of experimental studies of NEF arising during diffusion of colloidal suspensions is currently available,19,37 despite the importance of colloids in several fundamental and technological processes. One obstacle is that preparing an initial state with a macroscopic concentration gradient that is free of spurious flows is a rather challenging feat. Moreover, diffusion experiments are usually long, since diffusion of colloidal particles requires several days over relatively thick layers of liquid of the order of a few cm. As a consequence, only two experimental studies have been reported in the literature, both of them using optical shadowgraphy38 as a small-angle scattering probe of the NEF. The first study was performed by Croccolo et al.19 on a relatively dilute (4.1% weight fraction) aqueous suspension of silica particles (Ludox TMA). A dense (34% weight fraction) suspension of the same particles was investigated in the other study, by Oprisan et al.,37 together with a dilute (0.01% weight fraction) suspension of gold particles in water. In all cases the suspensions were made to diffuse against pure water. Experiments in ref. 19 investigated the dynamics of the NEF and found that a dilute colloidal suspension exhibits the transition, previously observed in molecular systems,25,26 from the diffusive decay of fluctuations at large wave vectors to the regime in which gravity is dominant at small wave vectors. The diffusion coefficient of the NEF was found to be nearly constant in time with a value 38.5 μm2 s−1 that was markedly different from the value 22 μm2 s−1, previously reported in other studies that made use of the same sample.39–41 In addition, the roll-off wave-vector qro, which marks the effect of gravity on the fluctuations, was found to slowly decrease with the diffusion time as td−1/8, in agreement with theory, but with a pre-factor smaller than the theoretical value by about 30%. On the other hand, the measurements on the more concentrated sample in ref. 37 were not of sufficient quality to allow for a quantitative comparison with theory. Indeed, the dynamics of the fluctuations showed only a qualitative agreement with theory and the amplitude of the fluctuations could not be reliably assessed because of the presence of the optical transfer function of the shadowgraph method, which modulates in a q-dependent fashion the scattering intensity. Even though in principle the transfer function can be independently measured and used to correct the experimental data,22,42,43 this procedure was not followed in ref. 37. It remains thus to be clarified experimentally whether both the statics and the dynamics of the NEF agree with an improved theoretical model for colloidal suspensions that includes gravitational effects, in particular for dense suspensions.
In this work, we obtain time-resolved small-angle scattering information during diffusion of a dense colloidal suspension in the presence of gravity. The sample is a dense colloidal suspension of Ludox TMA at 34% weight fraction, a system that provided contradictory results in previous studies.19,37 The study of the NEF is performed via the recently introduced differential dynamic microscopy (DDM),44,45 a fully quantitative method based on a commercial microscope that is used here to measure both the characteristic amplitude and correlation rate of the concentration fluctuations as a function of their wave vector q and of the time td elapsed from the beginning of diffusion. Compared to the previously used shadowgraphy and to other digital Fourier microscopy46 methods, the use of DDM allows an easier implementation, optical sectioning capabilities along the optical axis and a better rejection of multiple scattering. In addition, we took advantage of the microscope setup to devise a simple and novel diffusion cell based on liquid-bridging that enables the study of diffusion in very thin samples (less than 1 mm). This expedient guarantees that the whole diffusion process takes place over a reasonably short experimental duration compared to previous studies with colloids in ref. 19 and 37, in the absence of long lasting perturbations determined by the procedure used to start the diffusion process that plague other methods. Our experiments give quantitative access to the structure and dynamics of the dense colloidal suspension during the entire diffusion process. At various times td after the start of the diffusion process we find that single silica particles with diameter ≃22 nm coexist with a minority of large particles (we estimate 1 large particle every 10 000 small particles), presumably aggregates (diameter ≃130 nm), whose presence was previously detected also in ref. 37. By subtracting off the signal originated from the aggregates, we are able to identify two main regimes as a function of the wave-vector q of the fluctuations. For wave-vectors smaller than a cross-over wave-vector qco the scattering is dominated by NEF originated at the diffusing interface: for the largest wave-vectors in this range (qro < q < qco) the intensity of light scattered by the fluctuations follows a power law scaling with exponent − 4, and the relaxation of the fluctuations occurs diffusively with a diffusion coefficient D1; for the smallest wave-vectors (q < qro) both the amplitude and relaxation time of the fluctuations are quenched by gravity. Our sensitive diagnostics enables us to obtain scattering information also for q > qco, a region not easily accessible, because the scattering signal due to NEF becomes smaller than the corresponding equilibrium contribution. In this q-range, we indeed find that the scattering signal plateaus to an effective equilibrium value that corresponds to the instantaneous average concentration within the sample and that concentration fluctuations relax with a diffusion coefficient D2 that is markedly and unexpectedly different from D1. Both diffusion coefficients are found to vary in time: D2(td) decreases in time from 48 μm2 s−1 to 37 μm2 s−1, whereas D1(td) exhibits the opposite trend, increasing from 32 μm2 s−1 to 37 μm2 s−1.
We find that the decrease of D2 can be explained as the result of the decreasing overall particle concentration that occurs during diffusion. This hypothesis is confirmed by independent equilibrium measurements on samples with weight fraction ranging from the final one (17%) to the initial one (34%). An additional confirmation comes from estimates of the osmotic compressibility of the suspension that we could obtain in a rather unconventional way, i.e. by calculating the ratio of the scattering intensity at small q, where the scattering signal is dominated by NEF, and the one at large q, where the equilibrium scattering signal is recovered.
To ascertain whether the time-dependence observed for D1(t) could be a peculiar feature of the colloidal nature of our sample, we derive an expression for the dynamic structure factor of the concentration NEF in a dense colloidal suspension in the presence of gravity, by extending the analysis in ref. 28 to include gravity. When our experimental conditions are matched by taking the hydrodynamic limit of theory, our expression for the dynamic structure factor is found to coincide with the one derived by Vailati and Giglio15 for molecular mixtures, provided that structural effects of the dense suspension (entering mainly via osmotic compressibility) are properly taken into account. As a result, both the existence of a diffusion coefficient D1 = D2 and the observation of its time dependence remain uncaptured by linear fluctuating hydrodynamics, which leads us to speculate that a non-linear theory is needed to rationalize our observations.
2 Theory
In this section, we outline a theoretical framework for describing the correlation properties of the fluctuations arising in a dense colloidal suspension in a non-equilibrium time-dependent state during isothermal diffusion. Our aim is to obtain an expression for the dynamic structure factor S(q,ω) of the fluctuations to be used to interpret our quantitative microscopy experiments, which provide time-resolved, small-angle scattering information during diffusion.Light scattering experiments in binary mixtures or colloidal suspensions are sensitive to fluctuations δm in the refractive index m(r,t). The light scattering intensity I(q,ω) as a function of the wave-vector q and the frequency ω is given by
| I(q,ω) = A0〈|δm(q,ω)|2〉 | (1) |
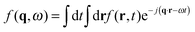 , with r the spatial variable, t the time and j the imaginary unit. If, as in our case, one is interested in Rayleigh scattering it is possible to neglect the effect of pressure fluctuations, thus focusing only on the effect of temperature fluctuations δT and concentration fluctuations δw. Since our experiments are performed at constant temperature with a colloidal suspension, one has
, with r the spatial variable, t the time and j the imaginary unit. If, as in our case, one is interested in Rayleigh scattering it is possible to neglect the effect of pressure fluctuations, thus focusing only on the effect of temperature fluctuations δT and concentration fluctuations δw. Since our experiments are performed at constant temperature with a colloidal suspension, one has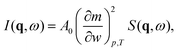 | (2) |
Since in typical light scattering experiments the correlations of the intensity of light scattered by the fluctuations are more often probed as a function of the delay time τ rather than frequency, an inverse Fourier transform in the frequency ω is required to pass from the dynamic structure factor to the intermediate scattering function 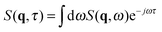 . For a molecular binary mixture and for a colloidal suspension that is either dilute or studied in the hydrodynamic limit, the dynamic structure factor is a Lorentzian function with decay rate Γ(q) and one obtains the simple result S(q,τ) = S(q)f(q,τ) for the intermediate scattering function, where the static structure factor S(q) = 〈|δw(q,t)|2〉t is given by eqn (9) and the normalized intermediate scattering function47 is given by f(q,τ) = e−Γ(q)τ. In the following sections we will sketch the main theoretical results that are obtained when fluctuating hydrodynamics is used to describe diffusion in colloidal suspensions. We first analyze the case in which gravitational effects are absent, and in particular the theory of Schmitz28 for dense colloidal suspensions. We then extend the Schmitz model, by introducing the effect of buoyancy. Finally, based on these results that are valid for stationary steady states, we describe time-dependent diffusion in a dense colloidal suspension. All the theoretical results that will be presented below are obtained in the approximation that the wave-vector q is perpendicular to the direction of the macroscopic concentration gradient, which is well justified in small-angle scattering experiments and, in particular, for our DDM experiments.
