Preparation of alumina-supported intermetallic compounds†
Abstract
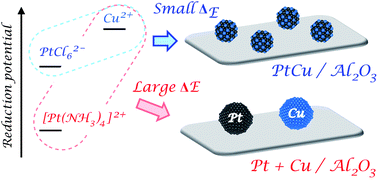
A series of alumina-supported intermetallic compounds, Pt3Co/Al2O3, PtCu/Al2O3, Pt3Sn/Al2O3 and Pd3Pb/Al2O3, being promising materials as catalysts, were prepared by reduction of two metal precursors co-impregnated on γ-Al2O3. As a Pt precursor, [Pt(NH3)4]2+ or PtCl62− was used coupled with the second metal precursors. Two different reduction procedures, gaseous H2 and LiBH4 in liquid phase, were also employed and compared. Using PtCl62− which possesses a more negative reduction potential than [Pt(NH3)4]2+ strongly enhanced formation of the desired Pt-based intermetallic nanoparticles regardless of the reduction procedure. A similar trend was observed in preparation of Pd3Pb/Al2O3 with PdCl42− compared to Pd2+. A strong reduction agent LiBH4 gave higher contents of the corresponding intermetallic phases than H2 in all cases. Single-phase intermetallic compounds supported on alumina were synthesized by employing the chloro-complexes and LiBH4 reduction. A systematic investigation indicates that the degree of intermetallic formation intrinsically depends on the difference in reduction potentials (ΔE) of the two metal precursors. Bimetallic combinations with small ΔE such as PdCl42−/Bi3+, Co2+/SnCl62− and Ni2+/SnCl62− also allow syntheses of PdBi/Al2O3, Co3Sn2/Al2O3, Ni3Sn/Al2O3 and Ni3Sn2/Al2O3 by H2 reduction, respectively. An appropriate choice of the metal precursor to reduce ΔE is an effective strategy to synthesize an alumina-supported intermetallic compound.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...