A process to enhance the specific surface area and capacitance of hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide†
Abstract
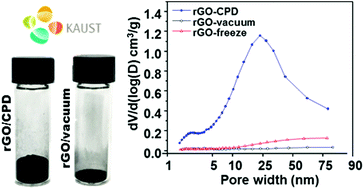
The impact of post-synthesis processing in reduced graphene oxide materials for supercapacitor electrodes has been analyzed. A comparative study of vacuum, freeze and critical point drying was carried out for hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide demonstrating that the optimization of the specific surface area and preservation of the porous network are critical to maximize its supercapacitance performance. As described below, using a supercritical fluid as the drying medium, unprecedented values of the specific surface area (364 m2 g−1) and supercapacitance (441 F g−1) for this class of materials have been achieved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...