. For a molecular binary mixture and for a colloidal suspension that is either dilute or studied in the hydrodynamic limit, the dynamic structure factor is a Lorentzian function with decay rate Γ(q) and one obtains the simple result S(q,τ) = S(q)f(q,τ) for the intermediate scattering function, where the static structure factor S(q) = 〈|δw(q,t)|2〉t is given by eqn (9) and the normalized intermediate scattering function47 is given by f(q,τ) = e−Γ(q)τ. In the following sections we will sketch the main theoretical results that are obtained when fluctuating hydrodynamics is used to describe diffusion in colloidal suspensions. We first analyze the case in which gravitational effects are absent, and in particular the theory of Schmitz28 for dense colloidal suspensions. We then extend the Schmitz model, by introducing the effect of buoyancy. Finally, based on these results that are valid for stationary steady states, we describe time-dependent diffusion in a dense colloidal suspension. All the theoretical results that will be presented below are obtained in the approximation that the wave-vector q is perpendicular to the direction of the macroscopic concentration gradient, which is well justified in small-angle scattering experiments and, in particular, for our DDM experiments.
2.1 Concentration fluctuations in isothermal non-equilibrium stationary states
When a colloidal suspension is subjected to a stationary concentration gradient ∇w, the coupling between the gradient and the velocity fluctuations parallel to the gradient induces long-ranged concentration NEF, similar to what happens in molecular binary mixtures.1 Experimentally, the concentration gradient is often induced through thermophoresis48 (also known as the Soret effect in binary mixtures) via the application of a macroscopic temperature gradient, which induces both concentration and temperature NEF. In the case of a concentration gradient in an isothermal colloidal system, the strength of the equilibrium temperature fluctuations is small and one can focus on the contribution of the concentration NEF, as shown by Schmitz in ref. 28. In this seminal paper, Schmitz calculates the dynamic structure factor S(q,ω) of the fluctuations for a buoyancy matched colloidal suspension in the presence of a steady concentration gradient maintained by continuous pumping of the solvent through semi-permeable walls. In principle, the expression for the dynamic structure factor S(q,ω) derived by Schmitz remains valid also if the concentration gradient is produced by other isothermal means, as it is the case of the present work. Experiments on a dilute suspension of small silica spheres19 showed that gravity affects the dynamics of the fluctuations in a way similar to molecular mixtures, for which it is known that also the amplitude of the fluctuations is strongly affected.49 This result suggests that – at least for the dynamics – there is a strong similarity between dilute colloidal suspensions and molecular mixtures. A model describing NEF in a dense colloidal suspension under the effect of gravity would serve to better understand how far the analogy with molecular mixtures can be brought.To achieve this task, we have extended the results provided in ref. 28 to include the effect of buoyancy. The detailed derivation of the dynamic structure factor of a dense colloidal suspension including buoyancy is reported in ESI.† We summarize here the final result which reads
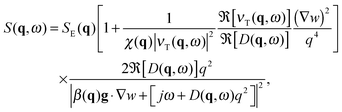 | (3) |
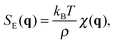 | (4) |
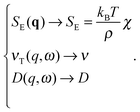 | (5) |
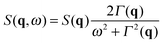 | (6) |
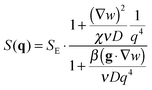 | (7) |
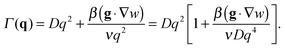 | (8) |
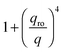 with
with 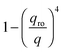 in the following expressions. In that case, buoyancy amplifies long wavelength fluctuations and hydrodynamic instability can set in if the concentration gradient exceeds a threshold value.1,39–41,50 In the stable case, eqn (7) and (8) can be rewritten in a more compact way
in the following expressions. In that case, buoyancy amplifies long wavelength fluctuations and hydrodynamic instability can set in if the concentration gradient exceeds a threshold value.1,39–41,50 In the stable case, eqn (7) and (8) can be rewritten in a more compact way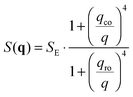 | (9) |
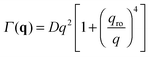 | (10) |
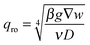 | (11) |
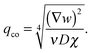 | (12) |
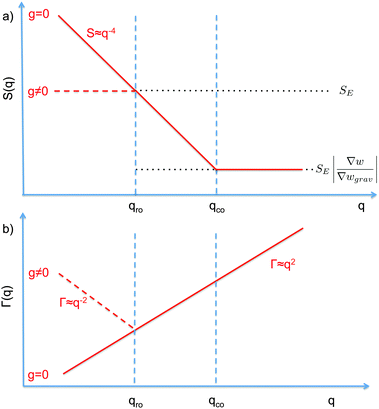 | ||
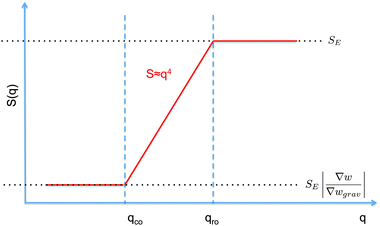
| Fig. 1 Schematic diagram showing the scaling regimes for the static structure factor S(q) (a) and the decay rate Γ(q) (b) of the concentration fluctuations in the hydrodynamic range qR ≪ R1 for a colloidal suspension of particles with radius R subjected to a macroscopic concentration gradient ∇w. Both plots are in the bi-logarithmic scale. The continuous line represents schematically the situation in the absence of buoyancy effects (g = 0). The dashed line depicts the effect of buoyancy, which appears only for q < qro. Here we depict only the most typical case qro < qco. A similar diagram can be drawn for qro > qco, as shown in Fig. 2 only for the case g ≠ 0. | ||
The crossover wave-vector does not influence the dynamics of the fluctuations which, in the absence of buoyancy (qro = 0), remain purely diffusive also in non-equilibrium conditions. When buoyancy is present (qro ≠ 0) two distinct regimes for the decay rate Γ(q) of the fluctuations exist (Fig. 1), which are identified by the asymptotic behaviors
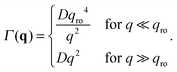 | (13) |
As far as the static properties of the fluctuations are concerned, three cases are obtained by comparing the values of qro and qco:
• When qro = qco, the concentration gradient is set by barodiffusion, i.e. ∇w = βgχ ≐ ∇wgrav. Under this condition, S(q) → SE but the dynamics of the fluctuations remains affected by the presence of the barodiffusion gradient, leading thereby to the possibility of observing the roll-off wave-vector qro also in experiments performed at equilibrium. To the best of our knowledge, this prediction has never been confirmed experimentally.
