Impact of oxygen exchange reaction at the ohmic interface in Ta2O5-based ReRAM devices
Abstract
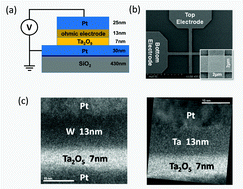
Interface reactions constitute essential aspects of the switching mechanism in redox-based resistive random access memory (ReRAM). For example, the modulation of the electronic barrier height at the Schottky interface is considered to be responsible for the toggling of the resistance states. On the other hand, the role of the ohmic interface in the resistive switching behavior is still ambigious. In this paper, the impact of different ohmic metal-electrode (M) materials, namely W, Ta, Ti, and Hf on the characteristics of Ta2O5 ReRAM is investigated. These materials are chosen with respect to their free energy for metal oxide formation and, associated, their impact on the formation energy of oxygen vacancy defects at the M/Ta2O5 interface. The resistive switching devices with Ti and Hf electrodes that have a negative defect formation energy, show an early RESET failure during the switching cycles. This failure process with Ti and Hf electrode is attributed to the accumulation of oxygen vacancies in the Ta2O5 layer, which leads to permanent breakdown of the metal–oxide to a low resistive state. In contrast, the defect formation energy in the Ta2O5 with respect to Ta and W electrodes is positive and for those highly stable resistive switching behavior is observed. During the quasi-static and transient-pulse characterization, the ReRAM devices with the W electrode consistently show an increased high resistance state (HRS) than with the Ta electrode for all RESET stop voltages. This effect is attributed to the faster oxygen exchange reaction at the W-electrode interface during the RESET process in accordance to lower stability of WO3 than Ta2O5. Based on these findings, an advanced resistive switching model, wherein also the oxygen exchange reaction at the ohmic M-electrode interface plays a vital role in determining of the resistance states, is presented.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...