Themed collection Global Energy Challenges: Hydrogen Energy

Why conclusions from platinum model surfaces do not necessarily lead to enhanced nanoparticle catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction
Platinum model-surface and nanoparticle catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction are enhanced by the presence of concave sites.

Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 2283-2289
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC04788B
Single-atom catalysts for CO2 electroreduction with significant activity and selectivity improvements
We propose the great potential of single atom catalysts (SACs) for CO2 electroreduction with high activity and selectivity predictions over a competitive H2 evolution reaction. We find the lack of an atomic ensemble for adsorbate binding and unique electronic structure of the single atom catalysts play an important role.
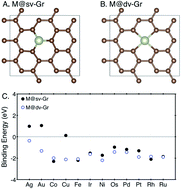
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 1090-1096
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC03911A
Gradient doping of phosphorus in Fe2O3 nanoarray photoanodes for enhanced charge separation
Highly-oriented Fe2O3 nanoarrays with a gradient phosphorus concentration result in enhanced charge separation in the bulk for photoelectrochemical water oxidation.

Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 91-100
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC03707K
A low-crystalline ruthenium nano-layer supported on praseodymium oxide as an active catalyst for ammonia synthesis
Low-crystalline Ru nano-layers and the strong basicity of Ru/Pr2O3 synergistically accelerated the rate-determining step of ammonia synthesis.
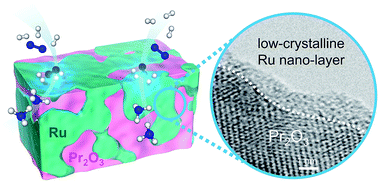
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 674-679
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC02382G
Covalent triazine framework supported non-noble metal nanoparticles with superior activity for catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane: from mechanistic study to catalyst design
Development of non-noble metal catalysts with similar activity and stability to noble metals is of significant importance in the conversion and utilization of clean energies.
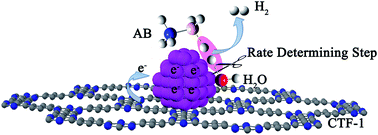
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 781-788
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC02456D
Proton-coupled electron transfer in the electrocatalysis of CO2 reduction: prediction of sequential vs. concerted pathways using DFT
We provide a complete and computationally detailed picture of the mechanism of the initial stages of the electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 in water catalysed by cobalt porphyrin complexes.

Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 458-465
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC02984A
Achievement of visible-light-driven Z-scheme overall water splitting using barium-modified Ta3N5 as a H2-evolving photocatalyst
Barium-modified Ta3N5 for the promotion of proton reduction is first employed as a H2-evolving photocatalyst for visible-light-driven Z-scheme overall water splitting.

Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 437-443
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC02750D
Metalloporphyrin-modified semiconductors for solar fuel production
A novel synthetic method is used to prepare metalloporphyrin-modified gallium phosphide photocathodes for solar-driven hydrogen evolution from water.
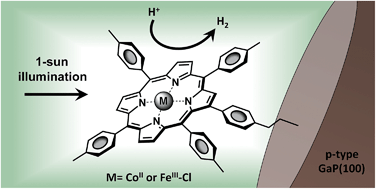
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 253-259
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC02664H
How covalence breaks adsorption-energy scaling relations and solvation restores them
We show that under vacuum various metalloporphyrins break the scaling relation between the adsorption energies of *OH and *OOH, which can potentially boost oxygen reduction and evolution. In aqueous solution, however, such scaling relation is restored.
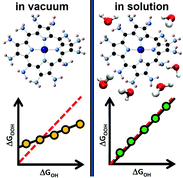
Chem. Sci., 2017,8, 124-130
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC02123A
Ru–protein–Co biohybrids designed for solar hydrogen production: understanding electron transfer pathways related to photocatalytic function
Two ruthenium-protein-cobaloxime biohybrids produce photocatalytic hydrogen through different catalytic pathways characterized by EPR and transient optical spectroscopies.

Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 7068-7078
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC03121H
Rhenium(I) trinuclear rings as highly efficient redox photosensitizers for photocatalytic CO2 reduction
Trinuclear Re(I)-rings were applied as redox photosensitizers in visible light-driven CO2 reduction in tandem with various catalysts, i.e., Re(I)-, Ru(II)- and Mn(I)-diimine metal complex. The quantum yields for the Ru(II) and Mn(I) catalysts were the among highest reported.
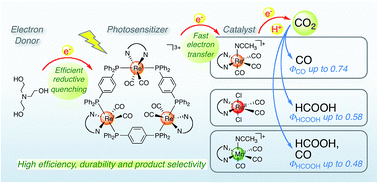
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 6728-6739
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC01913G
Accessing and predicting the kinetic profiles of homogeneous catalysts from volcano plots
Volcano plots, which generally describe only thermodynamics, are expanded to include kinetics that markedly influence the performance of homogeneous catalysts.

Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 5723-5735
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC01660J
Thin film transfer for the fabrication of tantalum nitride photoelectrodes with controllable layered structures for water splitting
Controlled layered structures fabricated by thin film transfer enhance the photoelectrochemical water splitting on Ta3N5 photoanodes.

Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 5821-5826
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC01763K
Photoelectrochemical hydrogen production in water using a layer-by-layer assembly of a Ru dye and Ni catalyst on NiO
Layer-by-layer assembly of a Ru dye and Ni catalyst on a p-type NiO photocathode enables photoelectrochemical H2 generation in water.
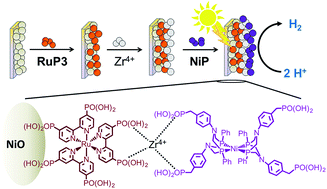
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 5537-5546
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00715E
Essential role of hydride ion in ruthenium-based ammonia synthesis catalysts
Ruthenium-loaded metal hydrides with hydrogen vacancies function as efficient catalysts for ammonia synthesis under low temperature and low pressure conditions.
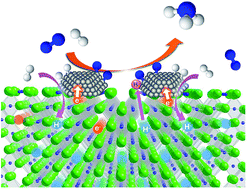
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 4036-4043
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00767H
Visible-light-driven CO2 reduction on a hybrid photocatalyst consisting of a Ru(II) binuclear complex and a Ag-loaded TaON in aqueous solutions
A hybrid photocatalytic system consisting of a Ru(II) binuclear complex and Ag-loaded TaON can reduce CO2 to HCOOH by visible light irradiation even in aqueous solution (TONHCOOH = 750, ΦHCOOH = 0.48%).

Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 4364-4371
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00586A
Precious-metal free photoelectrochemical water splitting with immobilised molecular Ni and Fe redox catalysts
Splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen with 3d transition metal molecular catalysts and light has been accomplished.

Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 4024-4035
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC04863J
Porous single-crystalline AuPt@Pt bimetallic nanocrystals with high mass electrocatalytic activities
This paper describes the design and synthesis of porous single-crystalline AuPt@Pt bimetallic nanocrystals with excellent mass activities for the oxygen reduction reaction and formic acid oxidation.
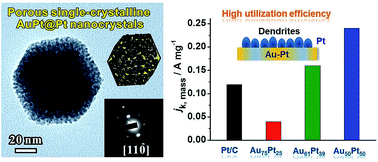
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 3500-3505
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6SC00083E
Overall water splitting by Pt/g-C3N4 photocatalysts without using sacrificial agents
Direct splitting of pure water into H2 and O2 in a stoichiometric molar ratio of 2 : 1 by conjugated polymers via a 4-electron pathway was established for the first time, as demonstrated here using a g-C3N4 polymer and redox co-catalysts of Pt and Co species.
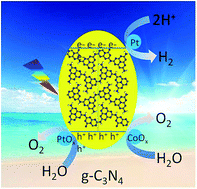
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 3062-3066
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC04572J
Decoration of Pt on Cu/Co double-doped CeO2 nanospheres and their greatly enhanced catalytic activity
In this paper, we report an efficient strategy for the synthesis of Cu/Co double-doped CeO2 nanospheres (CuxCo1−x–CeO2–Pt, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1), which were fabricated via a simple water–glycol system.

Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 1867-1873
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC04069H
Highly effective sites and selectivity of nitrogen-doped graphene/CNT catalysts for CO2 electrochemical reduction
The selectivity of CO2 electrochemical reduction can be tuned for N-doped graphene/CNT catalysts after active sites are determined.
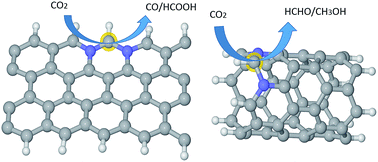
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 1268-1275
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC03695J
Photocatalytic proton reduction with ruthenium and cobalt complexes immobilized on fumed reversed-phase silica
Non-covalent binding of water reduction catalysts and photosensitizers to hydrophobic silica particles represents a general approach for heterogenizing molecular water splitting components.
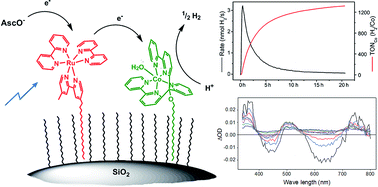
Chem. Sci., 2016,7, 436-445
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02124C
Discovery of low energy pathways to metal-mediated B![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond reduction guided by computation and experiment
N bond reduction guided by computation and experiment
The reduction of borazine-type heterocycles has been a challenge in the area of chemical hydrogen storage. Coordination to low valent metal carbonyls activates borazine for reduction by both 1 e− and 2 e− pathways.
![Graphical abstract: Discovery of low energy pathways to metal-mediated B [[double bond, length as m-dash]] N bond reduction guided by computation and experiment](/is/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C5SC02348C&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2015)
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 7258-7266
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02348C
Highly efficient, selective, and durable photocatalytic system for CO2 reduction to formic acid
Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to formic acid with high efficiency, durability, and rate.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 7213-7221
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02018B
Solar-microbial hybrid device based on oxygen-deficient niobium pentoxide anodes for sustainable hydrogen production
A new solar-microbial hybrid device based on oxygen-deficient Nb2O5 anodes for sustainable hydrogen generation without external bias was demonstrated.
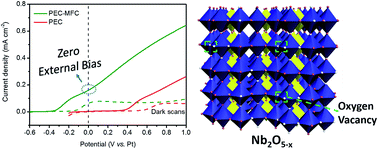
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 6799-6805
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC03249K
Galvanic replacement synthesis of AgxAu1−x@CeO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) core@shell nanospheres with greatly enhanced catalytic performance
A galvanic replacement strategy has been successfully adopted to design AgxAu1−x@CeO2 core@shell nanospheres derived from Ag@CeO2 ones.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 7015-7019
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02774H
Pt/Ni(OH)2–NiOOH/Pd multi-walled hollow nanorod arrays as superior electrocatalysts for formic acid electrooxidation
In this work, novel Pt/Ni(OH)2–NiOOH/Pd multi-walled hollow nanorod arrays are successfully synthesized.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 6991-6998
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02544C
Overpotential for CO2 electroreduction lowered on strained penta-twinned Cu nanowires
Penta-twinned Cu nanowires have a strain-tunable low overpotential for CO2 electroreduction.
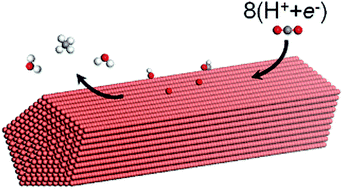
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 6829-6835
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02667A
Photoelectrochemical device based on Mo-doped BiVO4 enables smart analysis of the global antioxidant capacity in food
An ultrasensitive Mo-doped BiVO4 composite was used to engineer a photoelectrochemical platform for the direct analysis of the global antioxidant capacity. Using this principle, an integrated device was successfully exploited for the “smart” monitoring of antioxidant-rich foodstuffs.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 6632-6638
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02277K
Carbon nitride–TiO2 hybrid modified with hydrogenase for visible light driven hydrogen production
Solar light driven hydrogen production with a heterogenised hydrogenase on a carbon nitride–TiO2 hybrid is reported that sets a new benchmark for photo-H2 production.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 5690-5694
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC02017D
Possibility of designing catalysts beyond the traditional volcano curve: a theoretical framework for multi-phase surfaces
The current theory of catalyst activity in heterogeneous catalysis is mainly obtained from the study of catalysts with mono-phases, while most catalysts in real systems consist of multi-phases, the understanding of which is far short of chemists' expectation.
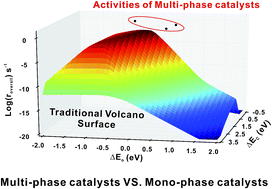
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 5703-5711
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC01732G
Self-assembly of a mesoporous ZnS/mediating interface/CdS heterostructure with enhanced visible-light hydrogen-production activity and excellent stability
We designed and successfully fabricated a ZnS/CdS 3D mesoporous heterostructure with a mediating Zn1−xCdxS interface.
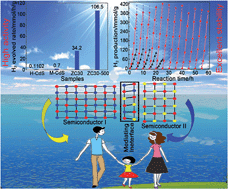
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 5263-5268
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC01586C
Photoanodic and photocathodic behaviour of La5Ti2CuS5O7 electrodes in the water splitting reaction
La5Ti2CuS5O7 embedded into the surface of Au and Ti substrates shows a photocurrent attributable to HER and OER.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 4513-4518
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC01344E
Unravelling the pH-dependence of a molecular photocatalytic system for hydrogen production
