Influence of an amine group on the highly efficient reversible adsorption of iodine in two novel isoreticular interpenetrated pillared-layer microporous metal–organic frameworks†
Abstract
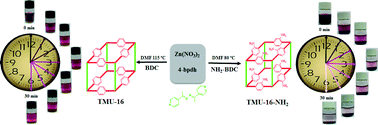
Two isoreticular microporous Zn(II)-MOFs were constructed using a bipyridyl-type linker mixed into two homologous ligands, 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate, [Zn2(BDC)2(4-bpdh)]·3DMF (TMU-16) and amino-1,4-benzenedicarboxylate, [Zn2(NH2-BDC)2(4-bpdh)]·3DMF (TMU-16-NH2). Both unmodified and amino functionalized MOFs can serve as a host for encapsulating I2. In particular, the amino functionalized MOF can find more applications for the encapsulation of iodine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...