Light emitting diodes based on carbon dots derived from food, beverage, and combustion wastes
Abstract
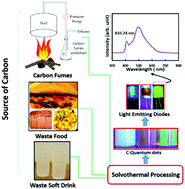
One important resource for material synthesis is waste. Utilization of waste as a resource for material synthesis is an environmentally responsible approach that reduces the need for virgin resources and subsequent processing. In this report a method to produce multicolored, luminescent carbon dots (CDs) and subsequent fabrication of light emitting diodes from food, beverage, and combustion wastes, is discussed. Apart from food and beverages, combustion exhaust was also utilized for CDs production. Optical characterization results suggest that CDs from waste food and beverages are more luminescent than those produced from combustion waste.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...