Themed collection Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts Recent HOT Articles

Critical review of fluorescence and absorbance measurements as surrogates for the molecular weight and aromaticity of dissolved organic matter
Optical surrogates are used to characterize dissolved organic matter composition like aromaticity and molecular weight. We both review the genesis of surrogate-composition relationships and critically evaluate additional supporting evidence.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1663-1702
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00183D
On the risk of a dissolved gas-triggered limnic eruption in Lake Kivu
Our simulation study predicts that chemocline strength in Lake Kivu is maintained over the next half-millennium.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2026, Advance Article
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00513B
Clean Water Irrigation Promotes Microbial Community Recovery in Acid Mine Drainage-Contaminated Paddy Soil: A Spatiotemporal Analysis Based on Simulated Soil Column Experiments from Dabaoshan Mine, China
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2026, Accepted Manuscript
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00762C
Size-resolved analyses of trace elements in snow from an open-pit bitumen mining and upgrading region
Most trace elements in the filterable fraction of snow are predominantly <300 Da, but their concentrations are extremely low.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 3403-3419
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00334B
Distinct impact of polystyrene microplastics on six species of common pathogenic and probiotic bacteria and their boosting support to Vibrio cholerae proliferation
Along with the widespread application of plastics, the release of polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs) into the environment raises concerns about the risks of PS-MPs to human health.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 2353-2366
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5EM00219B
Hybrid intelligence for environmental pollution: biodegradability assessment of organic compounds through multimodal integration of graph attention networks and QSAR models
Assessing the biodegradability of organic compounds is essential for reducing their environmental impact, ensuring regulatory compliance, promoting sustainable development and supporting effective pollution remediation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 981-991
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00594E
Sorption kinetics of metallic and organic contaminants on micro- and nanoplastics: remarkable dependence of the intraparticulate contaminant diffusion coefficient on the particle size and potential role of polymer crystallinity
We developed a mechanistic diffusion model to describe the sorption kinetics of metallic and organic contaminants on nano- and micro-plastics.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 634-648
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00744A
Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of physicochemical properties of waste plastics with different landfill age and depth
Plastics are widely used for their excellent properties, and the primary disposal method is sanitary landfilling.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 623-633
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00799A
In situ remediation of eutrophic Wolong Lake sediments using novel PVA-SA-biochar and PVA-SA-zeolite embedded immobilized indigenous microorganisms: a pilot study
Sediment restoration has become a key link in river and lake pollution control.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 597-622
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00580E
Reversible and irreversible retention of heavy metals in saturated porous media: association with kaolin
Competitive adsorption and cation exchange are critical processes for the reversible and irreversible interactions of heavy metals with environmental media.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 586-596
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00372A
The INGENIOUS project: towards understanding air pollution in homes
This paper provides an overview of the INGENIOUS (UnderstandING the sourcEs, traNsformations and fates of IndOor air pollUtantS) project, aiming to better understand air pollution in homes.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 355-372
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00634H
Dissolved phosphorous through dry–wet–dry transitions in a small-dammed river basin: integrated understanding on transport patterns, export controls, and fate
The connections between terrestrial DP sources and aquatic DP sinks were comprehended in a small-dammed watershed through an integrated understanding of DP transport patterns, export controls, and their fate over dry–wet–dry transitions.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 373-389
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00686K
Chemical characterization of polymer and chloride content in waste plastic materials using pyrolysis – direct analysis in real time – high-resolution mass spectrometry
This study presents an application of TPD-DART-HRMS for plastic, enabling rapid characterization of waste through Kendrick grouping and Tanimoto comparison.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 104-118
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00501E
Associations of coke oven emission exposure with pulmonary function, blood pressure, blood cell parameters, and biochemical indices in coking workers: a cross-sectional pilot study
The study clearly showed that PAH exposure could damage hematological parameters and blood lipids, and benzene exposure could increase blood pressure, and decrease PLT count.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2025,27, 91-103
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00306C
Fluorinated aromatic PBCTF and 6:2 diPAP in bridge and traffic paints
This study takes a multifaceted approach toward characterizing total fluorine and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in traffic and bridge paints.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2158-2165
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00546E
Mobile monitoring reveals the importance of non-vehicular particulate matter sources in London
A novel application of mobile monitoring to investigate the spatial distribution of vehicular and non-vehicular urban particulate matter sources in London, UK.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2145-2157
