Reconfigurable microfluidic systems with reversible seals compatible with 2D and 3D surfaces of arbitrary chemical composition†
Abstract
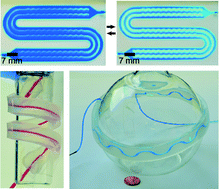
Microfluidic channels are typically fabricated in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) using soft lithography and sealed against a support substrate using various irreversible/reversible techniques—the most widely used method is the irreversible bonding of PDMS to glass using oxygen plasma. These techniques are limited in their ability to seal channels against rough, uneven, and/or three-dimensional substrates. This manuscript describes the design and fabrication of soft microfluidic systems from combinations of silicone elastomers that can be reversibly sealed against an array of materials of various topographies/geometries using compression. These soft systems have channels with cross-sectional dimensions that can be decreased, reversibly, by hundreds of microns using compressive stress, and the ability to interface with virtually any support substrate. These capabilities go beyond that achievable with devices fabricated in PDMS alone and enable the integration of microfluidic functionality directly with rough and/or 3D surfaces, providing new opportunities in solution processing useful to, for example, materials science and the analytical/forensic sciences.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...