Computer-guided design of a Cu(ii) receptor and sensor
Abstract
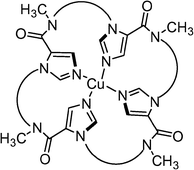
The computer program CAVEAT was used to design a linker structure to connect four imidazole 4-carboxamide groups in a distorted square planar arrangement optimal for binding Cu(II) ions. The resulting macrocyclic structure was prepared by the synthesis of a protected monomer followed by

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...