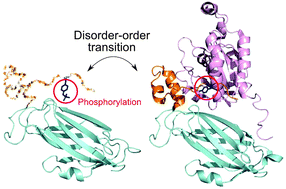
Phosphorylation offers a dynamic way to regulate protein activity, subcellular localization, and stability. The majority of signaling pathways involve an extensive set of protein–protein interactions, and phosphorylation is widely used to regulate protein–protein binding by affecting the stability, kinetics and specificity of interactions. Previously it was found that phosphorylation sites tend to be located on protein–protein binding interfaces and may orthosterically modulate the strength of interactions. Here we studied the effect of phosphorylation on protein binding in relation to intrinsic disorder for different types of human protein complexes with known structure of the binding interface. Our results suggest that the processes of phosphorylation, binding and disorder–order transitions are coupled to each other, with about one quarter of all disordered interface Ser/Thr/Tyr sites being phosphorylated. Namely, residue site disorder and interfacial states significantly affect the phosphorylation of serine and to a lesser extent of threonine. Tyrosine phosphorylation might not be directly associated with binding through disorder, and is often observed in ordered interface regions which are not predicted to be disordered in the unbound state. We analyze possible mechanisms of how phosphorylation might regulate protein–protein binding via intrinsic disorder, and specifically focus on how phosphorylation could prevent disorder–order transitions upon binding.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...