Design and synthesis of novel dual-target agents for HDAC1 and CK2 inhibition†
Abstract
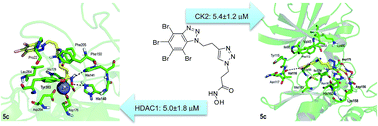
Drug entities able to address multiple targets can be more effective than those directed to just one biological target. We disclose herein a series of novel dual inhibitors to target histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC 1) and protein kinase CK2. Our bifunctional compounds combine two complementary chemo-active prototypical scaffolds: a hydroxamate essential for the chelation of the zinc ion present in the active site of HDAC (Zinc Binding Group), and a 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBB) moiety introduced to interact with the ATP binding site in CK2 and to act simultaneously as the cap group in the interaction with HDAC1. The synthesized dual-acting agents exhibited promising inhibitory activities towards HDAC1 and CK2. The best result was obtained for 5c with an IC50 of 5 μM for both enzymes. However, its N-2 substituted isomer 5e presented the best profile in cell-based assays, with cytotoxic activity in the low micromolar LC50 in two mammalian cancer cell lines and 4-fold less activity towards a pseudonormal mammalian cell line. Furthermore, this hybrid molecule induced apoptosis in leukemia cells in a concentration-dependent manner. All together this makes 5e a promising lead compound for future in vivo assays in animal tumor models.
- This article is part of the themed collection: A Decade of Progress in Click Reactions Based on CuAAC

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...