Composition dependent reactivity of titanium oxide clusters
Abstract
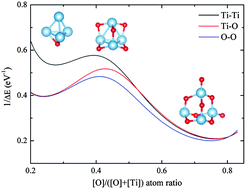
Based on first-principles calculations of titanium oxide clusters, TinOm (n = 1–4), we reveal the composition dependent reactivity of titanium oxide clusters. Our interesting results include: (1) the reactivity depends on the ratio of O atoms in the clusters, with smaller O ratios associated with higher reactivity; (2) among the different titanium oxide species investigated, the most stable structures are TinO2n, but their reactivities are relatively lower than the clusters with a smaller O atom ratio; moreover, (3) when the O atom ratio is small, the reactivity required to form the Ti–Ti bond is larger than either the Ti–O or O–O bond between two interacting titanium oxide clusters. These results will be useful for designing efficient titanium oxide catalysts, or photocatalysts, in particular, for energy and environmental applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...