A high-throughput photodynamic therapy screening platform with on-chip control of multiple microenvironmental factors†
Abstract
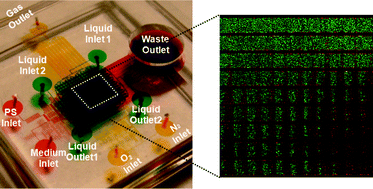
We present a novel high-throughput microfluidic platform that enables the evaluation of the anticancer efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT) drugs over multiple microenvironmental factors. PDT is uniquely complex, originating from its dependence on three separate but essential elements: drug (also called photosensitizer), oxygen, and light. Thus, obtaining a reliable evaluation of PDT efficacy is highly challenging, requiring considerable effort and time to evaluate all three interdependent parameters. In this paper, we report a high-throughput efficacy screening platform that we implemented by developing microfluidic components that individually control basic PDT elements (photosensitizer concentrations, oxygen levels, and light fluence) and then integrating them into a single triple-layer device. The integrated microfluidic chip consists of an array of small compartments, each corresponding to a specific combination of these three variables. This allows for more than 1000 different conditions being tested in parallel. Cancer cells are cultured within the device, exposed to different PDT conditions, and then monitored for their viability using live/dead fluorescence staining. The entire screening assay takes only 1 hour, and the collected PDT outcomes (cell viability) for combinatorial screening are analysed and reported as traditional dose–response curves or 3D bubble charts using custom software. As a proof of concept, methylene blue is adopted as a photosensitizer and its drug efficacy on C6 glioma cells has been successfully evaluated for a total of 324 PDT conditions using the fabricated chip. This platform can facilitate not only the development of new photosensitizers but also the optimization of current PDT protocols.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...