The electron-donating ability of the sacrificial agent and the protonation of the catalyst determine the optimum pH for hydrogen production.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 4855-4859
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC01349F
Synthesis of open-mouthed, yolk–shell Au@AgPd nanoparticles with access to interior surfaces for enhanced electrocatalysis
Open-mouthed, yolk–shell Au@AgPd nanoparticles are successfully produced via galvanic replacement reaction in water at room temperature.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 4350-4357
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC01088H
Ammonia decomposition catalysis using non-stoichiometric lithium imide
The non-stoichiometric lithium imide–amide system effectively decomposes ammonia to its constituents, hydrogen and nitrogen. Isotopic studies show that this bulk catalytic reaction has the potential to generate high-purity hydrogen for future energy and transport applications.
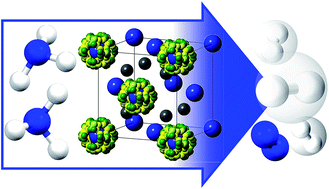
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 3805-3815
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00205B
Chemical looping of metal nitride catalysts: low-pressure ammonia synthesis for energy storage
Design principles for reducible metal nitride catalysts are developed and demonstrated for ambient-pressure solar-driven N2 reduction into NH3.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 3965-3974
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00789E
The atomistic origin of the extraordinary oxygen reduction activity of Pt3Ni7 fuel cell catalysts
Optimality of Pt : Ni 30 : 70 fully dealloyed nanoporous Pt particles in terms of size and coordination environment.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 3915-3925
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00840A
Highly stable PtP alloy nanotube arrays as a catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in acidic medium
Self-supporting PtP nanotube arrays composed of interconnected PtP alloy nanocrystals exhibited excellent activity and durability for the ORR in acidic medium.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 3211-3216
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00124B
Increasing the rate of hydrogen oxidation without increasing the overpotential: a bio-inspired iron molecular electrocatalyst with an outer coordination sphere proton relay
H2 oxidation by a molecular electrocatalyst is dramatically improved by controlling proton movement from iron to the outer coordination sphere.
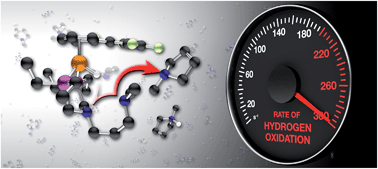
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 2737-2745
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00398A
Electrode initiated proton-coupled electron transfer to promote degradation of a nickel(II) coordination complex
Electrochemical analysis of a nickel compound that degrades permitted a peek into the decomposition mechanism.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 2827-2834
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00476D
Enhancing H2 evolution performance of an immobilised cobalt catalyst by rational ligand design
Rational ligand design was employed to improve the proton reduction activity of an immobilised cobalt diimine–dioxime catalyst.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 2727-2736
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC03946G
Turning it off! Disfavouring hydrogen evolution to enhance selectivity for CO production during homogeneous CO2 reduction by cobalt–terpyridine complexes
Understanding the activity and selectivity of molecular catalysts for CO2 reduction to fuels is an important scientific endeavour in addressing the growing global energy demand.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 2522-2531
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC03766A
Rapid water oxidation electrocatalysis by a ruthenium complex of the tripodal ligand tris(2-pyridyl)phosphine oxide
A ruthenium complex of the tripodal ligand tris(2-pyridyl)phosphine oxide exhibits rapid water oxidation electrocatalysis over a wide pH range.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 2405-2410
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5SC00032G
What is the trigger mechanism for the reversal of electron flow in oxygen-tolerant [NiFe] hydrogenases?
A new mechanistic model is developed for the sequence of events by which oxygen-tolerant [NiFe] hydrogenase enzymes respond to O2.
![Graphical abstract: What is the trigger mechanism for the reversal of electron flow in oxygen-tolerant [NiFe] hydrogenases?](/is/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C4SC03223C&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2015)
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 1433-1443
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC03223C
Durable hydrogen evolution from water driven by sunlight using (Ag,Cu)GaSe2 photocathodes modified with CdS and CuGa3Se5
The multilayer structure enhances the hydrogen evolution from water under simulated sunlight.

Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 894-901
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC02346C
Oxygen evolution on well-characterized mass-selected Ru and RuO2 nanoparticles
Well-defined mass-selected Ru and RuO2 nanoparticles exhibit an order of magnitude improvement in the oxygen evolution activity, relative to the state-of-the-art, with a maximum at around 3–5 nm.
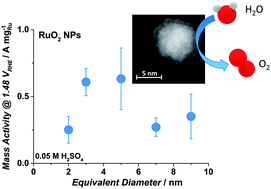
Chem. Sci., 2015,6, 190-196
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SC02685C
About this collection
We are delighted to present an online collection showcasing recently published articles in the field of energy. To address major issues facing our planet, researchers all over the world have increasingly focused their efforts on finding solutions to these energy challenges. These articles highlight some of the excellent work that tackles important global challenges related to energy. We hope you enjoy reading this collection!