Micellar nanoformulation of lipophilized bortezomib: high drug loading, improved tolerability and targeted treatment of triple negative breast cancer†
Abstract
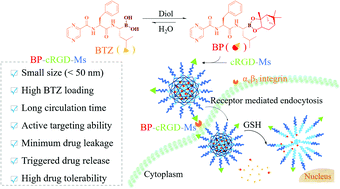
Bortezomib (BTZ) is the first proteasome inhibitor approved for the treatment of malignant tumors. The current clinical formulation, however, shows fast clearance, low tumor accumulation, and several side effects. Here, we report that micellar nanoformulation of lipophilized bortezomib achieves significantly enhanced drug loading, prolonged circulation time, improved tolerability and targeted treatment of triple negative breast cancer in vivo. Lipophilized bortezomib, bortezomib-pinanediol (BP), was readily prepared in high yield. Interestingly, cRGD-targeted micelles based on poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-dithiolane trimethylene carbonate) achieved a high drug loading content of 8.05 wt% BTZ equiv. for BP, which was more than 8-fold higher than BTZ. BP-loaded cRGD-decorated micelles (BP-cRGD-Ms) exhibited a small size (ca. 49 nm), reduction-triggered drug release, and active targeting ability to αvβ3-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells, resulting in a low IC50 of 0.986 μM. The in vivo studies displayed that BP-cRGD-Ms had a nearly 20-fold improvement in the elimination half-life and a 20-fold higher maximum-tolerated dose as compared to free BTZ. The biodistribution and therapeutic studies in MDA-MB-231 tumor-bearing nude mice demonstrated that BP-cRGD-Ms induced significantly better tumor accumulation and inhibition with fewer adverse effects than free BTZ, leading to greatly improved mice survival rates. This micellar nanoformulation of lipophilized bortezomib appears to be a novel and effective strategy to achieve targeted tumor chemotherapy with bortezomib.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...