Dissection of the neocarazostatin: a C4 alkyl side chain biosynthesis by in vitro reconstitution†
Abstract
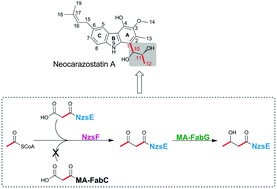
Neocarazostatin A (1) is a potent free radical scavenger possessing an intriguing tricyclic carbazole nucleus with a C4 alkyl side chain attached to ring “A”. Although the biosynthetic gene cluster of 1 (nzs) has been identified, and several key steps of the pathway have been well characterized, the enzyme(s) involved in the biosynthesis of the C4 unit still remains obscure. In this work, we demonstrate that three enzymes, including one (MA37-FabG) from primary fatty acid metabolism and two pathway-specific ones (NzsE and NzsF), are responsible for the formation of the side chain precursor. We show that NzsE is a free-standing acyl carrier protein (ACP), and NzsF, which is a homolog of β-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III (KAS III, also called FabH), catalyzes a decarboxylative condensation between an acetyl-CoA and the NzsE bound malonyl thioester to generate acetoacetyl-NzsE. We also show that NzsF can only accept NzsE as its cognate ACP substrate, suggesting that NzsE and NzsF constitute pathway-specific KAS III enzyme pairs for the assembly line of 1. Furthermore, we have identified two FabG (the NADPH-dependent reductase) homologs from the fatty acid biosynthesis pathway that can reduce the 3-keto group of acetoacetyl-NzsE to generate a 3-hydroxybutyl-NzsE product, which is the putative intermediate for the following incorporation into 1. Therefore, our work successfully reconstitutes the biosynthetic pathway of the C4 alkyl side chain of 1in vitro, and sheds light on the potential of engineering NzsE/F for producing novel neocarazostatin analogues in the host strain.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...