Synthesis of an amine-functionalized naphthalene-containing conducting polymer as a matrix for biomolecule immobilization
Abstract
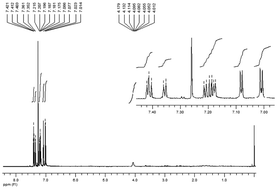
N-functionalized dithienopyrroles (DTP-NH2) were synthesized and electropolymerized onto a graphite electrode as a novel conducting polymer matrix for biomolecule immobilization. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR were utilized to investigate the characteristics of the monomer. After that, glucose oxidase (GOx) was immobilized onto the amino-functionalised matrix by means of glutaraldehyde. The surface morphologies of both DTP-NH2 and DTP-NH2–GOx were visualised by using SEM and fluorescence microscopy. The chronoamperometric signals of the electrochemical DTP-NH2–GOx biosensors were measured by monitoring the O2 consumption during an enzymatic reaction in the presence of glucose at −0.7 V. After the optimization of the pH and scan number of the polymer deposition in batch mode, the DTP-NH2–GOx biosensor was also tested in Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) mode. The DTP-NH2–GOx biosensors had a very good linearity between 0.05 and 1.0 mM, and between 0.1 and 2.5 mM for glucose in batch and FIA modes, respectively. Finally, it was applied for glucose analysis in real samples where commercial glucose kits were used as the reference method to verify the data obtained with the proposed biosensor.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...