Engineering of carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane nanocomposites with enhanced sensitivity for wearable motion sensors†
Abstract
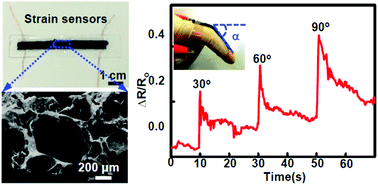
Nanocomposite based wearable strain sensors hold promise for a variety of applications from human body motion detection to soft robotics. However, improving the sensitivity of strain sensors while keeping their stretchability (i.e., strain detection range) is still a grand challenge in this area. In this research, a highly efficient and scalable method was developed to enhance the sensitivity of a strain sensor based on carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane (CNT/PDMS) nanocomposites. Through the introduction of porosity into the nanocomposites to form CNT/PDMS sponges using citric acid monohydrate particles, the sensitivity (GF = 15, strain (ε) > 15%; GF = 1.1, ε < 15%) is improved compared to the CNT/PDMS nanocomposites without a porous structure (GF = 3.2, ε > 10%; GF = 0.12, ε < 10%). The strain sensor based on the CNT/PDMS sponge not only shows the capability of monitoring human body motion, such as bending of a finger and elbow, speaking, drinking, and breathing, but also demonstrates potential applications in soft robotics, such as detection of the actuation of a dielectric elastomer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...