• When qro < qco one has |∇w| > |∇wgrav| and the static structure factor behaves as
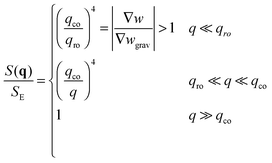 | (14) |
• The third case is obtained when qco<qro, which corresponds to |∇w|<|∇wgrav|. In that case we still have three regimes for the static structure factor
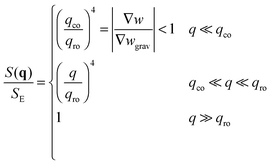 | (15) |
As a summary of this part we conclude by observing that, when the hydrodynamic limit is taken for our general expression (eqn (3)) for the dynamic structure factor of the fluctuations, a complete analogy with the theory for molecular mixtures is obtained. It remains however true that the analysis for arbitrarily large wave-vectors needs to be based on the expression in eqn (3), which represents the most accurate prediction for the dynamic structure factor of a non-equilibrium colloidal suspension in the presence of gravitational effects. It is worth noting that the theoretical results obtained in this section describe concentration fluctuations in a colloidal suspension under the influence of a macroscopic concentration gradient. In our experiment the gradient was obtained by physical separation of two portions of the sample with different concentrations of colloidal particles. However, as far as the interest is restricted to concentration fluctuations, the model just outlined can deal with several other cases involving colloidal suspensions, including the case in which the concentration gradient is obtained by thermophoresis.48,52–54
2.2 Non-equilibrium concentration fluctuations during isothermal diffusion
In Section 2.1 we have described the correlation properties of the concentration fluctuations for a stationary non-equilibrium state. However, it was shown for molecular mixtures in ref. 15 that these results can be easily adapted to describe time-dependent non-equilibrium states. Such adaptation is possible under the assumption that the macroscopic concentration profile w(r,t) evolves on time-scales that are large compared with the longest relaxation time of the concentration fluctuations. This adiabatic approximation is well justified on Earth, where the presence of gravity sets an upper limit to the relaxation time of the fluctuations, but not in microgravity, where the relaxation of fluctuations has been shown to occur always by diffusion.24 Very recent results show that, in principle, this upper limit could be larger than expected even on Earth if finite size effects are taken into account.55 However, such effects show up at very small wave-vectors that are not probed in our experiments. Moreover, the relaxation time associated to the finite size is in any case smaller than the one associated to bulk diffusion.Following ref. 15, we focus on a thin fluid layer placed at a height z within the sample (we assume here that the z axis is oriented parallel to gravity), where the concentration gradient ∇w(z,t) can be assumed to be constant. In the hydrodynamic limit, the corresponding space- and time-resolved intermediate scattering function for a dense suspension is given by Sz,t(q,τ) = Sz,t(q)fz,t(q,τ). The static structure factor Sz,t(q) is given by the expression in eqn (9), in which both the roll-off (eqn (11)) and the cross-over (eqn (12)) wave-vectors acquire (z,t) dependence that is brought in by ∇w(z,t), β(z,t), ν(z,t), χ(z,t) and D(z,t). Similar considerations can be made for the decay rate Γz,t(q) of the normalized intermediate scattering function fz,t(q,τ) = e−Γz,t(q)τ, which is given by eqn (10), with the proper (z,t) dependence taken into account.
It is worth noticing that the adiabatic assumption that we have made here to describe time dependent non-equilibrium cases matches the one made in DDFT studies, where density is assumed to evolve in time much slower than the correlation function of the particles flux, and at each moment in time the non-equilibrium state is described by a fictitious equilibrium system with the same one-body density.56 An extension of DDFT beyond the adiabatic approximations exists, which would yield (in principle) the true correlations.36 This is based on the theory of Brader and Schmidt,57,58 which is still under development (e.g. hydrodynamics is not considered) but appears promising.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Sample preparation and confinement
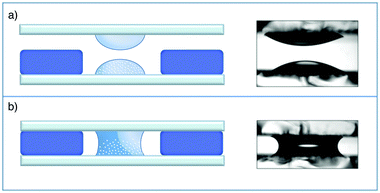
The sample is a Ludox TMA (Sigma) deionized colloidal suspension of silica particles dispersed in water. According to the producer, the nominal average radius of the nanoparticles is R = 22 nm and their nominal concentration is w0 = 34 wt%. The sample was first used without further processing but, due to the presence of small amounts of large aggregates, we used it after membrane filtration. To allow for a direct comparison with the results in ref. 37, the sample was filtered by using a 0.2 μm filter and used for the experiments without further dilution. Kinematic viscosity measurements were performed using a capillary viscometer at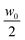 and w0 for which we found ν = (1.34 ± 0.04) × 10−6 m2 s−1 and ν = (2.52 ± 0.03) × 10−6 m2 s−1, respectively. The diffusion experiment was performed in a custom cell whose working principle is based on the concept of a liquid bridge.59 This choice greatly simplifies the preparation of an initial interface between the two liquids free of spurious disturbances generated by shear flow. Moreover, compared to previous approaches,19,37 it simultaneously allows a reduction of the diffusion time and of the amount of multiple scattering with concentrated colloids, which both increase with the sample thickness. Finally, our cell guarantees a very simple solution for repeated experiments. The cell is schematically depicted in Fig. 3 and is assembled as follows. Two standard microscope glass slides are accurately cleaned and one of them is positioned on the stage of a commercial microscope (Nikon Ti-U). A soft gasket is obtained from a rubber mat (Witte Blaue Matte) of thickness 1 mm by cutting a rectangular strip with the same dimensions as that of the glass slides. A circular hole is carefully punched at the center of the gasket, which is then mounted on the microscope stage onto the previously positioned glass slide. By means of a micro pipette, one drop (17 μl) of the concentrated colloidal suspension is carefully deposited on the glass slide inside the hole at the center of the gasket. An identically sized drop of MilliQ water is deposited on the other slide at the center. The final step of the cell assembly consists in shifting vertically the glass slide with the pure water drop to bring it in contact with the colloidal drop, when a liquid bridge is formed (Fig. 3b). The cell thickness is set by the gasket, which also minimizes sample evaporation during the experiments. The planarity of the interface separating the two fluids was checked by interferometry. The radius of curvature of the interface was found to be always more than 10 cm, which gives an upper bound of about 0.5 μm for the vertical deviation of the interface from planarity. The experiments were performed at the constant temperature T = 23 ± 2 °C. Before the creation of the liquid bridge, the microscope was aligned and the image plane was chosen to approximately match the position of the interface between the two liquids. A side view of the two drops immediately before being placed in contact is shown in Fig. 3b.
and w0 for which we found ν = (1.34 ± 0.04) × 10−6 m2 s−1 and ν = (2.52 ± 0.03) × 10−6 m2 s−1, respectively. The diffusion experiment was performed in a custom cell whose working principle is based on the concept of a liquid bridge.59 This choice greatly simplifies the preparation of an initial interface between the two liquids free of spurious disturbances generated by shear flow. Moreover, compared to previous approaches,19,37 it simultaneously allows a reduction of the diffusion time and of the amount of multiple scattering with concentrated colloids, which both increase with the sample thickness. Finally, our cell guarantees a very simple solution for repeated experiments. The cell is schematically depicted in Fig. 3 and is assembled as follows. Two standard microscope glass slides are accurately cleaned and one of them is positioned on the stage of a commercial microscope (Nikon Ti-U). A soft gasket is obtained from a rubber mat (Witte Blaue Matte) of thickness 1 mm by cutting a rectangular strip with the same dimensions as that of the glass slides. A circular hole is carefully punched at the center of the gasket, which is then mounted on the microscope stage onto the previously positioned glass slide. By means of a micro pipette, one drop (17 μl) of the concentrated colloidal suspension is carefully deposited on the glass slide inside the hole at the center of the gasket. An identically sized drop of MilliQ water is deposited on the other slide at the center. The final step of the cell assembly consists in shifting vertically the glass slide with the pure water drop to bring it in contact with the colloidal drop, when a liquid bridge is formed (Fig. 3b). The cell thickness is set by the gasket, which also minimizes sample evaporation during the experiments. The planarity of the interface separating the two fluids was checked by interferometry. The radius of curvature of the interface was found to be always more than 10 cm, which gives an upper bound of about 0.5 μm for the vertical deviation of the interface from planarity. The experiments were performed at the constant temperature T = 23 ± 2 °C. Before the creation of the liquid bridge, the microscope was aligned and the image plane was chosen to approximately match the position of the interface between the two liquids. A side view of the two drops immediately before being placed in contact is shown in Fig. 3b.
