Themed collection Polymeric biomaterials for cancer nanotechnology

Polymeric biomaterials for cancer nanotechnology
Jianjun Cheng and Suzie H. Pun introduce this themed issue of Biomaterials Science on polymeric biomaterials for cancer nanotechnology
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 891-893
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM90025E
Engineering DNA scaffolds for delivery of anticancer therapeutics
DNA scaffolds with programmability in size, shape and surface chemistry have been engineered for the delivery of various anticancer therapeutics.
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1018-1024
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00459K
Cyclodextrin-functionalized polymers as drug carriers for cancer therapy
This mini-review highlights the recent progress in cyclodextrin-functionalized polymers as drug carriers for cancer therapy.
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1050-1060
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00417E
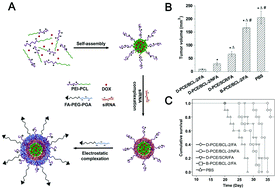
Drug and gene co-delivery systems for cancer treatment
Nano-delivery system has been widely studied and applied in cancer treatment over the past few decades. By taking advantage of both the drug and gene therapy, a growing number of co-delivery systems have been explored for cancer treatment recently.
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1035-1049
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00369A
Recent advances in targeted drug delivery approaches using dendritic polymers
Synthesis of dendrimers and their modified nanoparticles.
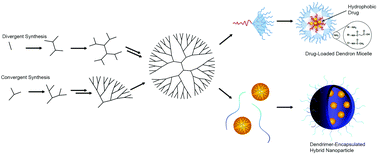
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1025-1034
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00351A
Polymeric biomaterials for the delivery of platinum-based anticancer drugs
This review discusses the recent research trends in the polymeric delivery systems for platinum-based anticancer drugs.
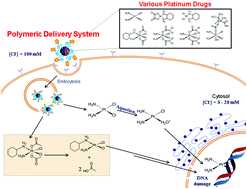
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1002-1017
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00039D
Emerging antitumor applications of extracellularly reengineered polymeric nanocarriers
The review gives a comprehensive summary and preliminary forecast of the extracellularly stimuli-mediated shell-sheddable polymeric nanocarriers for antitumor applications.
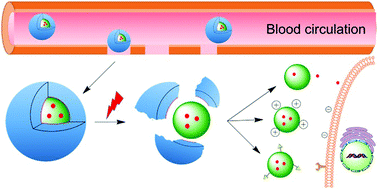
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 988-1001
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00044K
Shape control in engineering of polymeric nanoparticles for therapeutic delivery
This review discusses methods for generating polymer nanoparticles with controlled shapes and identifies key effects of shape in biological systems.
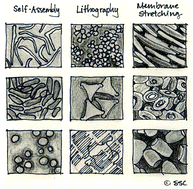
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 894-907
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00006H
Trigger responsive polymeric nanocarriers for cancer therapy
Strategies for the development of polymeric nanocarriers responsive to different internal and external triggers modulating the drug release in a tumor environment, are reviewed.
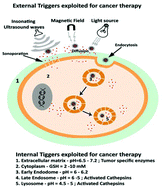
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 955-987
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00002E
Supramolecular hydrogels: synthesis, properties and their biomedical applications
The recent progress in synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of supramolecular hydrogels has been reviewed.
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 937-954
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00448E
Lipid-coated polymeric nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery
This review discusses the recent advancements and future directions in the application of lipid-coated polymeric nanoparticles for cancer drug delivery.
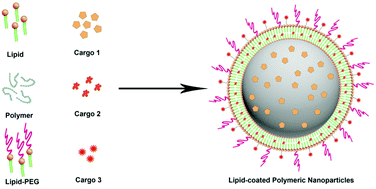
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 923-936
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00427B
Drug-free macromolecular therapeutics – a new paradigm in polymeric nanomedicines
This review highlights an exciting new field of polymeric nanomedicine research – drug-free macromolecular therapeutics for cell apoptosis induction.
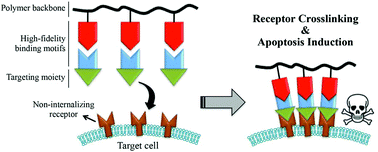
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 908-922
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00442F
Redox-responsive self-assembled chain-shattering polymeric therapeutics
A trigger responsive polymeric therapeutics with defined composition, controlled formulation and release profile, and excellent therapeutic response.
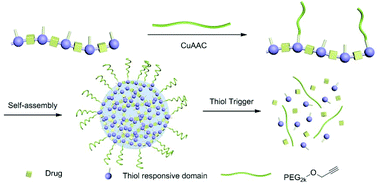
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1061-1065
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00452C
Near-infrared light-triggered drug release nanogels for combined photothermal-chemotherapy of cancer
Near-infrared (NIR) light-triggered drug release polymeric nanogels were fabricated based on host–guest interaction and were explored to encapsulate indocyanine green (ICG) and doxorubicin (DOX) for combined photothermal-chemotherapy of cancer.