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00552J
Associations of indoor airborne microbiome with lung function: evidence from a randomized, double-blind, crossover study of microbial intervention
Indoor airborne microbiome contributes to human lung function and can be modified by air purification.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2020-2035
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00392F
Physicochemical properties and their impact on ice nucleation efficiency of respiratory viral RNA and proteins
Ice nucleation processes in the earth's atmosphere are critical for cloud formation, radiation, precipitation, and climate change.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2010-2019
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00411F
Improved prediction of PFAS partitioning with PPLFERs and QSPRs
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are chemicals of high concern and are undergoing hazard and risk assessment worldwide.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1986-1998
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00485J
Formation of atmospheric molecular clusters containing nitric acid with ammonia, methylamine, and dimethylamine
This study investigates the formation of atmospheric molecular clusters containing ammonia (NH3, A), methylamine (CH3NH2, MA), or dimethylamine (CH3NHCH3, DMA) with nitric acid (HNO3, NA) using quantum mechanics.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 2036-2050
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00330F
Modeling of mercury deposition in India: evaluating emission inventories and anthropogenic impacts
Fragile ecosystems (Western Ghats and Himalayas), and major rice cultivation areas are vulnerable to highest Hg deposition. Indian anthropogenic emissions strongly influence deposition fluxes with varying regional impacts.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1999-2009
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00324A
A 150 years record of polycyclic aromatic compounds in the Sihailongwan Maar Lake, Northeast China: impacts of socio-economic developments and pollution control
The geochemical composition of sediment cores can serve as a proxy for reconstructing past human and nature-driven environmental and climatic changes.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1748-1759
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00309H
Emerging investigator series: in-depth chemical profiling of tire and artificial turf crumb rubber: aging, transformation products, and transport pathways
Chemical profiling of artificial turf crumb rubber reveals time-based trends in transformation products and transport pathways.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1703-1715
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00326H
Identifying initial transformation products during chlorination of the indole moiety and unveiling their formation mechanisms
Initial transformation products and their formation mechanisms in the chlorination of the indole moiety in tryptophan (Trp) are investigated using a quantum chemical computational method.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1629-1640
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00196F
Photodegradation of the main synthetic musk (HHCB) in water: kinetic study and influencing factors
Galaxolide (HHCB) is the most common synthetic musk compound detected in numerous daily products.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1571-1587
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00351A
Emerging investigator series: nontargeted screening of aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists in endangered beluga whales from the St. Lawrence Estuary: beyond legacy contaminants
Higher AhR activity measured in endangered SLE belugas compared to Arctic belugas was attributed to their exposure to polar contaminants.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1451-1464
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00243A
Development of a sampling protocol for collecting leaf surface material for multiphase chemistry studies
We describe a robust and flexible protocol to collect water-soluble chemicals from leaf surfaces for atmosphere-biosphere interaction studies.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1008-1021
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00065J
Potential effects of soil petroleum contamination on decomposition of Artemisia annua plant litter
Artemisia annua litter produced in soil contaminated with 15 and 30 g kg−1 of petroleum exhibited significantly lower decomposition rates than that from uncontaminated soil.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 1022-1030
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00096J
An uneven distribution of strontium in the coccolithophore Scyphosphaera apsteinii revealed by nanoscale X-ray fluorescence tomography
Coccolithophores are biogeochemically and ecologically important phytoplankton that produce calcium carbonate scales, or coccoliths. Here, we show that one species of coccolithophore grows coccoliths with uneven distribution of Sr, in contrast to current fractionation model theory.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 966-974
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00509G
Co-culture of benzalkonium chloride promotes the biofilm formation and decreases the antibiotic susceptibility of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain
The physiological and biochemical behaviors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa were modulated using benzalkonium chloride, potentially through the attenuation of the quorum sensing system.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 858-869
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00035H
Characteristics and adsorption behavior of typical microplastics in long-term accelerated weathering simulation
Adsorption of different organic pollutants by three microplastics before and after weathering.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 882-890
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00062E
The first report on the assessment of maximum acceptable daily intake (MADI) of pesticides for humans using intelligent consensus predictions
Direct or indirect consumption of pesticides and their related products by humans and other living organisms without safe dosing may pose a health risk.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 870-881
