On the electrochemical origin of the enhanced charge acceptance of the lead–carbon electrode†
Abstract
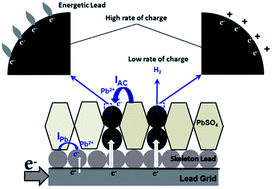
Bi-functional electrode materials, composed of capacitive activated carbon (AC) and battery electrode materials, possess higher power performance than traditional battery electrode materials. Negative electrodes of lead acid batteries with AC additives (i.e., lead–carbon electrodes) display much better charge acceptance than do traditional lead negative electrodes, and are suitable for energy storage in hybrid electrical vehicles. In this paper, we discuss the electrochemical processes on AC in lead–carbon electrodes. In the charging process of the lead–carbon electrode, lead electrodeposits on AC at potentials higher than the open circuit potential of lead, and the large surface area of AC provides extra active sites for lead electrodeposition and the growth of the electrochemical active surface area of lead. Namely, AC acts as an electron bumper and electron distributor in the charging process of the lead–carbon electrode. Most importantly, at high charge rates, the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) on AC is prohibited by reversible hydrogen adsorption; and meanwhile the adsorbed hydrogen contributes to the charging process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...