3.2 Characterization of the fluctuations
Once the liquid bridge was created by placing in contact the two drops (Fig. 3b), differential dynamic microscopy (DDM)44,45 was used to characterize the amplitude and dynamics of the fluctuations. Bright-field movies of the fluctuations arising as diffusion took place were recorded at different times (td = 180, 690, 1230, 2010, 3390, 6540, 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 s) from the creation of the liquid bridge that triggered the start of diffusion. For each movie, 8000 images were acquired at 100 frames per second. The study of the correlation properties of the intensity fluctuations in the microscope images allows extraction of typical quantities that are traditionally measured with scattering experiments47 such as the scattering intensity I(q) and the (normalized) intermediate scattering function f(q,Δt).45,46 The procedure is similar to that developed recently to extract I(q) and f(q,Δt) by using shadowgraphy21 or Schlieren interferometry.20
000 s) from the creation of the liquid bridge that triggered the start of diffusion. For each movie, 8000 images were acquired at 100 frames per second. The study of the correlation properties of the intensity fluctuations in the microscope images allows extraction of typical quantities that are traditionally measured with scattering experiments47 such as the scattering intensity I(q) and the (normalized) intermediate scattering function f(q,Δt).45,46 The procedure is similar to that developed recently to extract I(q) and f(q,Δt) by using shadowgraphy21 or Schlieren interferometry.20
In practice, if I(x,t) represents the spatial intensity distribution of an image of the fluctuations acquired at time t, the image structure function is calculated as
d(q,Δt) = 〈|![[scr F, script letter F]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e141.gif) [I(x,t + Δt) − I(x,t)]|2〉t [I(x,t + Δt) − I(x,t)]|2〉t | (16) |
![[scr F, script letter F]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e141.gif) represents the 2D Fourier transform operation from the real space variable x = (x,y) to the Fourier wave-vector q = (qx,qy). When, as in the case of interest here, the structure and the dynamics of the system are isotropic and spatially homogeneous in the image plane it is convenient to azimuthally average d(q,Δt) and obtain the one-dimensional structure function
represents the 2D Fourier transform operation from the real space variable x = (x,y) to the Fourier wave-vector q = (qx,qy). When, as in the case of interest here, the structure and the dynamics of the system are isotropic and spatially homogeneous in the image plane it is convenient to azimuthally average d(q,Δt) and obtain the one-dimensional structure function 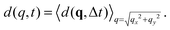 The image structure function is linked to the scattering intensity and to the intermediate scattering function by the relation
The image structure function is linked to the scattering intensity and to the intermediate scattering function by the relation| d(q,Δt) = A(q)[1 − f(q,Δt)] + B(q). | (17) |
Therefore, while a temporal analysis of the intensity fluctuations provides immediate access to f(q,Δt), access to I(q) requires previous knowledge of the optical transfer function T(q). In some cases, the transfer function can be modeled with the required accuracy, as done for instance in ref. 60, where the asymptotic behavior of T(q) for q → 0 was sufficiently regular. However, in general this is not always an easy task and it is often preferred to determine T(q) via calibration of the microscope with a dilute suspension of non-interacting colloidal particles for which the scattering intensity I(q) is q-independent in the accessible wave-vector range so that for the calibration sample A(q) ≃ const T(q). With such procedure, described in detail in ESI,† it is possible to determine T(q) up to a multiplicative constant.22 Once T(q) is known, the scattering intensity I(q) can be also determined from the amplitude A(q), which makes a DDM experiment equivalent to a combined static and dynamic light scattering experiment at small scattering angles. All the measurements presented in this work were obtained with a camera pixel size (after 10× magnification) dpix = 1.2 μm. Considering the image resolution (512 × 512 pixels) the accessible wave-vector range is theoretically comprised between qmin = 2π/(512dpix) = 1.0 × 10−2 μm−1 and qmax = π/dpix = 2.6 μm−1. However, T(q) for our bright-field microscopy experiment vanishes for both large q and small q,45,46 which implies that the experimentally accessible wave-vector range typically reduces to [5 × 10−2,1.4] μm−1.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Structure of the fluctuations
For each scattering wave-vector q, the output of the DDM analysis is the image structure function d(q,Δt) as a function of the time delay Δt. A typical structure function measured during the diffusion process at q = 0.45 μm−1 is shown in Fig. 4a, together with the corresponding intermediate scattering function f(q,Δt), shown in Fig. 4b. The intermediate scattering function exhibits a double relaxation process: a fast relaxation superimposed on a slower relaxation. The double relaxation process observed for f(q,Δt) is present for all the available wave-vectors and is well fitted to a linear combination of a slow stretched-exponential decay and a faster simple-exponential decay:| f(q,Δt) = af(q)e−Γf(q)Δt + as(q)e−[c(γ)Γs(q)Δt]γ | (18) |
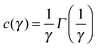 , where Γ is Euler's gamma function. By insertion of eqn (18) into eqn (17), it is possible to fit the experimental data for d(q,Δt) very accurately (Fig. 4a, blue line) and to obtain the amplitudes A(q), af(q), as(q), the rates Γf(q), Γs(q) and the noise term B(q). Within this model, the total scattering intensity I(q) = A(q)/T(q) is thus the sum of the scattering intensity Is(q) = A(q)as(q)/T(q) associated with the slow process and the scattering intensity If(q) = A(q)af(q)/T(q) associated with the fast process.
, where Γ is Euler's gamma function. By insertion of eqn (18) into eqn (17), it is possible to fit the experimental data for d(q,Δt) very accurately (Fig. 4a, blue line) and to obtain the amplitudes A(q), af(q), as(q), the rates Γf(q), Γs(q) and the noise term B(q). Within this model, the total scattering intensity I(q) = A(q)/T(q) is thus the sum of the scattering intensity Is(q) = A(q)as(q)/T(q) associated with the slow process and the scattering intensity If(q) = A(q)af(q)/T(q) associated with the fast process.
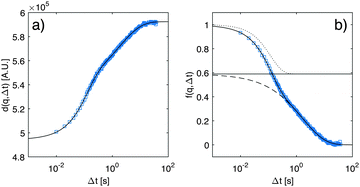 | ||
| Fig. 4 (a) Experimental results (blue squares) for the image structure function (a) and intermediate scattering function (b) measured at q = 0.45 μm−1, and at time td = 2010 s from the beginning of the diffusion process. The continuous line is the best fitting curve of the experimental data to a double exponential process as given by eqn (17) and (18). In (b) we decompose the decay described by eqn (18) into its two components, a fast one (dotted line) and a slow one (dashed line), with the horizontal line representing the amplitude as. | ||
As anticipated in Section 3.2, an accurate characterization of the transfer function T(q) is needed to obtain the scattering intensities Is(q) and If(q). The transfer function T(q), obtained with the calibration procedure described in ESI,† is shown in Fig. 1 (ESI†), where we also show that after division with T(q), the scattering intensity Is(q) is substantially flat in the accessible q-range for all values of td. As discussed in more detail in ESI,† the results for Is(q) can be attributed to the presence of colloidal aggregates of Ludox particles and will not be discussed further here. By contrast, the contribution If(q) (Fig. 5) associated to the fast process exhibits the expected excess of scattering at the smallest wave-vectors, which is the signature of NEF. In fact, fitting the data for If(q) to eqn (9) provides estimates at various td for the roll-off wave-vector qro, for the crossover wave-vector qco, and for the scattering intensity IE at equilibrium. We note that the roll-off wave-vector qro could not be determined reliably in the latest stages of the diffusion process (for td larger than about 6000 s), because the gravity-induced plateau lied outside the accessible q range. In fact, for large wave-vectors, the frame rate of the image acquisition prevents an accurate characterization of the relaxation when the lifetime of the fluctuations becomes comparable with the inverse of the frame rate and this occurs for q ≃ 1.5 × 106 m−1 (further details can be found in Section 4.2). For small q, the accurate determination of the amplitude is made difficult by (a) the overall duration of each movie that should be kept sufficiently small to avoid picking up the diffusion kinetics; (b) the presence of slow convective processes within the sample cell, mainly affecting the slow relaxation; and (c) the strong effect of the transfer function T(q) of the microscope that goes to zero for small values of q.