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00059E
Co-exposure to tire wear particles and nickel inhibits mung bean yield by reducing nutrient uptake
Tire wear particles and nickel have detrimental effects on plant health by causing blockage and altering nutrient hemotasis, ultimately reducing plant yield.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 832-842
https://doi.org/10.1039/D4EM00070F
Experimental factors influencing the bioaccessibility and the oxidative potential of transition metals from welding fumes
Experimental conditions such as extraction methods and storage conditions induce biases on the measurement of the oxidative potential and the bioaccessibility of transition metals from welding fumes.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 843-857
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00546A
Experimental determination of the partitioning of representative organic pollutants to the air–water interface
Glancing-angle laser-induced fluorescence is used to obtain adsorption isotherms of organic pollutants at the air–water interface.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 510-518
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00394A
Speeding it up: dual effects of biostimulants and iron on the biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) at mesophilic conditions
Biodegradation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) in compost environment enriched with iron, and gelatin significantly enhanced microbial enzymatic activity, thus accelerating PLA degradation at mesophilic conditions (home/backyard composting setting).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 530-539
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00534H
Atmospheric mercury uptake and accumulation in forests dependent on climatic factors
The uptake of total gaseous mercury (TGM) by Korean forest foliage is mainly affected by local wind speed, boosting its passage and absorption. Mercury levels and isotopic signatures in litter and topsoil fluctuate, particularly in areas with high wind speed, temperature, and low elevation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 519-529
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00454F
Characterization and dermal bioaccessibility of residual- and listed PFAS ingredients in cosmetic products
Estimation of dermal bioaccessibility and characterization of listed-ingredient and residual per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in cosmetic products.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 259-268
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00461A
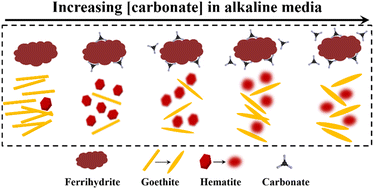
Effects of carbonate on ferrihydrite transformation in alkaline media
This study indicates that in alkaline media, carbonate slightly inhibits ferrihydrite transformation and suppresses goethite formation, but promotes hematite formation, which has important implications for elemental biogeochemical cycles.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 288-297
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00469D
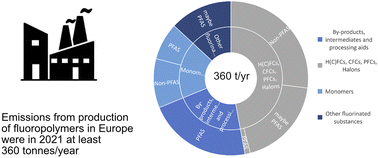
Emission inventory of PFASs and other fluorinated organic substances for the fluoropolymer production industry in Europe
This study assesses the environmental impact of the fluoropolymer industry in Europe by making an inventory of their emissions of PFASs and other fluorinated organic substances.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 269-287
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00426K
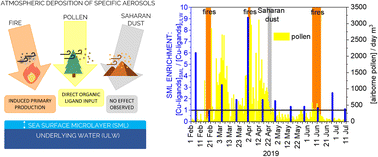
How do certain atmospheric aerosols affect Cu-binding organic ligands in the oligotrophic coastal sea surface microlayer?
We showed that oligotrophic coastal marine areas are susceptible to the deposition of pollen and aerosols from open-fire biomass burning, which alter Cu-binding organic ligands in the sea surface microlayer.
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 119-135
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00415E
Identification and quantification of fluorinated polymers in consumer products by combustion ion chromatography and pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Using the combination of total analysis and pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to identify fluoropolymers in a broad range of consumer products.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 82-93
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00438D
Understanding the importance of atmospheric transformation in assessing the hazards of liquid crystal monomers
The results suggest that atmospheric transformation can significantly change the hazard properties of LCMs, emphasizing the importance of atmospheric transformation when evaluating the hazards of LCMs.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 94-104
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00424D
Temperature and particles interact to affect human norovirus and MS2 persistence in surface water
To our knowledge, this study is the first to assess the effects of surface water particle content on human norovirus decay rate constants, which will be useful parameters in fate and transport models.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 71-81
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00357D
Predictive binary mixture toxicity modeling of fluoroquinolones (FQs) and the projection of toxicity of hypothetical binary FQ mixtures: a combination of 2D-QSAR and machine-learning approaches
We have developed conventional and machine learning-based mixture QSAR models from the toxicity data of the binary mixtures of fluoroquinolones in E. coli.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2024,26, 105-118
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00445G
Contact with soil impacts ferrihydrite and lepidocrocite transformations during redox cycling in a paddy soil
We studied the transformation of 57Fe-labelled ferrihydrite and lepidocrocite mixed with a flooded paddy soil by using 57Fe-Mössbauer spectroscopy.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1945-1961
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00314K
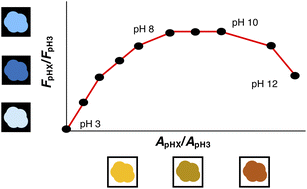
Evaluating the pH-dependence of DOM absorbance, fluorescence, and photochemical production of singlet oxygen
The protonation state of dissolved organic matter (DOM) impacts its structure and function in natural and engineered environmental systems, including DOM's ability to absorb light and form photochemically produced reactive intermediates (PPRI).
