Resistive switching memory: observations with scanning probe microscopy
Abstract
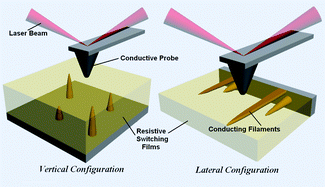
Recent advances in information technology require higher-speed and higher-density memory devices. In the past decade, resistance switching memory has emerged as a powerful alternative to existing charge-storage-based, non-volatile devices. Despite the extensive research, much of the underlying switching/conduction mechanism is still unknown and controversial. The versatile capability of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...