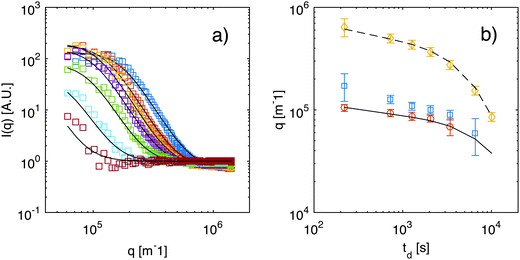 | ||
Fig. 5 (a) Scattering intensity If(q) obtained for a diffusing colloidal suspension at various times td from the beginning of diffusion: td = 180, 690, 1230, 2010, 3390, 6540, and 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 s (from top to bottom). Continuous lines are best fits to eqn (9). Data for Is(q) are shown in ESI.† (b) Roll-off wave-vector qro as a function of the time td elapsed from the beginning of diffusion, as obtained from the static (blue squares) and from the dynamic (orange circles) analysis of the NEF. The continuous line is a theoretical prediction from eqn (11), evaluated for z corresponding to the sample mid-plane. Yellow diamonds represent the crossover wave-vector qco. The dashed line is the theoretical prediction from eqn (12), again calculated for z corresponding to the sample mid-plane. In addition, the osmotic compressibility 000 s (from top to bottom). Continuous lines are best fits to eqn (9). Data for Is(q) are shown in ESI.† (b) Roll-off wave-vector qro as a function of the time td elapsed from the beginning of diffusion, as obtained from the static (blue squares) and from the dynamic (orange circles) analysis of the NEF. The continuous line is a theoretical prediction from eqn (11), evaluated for z corresponding to the sample mid-plane. Yellow diamonds represent the crossover wave-vector qco. The dashed line is the theoretical prediction from eqn (12), again calculated for z corresponding to the sample mid-plane. In addition, the osmotic compressibility ![[small chi, Greek, macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0d8.gif) is assumed to remain constant during diffusion. is assumed to remain constant during diffusion. | ||
![[D with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0044_0304.gif) ∇2w = 0 with the initial condition
∇2w = 0 with the initial condition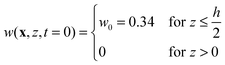 | (19) |
![[D with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0044_0304.gif) we used the value
we used the value ![[D with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0044_0304.gif) = 3.7 × 10−11 m2 s−1 that we obtained from equilibrium measurements performed at the average concentration
= 3.7 × 10−11 m2 s−1 that we obtained from equilibrium measurements performed at the average concentration 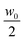 (see ESI,†Fig. 4). Even though the overall time dependence of the experimental qro is well reproduced by the theory, there is a systematic shift, corresponding to a factor of about 1.25. This discrepancy can be at least partly due to a systematic error introduced by an inaccurate estimate of the transfer function T(q) for q → 0. Indeed, in this limit the signal from the calibration sample is vanishingly small and the presence of large scale slow convective motions makes the determination of the dynamics of the sample and amplitude of T(q) less reliable. We also report in Fig. 5b the results for qro (orange circles) obtained from the analysis of the dynamics of the NEF, which appear in better agreement with theory. Further comments about the comparison of the experimental values for qro (from both the statics and dynamics of the NEF) and theory will be provided in Section 4.2.
(see ESI,†Fig. 4). Even though the overall time dependence of the experimental qro is well reproduced by the theory, there is a systematic shift, corresponding to a factor of about 1.25. This discrepancy can be at least partly due to a systematic error introduced by an inaccurate estimate of the transfer function T(q) for q → 0. Indeed, in this limit the signal from the calibration sample is vanishingly small and the presence of large scale slow convective motions makes the determination of the dynamics of the sample and amplitude of T(q) less reliable. We also report in Fig. 5b the results for qro (orange circles) obtained from the analysis of the dynamics of the NEF, which appear in better agreement with theory. Further comments about the comparison of the experimental values for qro (from both the statics and dynamics of the NEF) and theory will be provided in Section 4.2.
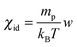 , which gives χid = 0.89 s2 m−2 for w = w0/2. It is however worth pointing out that the value obtained here for the osmotic compressibility represents a global estimate, roughly corresponding to the average concentration w0/2 of the sample and does not take into account the large changes in concentration occurring during the diffusion process.
, which gives χid = 0.89 s2 m−2 for w = w0/2. It is however worth pointing out that the value obtained here for the osmotic compressibility represents a global estimate, roughly corresponding to the average concentration w0/2 of the sample and does not take into account the large changes in concentration occurring during the diffusion process.
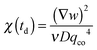 (the z-dependence of all the variables is lost since in our experiments we have access only to vertically averaged quantities). The results of this inversion are shown (red circles) in Fig. 6, in which we also plot with different units (left axis) the scattering intensity IE of the equilibrium fluctuations, obtained from the large-q behavior of the data in Fig. 5. The value of the unknown proportionality constant between IE and χ could be in principle determined by absolute calibration. Here, we determined such value by minimization of the mean square deviation between the two data sets, given that no absolute calibration was performed. An exponential increase with a characteristic time τA = (2.7 ± 0.3) × 103 s (black line in Fig. 6) is the best fit of the experimental data, which provides the estimate χ = (0.08 ± 0.01) s2 m−2 for the osmotic compressibility at equilibrium, when the concentration is equal to w0/2 everywhere in the sample.
(the z-dependence of all the variables is lost since in our experiments we have access only to vertically averaged quantities). The results of this inversion are shown (red circles) in Fig. 6, in which we also plot with different units (left axis) the scattering intensity IE of the equilibrium fluctuations, obtained from the large-q behavior of the data in Fig. 5. The value of the unknown proportionality constant between IE and χ could be in principle determined by absolute calibration. Here, we determined such value by minimization of the mean square deviation between the two data sets, given that no absolute calibration was performed. An exponential increase with a characteristic time τA = (2.7 ± 0.3) × 103 s (black line in Fig. 6) is the best fit of the experimental data, which provides the estimate χ = (0.08 ± 0.01) s2 m−2 for the osmotic compressibility at equilibrium, when the concentration is equal to w0/2 everywhere in the sample.