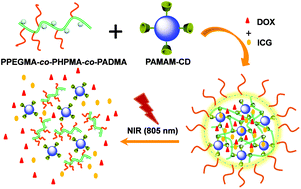
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1147-1156
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00048C
Reductively degradable α-amino acid-based poly(ester amide)-graft-galactose copolymers: facile synthesis, self-assembly, and hepatoma-targeting doxorubicin delivery
Multifunctional nanoparticles mediate specific and efficient intracellular doxorubicin delivery to asialoglycoprotein receptor-overexpressing hepatoma cells.
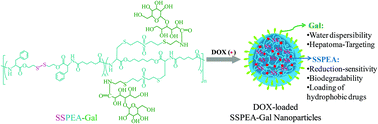
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1134-1146
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00436A
Mixing-sequence-dependent nucleic acid complexation and gene transfer efficiency by polyethylenimine
Determining roles of the mixing sequence in nucleic acid/cationic polymer polyplex preparation are reported with experimental characterization and a theoretical model.
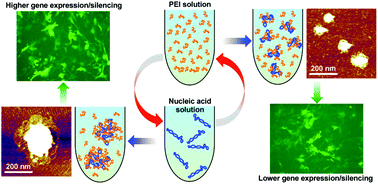
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1124-1133
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00041F
Balancing polymer hydrophobicity for ligand presentation and siRNA delivery in dual function CXCR4 inhibiting polyplexes
Dual-function polycations capable of simultaneously antagonizing CXCR4 receptors and delivering anti-PLK1 siRNA to achieve combination anticancer effect.
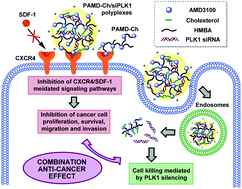
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1114-1123
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00003C
A block copolymer of zwitterionic polyphosphoester and polylactic acid for drug delivery
Zwitterionic polyphosphoester containing polymers are synthesized and evaluated as an alternative to poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymers for anticancer drug delivery.
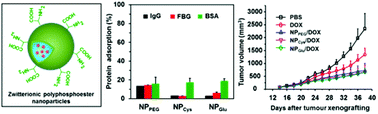
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1105-1113
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00430B
Enhanced tumor-targeted gene delivery by bioreducible polyethylenimine tethering EGFR divalent ligands
This work demonstrates successful delivery of a gene to EGFR-overexpressed cancer cells by using a rationally designed branched GE11 peptide as a targeting ligand.
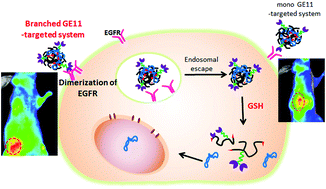
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1096-1104
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5BM00004A
Well-defined diblock brush polymer–drug conjugates for sustained delivery of paclitaxel
The synthesis, characterization and property studies of paclitaxel (PTXL)-containing brush polymer–drug conjugates (BPDCs) are presented and the influence of grafting structures of BPDCs on their assembly behaviour, drug release profile and therapeutic effects is discussed in this article.
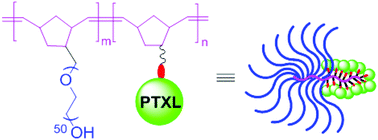
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1078-1084
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00458B
Polymeric assembly of hyperbranched building blocks to establish tunable nanoplatforms for lysosome acidity-responsive gene/drug co-delivery
A pH-reversible polymeric assembly approach was developed to build tunable nanoplatforms, based on the boronate-linked assembly between hyperbranched building blocks.
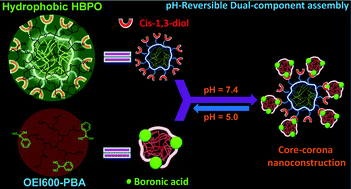
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1066-1077
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00382A
Enhanced transcellular penetration and drug delivery by crosslinked polymeric micelles into pancreatic multicellular tumor spheroids
The penetration of HPMA-based micelles into multicellular tumor spheroids depends on transcellular transport from peripheral to inner cells. Stabilisation by crosslinking facilitated the penetration.
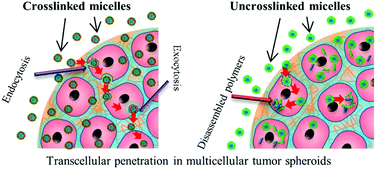
Biomater. Sci., 2015,3, 1085-1095
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4BM00323C
About this collection
This themed issue on polymeric biomaterials for cancer nanotechnology is Guest Edited by Jianjun Cheng (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA) and Suzie Pun (University of Washington, USA).
Polymeric biomaterials have been extensively used in nanomedicine formulations for cancer therapy. Preclinical and clinical studies have in general revealed that polymeric nanocarriers, when used for chemotherapeutic drug delivery, reduce systemic toxicity and thus mitigate adverse side effects of the drug. In order to continue and even improve on the clinical progress of polymeric anticancer drug formulations, new innovations and discoveries are being made in the following areas: (i) expanding the available suite of polymeric biomaterials that can be reproducibly and controllably manufactured at a suitable scale, (ii) designing carriers with improved biodistribution to tumor sites, (iii) increasing tumor distribution and penetration of polymeric nanocarriers, and (iv) controlling efficient drug release at a desired location and with optimal kinetics. This themed issue contains reviews and research articles in each of these areas. In addition, new advances in polymeric nanobiomaterials for both small molecule chemotherapeutics and anticancer nucleic acids are included.