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1974-1985
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00316G
Antioxidant N-acetylcysteine removing ROS: an antifouling strategy inspired by mussels
Inspired by the adhesion characteristics of mussels, this paper proposed an antifouling strategy of using antioxidants to remove ROS.
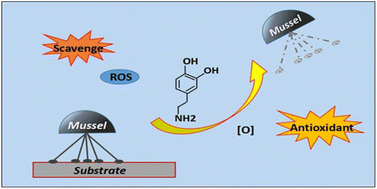
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1962-1973
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00191A
Adding open spectral data to MassBank and PubChem using open source tools to support non-targeted exposomics of mixtures
Adding mass spectra from complex mixtures of chemicals relevant for exposomics to open spectral libraries such as MassBank and chemical databases like PubChem empowers identification efforts for non-target high resolution mass spectrometry workflows.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1788-1801
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00181D
Mixture effect assessment applying in vitro bioassays to in-tissue silicone extracts of traditional foods prepared from beluga whale blubber
Mixtures extracted from beluga traditional food preparations activated oxidative stress response and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor but did not show any hormone-like effects.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1759-1770
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00076A
Autoxidation of glycols used in inhalable daily products: implications for the use of artificial fogs and e-cigarettes
The use of glycols is seen in various industries and occupations.
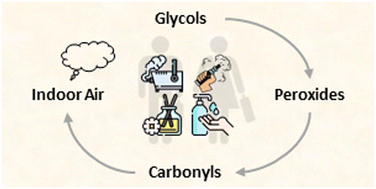
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1657-1669
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00214D
Kinetics of hypochlorous acid reactions with organic and chloride-containing tropospheric aerosol
This study describes laboratory experiments on the reaction HOCl with chloride-containing aerosol and aerosol containing selected organic compounds with and without chloride.
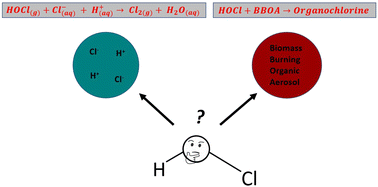
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1645-1656
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00292F
Read-across-based intelligent learning: development of a global q-RASAR model for the efficient quantitative predictions of skin sensitization potential of diverse organic chemicals
This computational work presents a novel similarity-based q-RASAR approach for the development of a global model that can quantitatively and efficiently identify the skin sensitization potential of hazardous chemicals.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1626-1644
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00322A
Formation of oil-particle aggregates in the presence of marine algae
After an oil spill, the formation of oil-particle aggregates (OPAs) is associated with the interaction between dispersed oil and marine particulate matter such as phytoplankton, bacteria and mineral particles.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1438-1448
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00092C
Non-extractable PFAS in functional textiles – characterization by complementary methods: oxidation, hydrolysis, and fluorine sum parameters
Oxidative methods (TOP and PhotoTOP) were combined with hydrolysis (THP assay) and fluorine sum parameters (EOF and TF) to characterize side-chain fluorinated polymers (SFPs) in functional textiles.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1298-1310
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00131H
Monitoring microplastic–contaminant sorption processes in real-time using membrane introduction mass spectrometry
The rate and extent of sorption of trace contaminants to microplastics was monitored in real-time using direct mass spectrometry.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1169-1180
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00083D
Wildfires in the western United States are mobilizing PM2.5-associated nutrients and may be contributing to downwind cyanobacteria blooms
Wildfire activity is increasing in the continental U.S. and can be linked to climate change effects and nutrient emissions, with potential effects on downwind ecosystems.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1049-1066
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00042G
The fate of organic peroxides indoors: quantifying humidity-dependent uptake on naturally soiled indoor window glass
The effect of humidity on organic hydroperoxide (ROOH) removal from air to real indoor surface films was investigated. A novel flow reactor for studying uptake kinetics of indoor pollutants on indoor materials is introduced.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 1031-1048
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00041A
Biogeochemical and hydrologic synergy control mercury fate in an arid land river-reservoir system
Methylmercury formed in anoxic reservoirs associates with organic-rich particles and is exported downstream.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 912-928
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00032J
Chemical characteristics, leaching, and stability of the ubiquitous tire rubber-derived toxicant 6PPD-quinone
We here report chemical characteristics relevant to the fate and transport of the recently discovered environmental toxicant 6PPD-quinone (2-((4-methylpentan-2-yl)amino)-5-(phenylamino)cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione or “6PPDQ”).