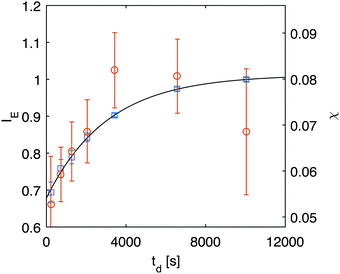 | ||
| Fig. 6 Right axis: osmotic compressibility χ (red circles) obtained during diffusion obtained from inversion of eqn (12). Left axis: equilibrium scattering intensity (blue squares) obtained from the large-q behavior in Fig. 5a. | ||
The observed temporal increase of the scattering intensity is an indication that we are well beyond the limit of validity of the van't Hoff law 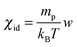 that would lead to a constant value for IE in time, since the average concentration remains constant. This hypothesis is well confirmed by a set of DDM experiments on colloidal suspensions prepared at a uniform concentration in the range [0.17,0.34], whose scattering intensity as a function of concentration is shown in ESI† (Fig. 3). The results show that at these concentrations, the osmotic compressibility of the suspension is actually decreasing with concentration, confirming that colloidal interactions in a dense colloidal suspension cannot be neglected during diffusion.
that would lead to a constant value for IE in time, since the average concentration remains constant. This hypothesis is well confirmed by a set of DDM experiments on colloidal suspensions prepared at a uniform concentration in the range [0.17,0.34], whose scattering intensity as a function of concentration is shown in ESI† (Fig. 3). The results show that at these concentrations, the osmotic compressibility of the suspension is actually decreasing with concentration, confirming that colloidal interactions in a dense colloidal suspension cannot be neglected during diffusion.
4.2 Dynamics of the fluctuations
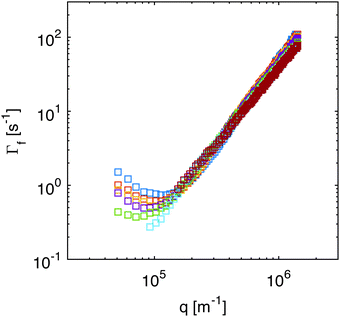
While in Section 4.1 we have focused on the amplitude of the fluctuations, equally important information can be extracted from the study of their lifetime.Indeed, fitting of the experimental intermediate scattering functions provides both the fast rate Γf(q) (Fig. 7) and the slow rate Γs(q) (ESI,†Fig. 2) and they are very well separated and clearly distinguishable. As discussed in more detail in ESI,† the slow process can be attributed to diffusing large aggregates of silica particles. As far as the fast process is concerned, inspection of Fig. 7 shows that the behavior of the correlation rate does not mirror exactly the predictions from eqn (10). This can be better appreciated in Fig. 8a, where for clarity we report only the curve obtained for td = 690 s. The experimental data for Γf(q) conform to the expected behavior (continuous line) only in the low-q region, where the position of the minimum allows determining qro and the q2 scaling provides an estimate for the diffusion coefficient D1. Interestingly, at the large wave vectors we observe a transition to a different diffusive behavior characterized by a diffusion coefficient D2, such that D2 > D1. This behavior, which is observed here for the first time, can be monitored during diffusion to obtain the temporal dependence of the two diffusion coefficients (Fig. 8b) and the roll-off wave-vector qro (Fig. 5b, orange circles).
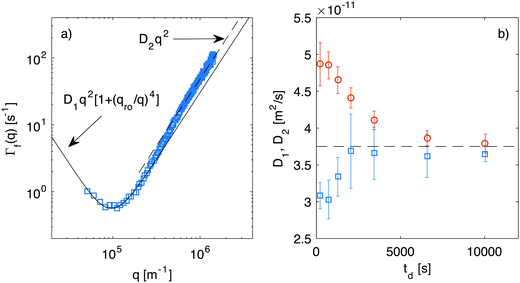 | ||
| Fig. 8 (a) Correlation rate of the fast relaxation mode of concentration fluctuations in a diffusing non-equilibrium colloidal suspension as a function of the scattering wave-vector q, measured at td = 690 s after the beginning of diffusion. The continuous line is the best fit of the low-q data with eqn (10), which provides an estimate for the roll-off wave-vector qro and for the diffusion coefficient D1. The dashed line is a fit of the high-q data with Γ(q) = D2q2, where D2 > D1. (b) Diffusion coefficients D1 (squares) and D2 (circles) extracted as shown in panel (a) at different times during diffusion. The corresponding values for qro are reported in Fig. 5b as orange circles. | ||
As far as the roll-off wave-vector is concerned, the estimate obtained from the dynamics (Fig. 5b, orange circles) is about 20% smaller than the one obtained from the statics (Fig. 5b, blue squares) and agrees well with the theoretical prediction from eqn (11), evaluated for z corresponding to the sample mid-plane (Fig. 5b, continuous line). The estimate obtained from the dynamics is expected to be more robust, as it is substantially independent from any calibration procedure. In fact, it is not affected by errors in the determination of the transfer function T(q), which plays a crucial role in the reconstruction of the true scattering intensity I(q). It might be however possible that only part of the observed discrepancy is due to systematic errors. Indeed, it was recently observed in experiments62 that the roll-off wave-vector determined from the statics is always about 11% larger than the one determined from the dynamics, an effect that is presently not accounted for by available theories.
We also observe that both D1 and D2 depend on time. However, while the value of D1 increases during diffusion, the opposite trend is exhibited by D2. Both diffusion coefficients relax exponentially to the same value (of about 3.7 × 10−11 m2 s−1) with time constants that are compatible with the relaxation of the macroscopic concentration gradient. Comparison of Fig. 5 and 7 shows that the transition from the diffusive behavior with diffusion coefficient D1 to the one with diffusion coefficient D2 takes place roughly at q = qco. This suggests that while for q < qco the signal is dominated by the giant NEF occurring during diffusion, at large q, where the amplitude of the NEF vanishes, the equilibrium properties of the suspension are probed. At the beginning of the experiment, the signal from the NEF originates from a thin layer at the mid-height of the sample (average concentration w0/2), where the concentration gradient is maximum, while the equilibrium scattering originates from the lower part of the cell, where almost all the colloidal particles are confined (average concentration w0). By contrast, at the end of the experiment, the concentration is the same (w0/2) everywhere and NEF are not present anymore. At intermediate times during diffusion, the equilibrium scattering signal can be thought of as the superposition of three contributions: one from the bottom layer of the suspension, with concentration decreasing in time; one from the upper layer with concentration increasing in time; and one from the central part, in which the average concentration remains locked to w0/2.
In this picture, owing to the concentration dependence of the diffusion coefficient of the colloidal suspension, we expect that the diffusion coefficient D2 should change during diffusion, mirroring the sample concentration decrease from w0 = 34% to w0/2 = 17%. To check if the observed change of D2 can be accounted for by this effect we have characterized the dynamics of colloidal suspensions prepared at a uniform concentration. The results (ESI,†Fig. 4) show that the diffusion coefficient of a homogeneous Ludox suspension with concentration w varies in the range [3.7,4.8] × 10−11 m2 s−1 when w goes from 0.17 to 0.34. The upper and lower bounds of this interval, i.e. D(w0) ≃ 4.8 × 10−11 m2 s−1 and D(w0/2) ≃ 3.7 × 10−11 m2 s−1, are consistent with the value of D2 measured at the beginning and at the end of our diffusion experiment, confirming thereby the validity of our picture.
By contrast, the 15% increase of D1 observed during diffusion is more difficult to rationalize. Indeed, previous experiments on a dilute Ludox suspension (concentration 4.1%) found that a constant diffusion coefficient 38.5 μm2 s−1 described the data for all times during diffusion,19 in agreement with the linearized fluctuating hydrodynamics theory presented in Section 2. The same behavior is expected also for a dense colloidal suspension such as the one investigated here (concentration 34%) provided that the hydrodynamic range is probed. This expectation is not met by our experiments in which we observe an increase in time of D1, pointing to a transient slowing down of the dynamics with respect to the long-time equilibrium behaviour that is monotonically vanishing with the concentration gradient.
