Direct characterization of graphene doping state by in situ photoemission spectroscopy with Ar gas cluster ion beam sputtering†
Abstract
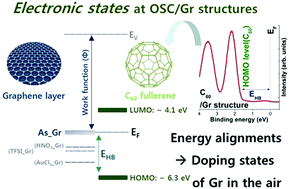
On the basis of an in situ photoemission spectroscopy (PES) system, we propose a novel, direct diagnosis method for the characterization of graphene (Gr) doping states at organic semiconductor (OSC)/electrode interfaces. Our in situ PES system enables ultraviolet/X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS/XPS) measurements during the OSC growth or removal process. We directly deposit C60 films on three different p-type dopants—gold chloride (AuCl3), (trifluoromethyl-sulfonyl)imide (TFSI), and nitric acid (HNO3). We periodically characterize the chemical/electronic state changes of the C60/Gr structures during their aging processes under ambient conditions. Depositing the OSC on the p-type doped Gr also prevents severe degradation of the electrical properties, with almost negligible transition over one month, while the p-type doped Gr without an OSC changes a lot following one month of aging. Our results indicate that the chemical/electronic structures of the Gr layer are completely reflected in the energy level alignments at the C60/Gr interfaces. Therefore, we strongly believe that the variation of energy level alignments at the OSC/graphene interface is a key standard for determining the doping state of graphene after a certain period of aging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...