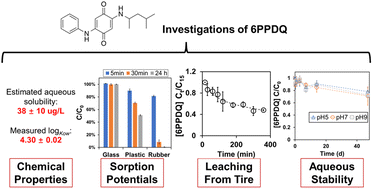
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 901-911
https://doi.org/10.1039/D3EM00047H
An amended in vitro–in vivo extrapolation model that accounts for first pass clearance effects on chemical bioaccumulation in fish
An amended in vitro–in vivo extrapolation model that accounts for first pass clearance effects on chemical bioaccumulation in fish. Pre-systemic biotransformation can significantly reduce chemical oral bioavailability, which can reduce dietary chemical bioaccumulation potential.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 741-754
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00522K
Emerging investigator series: an instrument to measure and speciate the total reactive nitrogen budget indoors: description and field measurements
A robust and quantitative instrument that measures total gas-phase reactive nitrogen (tNr) has been developed for indoor air quality surveys. It can focus on NOx, HONO, and NH3 levels indoors, from the complete tNr budget, on timescales of 5–20 min.
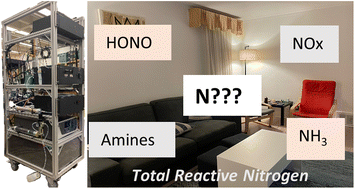
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 389-404
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00446A
Kinetics of the nitrate-mediated photooxidation of monocarboxylic acids in the aqueous phase
This work highlights how the pH of the atmospheric aqueous phase can influence the degradation of carboxylic acids during nitrate-mediated photooxidation.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 461-471
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00458E
Crystal lattice defects in nanocrystalline metacinnabar in contaminated streambank soils suggest a role for biogenic sulfides in the formation of mercury sulfide phases
At mercury (Hg)-contaminated sites, streambank erosion can act as a main mobilizer of Hg into nearby waterbodies.
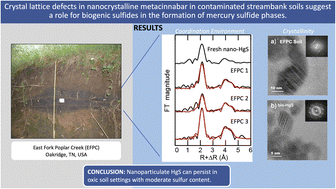
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 445-460
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00549A
Photochemical weathering of polyurethane microplastics produced complex and dynamic mixtures of dissolved organic chemicals
Sunlight exposure can naturally mitigate microplastics pollution in the surface ocean, however it results in emissions of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) whose characteristics and fate remain largely unknown.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 432-444
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00415A
Effect of geochemical conditions on PFAS release from AFFF-impacted saturated soil columns
Certain PFAS, such as 4:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate, eluted faster from high pH, high sodium columns compared to neutral columns packed with field-collected soil. Other PFAS had more mass eluted from the high pH, high sodium columns.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 405-414
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00367H
Influence of microbial weathering on the partitioning of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in biosolids
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a large group of man-made fluorinated organic chemicals that can accumulate in the environment.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2023,25, 415-431
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2EM00350C
Groundwaters in Northeastern Pennsylvania near intense hydraulic fracturing activities exhibit few organic chemical impacts
Hydrogeologic transport contributes to limited organic chemical contamination in a region of intense gas extraction, even 10 years post-development.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 252-264
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00124H
Investigation of perfluoroalkyl substances in proglacial rivers and permafrost seep in a high Arctic watershed
We measured perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in proglacial rivers and along a non-glacial freshwater continuum to investigate the role of snow and ice melting in their transport and fate within the Lake Hazen watershed (82° N).

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 42-51
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00349F
Aerobic biotransformation of a novel highly functionalized polyfluoroether-based surfactant using activated sludge from a wastewater treatment plant
We incubated a novel fluorosurfactant with wastewater treatment plant sludge and identified smaller PFAS biotransformation products with lower bioaccumulation potential compared to the starting material.

Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2022,24, 62-71
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EM00358E
About this collection
Here is a collection of recent Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts articles which have been classified as ‘HOT articles’ due to receiving particularly high scores at peer review.