We made a first attempt to justify the observed time-dependence for D1 by considering the fact that the information about the fluctuations that we obtain in our experiments is averaged across the sample thickness. The contribution of the NEF is originated in the region where the concentration of the suspension is not uniform due to the presence of the macroscopic gradient. In the case of a linear concentration profile, the average diffusion coefficient coincides with the value at the cell mid-height, where the concentration remains locked to w0/2. While for a dilute suspension non-linearities of the concentration profile can safely be assumed to be small, in concentrated suspensions this might not be the case. A direct experimental measurement of the vertical concentration profile during diffusion on such thin samples is almost impossible. As previously done in other scattering experiments,1,15 we addressed this issue by solving the diffusion equation with the appropriate boundary and initial conditions. In particular, to fully account for the concentration dependence of the diffusion coefficient in our sample, we used the non-linear diffusion equation:61 ∂t2w − ∇(D(w)∇w) = 0, where we assumed concentration dependence: D(w) = D0(1 + Kw) (D0 = 28 μm2 s−1, K = 1.8), compatible with our results from equilibrium measurements (ESI,†Fig. 4). By solving the non-linear diffusion equation with the initial and boundary conditions given by eqn (19), we find that the diffusion coefficient corresponding to the height where the concentration gradient has a maximum differs from the average value 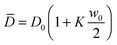 by less than 1%, ruling out this effect as a possible explanation for the observed time-dependence of D1, which involves changes of roughly 15%.
by less than 1%, ruling out this effect as a possible explanation for the observed time-dependence of D1, which involves changes of roughly 15%.
Another explanation for the observed increase of D1 might come from the results of Brogioli and Vailati in ref. 16. They used linearized fluctuating hydrodynamics to calculate the advective contributions of non-equilibrium concentration fluctuations to the net mass transfer during a diffusion experiment. These advective contributions are second order terms neglected in the linearized equation and should represent in principle small perturbations of the macroscopic state. Surprisingly, Brogioli and Vailati showed that the mass flux obtained from the superposition of these contributions coincides with the one expected from the phenomenological Fick's law. Therefore, the entire diffusive mass transfer can be thought of as generated by non-equilibrium fluctuations. In order to obtain a consistent model for the mass transfer by non-equilibrium fluctuations, they then renormalized the hydrodynamic equations and found that the macroscopic diffusion coefficient D(g) in the presence of gravity is related to the diffusion coefficient ![[D with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_0044_0304.gif) that describes macroscopic diffusion in the absence of gravity at the same average concentration by the equation
that describes macroscopic diffusion in the absence of gravity at the same average concentration by the equation 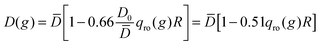 . Since qro depends on ∇w this relation indicates that the diffusion coefficient is depressed when a concentration gradient is present, as a consequence of the fact that large scale fluctuations relax by gravity. However, an estimate for our experimental conditions at t = 200 s when qro ≃ 1 × 105 m−1 provides 0.51 qro(g)R = 0.1%, which is two orders of magnitude smaller than the experimentally observed 15% difference.
. Since qro depends on ∇w this relation indicates that the diffusion coefficient is depressed when a concentration gradient is present, as a consequence of the fact that large scale fluctuations relax by gravity. However, an estimate for our experimental conditions at t = 200 s when qro ≃ 1 × 105 m−1 provides 0.51 qro(g)R = 0.1%, which is two orders of magnitude smaller than the experimentally observed 15% difference.
Finally, we note that the presence of a concentration gradient across a colloidal suspension has been found to quench the velocity fluctuations during colloidal sedimentation of large spheres.63,64 This phenomenon has not yet been confirmed for small Brownian particles, but of course it could represent a mechanism by which in a stratified sample diffusion takes place slower than in a homogeneous case.
It remains true that non-linearities can affect in subtle and unexpected ways the validity of the theoretical model that we have used for describing our experiment since some of the assumptions made in deriving the linearized fluctuating hydrodynamics theory presented in Section 2 and based on ref. 28 could be violated at the beginning of our experiments, when the concentration gradient is very large. A non-linear fluctuating hydrodynamics approach, already advocated by other investigators,2 could bypass this limitation and possibly explain our results. Such challenging extension is well beyond the aim of the present work.
5 Conclusions
Diffusion, one of the most widely studied transport mechanisms with a wealth of applications ranging from the transport of molecules at the cellular level to the gravitational settling of atoms in stars, represents an effective test-bench for theories aiming at obtaining a macroscopic description of out-of-equilibrium systems. During diffusion, a key role is played by non-equilibrium concentration fluctuations, whose amplitude, life-time and correlation range are strongly enhanced with respect to equilibrium, in both molecular and macromolecular fluids.14,19,25 Quite surprisingly, while the case of diffusion in dilute suspensions received some attention in the past19,28,37 no quantitative results are available for dense colloids, neither theoretical, nor experimental.In this work, we have extended the results of ref. 28 to obtain a theoretical prediction for the dynamic structure factor of the concentration fluctuations in out-of-equilibrium dense suspensions in the presence of buoyancy effects. The development of a novel sample cell, based on liquid bridging, enabled us to study isothermal diffusion in thin layers of a dense suspension of silica particles. The concentration fluctuations have been characterized by means of differential dynamic microscopy (DDM),44,45 a method based on a commercial microscope that was used here to obtain both static and dynamic scattering information on the suspension, i.e. both the amplitude and correlation rate of the concentration fluctuations as a function of their wave vector q and of the time td elapsed from the beginning of diffusion. The static scattering results are in good agreement with the theoretical expectations, with an excess of scattering signal at small q caused by the non-equilibrium fluctuations and the presence of an equilibrium contribution at the largest observed q. The simultaneous determination of the scattering intensity of both equilibrium and non-equilibrium fluctuations allowed the direct determination of the osmotic compressibility of the suspension from the ratio of the two signals, a procedure that does not require an absolute calibration of the instrument. As far as the dynamics is concerned, the relaxation of concentration fluctuations is determined by gravity at small wave-vectors, while at intermediate wave vectors they relax diffusively with a diffusion coefficient D1, in agreement with theoretical predictions. For large q, in the regime where equilibrium scattering is recovered, the concentration fluctuations exhibit a diffusive relaxation with diffusion coefficient D2 that is surprisingly different from D1. In addition, when these two coefficients are monitored during diffusion we find an unexpected monotonic increase of D1 (about 15%), in contrast with a monotonic decrease of D2 (about 17%). While the decrease of the diffusion coefficient D2 could be rationalized by the varying concentration of the sample during diffusion, as confirmed by independent equilibrium measurements, the increase of the diffusion coefficient D1 remains uncaptured by current theoretical models. The observation that D1 changes in time at a constant average concentration and depends on the local concentration gradient suggests that D1 cannot be derived solely from local equilibrium considerations. Also, we believe that, despite the efforts made here to maximize the output from existing theoretical approaches based on linearized fluctuating hydrodynamics,28 it is possible that the observed temporal increase of the diffusion coefficient of the NEF might not be captured by current linear theories and an extension to include non-linear terms might be needed.2 DDFT might also represent a useful tool, especially in light of recent developments aimed at merging the gap with non-equilibrium fluctuations65 and reinforcing the link with scattering experiments.35,36 Finally, additional experiments, possibly aiming at outlining in a clearer way the contribution of non-local and memory effects in dense colloidal suspensions, might be useful in particular for large values of qR. Clarifying these issues appear particularly relevant because colloidal suspensions seem to be very suitable candidate samples for verifying experimentally the existence of recently predicted Casimir forces that arise during diffusion as a consequence of the long-ranged nature of the non-equilibrium concentration fluctuations.66,67
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Rossetto for testing of the liquid-bridge cell. We are indebted to S. Buzzaccaro, F. Croccolo, A. Donev and A. Fortini for useful and illuminating discussions. We acknowledge funding by the Italian Ministry of Education and Research, “Futuro in Ricerca” Project ANISOFT (RBFR125H0M).References
- J. M. Ortiz De Zárate and J. V. Sengers, Hydrodynamic fluctuations in fluids and fluid mixtures, Elsevier, 2006 Search PubMed.
- T. R. Kirkpatrick and J. R. Dorfman, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2015, 92, 022109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. R. Kirkpatrick, E. G. D. Cohen and J. R. Dorfman, Phys. Rev. A: At., Mol., Opt. Phys., 1982, 26, 950 CrossRef.
