Themed collection Functional Co-crystals

Front cover

Inside front cover

Back cover

Contents list
Editorial
Welcome to this CrystEngComm themed issue on functional co-crystals.

CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5752-5752
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE90086C
Pharmaceutical co-crystals – are we there yet?
Progression from drug to co-crystal to medicine.
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5753-5761
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00127C
Head-to-tail photodimerization of a thiophene in a co-crystal and a rare adipic acid dimer in the presence of a heterosynthon
Head-to-tail photodimerization of thiophene is achieved in a co-crystal while a co-crystal with an acid dimer and heterosynthon is also described.
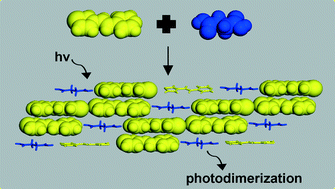
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5762-5764
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00481G
The crystal structure and optical properties of a pharmaceutical co-crystal – the case of the melamine–barbital addition compound
The melamine barbital co-crystal is an optically stable NLO material, engineered from the pharmaceutically active barbital molecule, showing SHG efficiency higher than that of KDP.
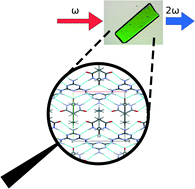
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5765-5768
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00178H
Crystal form selectivity by humidity control: the case of the ionic co-crystals of nicotinamide and CaCl2
Post-synthesis (de)hydration techniques were used here to explore further hydrated forms of ionic co-crystals (ICCs) of nicotinamide with CaCl2.
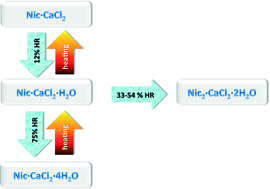
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 7452-7458
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00464G
Intermolecular hydrogen transfer and solubility tuning in multi-component molecular crystals of the API piroxicam
Twelve multi-component molecular crystals of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) piroxicam (PX) are described contrasting those with basic N-heterocycles with those formed with strong haloanilic acids. The effect on the solubility of this API is discussed, with evidence of enhanced solubility in the multi-component crystals formed.
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5924-5932
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00246F
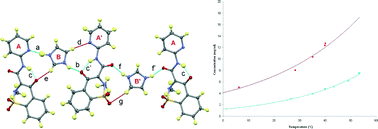
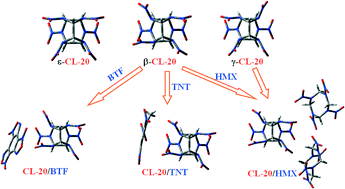
Toward low-sensitive and high-energetic co-crystal II: structural, electronic and energetic features of CL-20 polymorphs and the observed CL-20-based energetic–energetic co-crystals
The O⋯O, O⋯H and O⋯N interactions dominantly hold all the crystal packing.
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5905-5916
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00584H
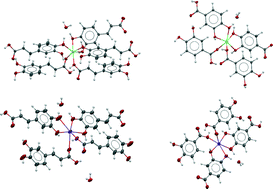
Functional hybrid co-crystals of humic substances: a growth forecast
Basing our reasoning on the only known and available crystalline structure of a hybrid co-crystal of caffeic acid, we extended our study to the analysis of the behaviour of another humic substance, the protocatechuic acid.
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5917-5923
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00191E
Proton location in acid⋯pyridine hydrogen bonds of multi-component crystals
Role of local crystal environment on proton location was modelled using DFT calculations. Alteration in the strength of the hydrogen bonding can convert a system from a salt to a co-crystal.

CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5878-5886
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00043A
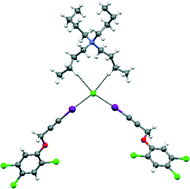
Polymorphs and co-crystals of haloprogin: an antifungal agent
Haloprogin is a widely used antifungal agent. Here we report the first polymorphs and halogen-bonded co-crystals ever described.
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5897-5904
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00367E
Ionic co-crystals of racetams: solid-state properties enhancement of neutral active pharmaceutical ingredients via addition of Mg2+ and Ca2+ chlorides
Reaction of brivaracetam (BRV) and seletracetam (SEL) with MgCl2 and CaCl2 yields ionic co-crystals with improved physico-chemical properties with respect to pure drugs.
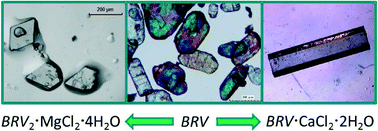
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5887-5896
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00409D
Organizing a bis(iminoylnitroxide) diradical into antiferromagnetically coupled chains by co-crystallization with dichloromethane
Crystallization of a meta-bis(iminoylnitroxide) with dichloromethane (DCM) gives co-crystal in which DCM planarizes the diradical, enabling pi-stacks with 1-D antiferromagnetic exchange between radical units.
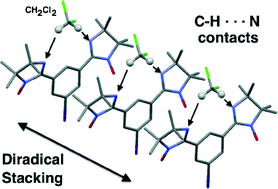
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5832-5838
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00207E
Modulating the solubility of sulfacetamide by means of cocrystals
The antibacterial drug sulfacetamide was screened with pharmaceutically acceptable coformers to discover solid forms with low solubility. Cocrystals with INIC and CAF exhibited 0.64 and 0.68 times the IDR of the parent drug. SACT–CAF cocrystal with lower solubility and good stability is a potential candidate to increase the drug residence time at the site of action for improved therapeutic efficacy.
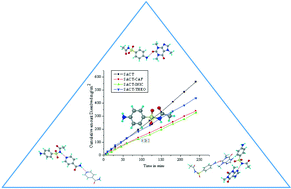
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5859-5869
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00103F
Knowledge-based approaches to co-crystal design
Current approaches for knowledge-based co-crystal design are explained and exemplified, followed by presentation of emerging methodologies which build on these concepts.
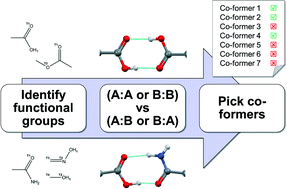
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5839-5848
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00316K
Turning colour on and off using molecular disorder and proton transfer in multi-component molecular complexes
Three pairs of molecular complexes based around 4-iodoaniline and 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid are reported. Within each pair, one complex is colourless and one red; the influences on the colour are discussed including the role of molecular disorder and proton transfer.

CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5849-5858
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00229F
Altering physical properties of pharmaceutical co-crystals in a systematic manner
Systematic structure–property studies on a series of co-crystals of potential cancer drugs with aliphatic dicarboxylic acids were undertaken.
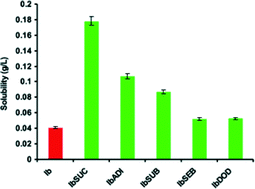
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5870-5877
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00206G
From discovery to scale-up: α-lipoic acid : nicotinamide co-crystals in a continuous oscillatory baffled crystalliser
Discovery, characterisation and scale-up of novel α-lipoic acid co-crystals using continuous crystallisation in a COBC is demonstrated.

CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5769-5780
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00154K
Drug solid solutions – a method for tuning phase transformations
Tuning phase transformation temperatures through the use of solid solutions.
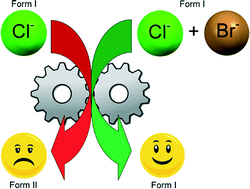
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5827-5831
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CE00211C
Investigation of molecular arrangements and solid-state fluorescence properties of solvates and cocrystals of 1-acetyl-3-phenyl-5-(9-anthryl)-2-pyrazoline
The arrangement of the title compound (crystal I) was regulated via different solvates and cocrystals (crystals II–V) for fluorescence modulation.
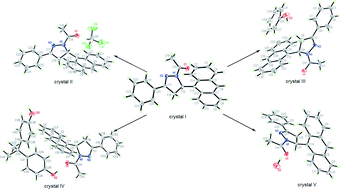
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5820-5826
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE42210K
Structures of benzoic acids with substituted pyridines and quinolines: salt versus co-crystal formation
Acids and bases were crystallized so that their ΔpKa spans the ‘uncertainty’ region for the formation of salt versus co-crystals.
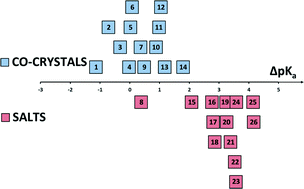
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5802-5810
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE41963K
Crystal engineering of homochiral molecular organization of naproxen in cocrystals and their thermal phase transformation studies
Crystal engineering principles were used to produce the homochiral R- and S-chains of naproxen (NPX) by cocrystallization with bipyridine (BPY) and piperazine (PIZ).

CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5811-5819
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE42415D
Cocrystallization with flufenamic acid: comparison of physicochemical properties of two pharmaceutical cocrystals
A 1 : 1 cocrystal of flufenamic acid with theophylline shows improved solubility and dissolution rate when compared to flufenamic acid and the recently reported cocrystal with nicotinamide, which also helps to inhibit the hygroscopic nature of theophylline and is stable under slurry conditions.

CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5793-5801
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE42182A
Alternative solid-state forms of a potent antimalarial aminopyridine: X-ray crystallographic, thermal and solubility aspects
Hydrogen bonding patterns for a cocrystal and a series of salts of an orally active antimalarial drug candidate are presented, together with thermal stability and solubility data as part of a programme aimed at early identification of new crystal forms of the active compound.
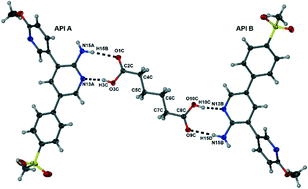
CrystEngComm, 2014,16, 5781-5792
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE41798K
About this collection
Guest edited by Colin Pulham, the focus of this issue is to present current research that highlights how co-crystals with specific functionalities across a range of potential and actual applications can be designed and prepared.