- T. R. Kirkpatrick, E. G. D. Cohen and J. R. Dorfman, Phys. Rev. A: At., Mol., Opt. Phys., 1982, 26, 972 CrossRef.
- T. R. Kirkpatrick, E. G. D. Cohen and J. R. Dorfman, Phys. Rev. A: At., Mol., Opt. Phys., 1982, 26, 995 CrossRef.
- D. Ronis and I. Procaccia, Phys. Rev. A: At., Mol., Opt. Phys., 1982, 26, 1812 CrossRef.
- B. M. Law, R. W. Gammon and J. V. Sengers, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1988, 60, 1554 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. N. Segrè, R. W. Gammon, J. V. Sengers and B. M. Law, Phys. Rev. A: At., Mol., Opt. Phys., 1992, 45, 714 CrossRef.
- W. B. Li, P. N. Segrè, R. W. Gammon and J. V. Sengers, Physica A, 1994, 204, 399 CrossRef CAS.
- W. B. Li, K. J. Zhang, J. V. Sengers, R. W. Gammon and J. M. Ortiz De Zárate, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1998, 81, 5580 CrossRef CAS.
- W. B. Li, K. J. Zhang, J. V. Sengers, R. W. Gammon and J. M. Ortiz De Zárate, J. Chem. Phys., 2000, 112, 9139 CrossRef CAS.
- E. L. Cussler, Diffusion: mass transfer in fluid systems, Cambridge university press, 2009 Search PubMed.
- A. Fick, Ann. Phys., 1855, 170, 59 CrossRef.
- A. Vailati and M. Giglio, Nature, 1997, 390, 262 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Vailati and M. Giglio, Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top., 1998, 58, 4361 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Brogioli and A. Vailati, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2001, 63, 012105 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Donev, J. B. Bell, A. de la Fuente and A. L. Garcia, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2011, 106, 204501 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Donev, T. G. Fai and E. Vanden-Eijnden, J. Stat. Mech.: Theory Exp., 2014, 2014, P04004 CrossRef.
- F. Croccolo, D. Brogioli, A. Vailati, M. Giglio and D. S. Cannell, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2006, 1077, 365–379 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Croccolo, D. Brogioli, A. Vailati, M. Giglio and D. S. Cannell, Appl. Opt., 2006, 45, 2166 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Croccolo, D. Brogioli, A. Vailati, M. Giglio and D. S. Cannell, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2007, 76, 041112 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Vailati, R. Cerbino, S. Mazzoni, C. J. Takacs, D. S. Cannell and M. Giglio, Nat. Commun., 2011, 2, 290 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Vailati, R. Cerbino, S. Mazzoni, M. Giglio, C. J. Takacs and D. S. Cannell, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2012, 24, 284134 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Cerbino, Y. Sun, A. Donev and A. Vailati, Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 14486 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Brogioli, A. Vailati and M. Giglio, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2000, 12, A39 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Brogioli, A. Vailati and M. Giglio, Phys. Rev. E: Stat. Phys., Plasmas, Fluids, Relat. Interdiscip. Top., 2000, 61, R1 CrossRef CAS.
- L. D. Landau and E. M. Lifshitz, Fluid Mechanics, Addison-Wesley, 1959 Search PubMed.
- R. Schmitz, Physica A, 1994, 206, 25 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Löwen, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2002, 14, 11897 CrossRef.
- R. Evans, Adv. Phys., 1979, 28, 143 CrossRef CAS.
- U. M. B. Marconi and P. Tarazona, J. Chem. Phys., 1999, 110, 8032 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wu and Z. Li, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2007, 58, 85–112 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Angioletti-Uberti, M. Ballauff and J. Dzubiella, Soft Matter, 2014, 10, 7932 RSC.
- H. Löwen and M. Heinen, Eur. Phys. J.: Spec. Top., 2014, 223, 3113 CrossRef.
- A. J. Archer, P. Hopkins and M. Schmidt, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2007, 75, 040501 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Hopkins, A. Fortini, A. J. Archer and M. Schmidt, J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 133, 224505 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Oprisan, S. Oprisan and A. Teklu, Appl. Opt., 2010, 49, 86–98 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. P. Trainoff and D. S. Cannell, Phys. Fluids, 2002, 14, 1340 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Cerbino, A. Vailati and M. Giglio, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2002, 66, 055301 CrossRef PubMed.
- R. Cerbino, S. Mazzoni, A. Vailati and M. Giglio, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2005, 94, 064501 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Mazzoni, R. Cerbino, D. Brogioli, A. Vailati and M. Giglio, Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys., 2004, 15, 305 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Cerbino, L. Peverini, M. Potenza, A. Robert, P. Bösecke and M. Giglio, Nat. Phys., 2008, 4, 238 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Cerbino and A. Vailati, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 2009, 14, 416 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Cerbino and V. Trappe, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, 100, 188102 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Giavazzi, D. Brogioli, V. Trappe, T. Bellini and R. Cerbino, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2009, 80, 031403 CrossRef PubMed.
- F. Giavazzi and R. Cerbino, J. Opt., 2014, 16, 083001 CrossRef.
- B. J. Berne and R. Pecora, Dynamic light scattering: with applications to chemistry, biology, and physics, Courier Dover Publications, 2000 Search PubMed.
- R. Piazza, Soft Matter, 2008, 4, 1740 RSC.
- P. N. Segrè and J. V. Sengers, Physica A, 1993, 198, 46 CrossRef.
- F. Giavazzi and A. Vailati, Phys. Rev. E: Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2009, 80, 015303(R) CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Vailati and M. Giglio, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77, 1484 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wongsuwarn, D. Vigolo, R. Cerbino, A. M. Howe, A. Vailati, R. Piazza and P. Cicuta, Soft Matter, 2012, 8, 5857 RSC.
- Z. Wang, H. Kriegs, J. Buitenhuis, J. K. Dhont and S. Wiegand, Soft Matter, 2013, 9, 8697 RSC.
- A. Königer, N. Plack, W. Köhler, M. Siebenbürger and M. Ballauff, Soft Matter, 2013, 9, 1418–1421 RSC.
- C. Giraudet, H. Bataller, Y. Sun, A. Donev, J. M. Ortiz De Zárate and F. Croccolo, EPL, 2015, 111, 60013 CrossRef.
- P. Español and H. Löwen, J. Chem. Phys., 2009, 131, 244101 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. M. Brader and M. Schmidt, J. Chem. Phys., 2013, 139, 104108 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Fortini, D. de las Heras, J. M. Brader and M. Schmidt, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2014, 113, 167801 CrossRef PubMed.
- P.-G. De Gennes, F. Brochard-Wyart and D. Quéré, Capillarity and wetting phenomena: drops, bubbles, pearls, waves, Springer, 2004 Search PubMed.
- F. Giavazzi, S. Crotti, A. Speciale, F. Serra, G. Zanchetta, V. Trappe, M. Buscaglia, T. Bellini and R. Cerbino, Soft Matter, 2014, 10, 3938 RSC.
- J. Crank, The mathematics of diffusion, Oxford university press, 1979 Search PubMed.
- F. Croccolo, H. Bataller and F. Scheffold, Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys., 2014, 37, 105 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. J. Mucha, S.-Y. Tee, D. A. Weitz, B. I. Shraiman and M. P. Brenner, J. Fluid Mech., 2004, 501, 71 CrossRef.
- R. Piazza, Rep. Prog. Phys., 2014, 77, 056602 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Donev and E. Vanden-Eijnden, J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 140, 234115 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Aminov, Y. Kafri and M. Kardar, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, 114, 230602 CrossRef PubMed.
- T. R. Kirkpatrick, J. M. Ortiz De Zárate and J. V. Sengers, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2015, 115, 035901 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c6sm00935b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 |